MCAT Compounds and Stoichiometry
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Moles from mass equation:
(what do you divide?)

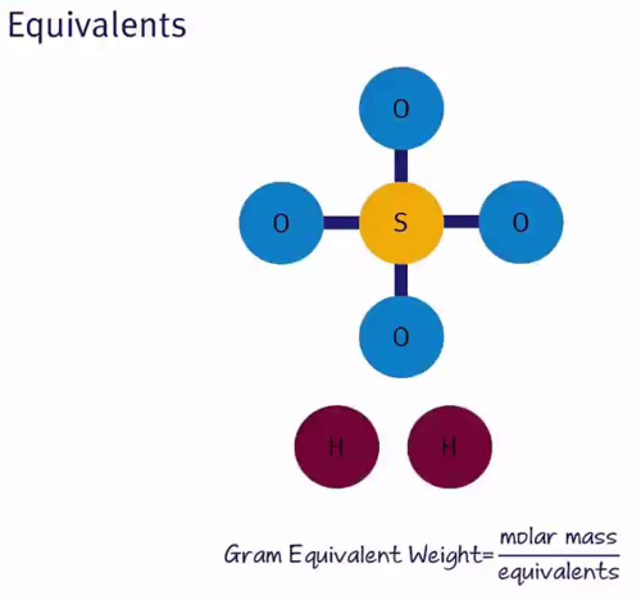
Gram equivalent weight equation:
n - # of particles of interest produced or consumed per molecule of the compound in the reaction (mol of H+ or e-)
n is the number of protons, hydroxide ions, electrons, or ions produced or
consumed by the solute.
Mass of an acid that yields 1 mole of H+ or
mass of a base that reacts with 1 mole of H+.
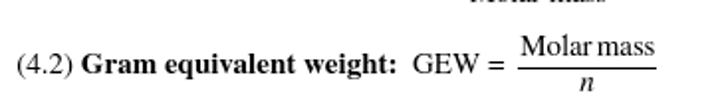
What is the gram equivalent weight of sulfuric acid?
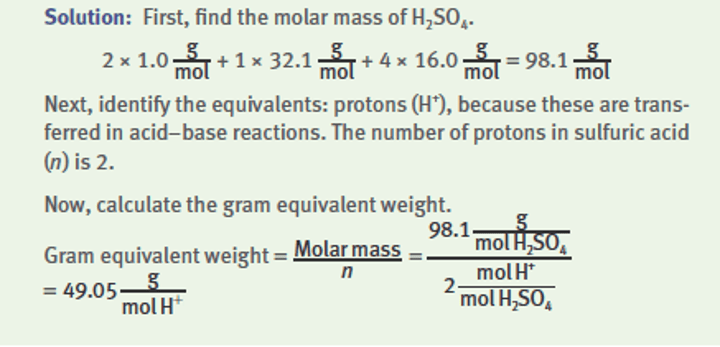
What is the normality of a 2 M Mg(OH)2 solution?
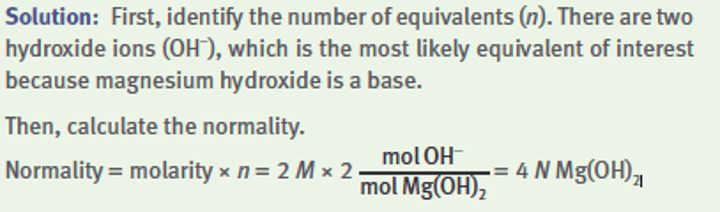
Equivalents from mass equation:

Molarity from normality equation:
Normality (N)
is a measure of concentration, given in the units
equivalents
L
1 N HCl solution, the molarity of HCl is 1 M because HCl is a
monoprotic acid; in a 1 N H2CO3 solution, the molarity of H2CO3 is 0.5 M because
H2CO3 is a diprotic acid.

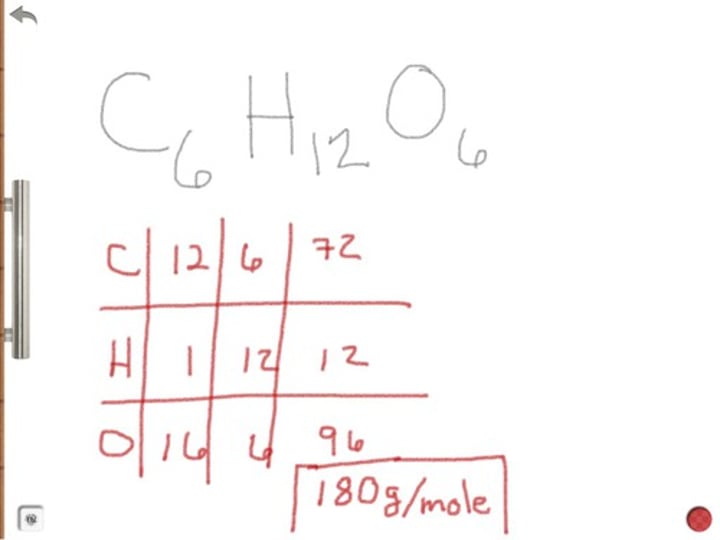
Percent composition equation:
any pure sample of a given compound
will contain the same elements in an identical mass ratio.
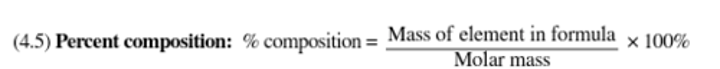
Percent yield equation:
Compounds
Substances composed of two or more elements in a fixed proportion.
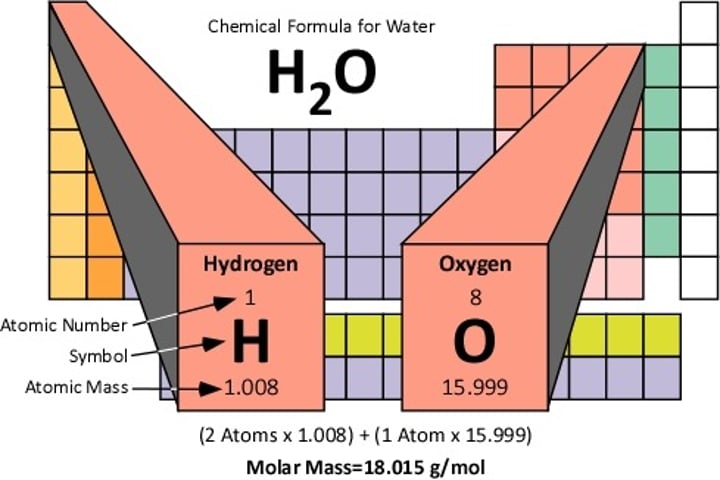
Molecular weight
The mass (in amu/molecule) of the constituent atoms in a compound as indicated by the molecular formula.
-similar to atomic weight- which is the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
Molar mass
The mass of one mole (Avogadro's number 6.022x10^23 particles) of a compound; usually measured in grams/ mole.
Gram equivalent weight (definition)
A measure of the mass of a substance that can donate one equivalent of the species of interest.
Normality
The ratio of equivalents per liter; it is related to molarity by multiplying the molarity by the number of equivalents present in one mole of a compound.

Equivalents
Moles of the species of interest, equivalents are most often seen in acid-base chemistry ( H+ ions or -OH ions) and oxidation-reduction reactions.
-how many moles of the thing we are interested in will one mole of the compound produce?
The law of constant composition
States that any pure sample of a compound will contain the same elements in the same mass ratio.
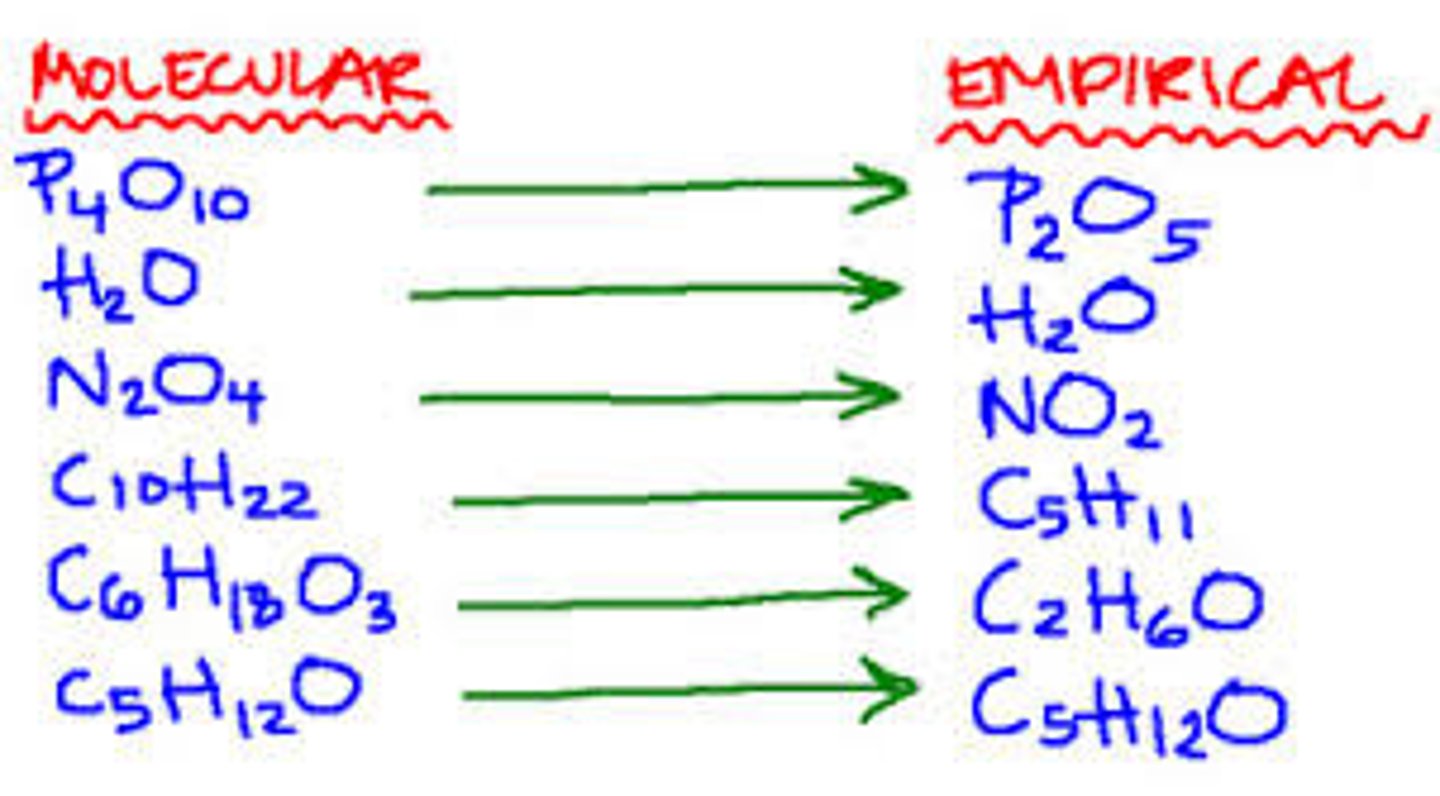
Empirical formula
(what is benzes)
The smallest whole number ratio of the elements in a compound.
CH
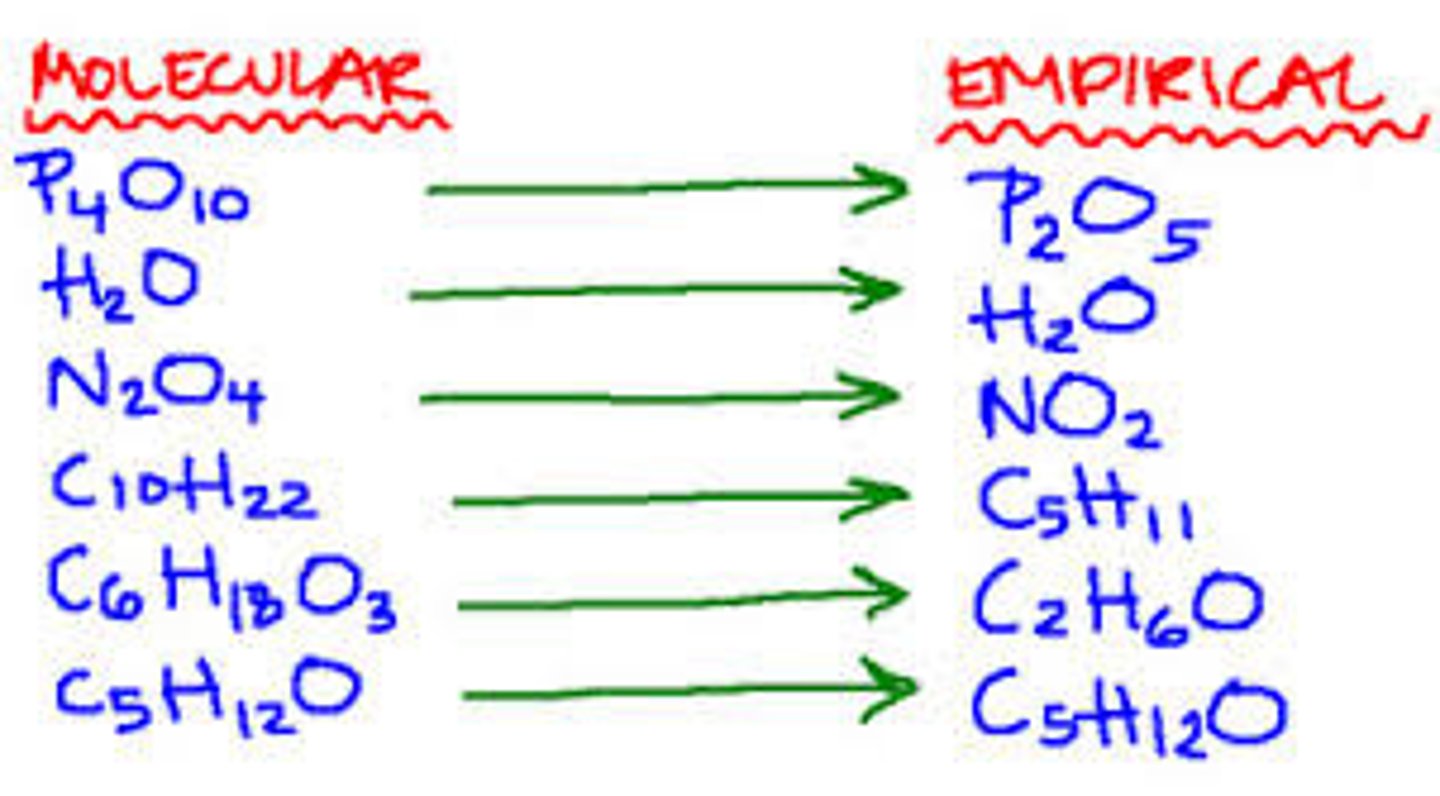
Molecular formula
Either the same as the empirical formula or a multiple, it gives the exact number of atoms of each element in a compound.
Percent composition (how do you get it)?
To calculate percent composition:
1) Determine mass of individual element
2) Divide by molar mass of compound
What is the percent composition of chromium in K2Cr2O7?
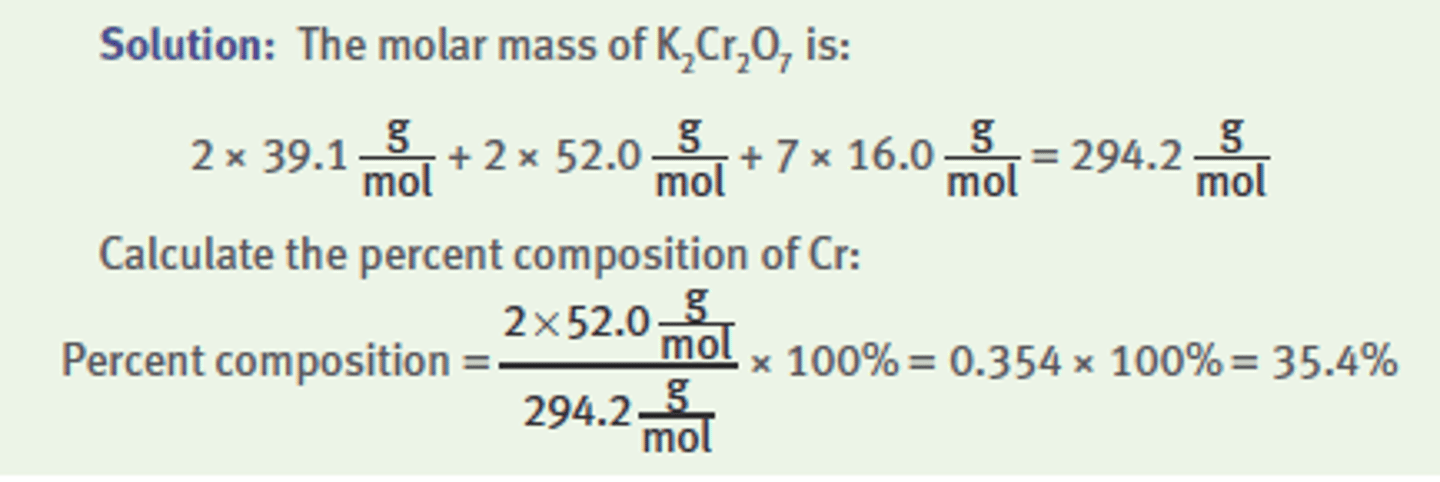
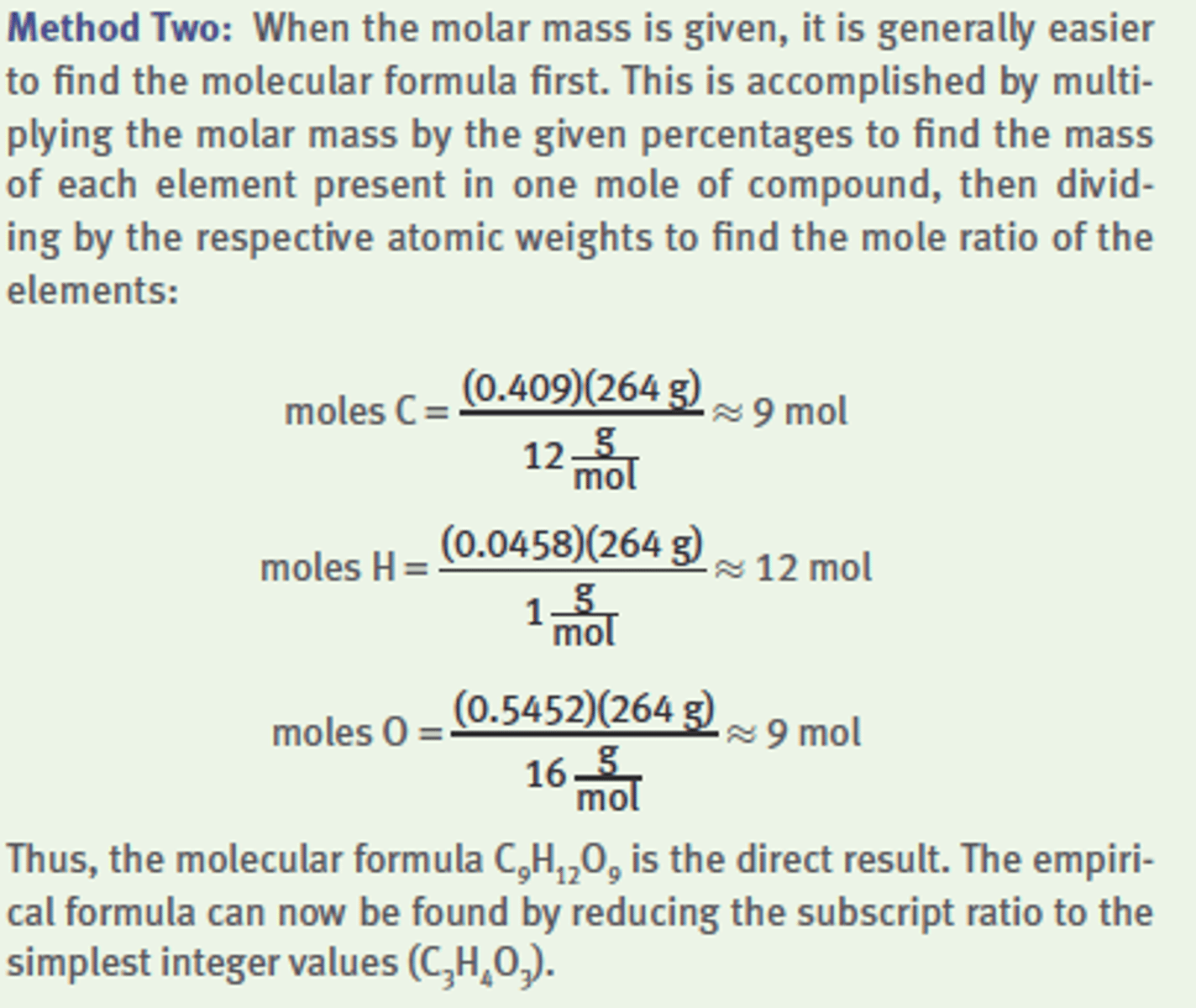
What are the empirical and molecular formulas of a compound
that contains 40.9% carbon, 4.58% hydrogen, and 54.52%
oxygen and has a molar mass of 264 g
mol
?
Types of chemical reactions?
1) Combination reaction
2) Decomposition reaction
3) Displacement reaction - single or double
4) Neutralization reaction
5) Combustion
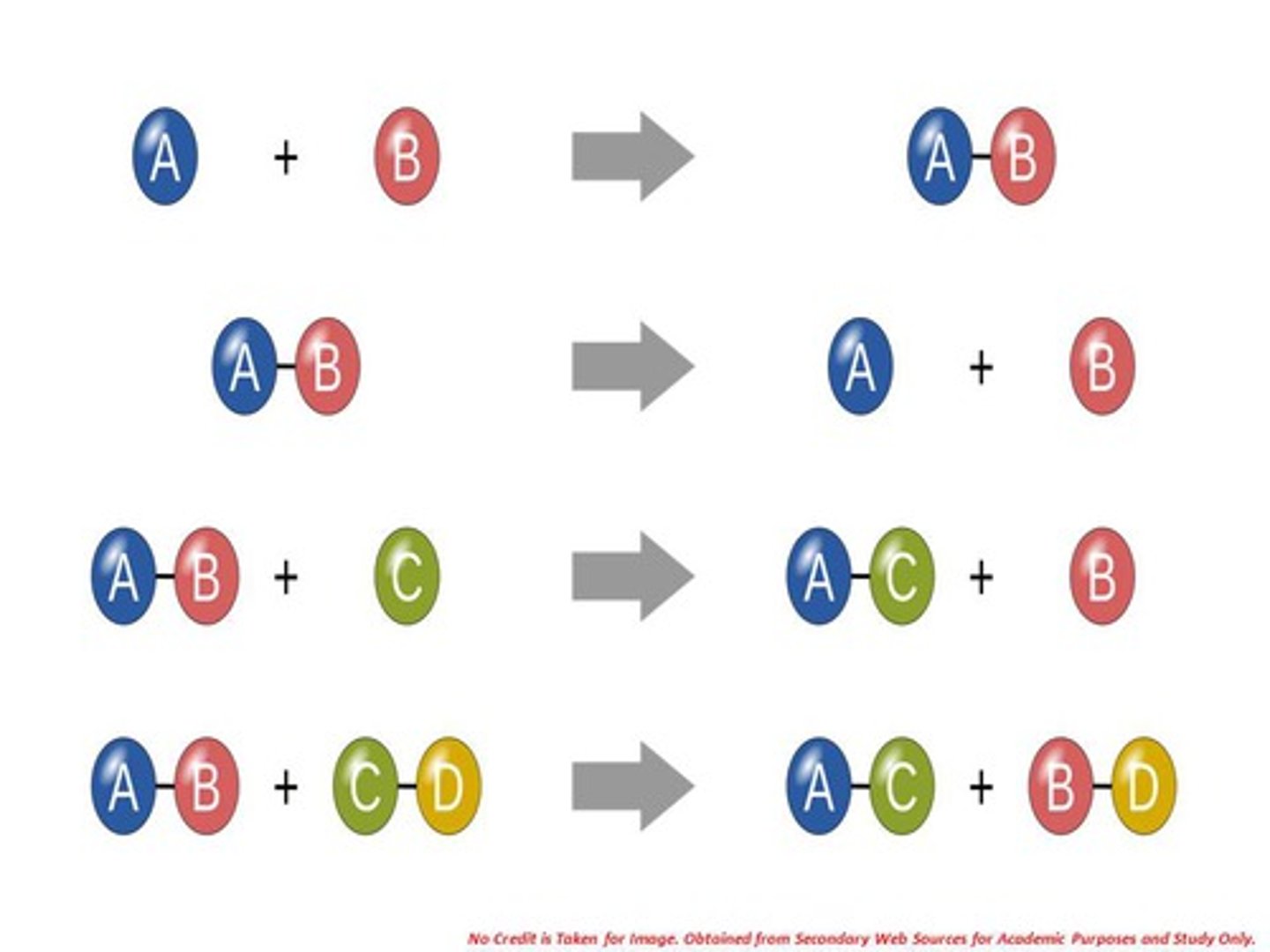
Combination reaction
When two or more reactants combine to form one product.
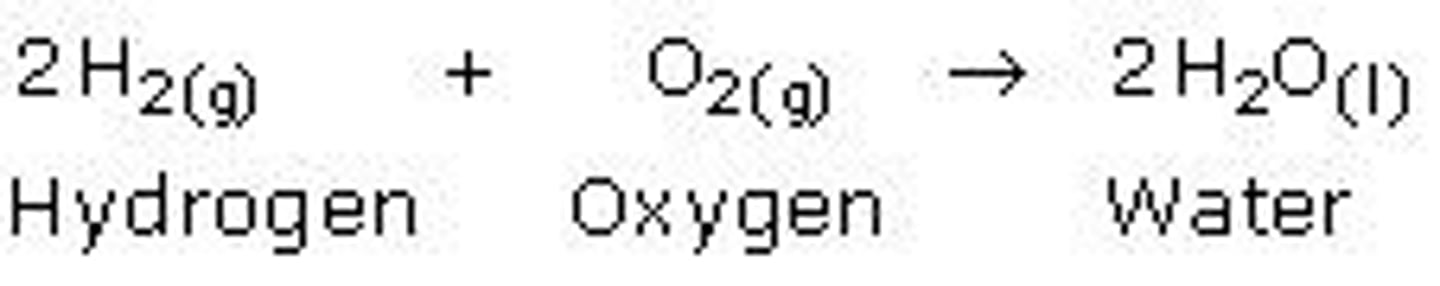
Decomposition reaction
When one reactant is chemically broken down into two or more products.

Displacement reaction
Occurs when one or more atoms of one compound and replaced with one or more atoms of another compound.
Two types:
1) Single displacement
2) Double displacement
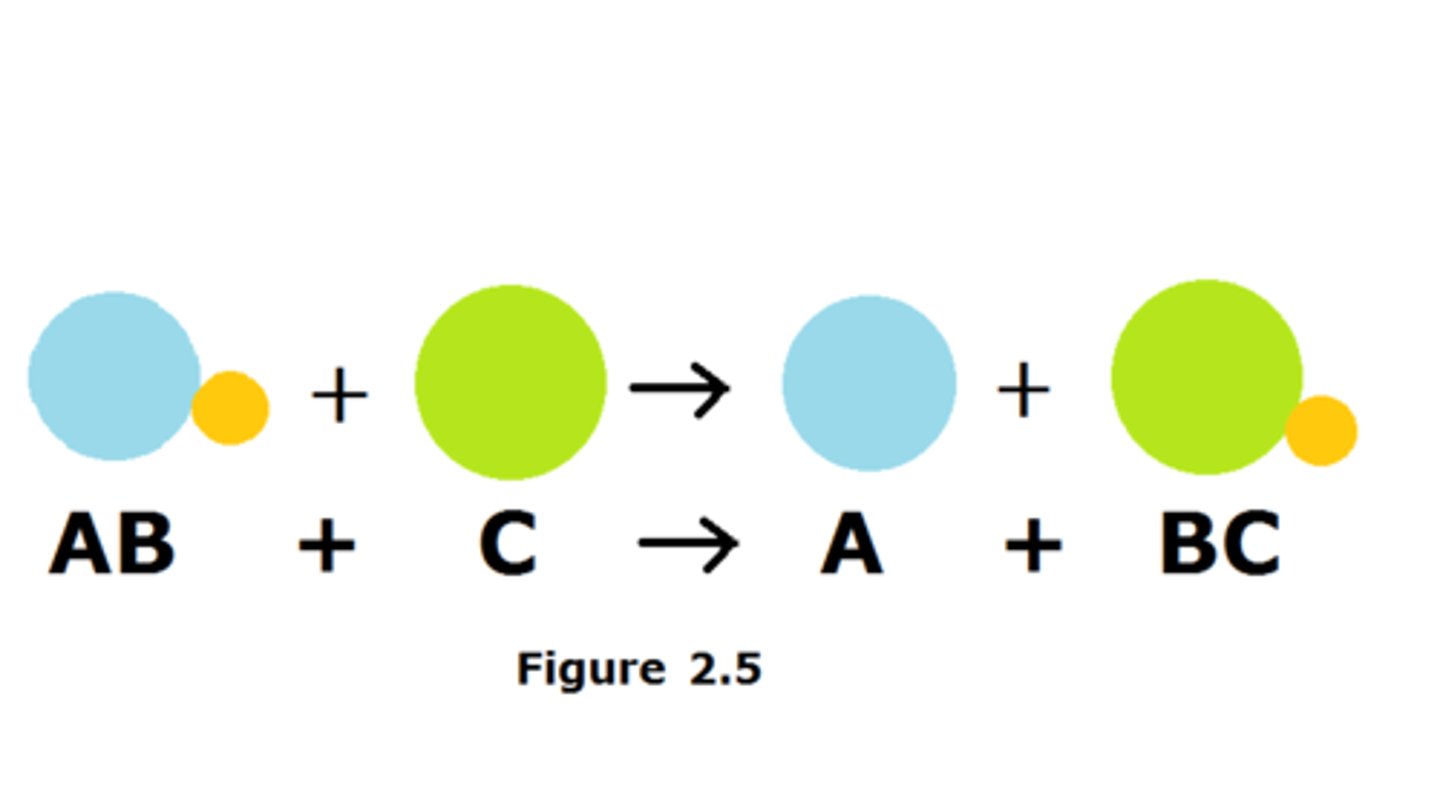
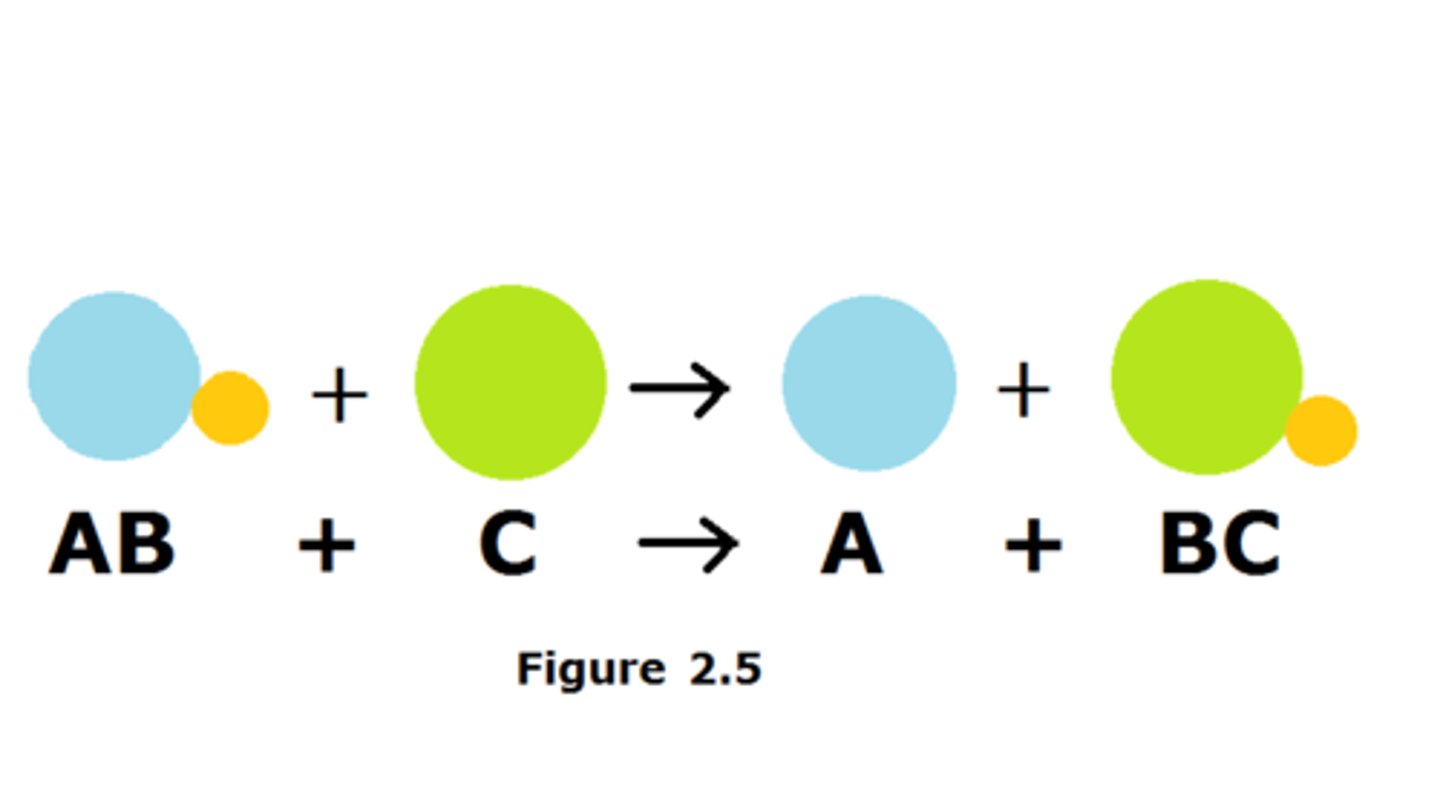
Single displacement reaction
Occur when an ion of one compound is replaced by another element.
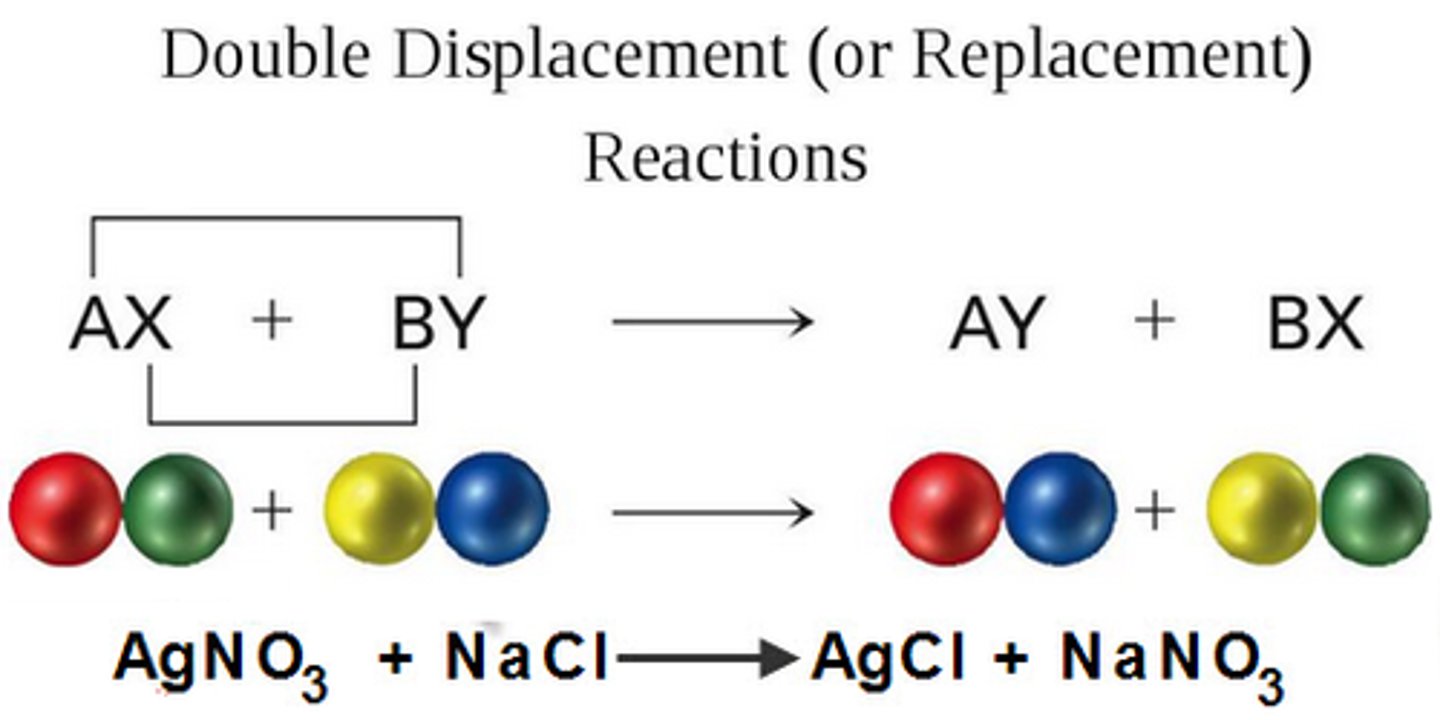
Double-displacement reaction (metathesis reactions)
When elements from two different compounds trade places with each other to form two new compounds.
Neutralization reaction
Those in which an acid reacts with a base to form a salt (and, usually, water)
Acids and bases combine in neutralization
reactions to produce salts (and,
usually, water)

Combustion reaction
Occurs when a fuel and an oxidant (typically oxygen) react, forming the products water and carbon dioxide ( If the fuel is a hydrocarbon).
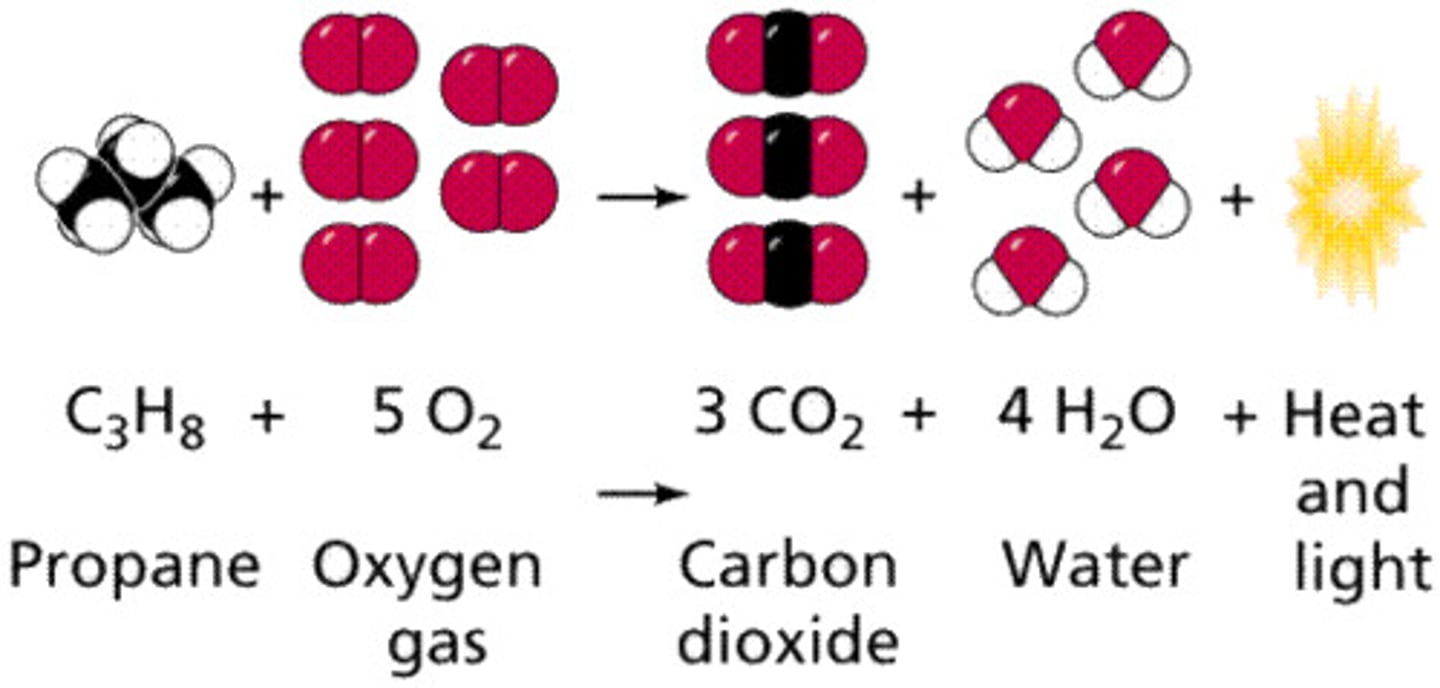
Balancing chemical equations:
1) balance least common atoms
2) Balance more common atoms ( usually H or O)
3) Balance charge (if necessary)
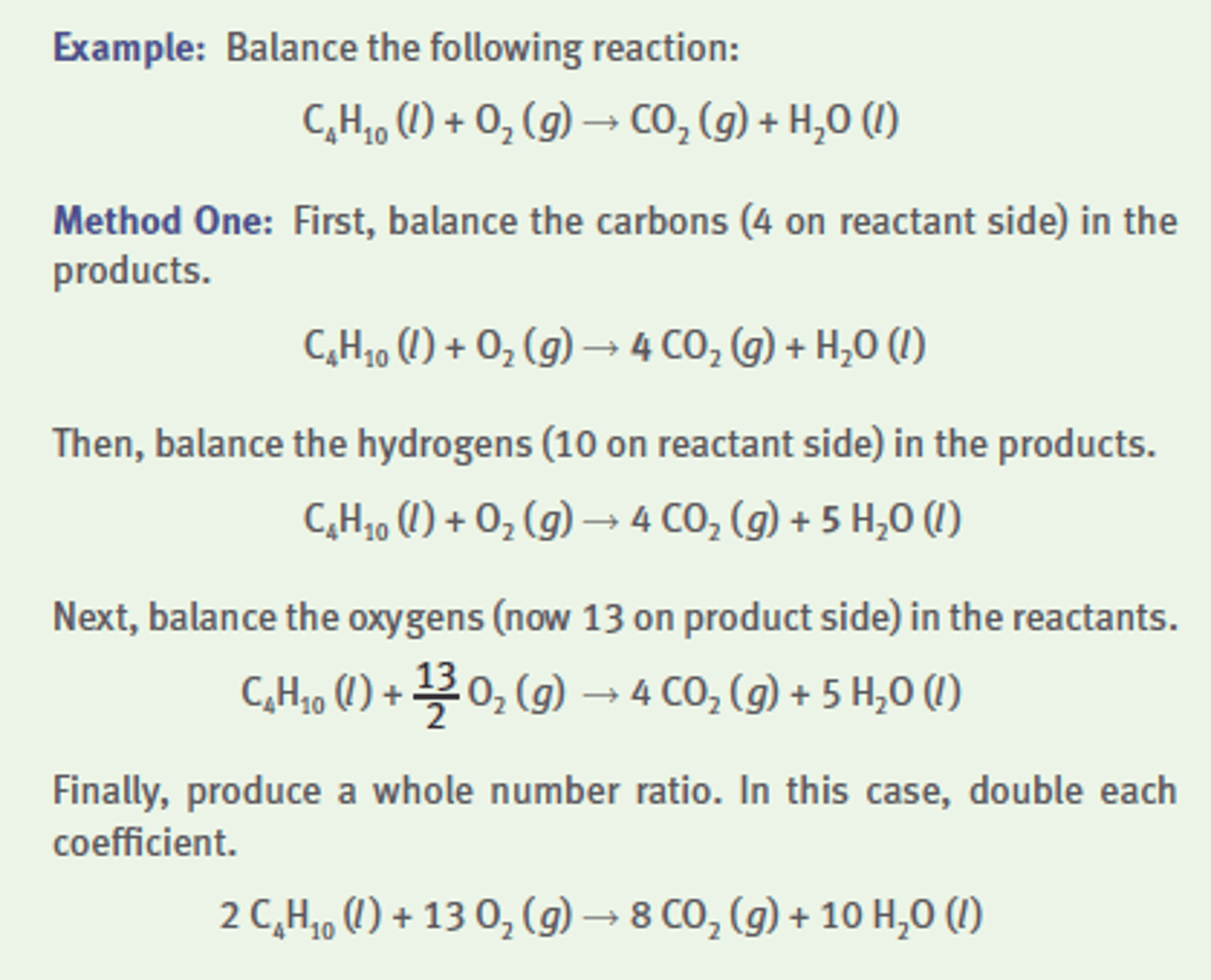
Limiting reagent
The reactant that will be consumed first in a chemical reaction. Determines the amount of product that can be formed.
(is the least number - after you find the moles)
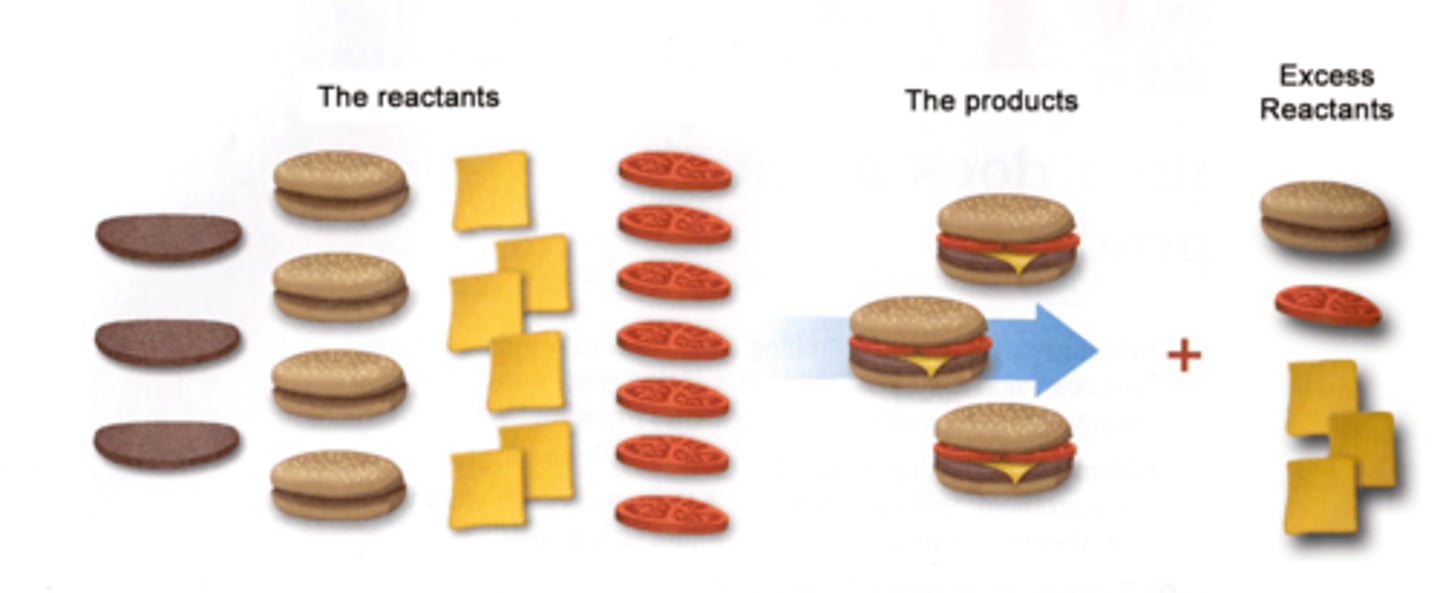
Excessive reagents
The reagents left over after limiting reagent is consumed.
(subtractive what was needed by how much you got for dis)
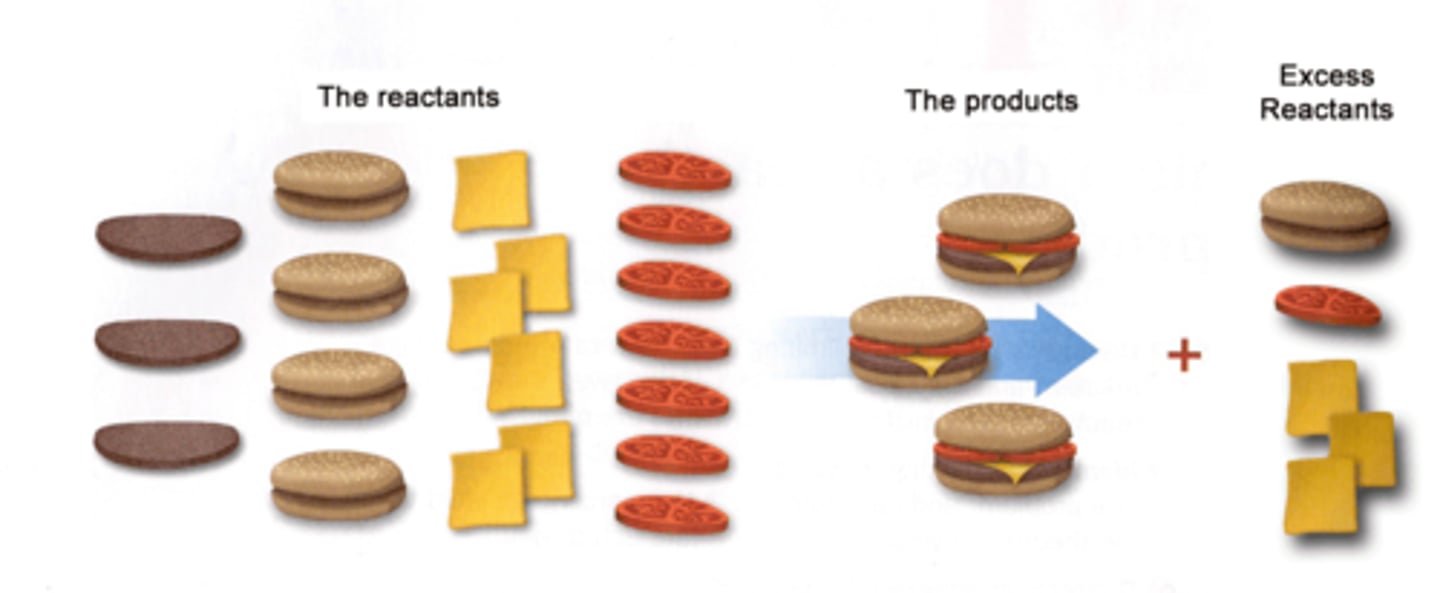
Theoretical yield
The amount of product generated if all of the limiting reactant is consumed with no side reactions.
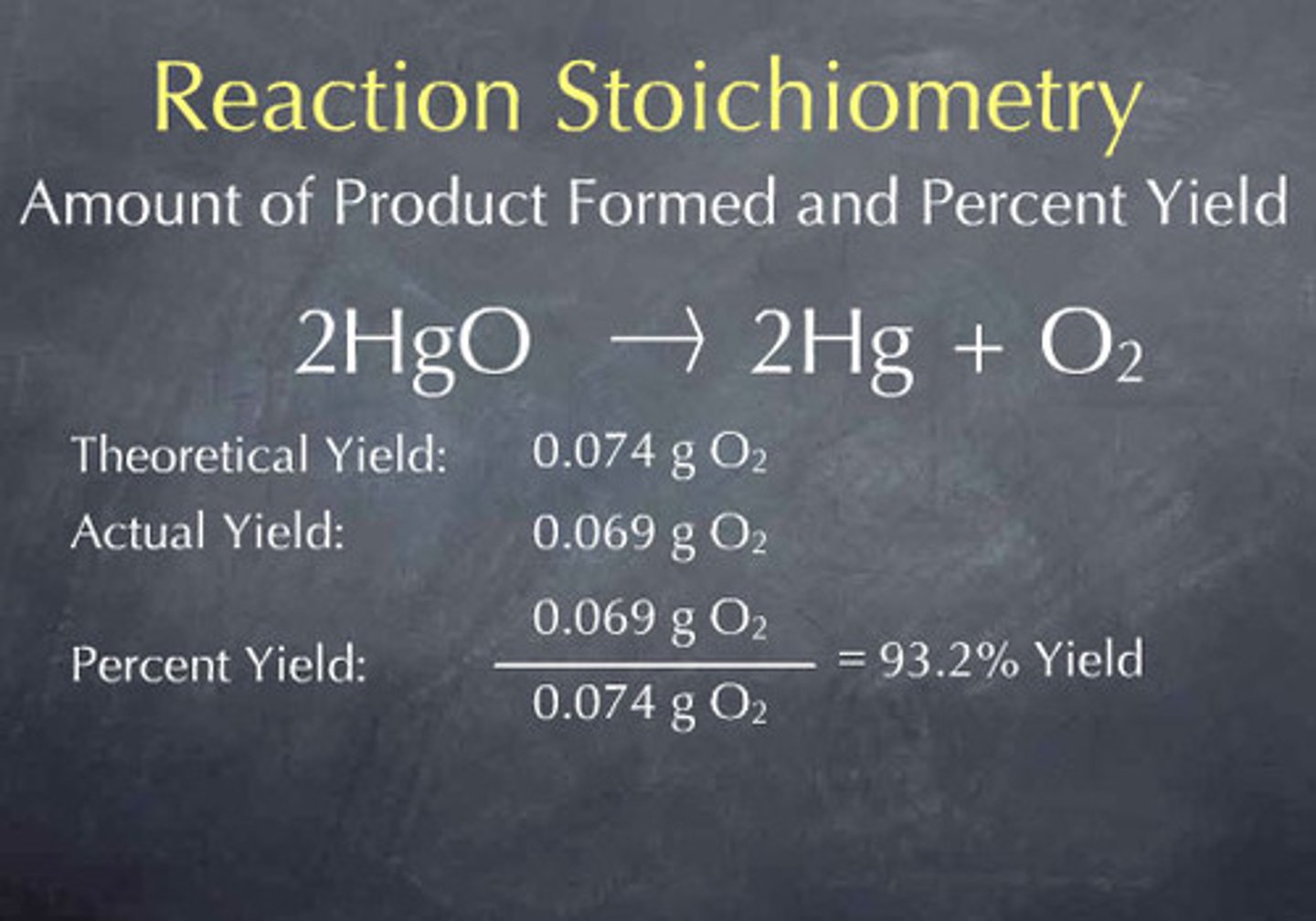
Actual yield
What you actually get; typically lower than theoretical yield.
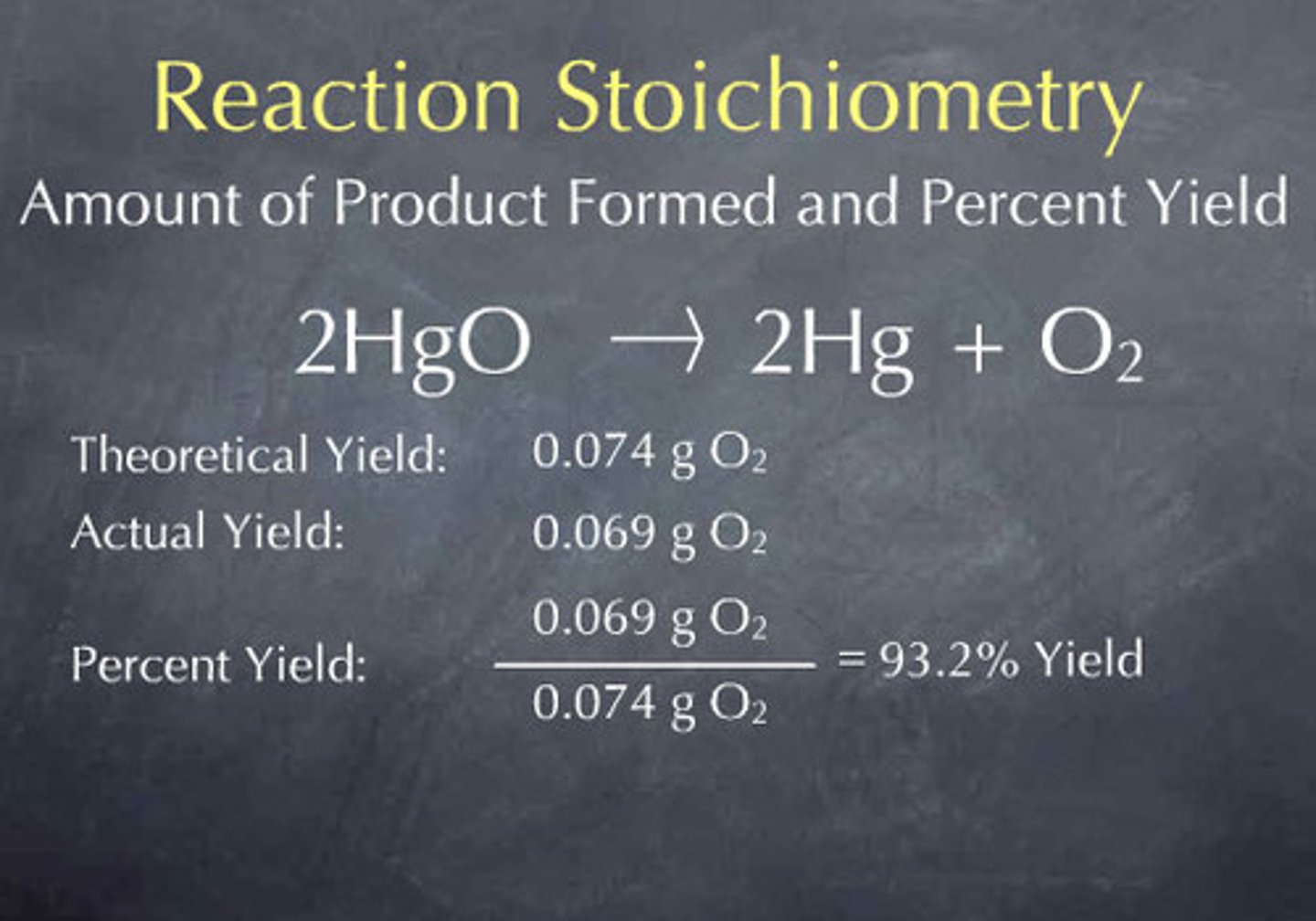
Percent yield
Calculated by dividing actual yield by theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.

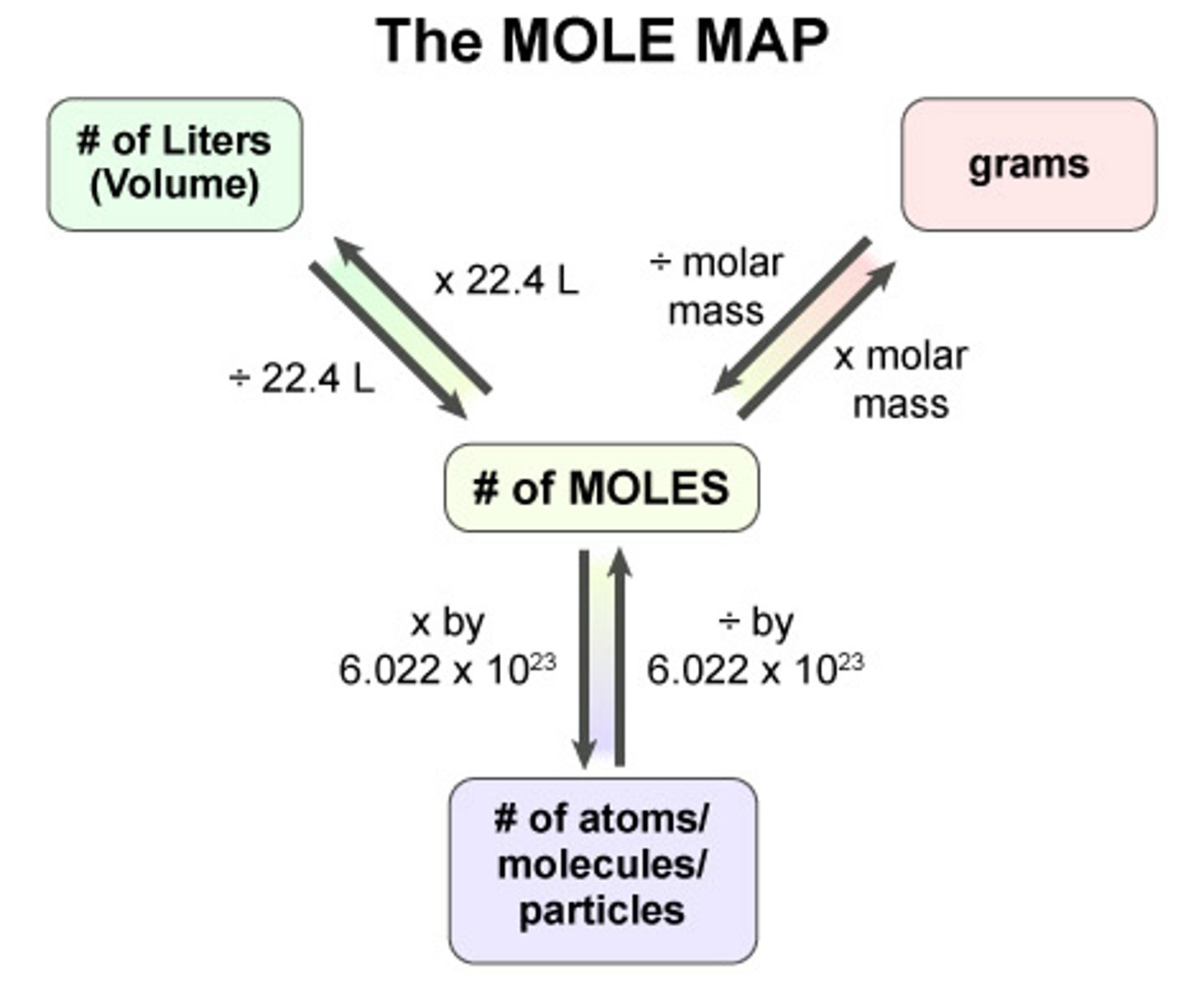
Mole Conversion
STP , molecules ?
1 mole is = to
22.4L = STP
6.022 X 10^23 particles
Molar mass of substance
Ionic compound nomenclature:
What does the roman numeral in Fe (II) mean?
Roman numeral denotes the ionic charge on atoms that posses more than one ionic state.
I.e., Fe(II) = Fe2+ vs Fe(III) = Fe3+
Monoatomic ions named by what suffix?
Monoatomic ions are named by dropping the ending of the name of the element and adding -ide.
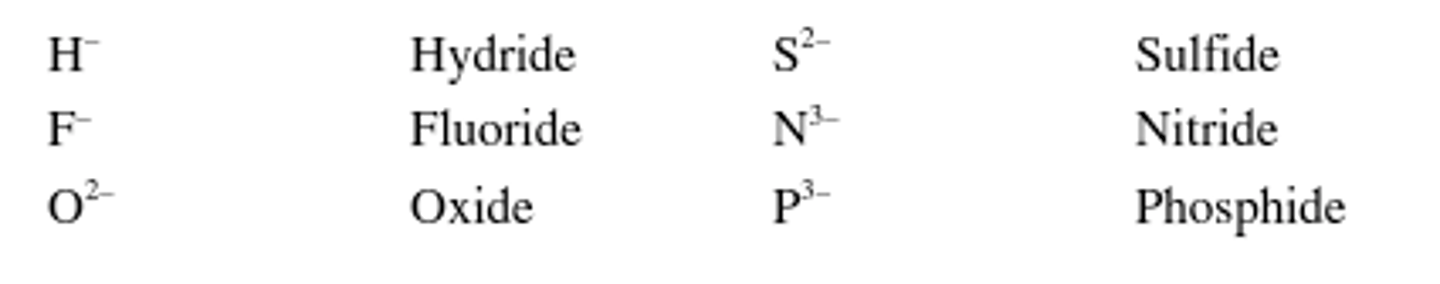
Polyatomic anions named by what suffix?
bigger one? less one?
Many polyatomic anions contain oxygen and are called oxyanions.
When an element forms two oxyanions, the smaller - its and the larger = ate.

Multiple oxyanions? Hypo and Per mean what?
If an extended series of oxyanions, Hypo goes first and per goes last.

Nitrite
NO2-
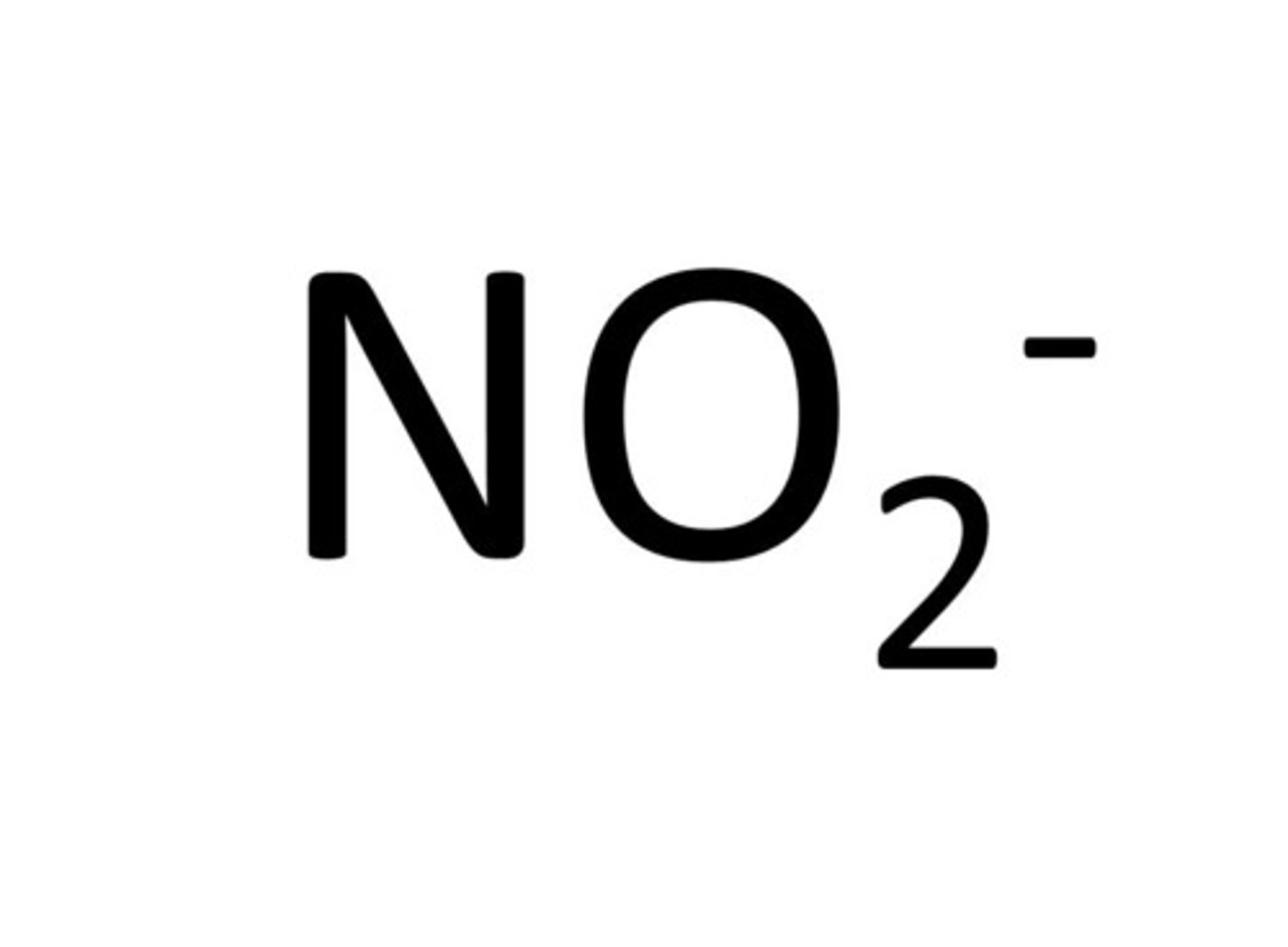
Nitrate
NO3-
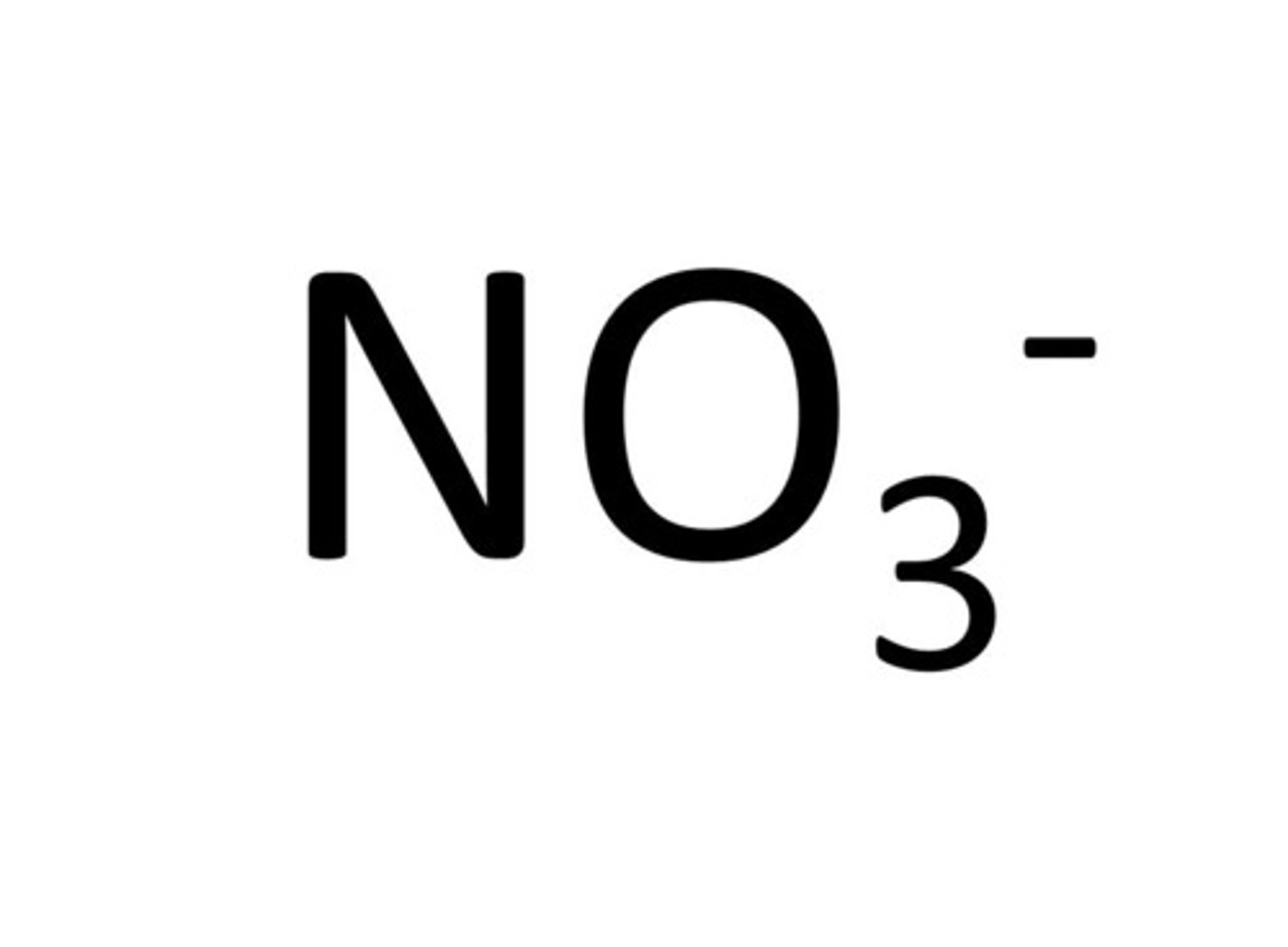
Sulfite
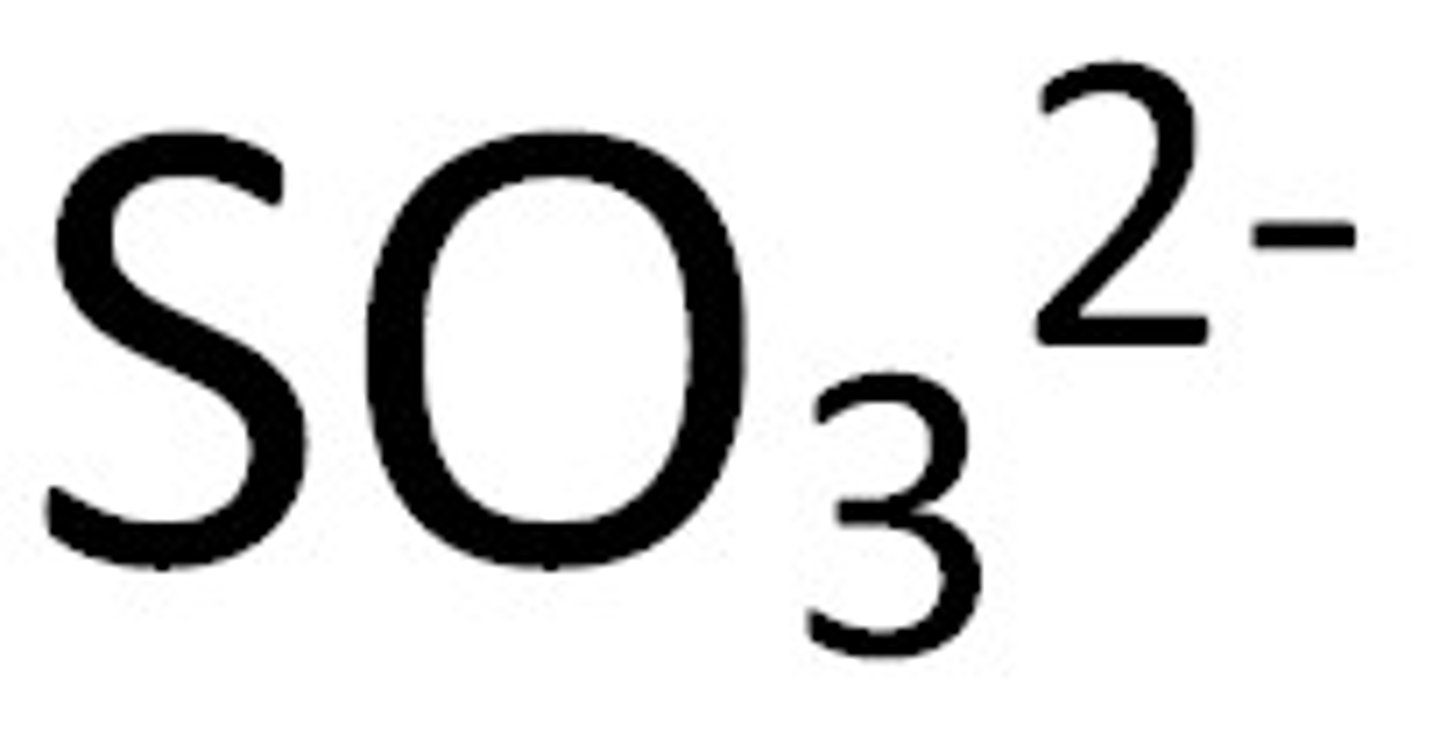
Sulfate
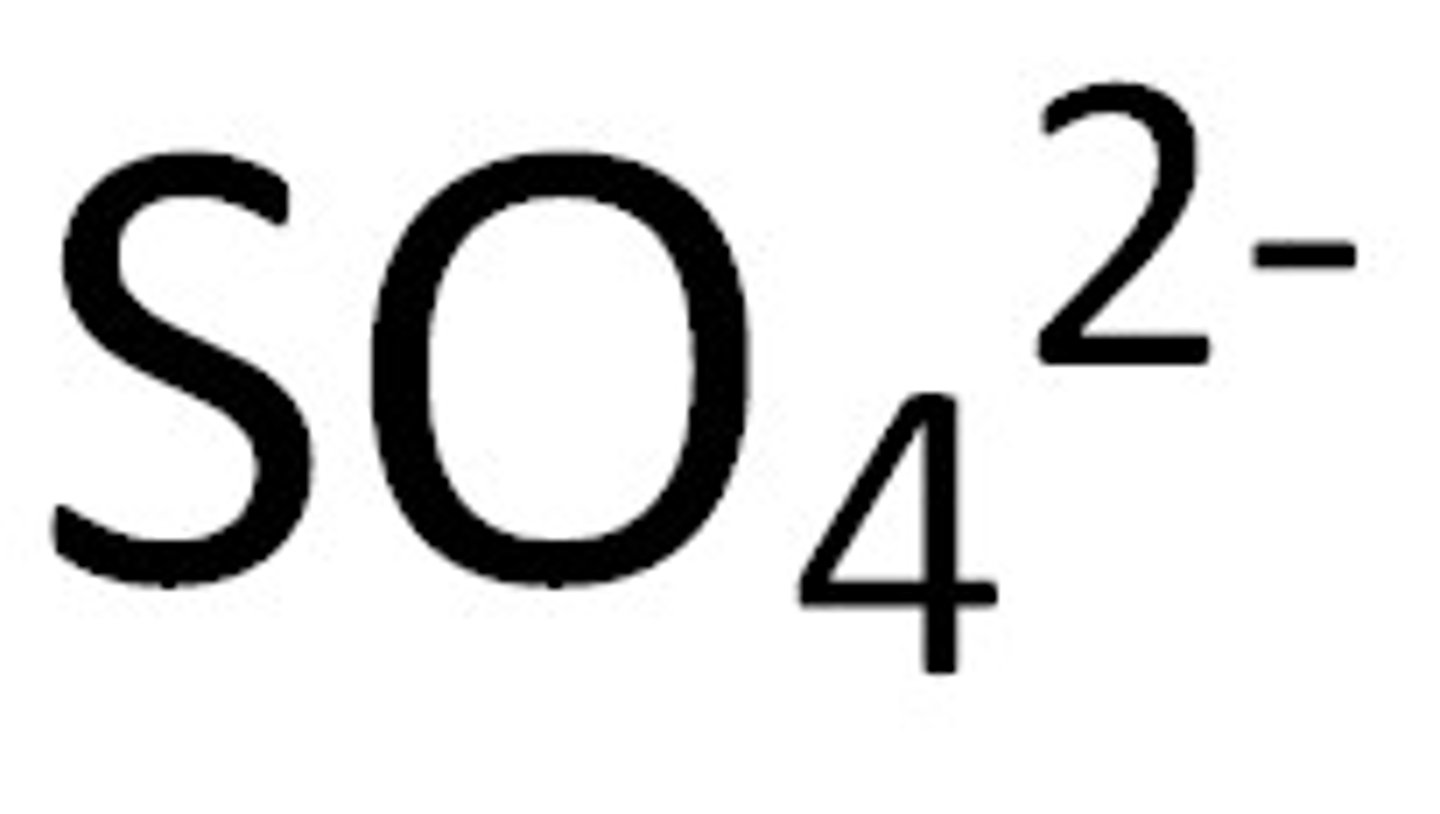
Hypochlorite
ClO-
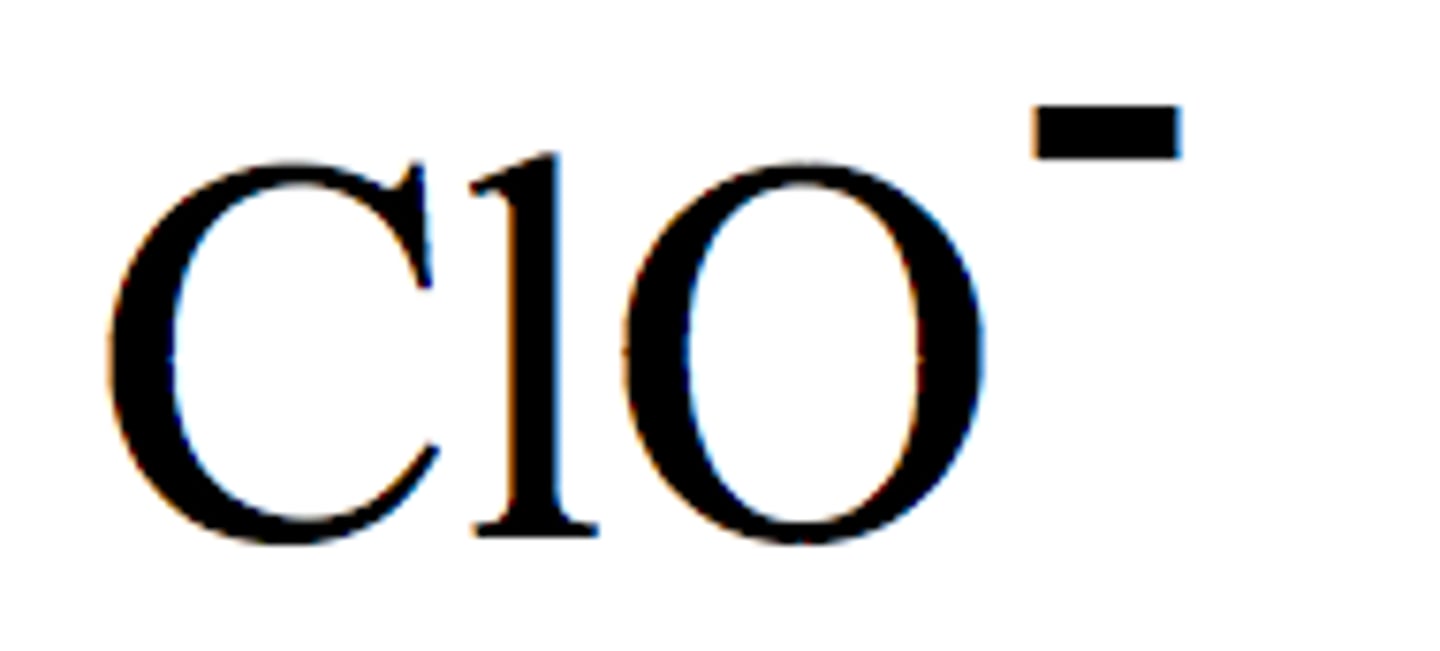
Chlorite
ClO2-
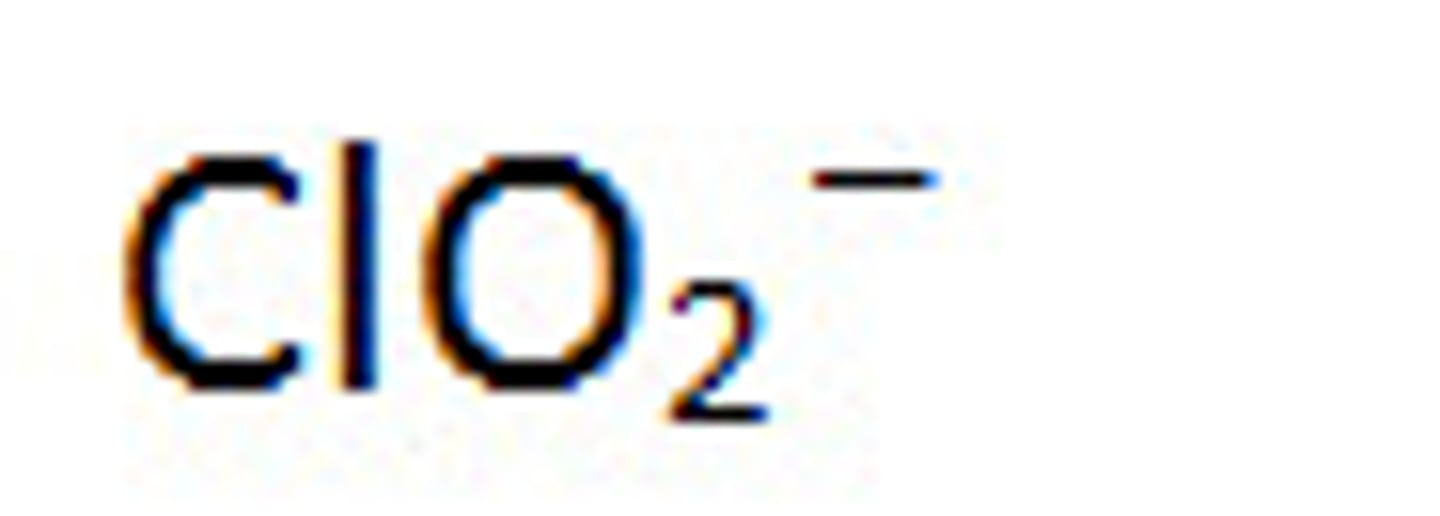
Chlorate
ClO3-
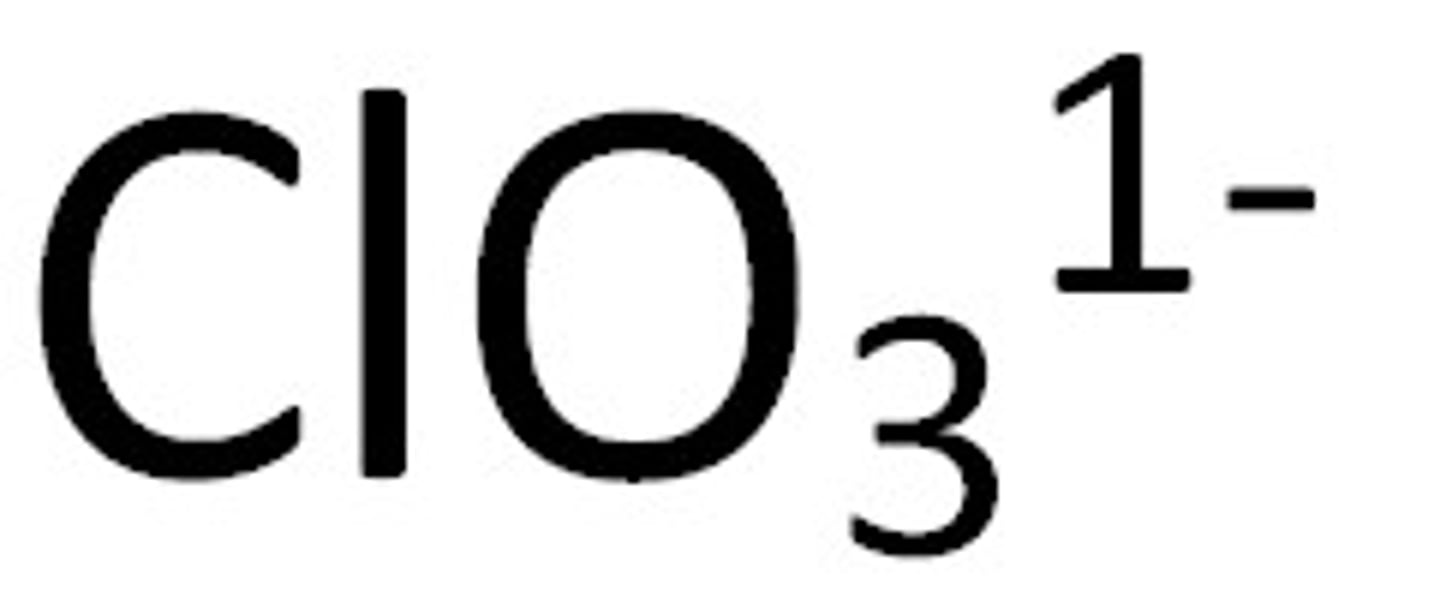
Perchlorate
ClO4-
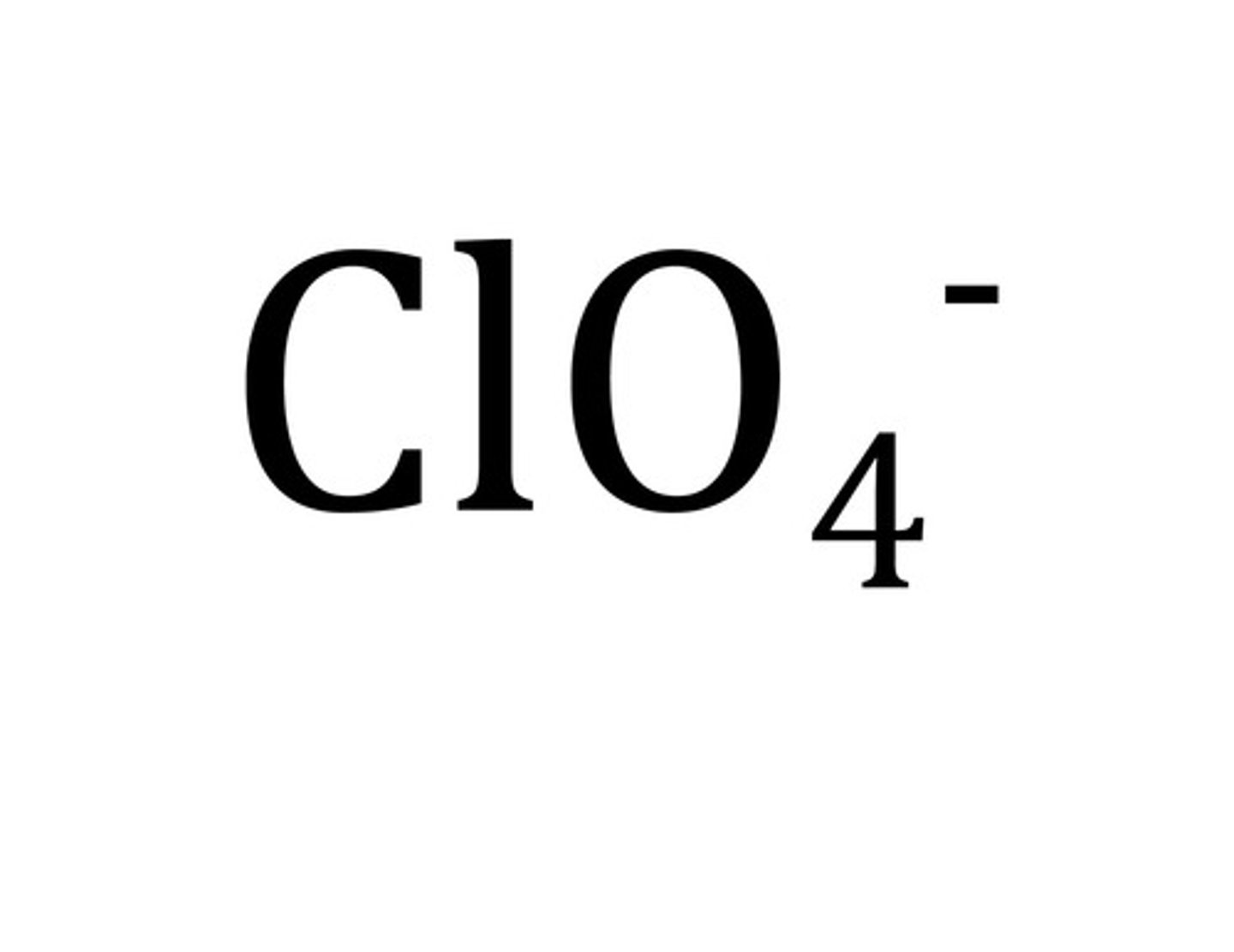
Polyatomic anions with H+?
what happens to the naming when you add it?
Polyatomic anions often gain one or more H+. The resulting ions are named by adding hydrogen or dihydrogen in front of the anion's name.

Mnemonic for -ite vs -ate?
The l-IGHT-est anions have the fewest oxygens, the heaviest anions ATE the most oxygens.
Common polyatomic ions to know:
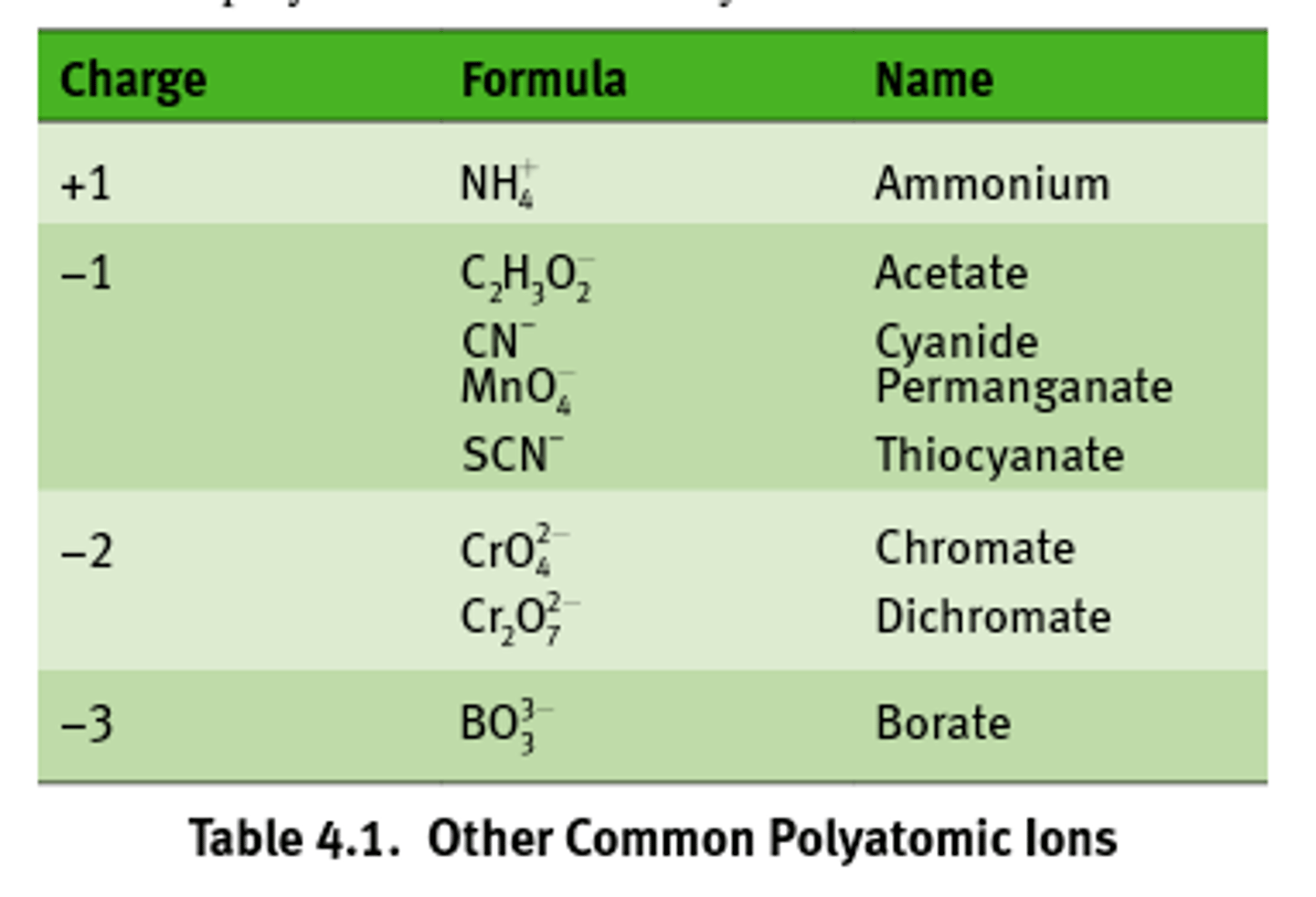
Ionic charge
can find it how?
Predictable by group number and the type of element (metal vs nonmetal) for respective elements.
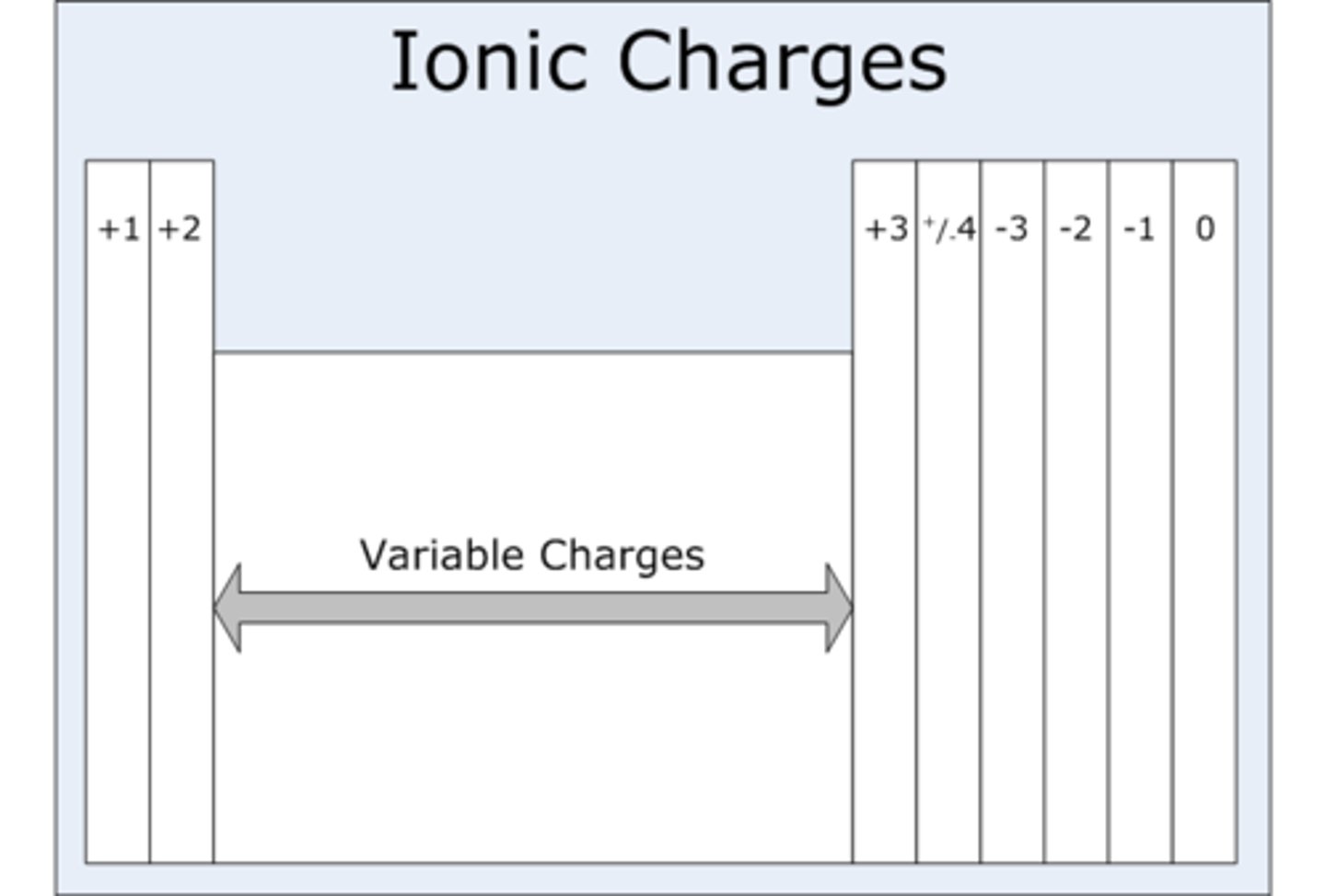
What charges will metals form?
based on what?
Metals for positively charged cations based on group number.
What change will nonmetals form?
Nonmetals form negatively charged anions based on the number of the electrons needed to achieve the octet.
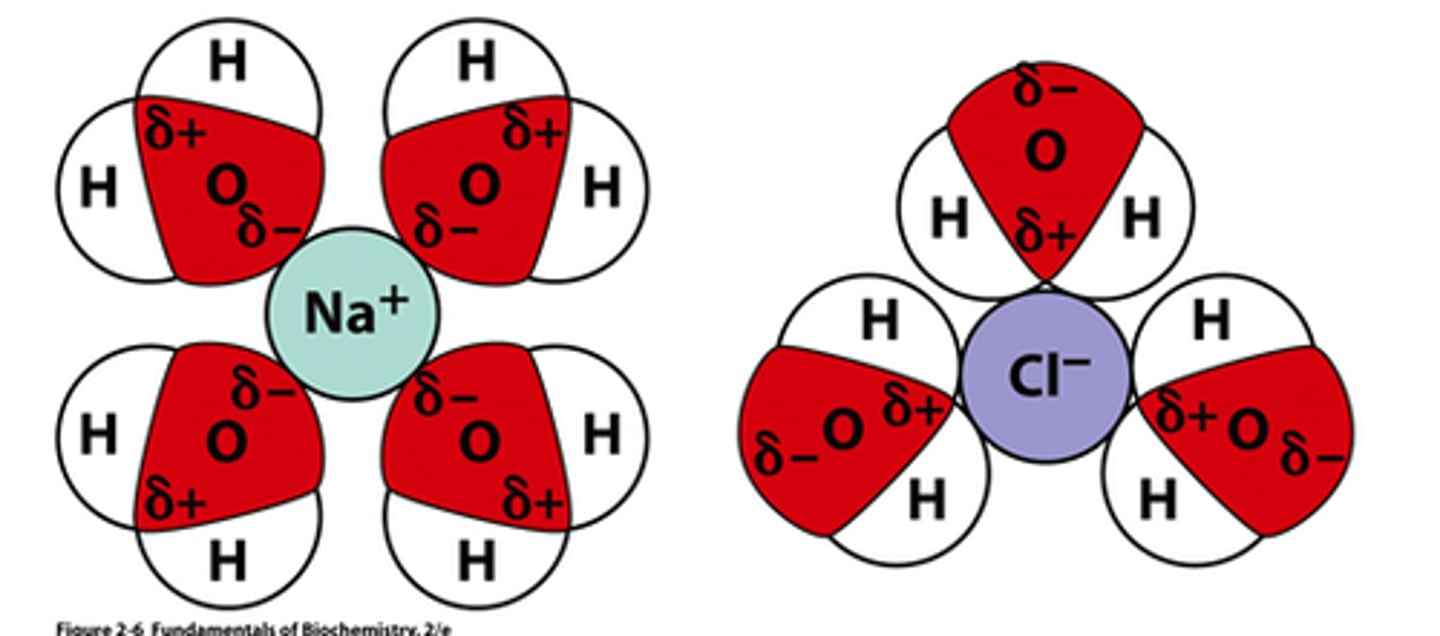
Electrolytes
Contain equivalents of ions from molecules that dissociate in solution.
The strength of an electrolyte depends on the degree of solvation.
What compounds are good electrolytes and why?
Ionic compounds make good electrolytes
because they dissolve most readily.
Nonpolar covalent compounds are
the weakest because they do not form
current-carrying ions.
Solvation
the process by which the positive and negative ions of an ionic solid become surrounded by solvent molecules