Neuro: Arousal and Attention
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Attention
- More than just sensation and perception; uses stimuli to measure arousal levels
- There can be attentional deficits present in perfectly awake individuals
Attention is a limited resource
What can impair the flexibility of attention?
Extreme arousal (pain, terror, overstimulation)
What are the three characteristics of attention?
Consciousness (alert, arousal)
Awareness (alert, arousal)
Cognitive effort (key piece to attention)
Psychological level
how we process and respond to resources
Neural level
alternations of selective activity; intensity and duration of neural responses
arousal
being awake enough to perceive a stimulus (pain, sound, touch, etc)
Reticular activating system
Cells in the reticular formation can set the pace of activity of cells throughout the brain
Raphe nuclei & locus coeruleus
raphe nuclei
sleep wake cycle; arousal
locus coeruleus
attention
What does damage to reticular activating system cause?
reduced attention, confusion, may lead to a coma
Serotonin
Generalized arousal & sleep wake cycle
origin- raphe nuclei
Norepinephrine
attention (direction of consciousness) & alertness
origin- locus coeruleus and medial reticular zone
Acetylcholine
selection of object of attention, based upon goals & orientation
origin- pedunculopontine nucleus
dopamine
motivation, motor activity, cognition, and executive attention
origin- substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area
Attentional orientation/Orienting Reflex
An individual's immediate response to a novel change in its environment. It is the direction of attention to the novel stimulus.
Sustained attention
- Attending to one stimulus over increasing period of time. Is the ability to sustain alertness (monitor a stimulus) continuously.
- important when a task demands that you cannot "tune out" and must be attentive
ex: in a classroom, operating machinery
Selective (focused) attention
Prioritizing attention to one stimulus over the other(s); conscious
ex: if 2 people are talking, who do you prioritize/tune into more
Filtering process which allows us to hone in on critical information from the vast amount of information that is available (cocktail party effect)
Divided attention
Dividing attention between 2 or more different stimuli.
*attention is a limited resource
Easier to split attention between different modalities than two similar modalities
ex: Talking to someone while driving is easier than listening to 2 people talk at the same time
Involved in dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex
What is orienting?
aligning attention with a source of the sensory signals
3 stages of Attentional shift/ Orienting reflex:
1. disengage from the current stimuli
2. shift attention from current stimuli to a new one
3. attention would be engaged, or focused onto the new target.
Overt
Movement of eye/head towards the novel stimulus. However, prior to this, covert attention shifts to this location
Covert
Attention may shift covertly even without an overt eye/head response.
You can have both covert and overt, or just covert.
3 subsystems of attentional orienting/shift
Posterior attentional systems which is involved in orienting to visual locations
Posterior/superior parietal lobe
Superior colliculus
Thalamic lateral pulvinar nucleus
- frontal eye fields also involved
What happens to human performance over time regarding sustained attention?
Human performance decreases with time due to loss of sensitivity and attention drifting from habituation.
3 subsystems of sustained attention
Reticular activating system
Thalamus
Frontal and inferior parietal regions
What does the width of focus refer to in selective attention?
Focus can be broad or narrow.
broad example- teaching to a whole class
narrow- talking to one individual
What does the direction of focus refer to in selective attention?
Focus can be external or internal.
external example- directing focus to external environment
internal example- directing focus internally
3 subsystems of selective/focused attention
Anterior Attentional System
- Superior colliculus
- Thalamus
- Parietal Lobe
- Medial frontal lobe
- Lateral prefrontal cortex
How are attentional resources allocated?
Attentional resources are allocated depending on the processing needs.
filter theory
bottle neck theory; take in a little information at once
serially process multiple tasks to complete one and then the other
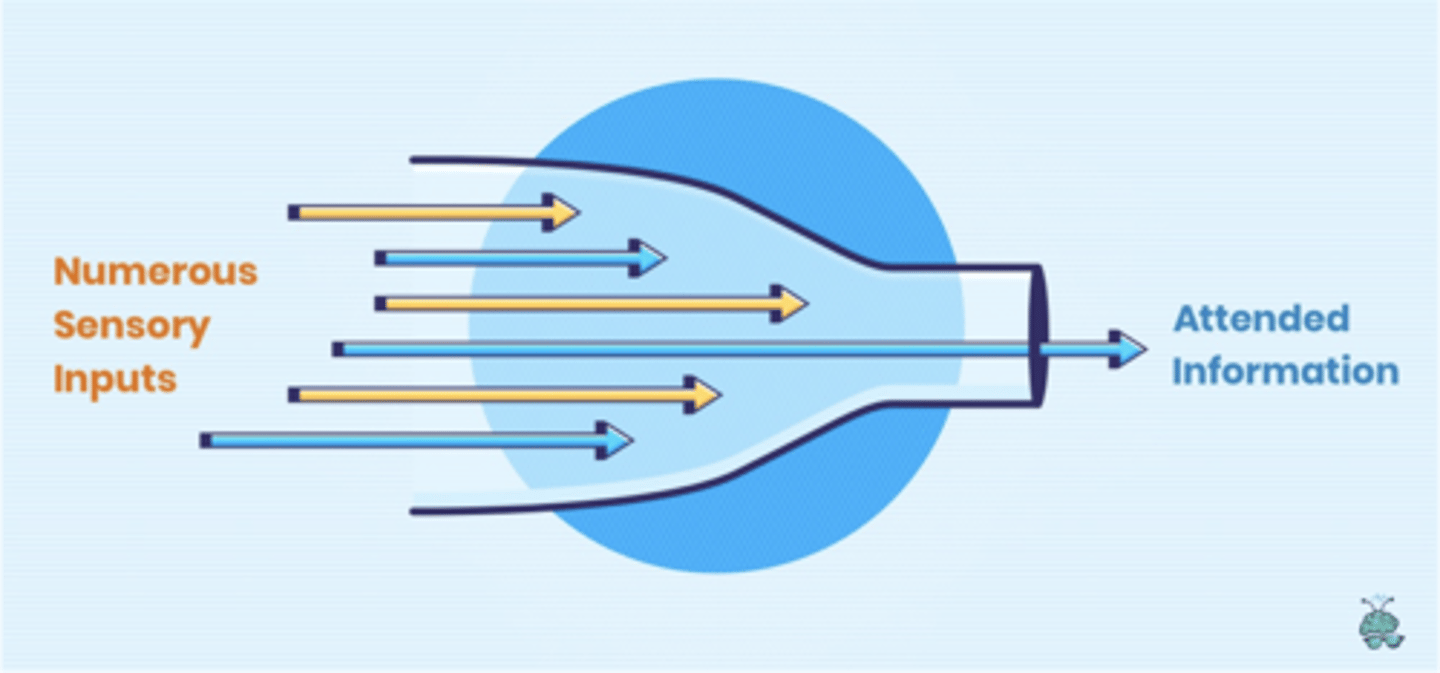
resource capacity
each resource has a limited capacity (visual sys., hearing, tactile, etc) the things we do the most get the most allocation
example: can look at the tv while doing something with my hands and listening to something else other than what im looking at
central resource capacity
Kahneman's attention
one central resource that determines our capacity - as long as resource is not at its capacity, we can be successful
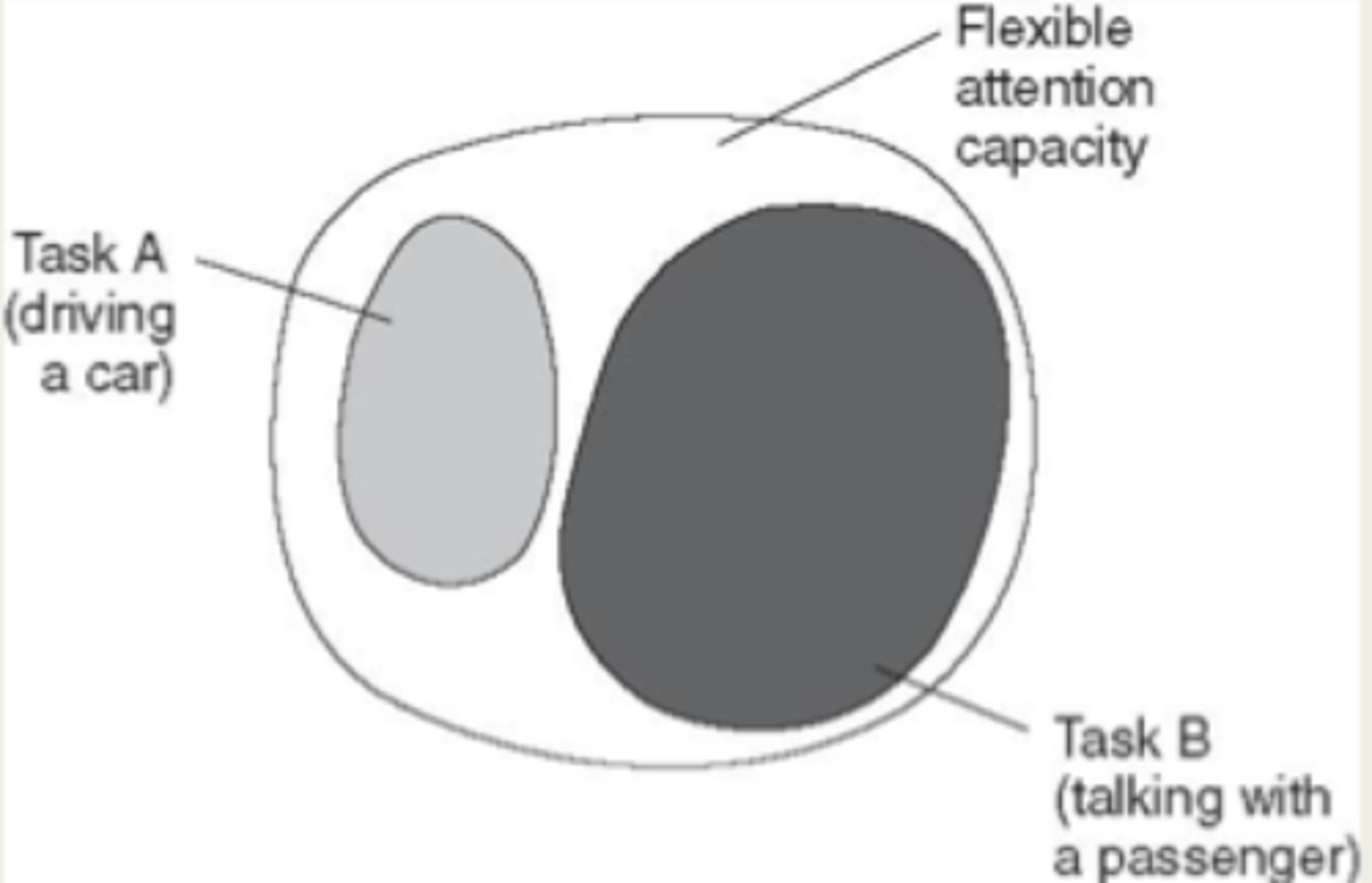
multiple resource
multitasking
- several resources for attention
- depends on type/need
- Success with multitasking as long as resources aren't competing against each other/ Cannot maximize or task becomes unsuccessful based on clients ability
- Cannot use for clients who can only follow one step commands