BIS 2C Midterm 2
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
This part of the eukaryotic cell…
- contains most of the DNA
- is the site of DNA replication and where gene transcription occurs
- surrounded by double membrane
nucleus
Do asgard archaea have a nucleus? (Y/N)
N
This part of the eukaryotic cell…
- site of respiration and production of ATP for eukaryotes
- energy in fuel molecules transformed to bonds of ATP
- cells that require a lot of energy have many of this!
- two membranes
mitochondria
The (inner/outer) membrane of the mitochondria folds into ____________ to create high surface area for respiration.
inner, cristae
The ___________________ Theory: Mitochondria and other organelles originated from bacteria that were brought inside eukaryotic cells long in the past.
endosymbiotic
The fact that mitochondria look a lot like bacteria means they must have once been bacteria. (T/F)
F
Mitochondria have their own genomes and replicate independently of the nucleus. (T/F)
T
The fact that mitochondria have DNA genomes shows that they are derived from bacteria. (T/F)
F
Mitochondria trace a common ancestry to the ________ subgroup of __________________.
alpha, proteobacteria
Mitochondria are (paraphyletic/polyphyletic/monophyletic).
monophyletic
Can the antibiotics that target peptidoglycan have detrimental effects on mitochondria? (Y/N)
N
symbiosis where host brings another organism inside of its cells
endosymbiosis
when symbiont is experiencing its first endosymbiosis
primary endosymbiosis
The endosymbiosis model for mitochondrial origins represents the MRCA of all eukaryotes. (T/F)
F
Every single eukaryote has a mitochondria. (T/F)
F
These two excavates do not have a mitochondria.
diplomonads, parabasalids
This part of the eukaryotic cell is…
- used by plants and other euk. to carry out photosynthesis
- inner membrane forms thylakoids with pigments to harvest light energy
- fatty acid synthesis and energy storage
- double membrane
chloroplast
Chloroplasts trace a common ancestry to a single lineage within the ________________ phylum.
cyanobacteria
Chloroplasts are (paraphyletic/polyphyletic/monophyletic).
monophyletic
Chloroplasts originate from (primary/secondary/tertiary) endosymbiosis. (IN EUKARYOTES)
secondary
The symbiont cell wall is lost in every single chloroplast. (T/F)
F
Which hypothesis is NOT supported by analysis of phylogeny of chloroplasts?
A. ancestral and loss —> chloroplast is an ancestral trait and lost in later lineages
B. diversification of major lineages —> endosymbiosis in Plantae ancestor, then other organisms with chloroplasts got them later
A
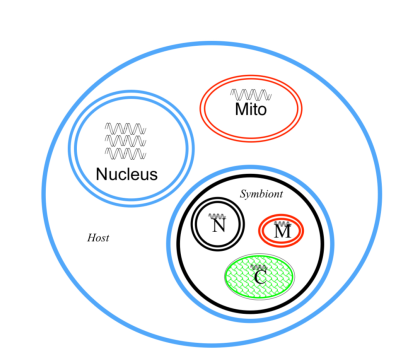
How many different histories could there be in an organism after it has gone through a secondary endosymbiosis? (Number)
5
These excavates are…
- MOST unicellular
- swim with flagella
- many photoautotrophic with chloroplast and some can be heterotrophic
euglenids
In euglenids, we learned that the Plantae endosymbiont was a ______________.
chlorophyte
These stramenopiles are…
- unicellular but many associate in filaments
- carotenoids + appear yellow/brown
- most phototrophic with chloroplasts
- responsible for 20% of all carbon fixation
diatoms
In diatoms, we learned that the Plantae endosymbiont was a ________ ___________.
red algae
a practice that learns from and copies the strategies found in nature to solve human design challenges in a regenerative way
biomimicry
What lineage of plantae kept the peptidoglycan cell wall after primary endosymbiosis?
glaucophyte
The branch to red algae and green plans include (gain/loss) of peptidoglycan.
loss
Which green plant has developed a multilayered structure?
A. chlorophyte
B. streptophyte
B
The multi-layered structure in ____________________ acts as a lineage marker. It is also known was a _________________.
streptophytes, synapomorphy
What are plant stem cells called?
meristems
In land plants, apex = highest point, so we get ________________ meristems.
apical
Land plants developed phragmoplast, which is a cell plate with __________________. It allows cells to communicate.
plasmodesmata
What lineage developed…
- branched filaments
- apical growth (meristems)
- phragmoplast, plasmodesmata
land plants
reproductive cells that are not gametes
spores
reproductive cells that can be identical (not male/female) or unequal in size
gametes
The larger, non-motile gamete is the ________ and the smaller, more motile gamete is the _____________.
egg, sperm
plant
phyte
plant stage (body) that makes spores
sporophyte
plant stage (body) that makes gametes
gametophyte
In chlorophytes, the ___________________ germinate to be gametophytes. This is the starting condition for the ________________________ life cycle.
zoospores, streptophyte
This refers to the development of egg and sperm.
oogamy
structures to make gametes
gametangia
structure that makes eggs
archegonium
structure that makes sperm
antheridia
Archegonium and antheridia are both _________________.
gametangia
base of archegonium that grows around embryo
protected embryo
structure that makes spores developed in land plants
sporangia
The delay of meiosis leads to a _______________________ stage.
sporophyte
In land plants, spores grow into _____________________.
gametophytes
The reproductive cycle of land plants is known as ___________________ _____ __________________.
alternation of generations
The sporophyte is (diploid/haploid) and makes (diploid/haploid) spores.
diploid, haploid
In land plants, eggs and sperms are made by (meiosis/mitosis). This is because the ____________________ is (diploid/haploid).
mitosis, gametophyte, haploid
Land plants are also called ___________________ due to the retained protected embryo.
embyrophytes
The starting conditions of land plants came from aquatic ancestors. Spores are present, but to disperse on land a ____________________ wall evolves.
sporopollenin
In land plants, the plant body evolves a ______________ to reduce water loss.
cuticle
Water no longer surrounds the body of land plants, so uptake occurs by ___________.
rhizoids
Rhizoids are true roots. (T/F)
F
These three plants are non-vascular…
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
Alternation of generations caused the origin of ___________________.
sporophytes
Alternation of generations, antheridia, archegonia, sporangia, air-dispersed spores, cuticle, rhizoids, and mycorrhizae all evolved in ______________ ________________.
land plants
“fungus roots”, liverworts had a particular symbiosis with these fungi
mycorrhizae
Did liverworts develop stomata? (Y/N)
N
Do liverworts, mosses, hornworts make up a clade? (Y/N)
N
Liverworts come in these two types…
thalloid, leafy
The sporophyte is nutritionally dependent on the _____________________.
gametophyte
The sporangium in sporophytes release _________________.
spores
Aquatic plants are supported by water, but in the earliest land plants, liquid water is required for:
A. gas exchange
B. reproduction
C. embryo protection
D. a supply of carbon
B
Which of the following traits of terrestrial plants reduce water loss (dessication)?
A. cuticle
B. stomata as opposed to open pores
C. gametangia
D. presence of chlorophyll b
E. A and B
E
Which statement about alternation of generations is true?
A. the life cycle includes both multicellular gametes and multicellular spores
B. gametophytes product gametes by mitosis
C. sporophytes produce spores by mitosis
D. sporophytes produce gametes by meiosis
B
In nonvascular land plants, sperm have evolved to not need to swim anymore to meet the egg. (T/F)
F
In mosses, the sporophyte is (brown/green).
brown
Mosses do not have chlorophyll in the sporophyte so it cannot feed itself and is nutritionally dependent on the __________________.
gametophyte
Moss have “upgraded” from pores in the cuticle to _________.
stomata
___________ moss creates peat bogs which are acidic wetlands with faster deposition than decay. There is (high/low) oxygen in these lands.
spagnum, low
Hornworts have a persistently (green/brown) sporophyte. In these types of nonvascular plants, the sporophyte is no longer nutritionally dependent on the ________________.
green, gametophyte
Hornworts have internal symbiotic cyanobacteria that can fix ______________.
nitrogen
___________________ are also called club moss.
lycophytes
Lycophytes are (nonvascular/vascular) plants and are the only plants that have (microphylls/megaphylls).
vascular, microphylls
These plants are all extinct but had basic vascular tissue.
rhyniophytes
Rhyniophytes have ________________ branching and uses _____________ attached to rhizomes to collect H2O.
dichotomous, rhizoids
In the stem, the _____________ conducts water and the _______________ conducts sugars, etc.
xylem, phloem
moves water and lignified walls of cells provide support
xylem
first vascular tissue; dead cells, they were connected to form hollow tubes that use to move water (evapotranspiration)
tracheid
To get the (source/sink) to the (source/sink), a __________ is used to transport the sugars.
source, sink, phloem
In a plant the sites of photosynthesis (makes sugars) is the _________ and where the sugar made is ended up is the _________.
source, sink
What are the extant relatives of the tree lycophyta that existed in the Carboniferous?
quillworts
Sterilized sporangium hypothesis for the evolution of microphyll leaves:
(Vertical/Lateral) sporangia occurred first, then were “sterilized” to become (microphylls/megaphylls).
lateral, microphylls
Do lycophytes have flowers? (Y/N)
N
In lycophytes the ______________ is a leaf that bears sporangia.
sporophyll
Sporophylls are grouped into _____________, which are also called cones. The sporangia is grouped into clusters.
strobili
Lycophytes go through alternation of generations, but the two different types of cycles are _____________ (same spores) and ________________ (different spores).
homospory, heterospory
In heterospory, the megaspore forms into the megagametophyte which makes the (sperm/egg). The microspore goes from the microgametophyte to the (sperm/egg).
egg, sperm
In sporophytes, the two different types of sporangium are the _______________ (egg) and __________________ (sperm).
megasporangium, microsporangium
The origin of the megaphyll began from the dichotomous branching of the ___________________.
rhyniophytes
After the rhyniophytes developed dichotomous branching, _______________ evolved, which is unequal branching (lateral branch). After this stage, branching in one plane developed, which flattens veins to be parallel. This is called _____________.
overtopping, planation
The last step of the origin of the megaphyll is the marginal meristem forming. ____________ is created from meristem tissue and becomes a leaf.
webbing
Do tree ferns have woody tissue? (Y/N)
N