Week 7 BIOL Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Cell Cycle
A Series of Phases That Lead to Cell Division + highly regulated process, to ensure that cell division occurs at the appropriate time.
What are two techniques that can be used to compare the level of an mRNA between two samples?
A transcription factor was recently found to play a role in drought tolerance in plants. You want to study the effect of knocking out and overexpressing this transcription factor on gene expression. What technique would you use and why?
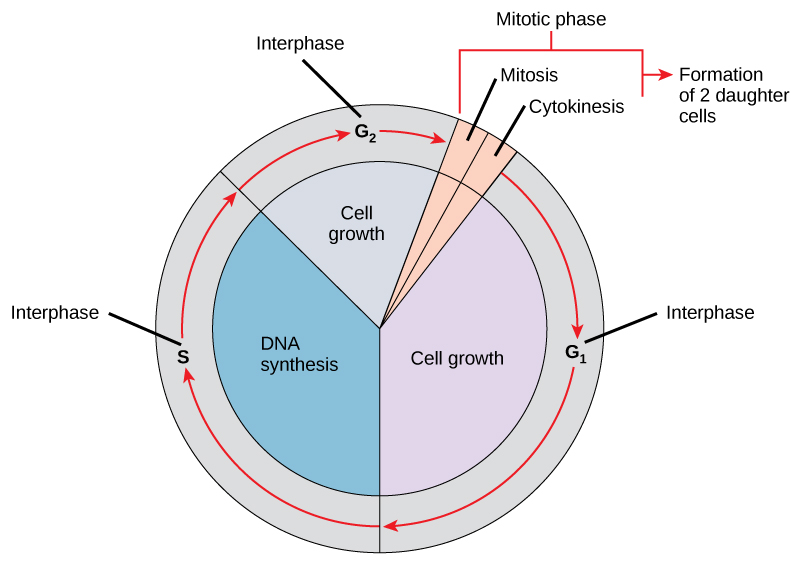
Interphase
In actively dividing cells, the G, S, and G, phases are collectively known
The cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division.
G1 Phase (Gap 1)
Characterized by cellular growth and the accumulation of molecular signals that determine whether the cell will proceed to division. Progression through this phase depends on environmental conditions and regulatory signaling molecules.
S Phase (Synthesis)
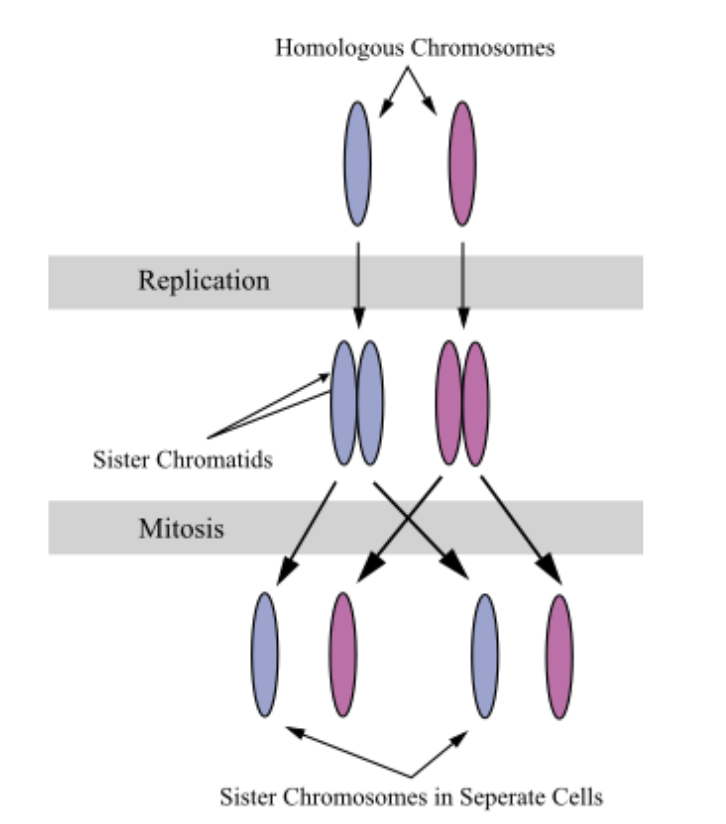
Each chromosome is replicated to form a pair of sister chromatids
A cell has twice as many chromatids as the number of chromosomes in the G, phase.
46 pairs of sister chromatids,
92 chromatids
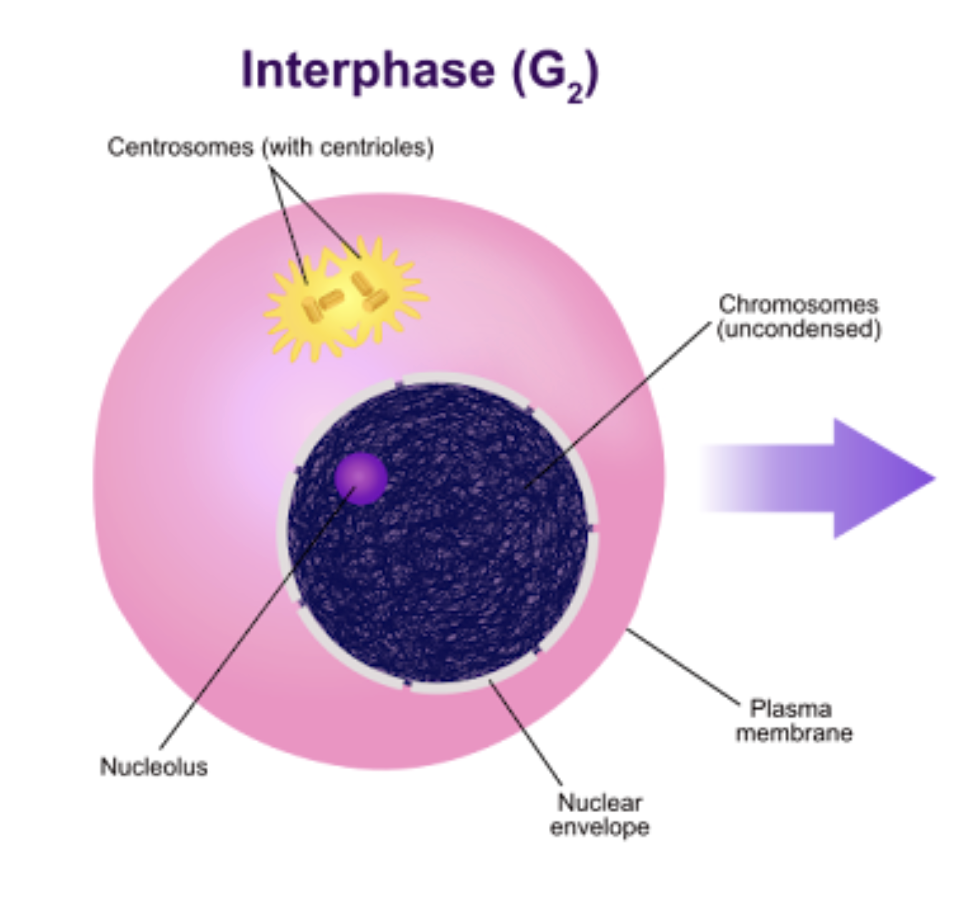
G2 Phase (Gap 2)
During the G, phase, a cell synthesizes the proteins necessary for chromosome sorting and cell division. Some cell growth may occur.
M Phase (Mitosis)
Divide one cell nucleus into two nuclei, distributing the duplicated chromosomes so that each daughter cell receives the same complement of chromosomes
1 hour
Controlled by
External factors: environmental
conditions & signaling molecules.
Internal factors: Cell cycle control molecules and checkpoints,
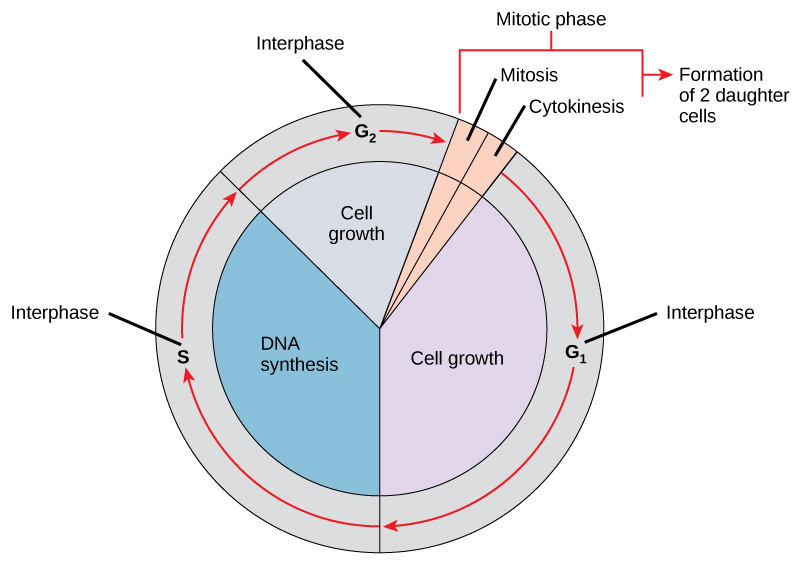
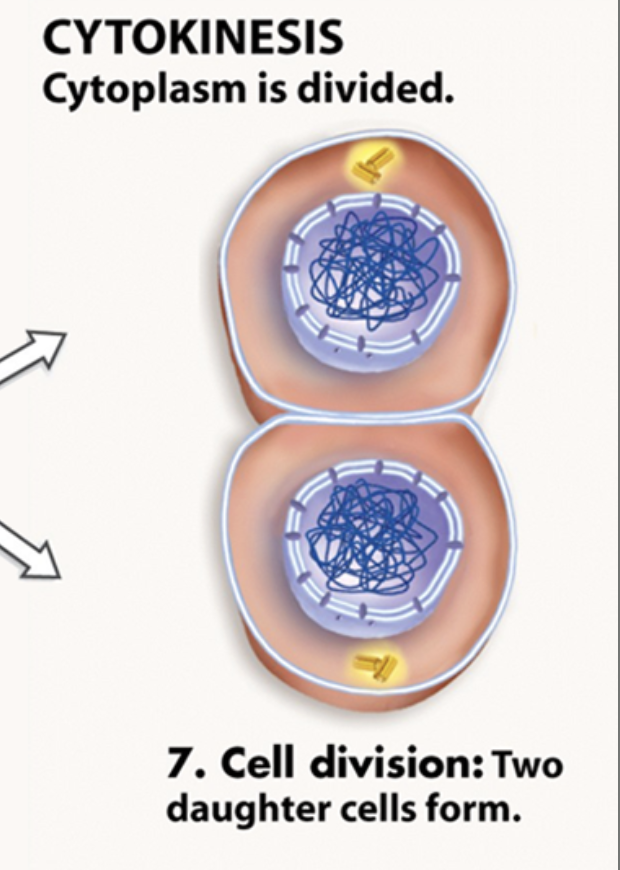
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm to produce two distinct daughter cells (Happens after mitosis)
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes.
Chromatin is formed when long strands of DNA wrap around histone proteins, creating bead-like structures known as nucleosomes.
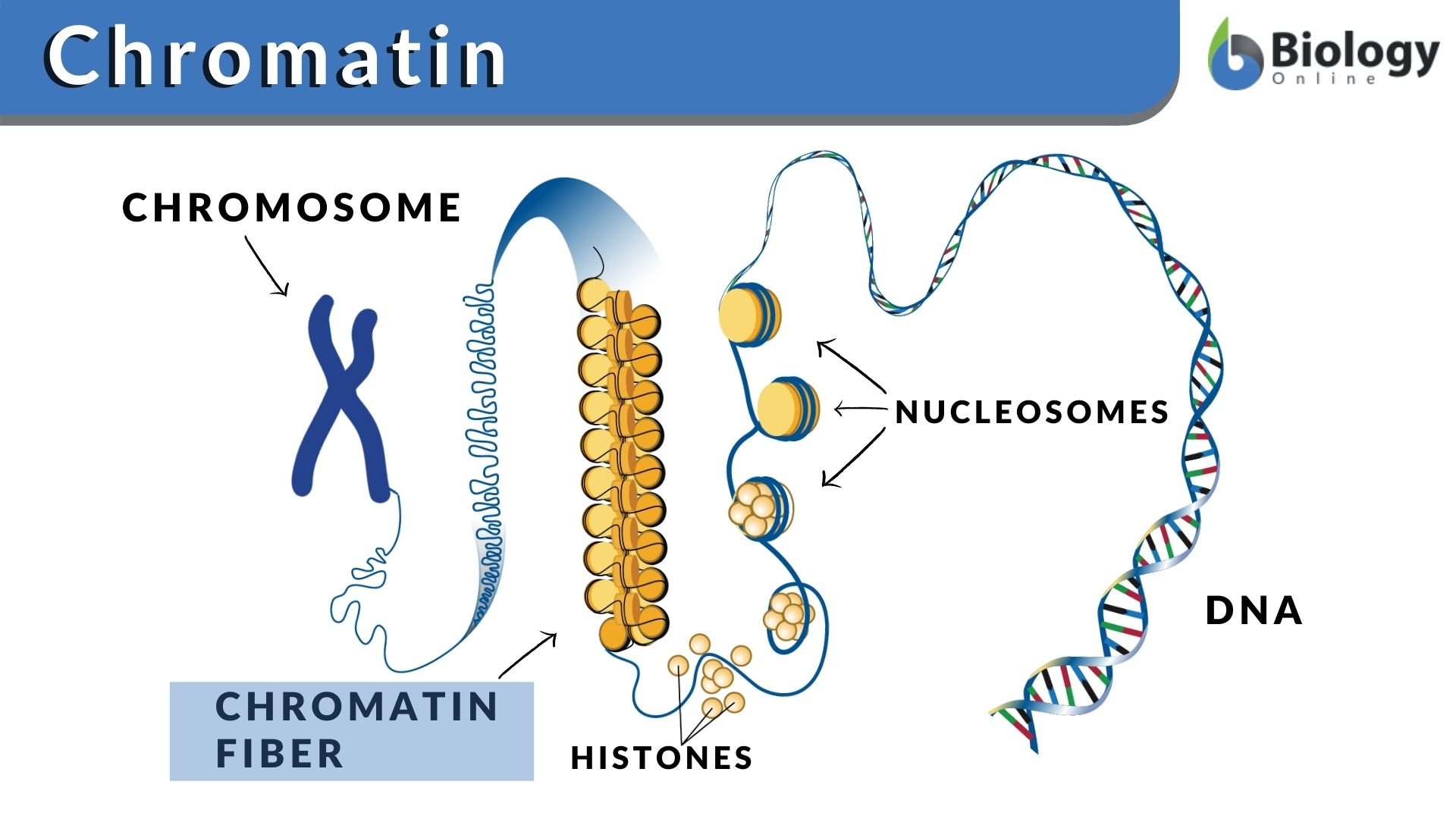
Chromosome
A discrete unit of genetic material composed of DNA and associated proteins. Eukaryotes have chromosomes in their cell nuclei and in plastids and mitochondria.
23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes.
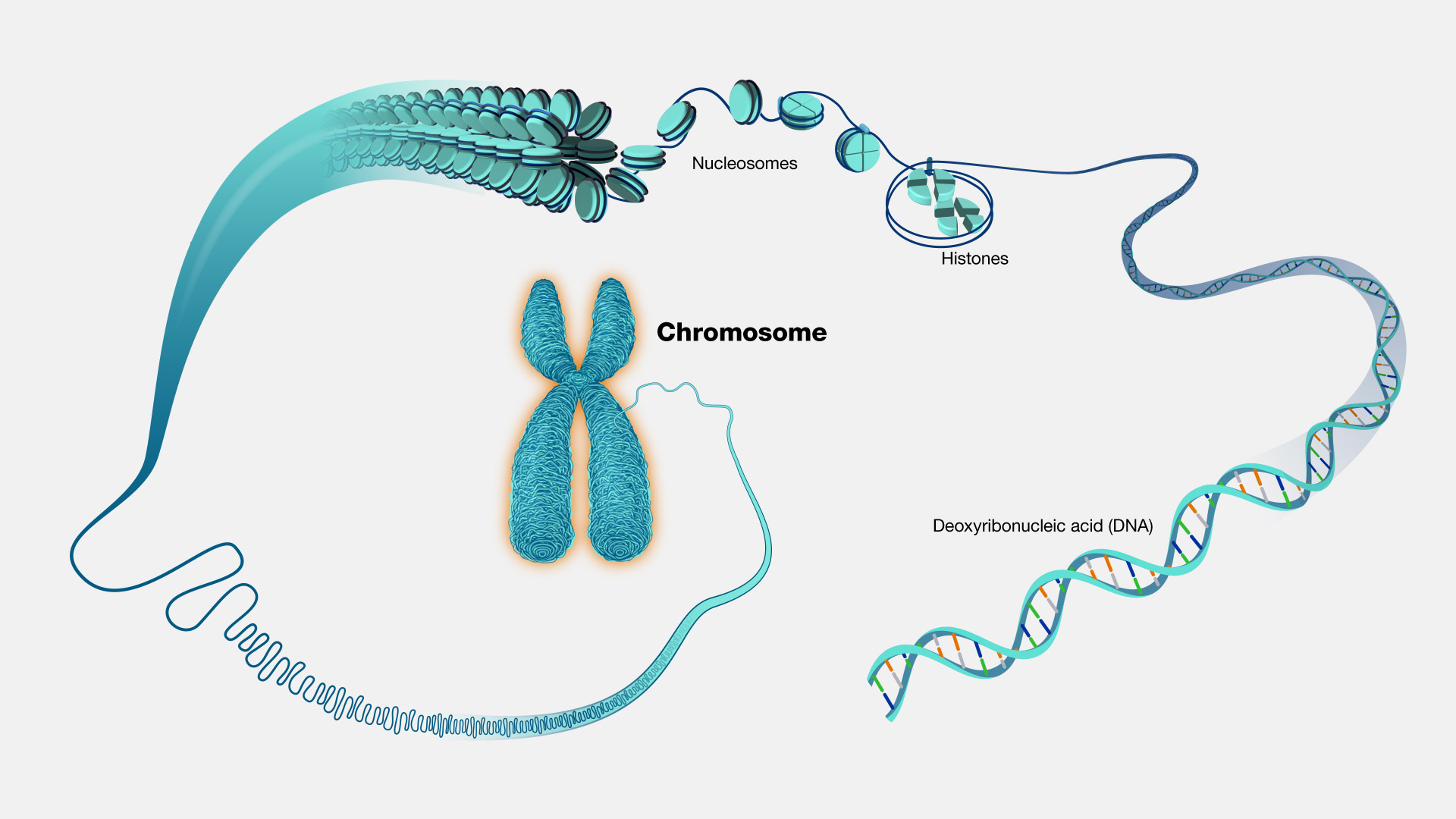
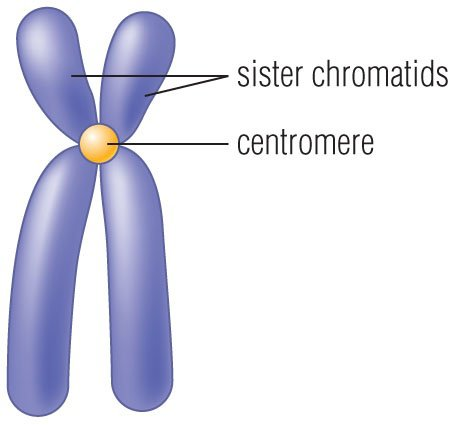
Sister Chromatids
The two duplicated chromatids that are still joined to each other after DNA replication.
A chromatid is one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division.
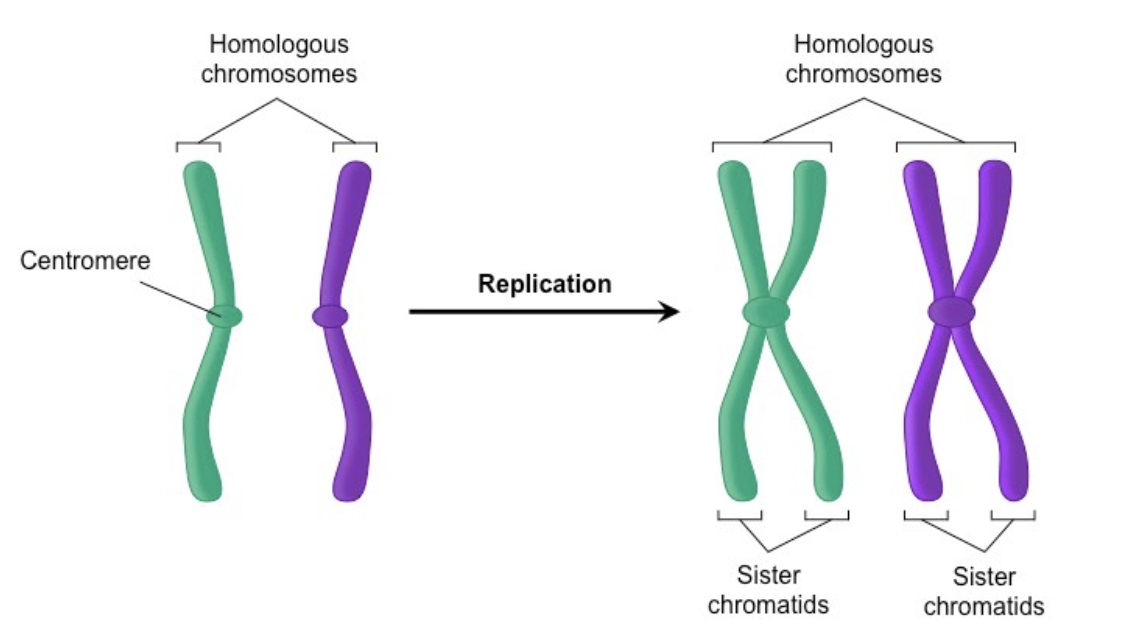
Centromere
Structure in a chromosome that holds together the two chromatids
the site for the attachment of spindle fibre
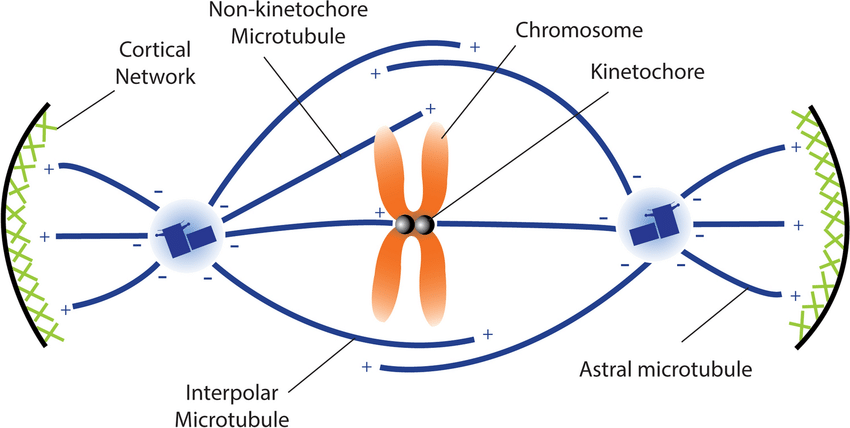
Mitotic Spindle
A characteristic arrangement of microtubules shaped like a spindle during mitotic division of a cell nucleus to align and move chromosomes at metaphase and anaphase
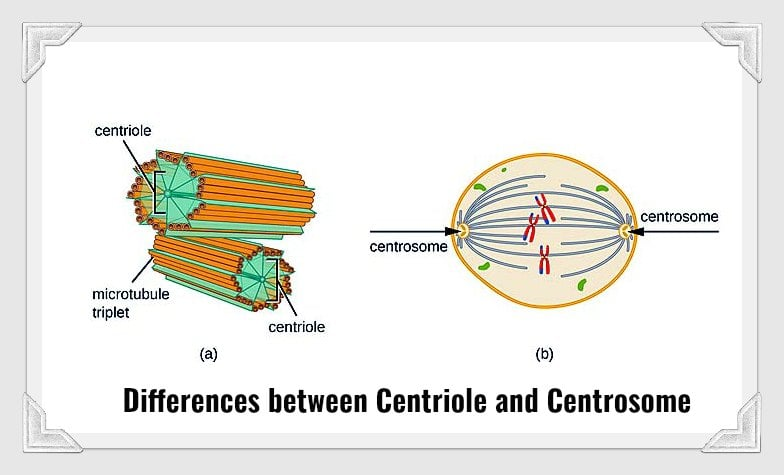
Centrioles
Paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
Organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system.
They help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles within the cell.
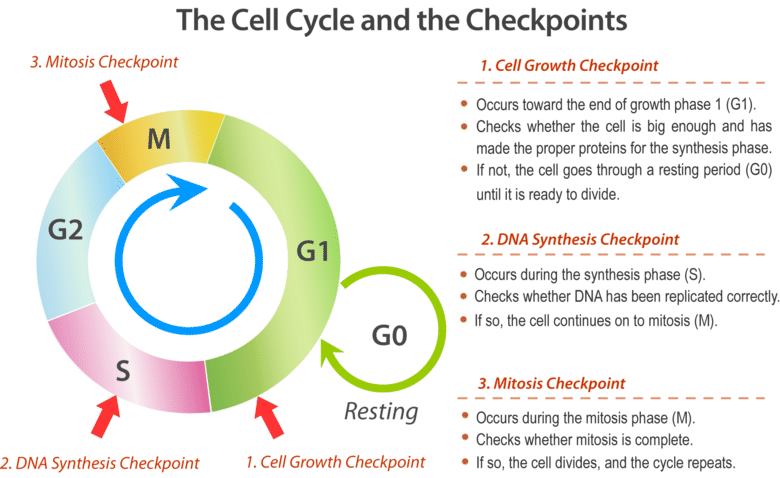
S Phase Checkpoint
The cell examines whether all the sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle microtubules
cycle will not proceed until all the chromosomes are firmly attached to at least two spindle fibers from opposite poles of the cell.
look for "straggler" chromosomes that are in the wrong place (e.g., floating around in the cytoplasm)
If a chromosome is misplaced, the cell will pause mitosis, allowing time for the spindle to capture the stray chromosome.
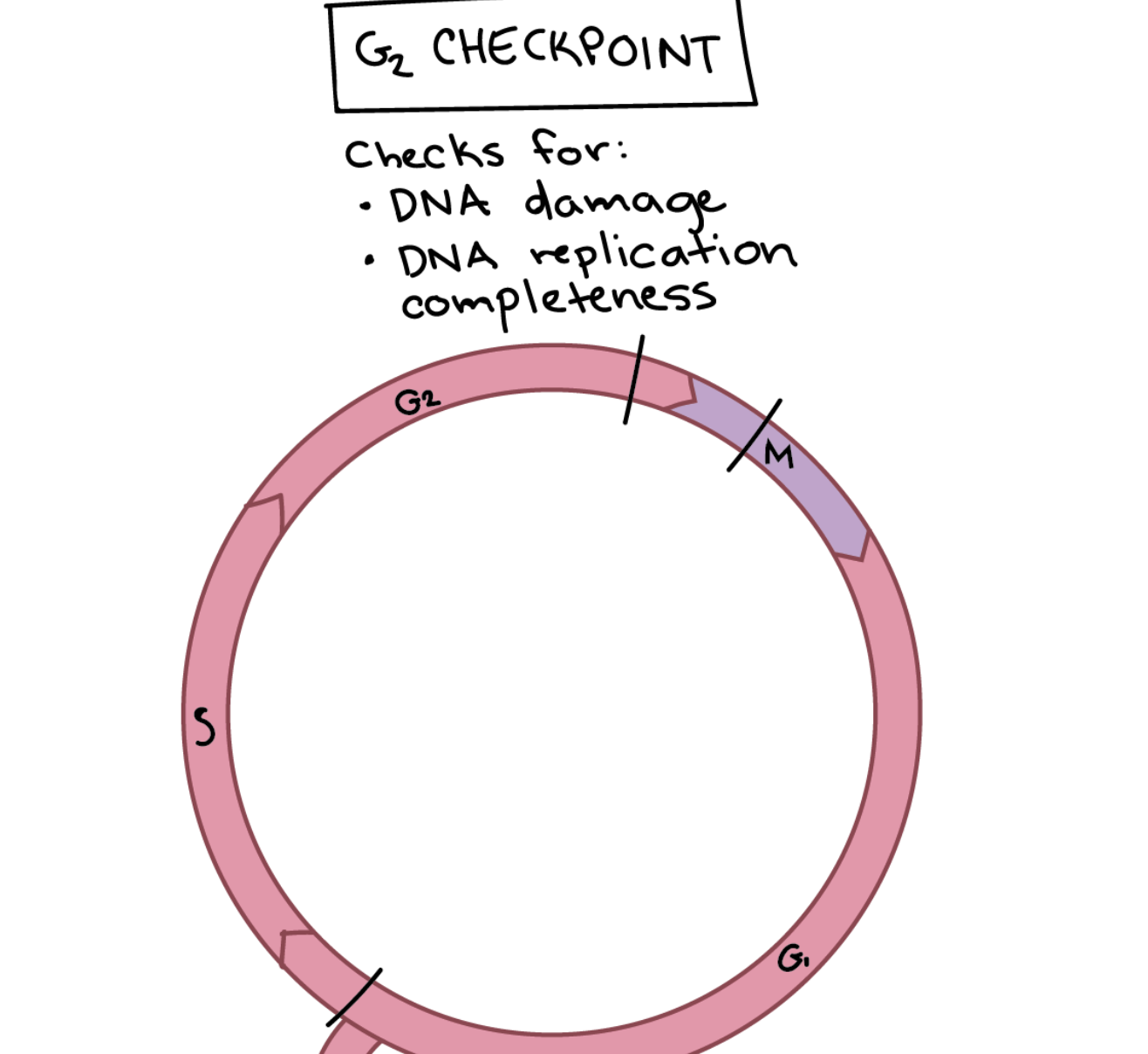
G2 Phase Checkpoint
Prevents cells from entering mitosis when DNA is damaged. Either complete DNA replication or repair the damaged DNA.
DNA integrity. Is any of the DNA damaged?
DNA replication. Was the DNA completely copied during S phase?
May undergo apoptosis,
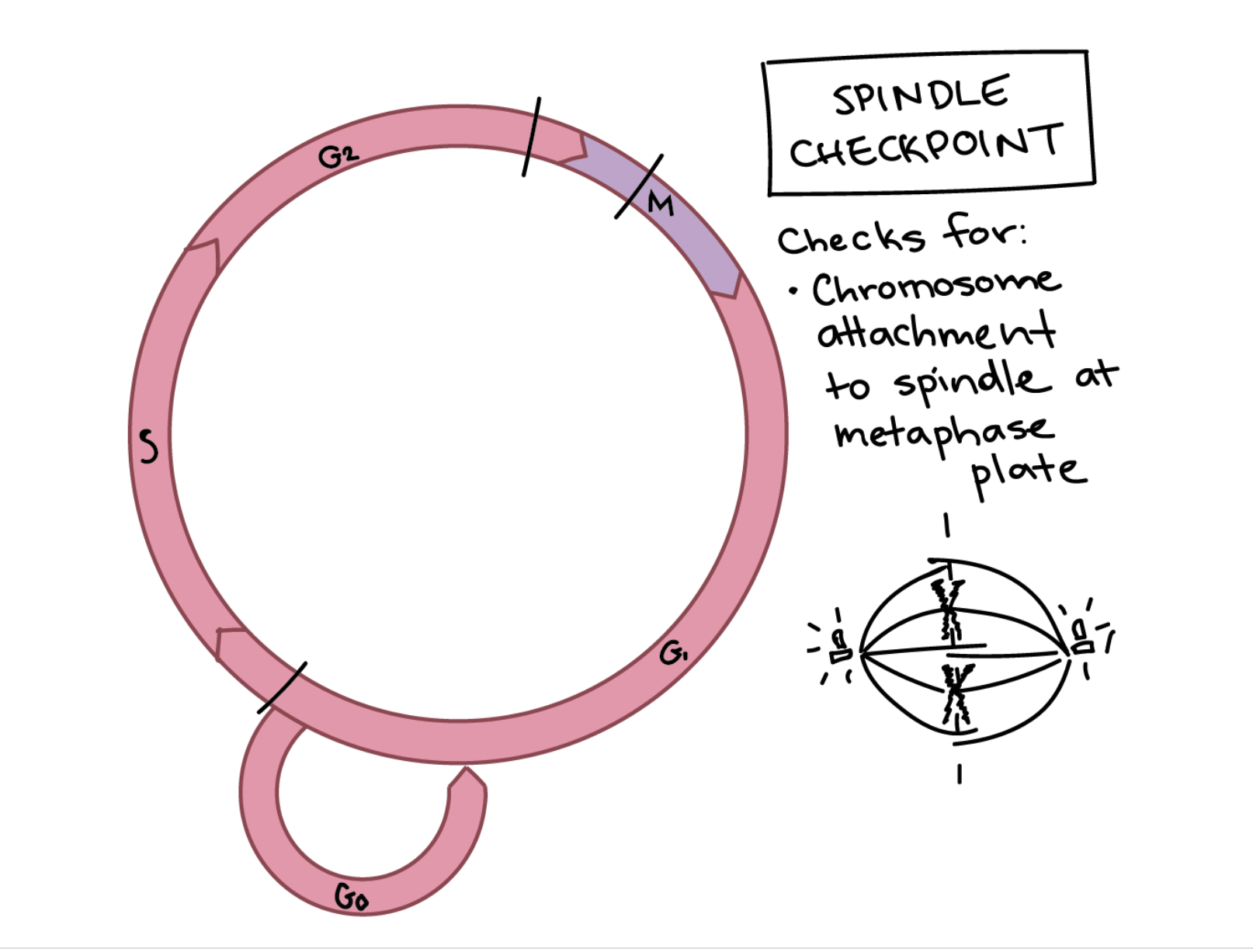
M Phase Checkpoint
Also known as the spindle checkpoint
whether all the sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle microtubules.
will happen if chromosomes are firmly attached to at least two spindle fibers from opposite poles of the cell
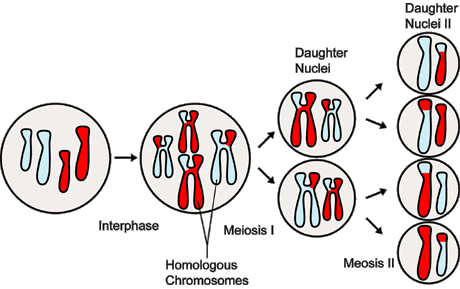
Recombination
The exchange of DNA segments between the two copies of a chromosome (one maternally inherited and one paternally inherited). This occurs during the creation of an egg or sperm for the next generation
mechanism that enacts it, crossing over, happens during Prophase I of Meiosis I
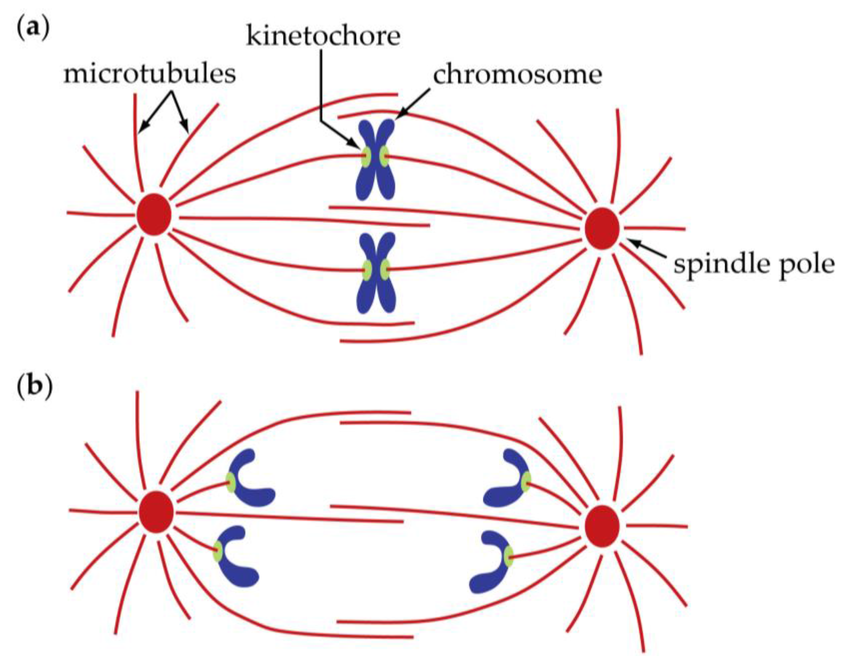
Spindle Fibers
(microtubules)
Originate from the centriole
Separate sister chromatids between daughter cells
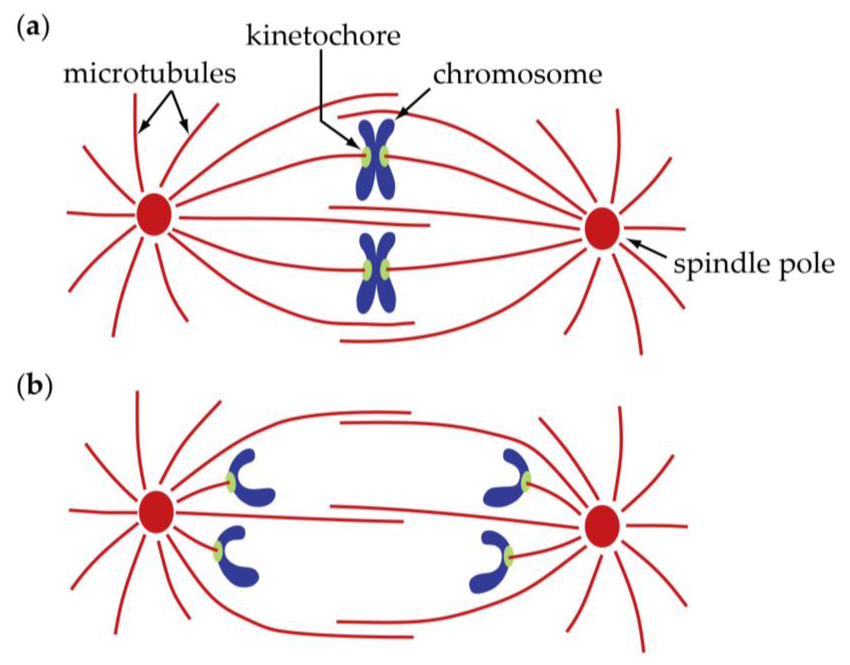
Kinetochore
Originate from the centromere
Makes binding of the spindle fibers to the chromosomes
Protein complexes on centromeres that hold the sister chromatids together
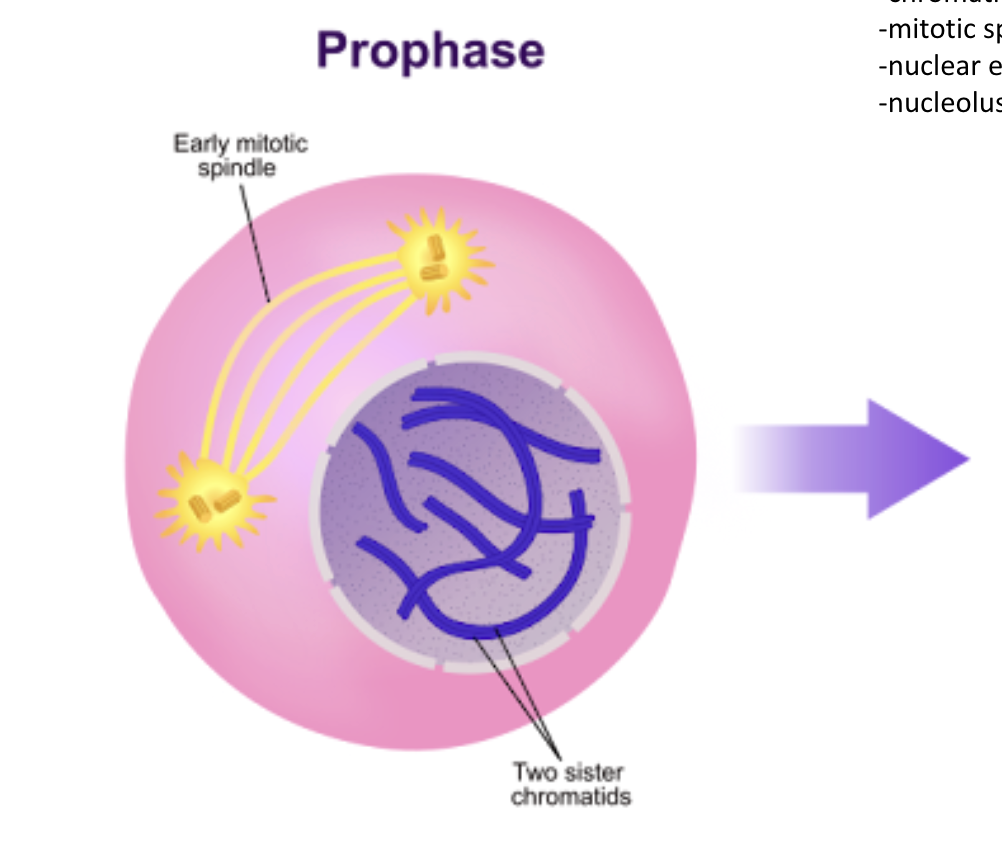
Prophase
chromatids condense
mitotic spindle forms
nuclear envelope breaks
nucleolus gone
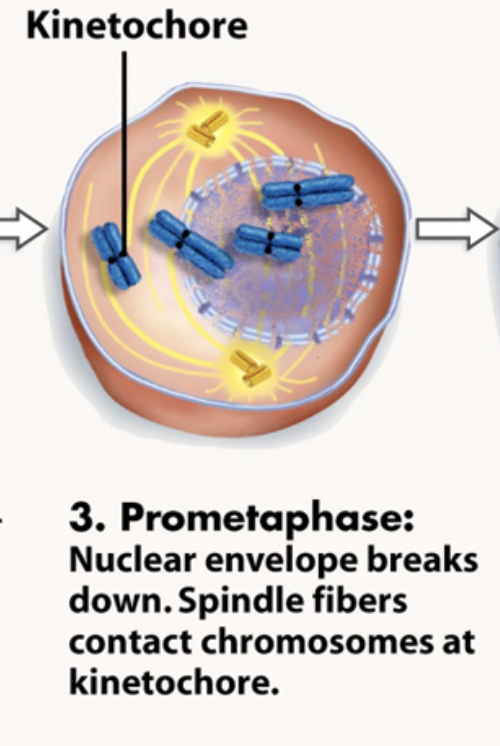
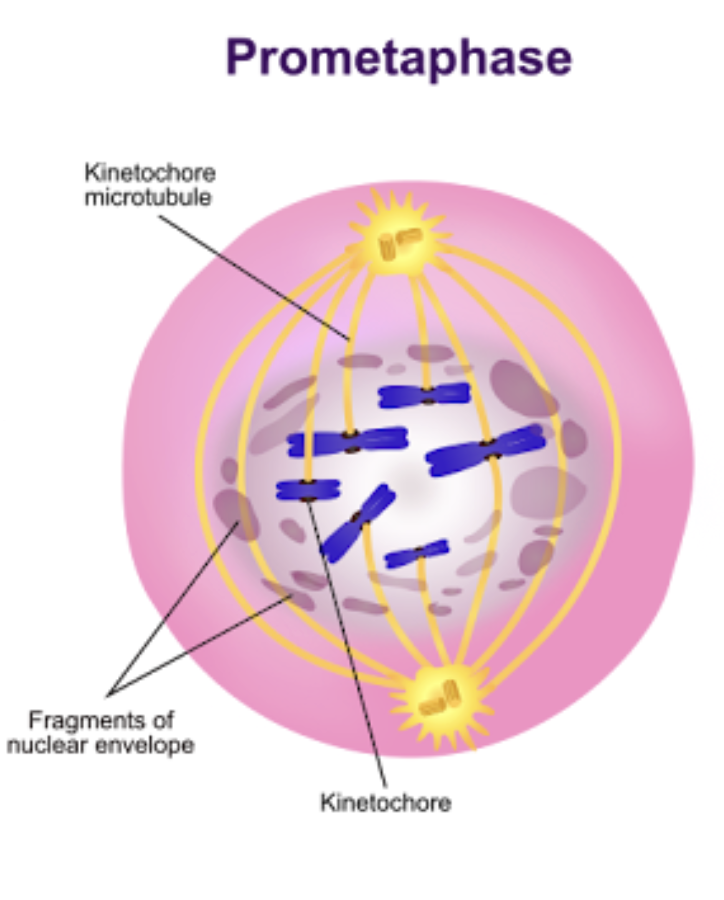
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope gone
mitotic spindle formed
chromatids attach to spindle
Metaphase
Sister chromatids align along metaphase plate
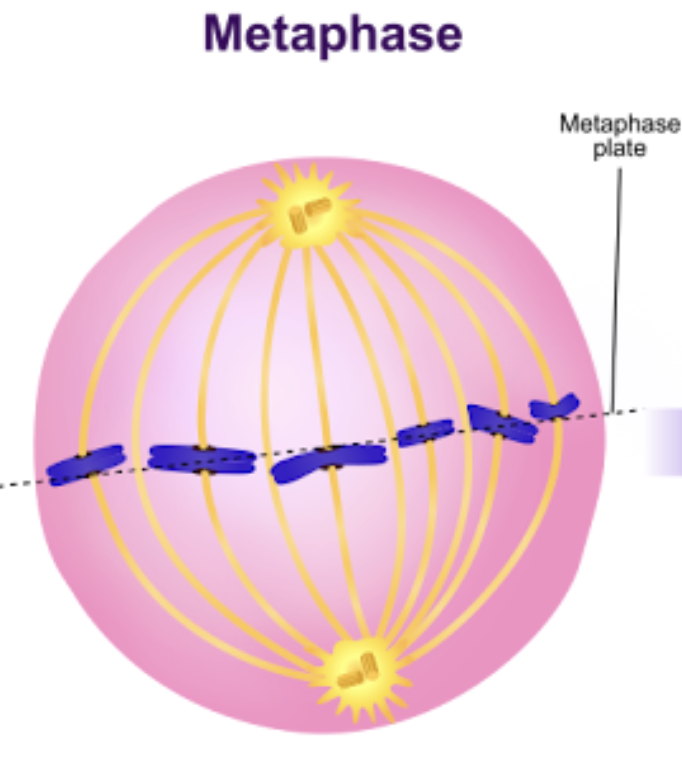
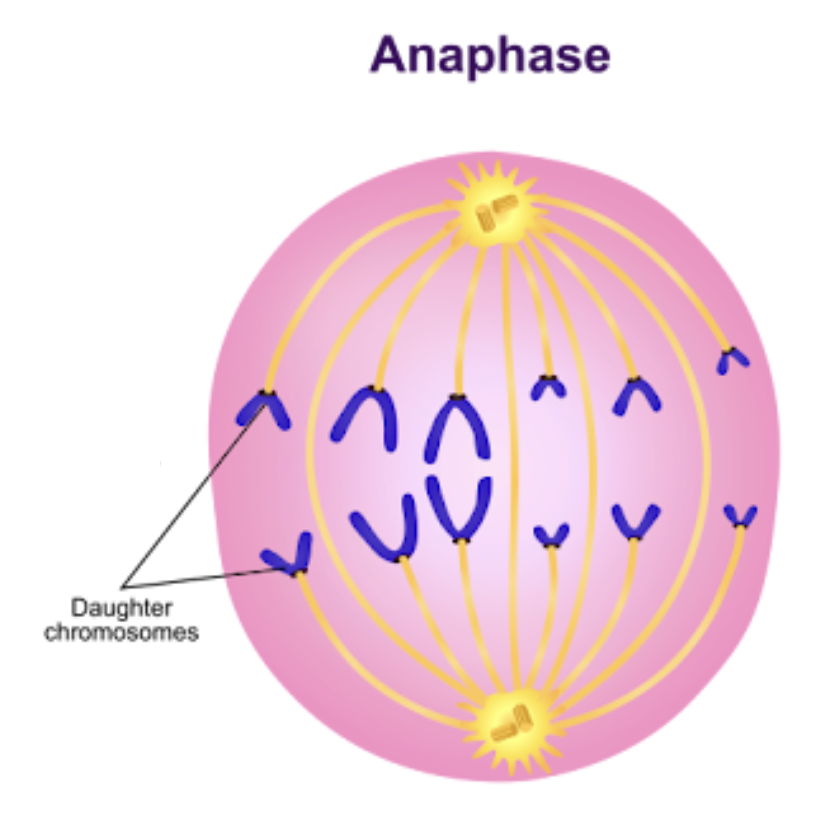
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate
chromosomes move toward poles
poles pushed apart
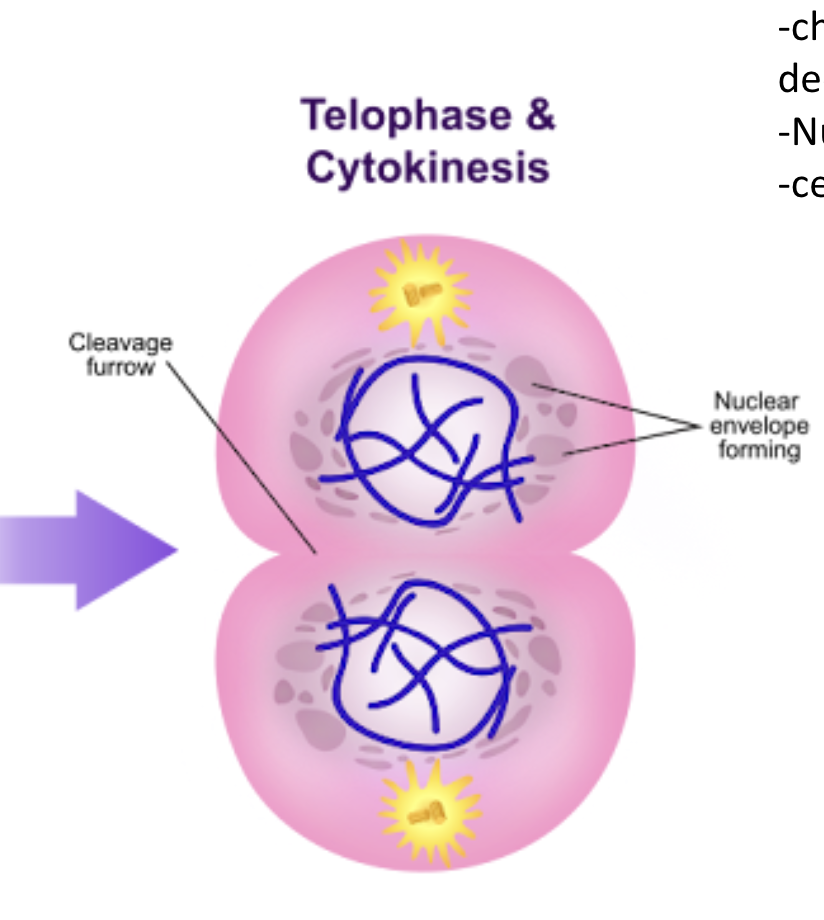
Telophase
chromosomes decondense
Nuc. envelope forms
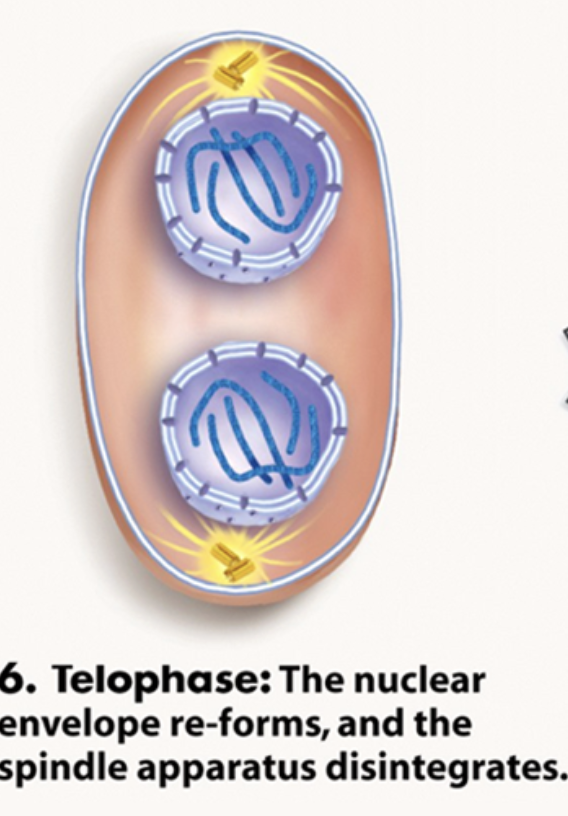
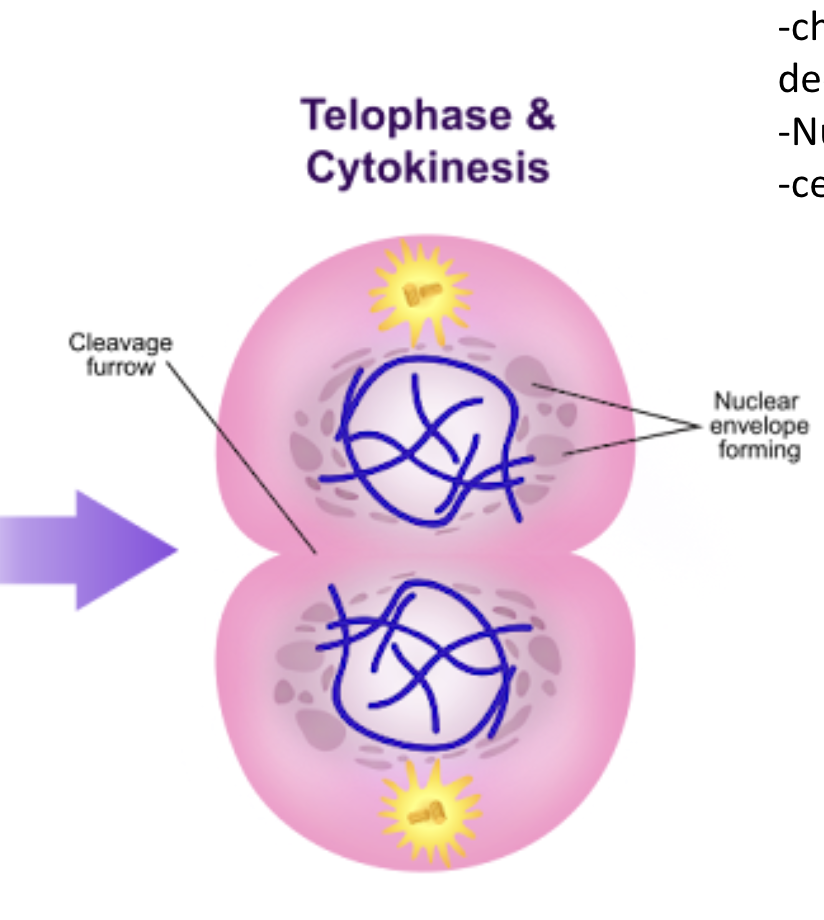
Cytokinesis
cells split in two
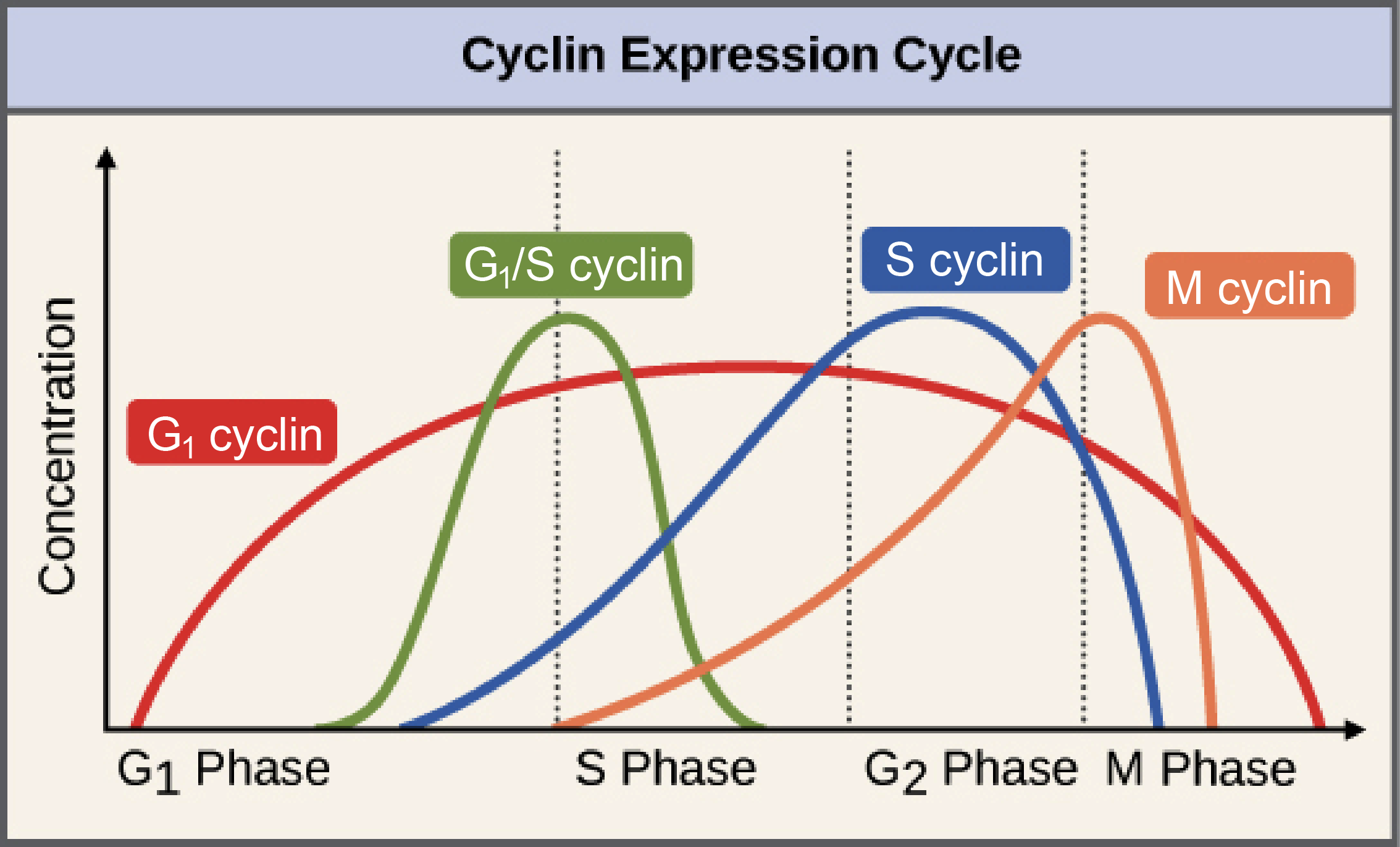
Cyclins
Control progression through cell-cycle checkpoints by phosphorylating and inactivating target substrates.
any of a group of proteins that regulates the cell cycle by forming a complex with kinases.
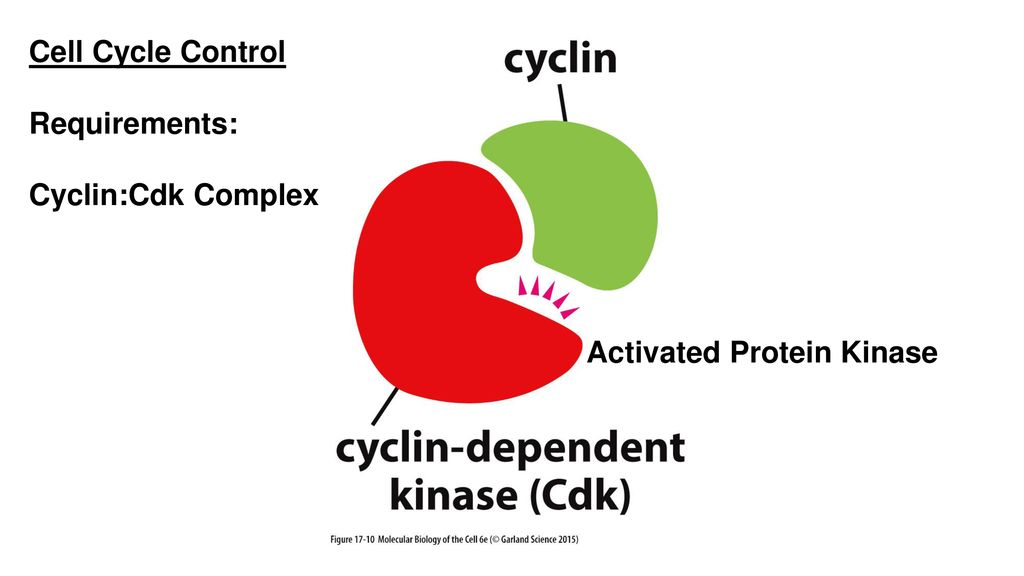
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
Regulating cell-cycle checkpoints and transcriptional events in response to extracellular and intracellular signals
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
A stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and "decides" whether or not to move forward with division.
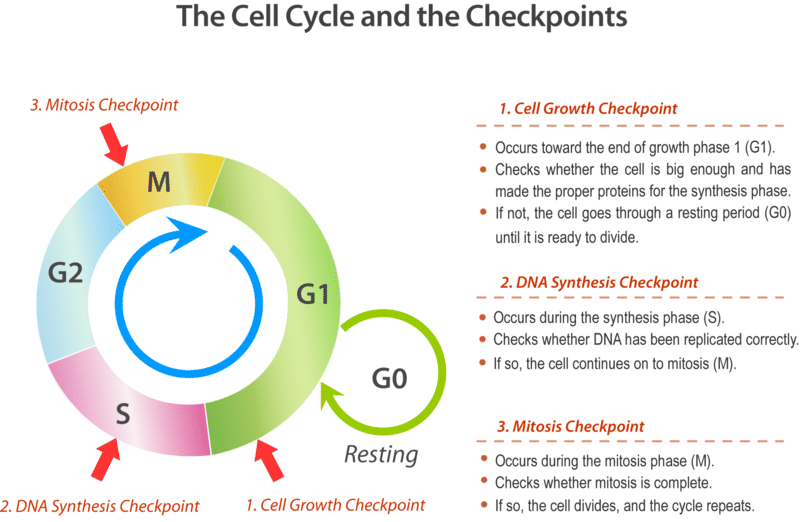
Apoptosis
An inability to repair the damage can trigger apoptosis during G1/S checkpoint
mitochondria executes the cell
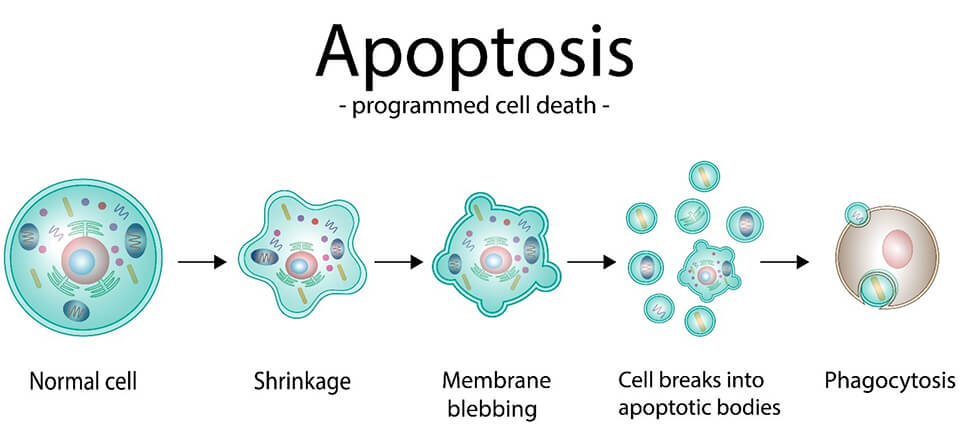
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Genes that code for protein products that regulate and slow down the cell cycle,
promote apoptosis, which is programmed cell death.
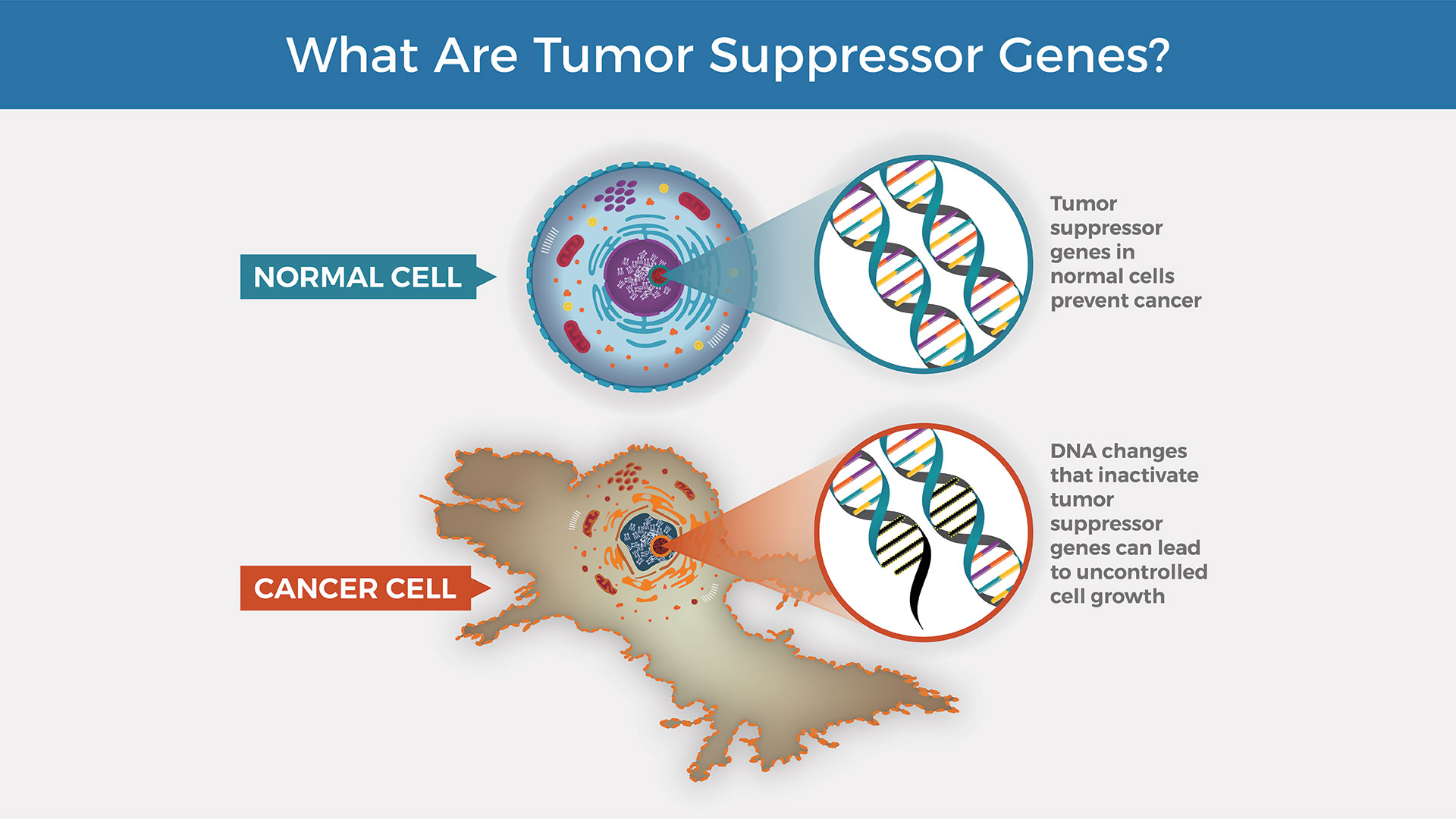
DNA Replication
Each strand in the DNA double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand
Proto-oncogene
A normal gene that helps cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Proto-oncogenes encode products like growth factors, cell cycle regulators, and transcription factors. (e.g. p53 protein)
Oncogene
A mutated proto-oncogene that can cause cancer.
cause normal cells to become cancer cells by making too many copies of themselves or becoming more active than normal.
Asexual Reproduction
Generates offspring that are genetically identical to a single parent
without the occurrence of fertilization.
Growth Factors
Promote cell division.
Nuclear Envelope
Separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm and provides the structural framework of the nucleus