OCR A-Level Chemistry: Module 6
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
What is the structure and formula of benzene?
C6H6
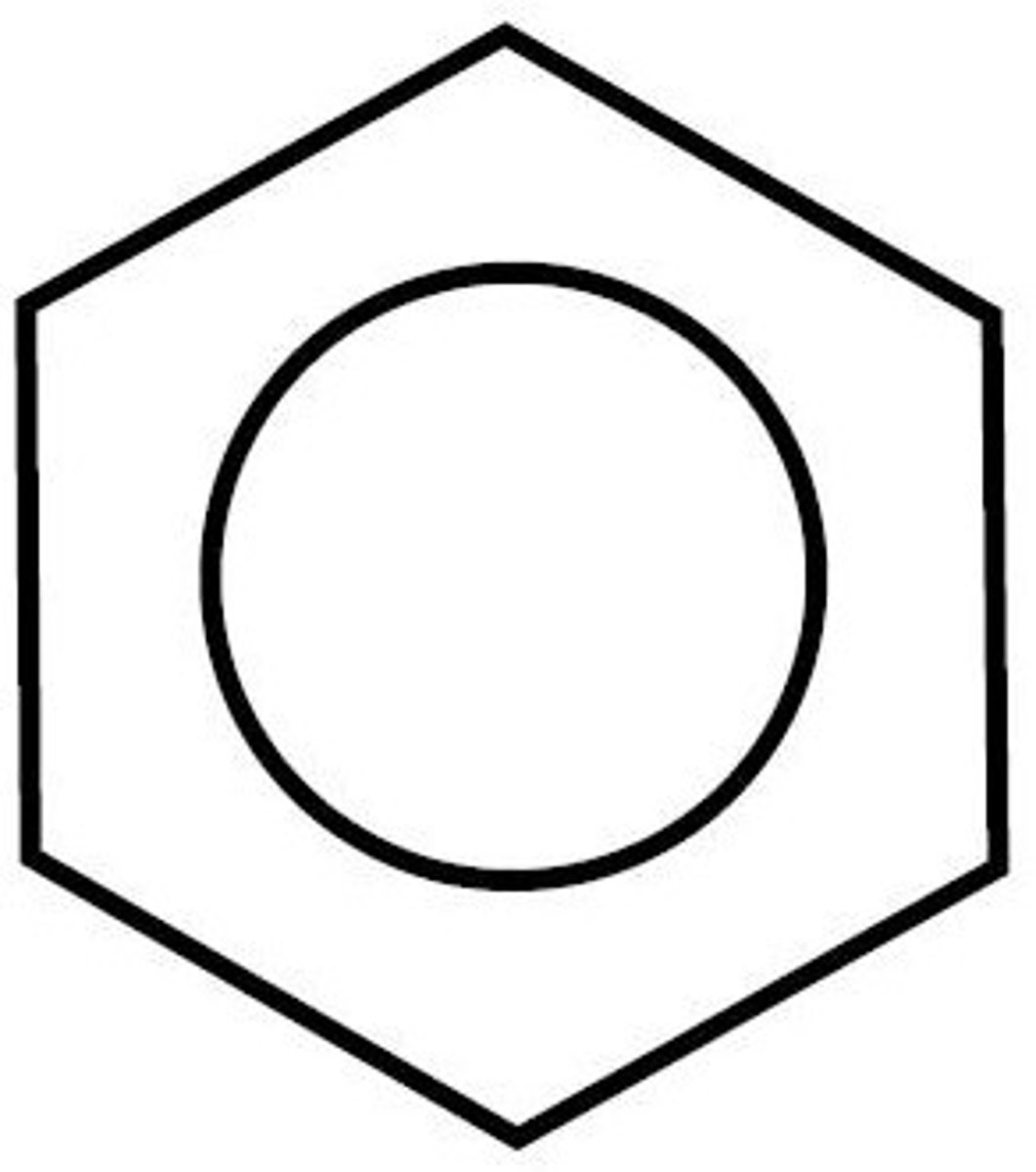
What is the empirical formula of benzene
ch
What is the state of benzene at room temperature?
liquid
What is the bond angle of benzene?
120
What are the three features of benzene that don't support Kekule's model?
Benzene is resistant to addition reactions.
Enthalpy change of hydrogenation of benzene is more stable than predicted.
All the carbon bonds are the same length.
What technique is used to find the bond lengths of benzene?
X ray diffraction.
What happens to the 4th electron in the p orbital of each carbon atom in benzene?
It delocalizes to form rings of electron density above and below the hexagon, forming rings of delocalized electron density above and below the hexagon.
How do the rings of electron density affect the stability of benzene?
It makes benzene very stable, even though it is unsaturated.
Why does benzene have a relatively high melting point?
Close packing of flat hexagonal molecules when solid.
Is benzene soluble in water and why?
No, because it's non polar.
Why is benzene not used in schools?
It is a carcinogen
How'd you name compounds containing a benzene ring?
-benzene/phenyl-
Why is benzene attacked by electrophiles?
It has a high electron density above and below the ring due to the delocalized electrons.
Nitration of benzene is what type of reaction.
Electrophilic substitution reaction
Which ion is used to nitrate benzene?
NO2+
What is the catalyst in nitration of benzene?
sulfuric acid
How is the NO2+ generated for nitration of benzene
HNO3 + H2SO4 ---> NO2+ + H2O + HSO4-
How is the H2SO4 catalyst regenerated in the nitration of benzene?
HSO4- + H+ = H2SO4
What type of catalyst is used for a friedel craft's reaction?
A halogen carrier such as AlCl3.
Why does benzene not react directly with halogens?
The aromatic ring is too stable
What is happening when AlCl4- is formed in terms of electrons?
The lone pair of Electrons on the chlorine atom is forming a coordinate bond to the Al
How is the AlCl3 catalyst reformed?
AlCl4 - + H+ → HCl + AlCl3 (H+ from benzene)
How could you use a friedel crafts mechanism to add a methyl group to a benzene ring?
Use a haloalkane and AlCl3 to create an electrophile that can attack benzene.
What reactions can you carry out to show the weak acidity of phenol?
A neutralisation reaction with sodium hydroxide occurs, but doesn't react with carbonates.
What is the relative ease of electrophilic substitution of phenyl compared to benzene and why?
It is easier for electrophilic substitution to occur with phenyl because the oxygen lone pair of electrons from the oh group are partially delocalized into the ring. Therefore this increases the electron density and thus electrophiles are more attractive to phenol.
What is the directing effect of the electron donating group's OH and NH2
They direct group to the 2 and four position of the ring in the electrophilic substitution of aromatic compounds.
What is the directing effect of electron withdrawing group NO2?
It directs atoms to the three position on the ring In electrophilic substitution of aromatic compounds
What is the carbonyl group?
C=O
What is the functional group of an aldehyde?
RCHO
What's the functional group of a ketone?
RCOR'
How'd you name aldehydes?
-al suffix
How'd you name ketones?
-one suffix
What kind of intermolecular forces do molecules with the carbonyl group have? And why?
Permanent dipole dipole interactions due to the polar CO bond.
A carbonyl compound soluble in water and what influences solubility.
They all soluble as they form hydrogen bonds between water molecules and oxygen of the CO bond as carbon chain length increases solubility decreases.
Which bond in carbonyl compound is usually involved in the reactions and why?
The CO bond due to the polarity of the bond, there is a large difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen.
What is the strongest bond in carbonyl compounds?
C=O
What is the addition of HCN important?
It increases the length of the carbon chain by one carbon atom, allowing more useful molecules to be made.
Will the product of HCN added to carbonyl compound have optical isomers and why?
They will, as in the aldehyde or ketone, the carbonyl carbon is planar, so the :CN- can attack from either above or below. This forms two enantiomers
What is the name of the product when HCN is added to a carbonyl compound?
Hydroxynitriles.
What is fehling solution and what colour is it?
A copper ion complex: blue.
What happens when an aldehyde is added to fehling solution?
It reduces the copper to Cu+ ions and the colour changes to brick red participate.
What happens when a ketone is added to fehling solution?
There is no visible change and the solution stays blue.
How'd you test for carbonyl compound?
Use 2,4-DNP: if a carbonyl compound is present an Orange precipitate is formed.
What is Tollen's reagent?
Silver complex ions, colourless solution
What happens when an aldehyde is added to Tollen's reagent?
A silver mirror forms as a silver ions are reduced to silver solid.
What happens when a ketone is added to Tollen's reagent?
no visible change
What is another oxidising agent for alcohols and aldehydes? And what colour change does this undergo?
Acidified potassium dichromate: orange to green
What is a reducing agent for aldehydes and ketones? What ions does this release in solution?
NaBH4
releases H- ion
How'd you convert an aldehyde to form a carboxylic acid?
oxidise it using acidified potassium dichromate.
What is the functional group of a carboxylic acid?
COOH
How'd you name carboxylic acids?
-oic acid
Our carboxylic acid soluble in water. Why and what influences their solubility?
Yes, the acid group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
What are the intermolecular forces in carboxylic acids?
Hydrogen bonds
What are esters? What is their functional group?
They are formed from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
RCOOR'
How'd you name esters?
Start with the alcohol group that has replaced the hydrogen. Then add the acid part.
For example, Propyl (from alcohol) ethanoate (from cooh)
What characteristic physical properties do Ester's have?
They are volatile and have a pleasantly fruity smell.
What are some uses of esters?
flavourings, perfumes, solvents, plasticisers
How could you distinguish carboxylic acids from other oh containing compounds?
Add sodium hydrogen carbonate, a carboxylic acid will produce sodium salt., water and carbon dioxide.
What catalyst is needed for the formation of esters from alcohols and carboxylic acids?
Concentrated strong acids such as sulfuric
What catalyst is needed for the hydrolysis of esters?
A dilute strong acid such as sulfuric
What is an alternative method for hydrolysis of esters?
Base hydrolysis.
What the advantages of base hydrolysis?
The reaction goes to completion due to the neutralisation by the base. There is more product in the mixture than acid catalysed hydrolysis.
What are carboxylic acid derivatives?
Molecules that have the acyl group as part of their structure, formed from carboxylic acids
Name two acid derivatives and give their functional groups
Acyl chlorides - RCOCl
acid anhydrides - RCOOCR / (RCO)2O
How'd you form an acyl chloride?
React to carboxylic acid with SOCl2
If the nucleophile is ammonia for the acylation of acyl chlorides, or acid anhydrides, what are the products of the reaction?
an amide
Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and ammonia.
CH3COCl + 2NH3 = CH3CONH2 + NH4Cl
If the nucleophile is a primary amine, what are the products of the acylation of acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides?
N-substituted amide
Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and methylamine
CH3COCl + CH3NH2 = CH3CONHCH3 + CH3NH3Cl
If the nucleophile is an alcohol, what are the products of the acylation of acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides?
an ester
Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and ethanol
CH3COCl + CH3CH2OH = CH3COOCH2CH3 + HCl
If the nucleophile is water, what are the products of the acylation of acyl chloride or acid anhydrides?
Carboxylic acid as hydrolysis produces an ester linkage.
What is the name of the reaction where an alkylation of an acyl chloride or acid anhydride reacts with water?
hydrolysis
How'd you name Amines?
-amine / amino-
Why are amines so reactive?
The lone pair of Electrons in the nitrogen. This is due to the polar NH bond.
What shape are amines around the n? And what is the bond angle?
pyramidal 107
What kind of Intermolecular forces do amines have and why?
Hydrogen bonding due to the polar nh bond and loan pairs of the electrons on the N Atom.
Do amines have intermolecular forces, which are stronger or weaker than alcohols. And why?
They are weaker as the nitrogen has a lower electronegativity than the oxygen. So the hydrogen bonding is weaker.
How and when do amines act as bases?
The lone pair on the nitrogen atom accepts a proton.
How can/when do amines act as nucleophiles?
When they bond with an electron-deficient C atom (donate lone pair from N)
What is the product from the basic action of an amine with water?
RNH3+ ammonium ion which forms a salt and an anion
Write an equation for methylamine reacting with hydrochloric acid.
CH3NH2 + HCl = H3CNH3+Cl-
In order to be the strongest base, what must a particular amine have (out of a set of amines)?
The greatest electron density around the nitrogen atom, making it a better electron pair donor as it attracts protons more.
What effect do alkyl groups have on electron density and base strength in amines?
They have a positive inductive effect as they increase the electron density around the nitrogen, making it a stronger base.
Place the following in order of base strength in general: NH3, primary amine, secondary amine, phenylamine
secondar>primary>NH3>phynyl
How can primary amines then form secondary tertiary and quaternary ammonium ions? is this efficient?
Through multiple substitutions, a primary aiming is a nuclear father attacks the original halo alkane.
This is not efficient as the low yield of primary amine due to multiple substitutions.
How would you maximise the yield of primary amine?
Use excess ammonia
What type of mechanism is the reaction of a haloalkane with a cyanide ion?
nucleophilic substitution
What conditions does the reaction of a halo alkane with a cyanide ion require on what is formed?
Ethanol is used as a solvent and a nitrile is formed.
How'd you get from a nitrile to a primary amine? why is this a purer method of synthesising amines?
Reduction using a nickel and hydrogen catalyst.
only primary amine is formed
What conditions are needed to form nitrobenzene from benzene?
Concentrated sulfuric acid and nitric acid to form the NO2+ ion for electrophilic attack.
How do you form an ammonium chloride salt from nitrobenzene? And what are the conditions needed?
Reduce the nitrile using tin and hydrochloric acid to form an ammonium salt with chloride ions at room temperature.
What mechanism is used for forming amides from acyl chlorides and amines?
nucleophilic addition/elimination
What are the two functional groups of amino acids?
carboxyl group and amino group
are amino acids chiral and why?
Yes
One carbon has 4 different substituents
Except glycine where R=H
Definers zwitterion.
Ions that both have a permanent positive and negative charge, but a neutral overall.
How do you zwitterions occur in amino acids?
The carboxylic acid is deprotonated and the amine group is protonated.
What happens to amino acid in acidic conditions?
The Amine group gains a proton.
What happens to amino acids in alkaline conditions?
Loses a proton from the carboxylic acid group.
What is the peptide linkage?
CONH