Systems path exam 1 NOT FINISHING!!!!!!!
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
What is diaphysis?
shaft of bone
What is metaphysis?
Neck of a bone (contains growth plates)
What is epiphysis?
End of a long bone (articular cartilage)
What is characteristics compact bone?
Densely packed, tightly organized
What are some characteristic of spongy bones?
Sparsely packed, random, arranged along lines of stress
What are the cellular (organic)components of a bone?
- osteoblast
- osteoclast
- osteocytes
- Osteoprogenitor cells
What are the proteins of a bone?
Collagen, Osteoid
What are the minerals of bones
• Hydroxyapatite
• Calcium
• Phosphorus
Components of woven bone?
• Immature osteoid
• Highly cellular
• Disorganized
• Abnormal in adults
What are components of lamellar bones?
• Mature
• Less cellular (more matrix)
• Organized along stress lines
• Normal in adults
What type of bone cells are stem cells and differentiate into osteoblasts?
Osteoprogenitor Cells
What are the bone forming cells?
Osteoblast
What do the osteoblast mature into?
osteocytes
What are mature bone cells called?
osteocytes
What type of bone cells maintain the bony matrix, Wolff's law, and Skelton replacement?
Osteocytes
What bone cells are responsible for bone resorption?
osteoclasts
Osteoclast mature from the same stem cells as _____________.
Macrophages
True or false: Before the age of 30 there is a net equilibrium in bones remodeling
True
A slight shift towards bone loss after age _____ often occurs.
30
Osteoclast precursor has _________ receptor
Rank
What do RANK ligands bind to?
RANKL from osteoblast
What is Dysostosis?
developmental anomaly of bone or cartilage
What are some characteristics of congenital disorders?
- dysostosis
- localized abnormality
- mutations
- supernumerary digit
- Klippel-Feil Syndrome, Congenital Kyphosis
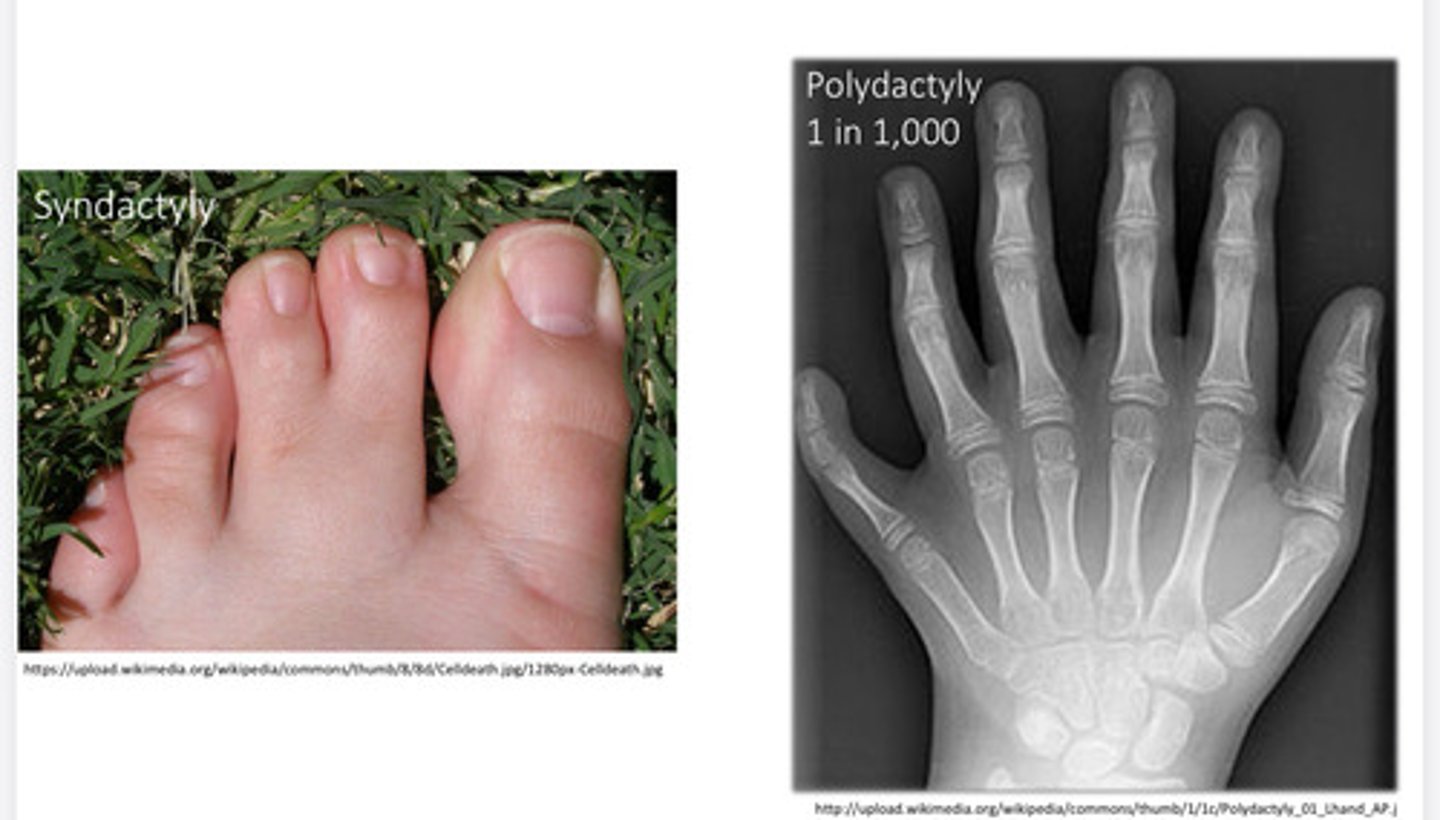
Dysostoses
Skeletal disorder that results from abnormal bone patterning, genetic or environmental. Extra digits or fusion of digits
What is kipper-feil syndrome?
Congenital fusion of ≥2 cervical vertebrae
Idiopathicl: 1/40,000
What is another disorder also associated with klippel-feil syndrome.
Sprengle's deformity
What is Sprengel's deformity?
Fused scapula
Congenital failure of scapula to descent
Elevation of the scapula, and limited humeral abduction
What malformations are common with klippel-feil syndrome?
renal & cardiac malformations are common as well
What is congenial kyphosis?
An severe kyphotic curve
What type of Congenital Kyphosis
Is worse?
Type 1
What are some characteristics of congenital kyphosis?
Failed development
- severe
- deformity
- possible cord compression
What are some characteristic of type 2 congenital kyphosis?
Failed segmentation (Type II)
• Mild compared to type I
• Mild Deformity
Surgical fusion
Dysplasia?
mutations interfere with growth & bone remodeling
How is dysplasia related to the congenital disorders?
- Effecting multiple bones or entire skeleton
- not pre-cancerous
What are some example of congential disorders that are associated with dysplasia?
Achondroplasia, Cleidocranial dysplasia,
Osteogenesis imperfecta, Osteopetrosis
Type I spondylolisthesis
Genetic Etiology
What is cleidocranial dysplasia?
- Absent/ under-developed clavicles (dental abnormalities)
- delayed closure of cranial sutures
- short stature
What gene is affected by Cleidocranial Dysplasia?
RUNX2 gene
What is RUNX2 gene important for?
function during skeletal formation & bone maintenance
What is Achondroplasia?
Most common cause of dwarfism and most common skeletal dysplasia
Height of Individuals with dwarfism?
Adult Height ≤4' 10"
True or false: achondorplasia is the only cause of dwarfism.
False (Hypopituitary, Turner Syndrome, malnutrition, osteogenesis imperfecta)
How doe achondroplasia affect the foramen magnum and spinal stenosis?
Increase stenosis
What are some spinal abnormalities of individuals with achondroplasia?
• Bullet vertebrae
• Stenosis
What are the effects of a bullet vertebrae?
• hyperlordosis & kyphosis
• scoliosis
What undergoes stenosis with individuals with achondroplasia?
1. foramen magnum
• brain stem, may be lethal
2. lumbar spinal canal
• radiculopathy
What congenital disorder is trident hand associated with?
Achondroplasia
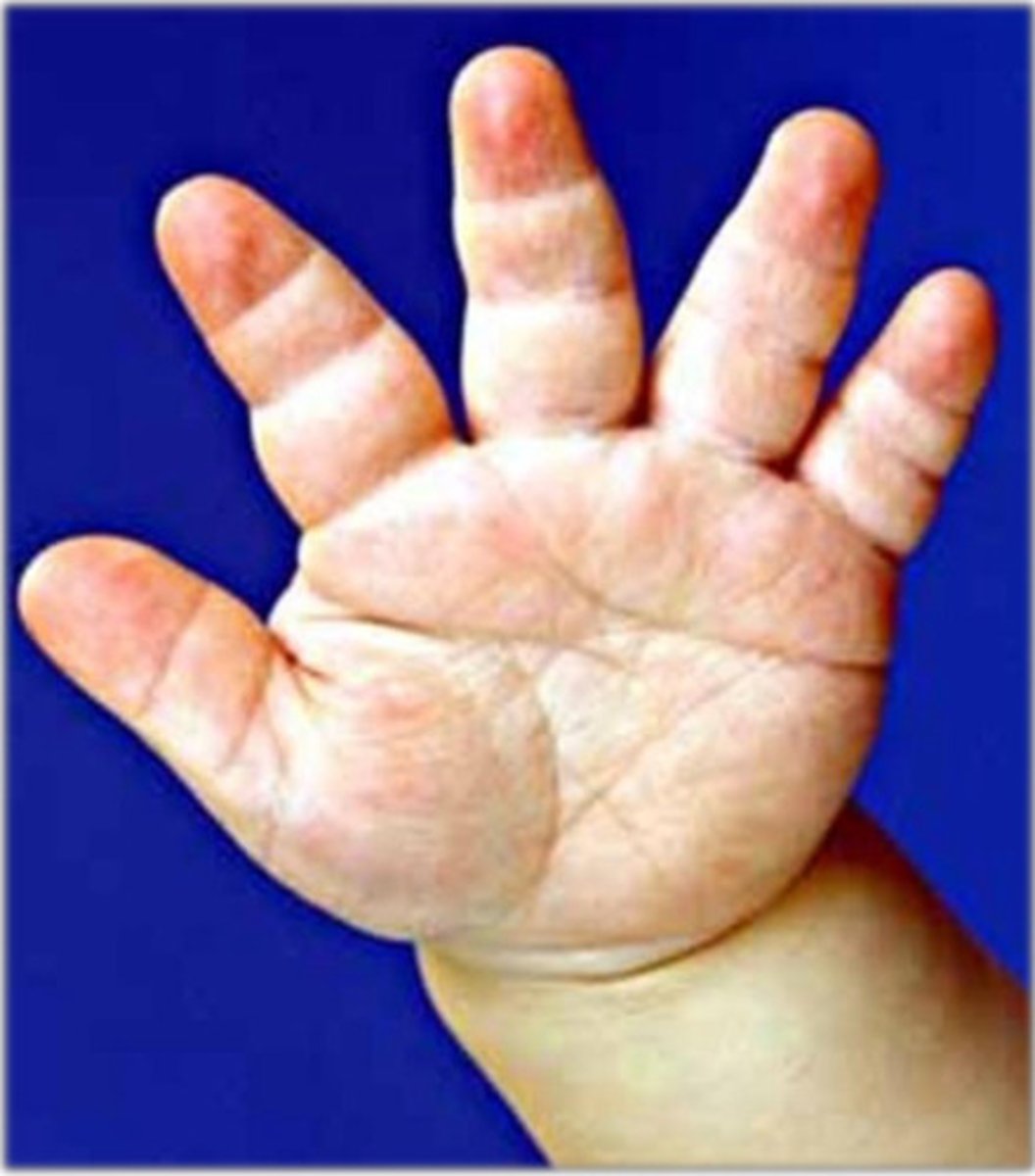
What causes achondroplasia happen?
• Inhibited Endochondral growth
• ↓ cartilage synthesis
• short / bowed long bones
• frontal bossing, midface hypoplasia
What gene is associated with achondroplasia?
FGFR3
True or false: achondroplasia is most commonly inherited.
False (90% are spontaneous -- MC from sperm (dad), 10% are autosomal dominant)
What is Thanatophoric Dwarfism?
- Extremely rare form of dwarfism, more severe than achondplasia.
- small thorax. Short long bones
- fatal (still birth, perinatal respiratory failure)
Other names of Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
"brittle bone disease" or Type I Collagen Disease
What causes osteogenesis imperfecta?
weak connective tissue due to altered type 1 collagen ( weak foundation for hydroxyapatite deposition)
What features are often affected by Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Bones, eyes, teeth, inner ear bones, skin, joints
What are the different types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Type I = normal lifespan
Type II = lethal in utero
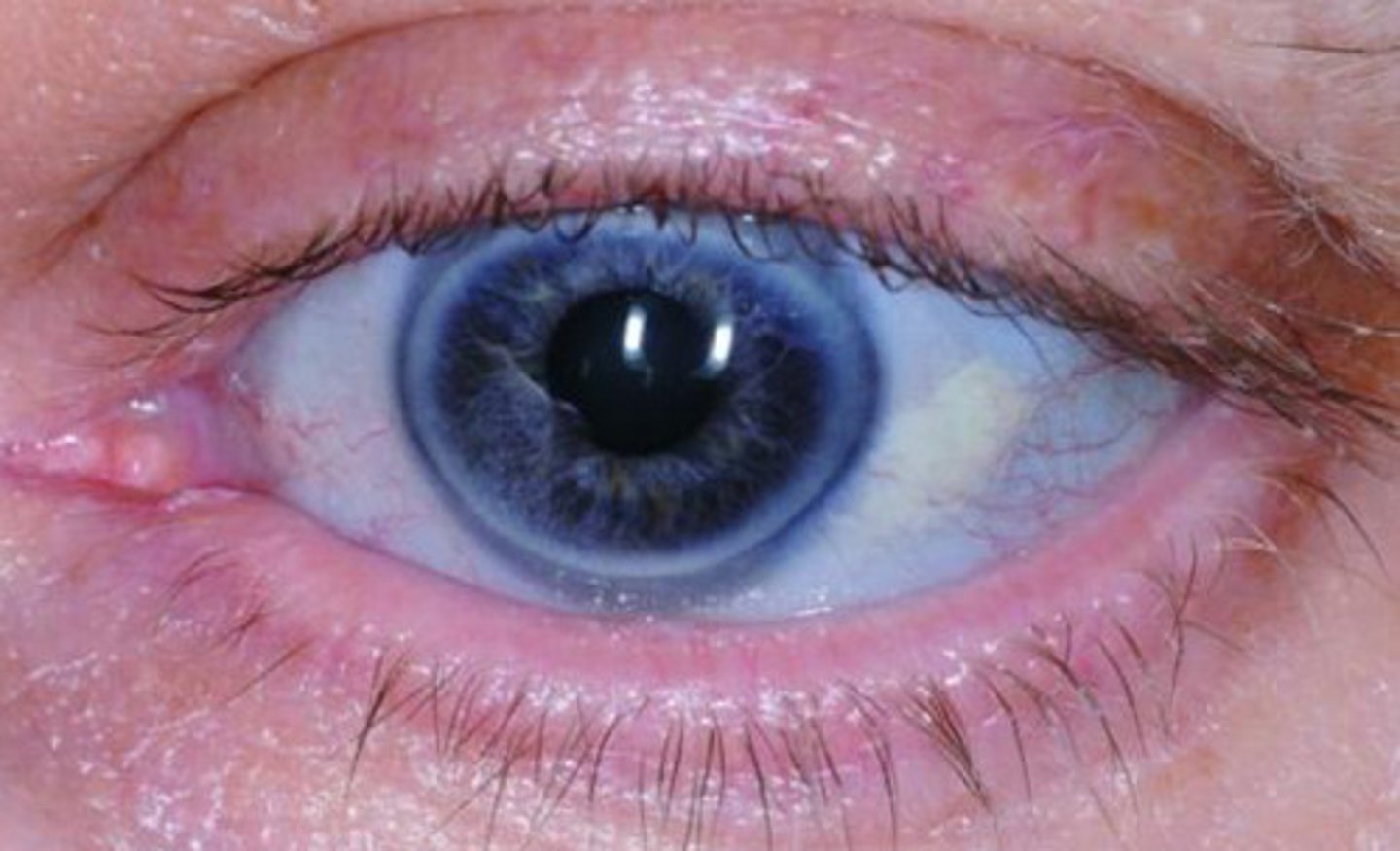
What is a very common sign of osteogenesis imperfecta?
Blue Sclerae - Translucent (visualize underlying choroid blood vessels)
What are some childhood signs of brittle bone syndrome?
• fractures, bowing, scoliosis
• hearing loss
• dwarfism
What condition does the zebra stripe sign refer to?
Osteogenesis imperfecta
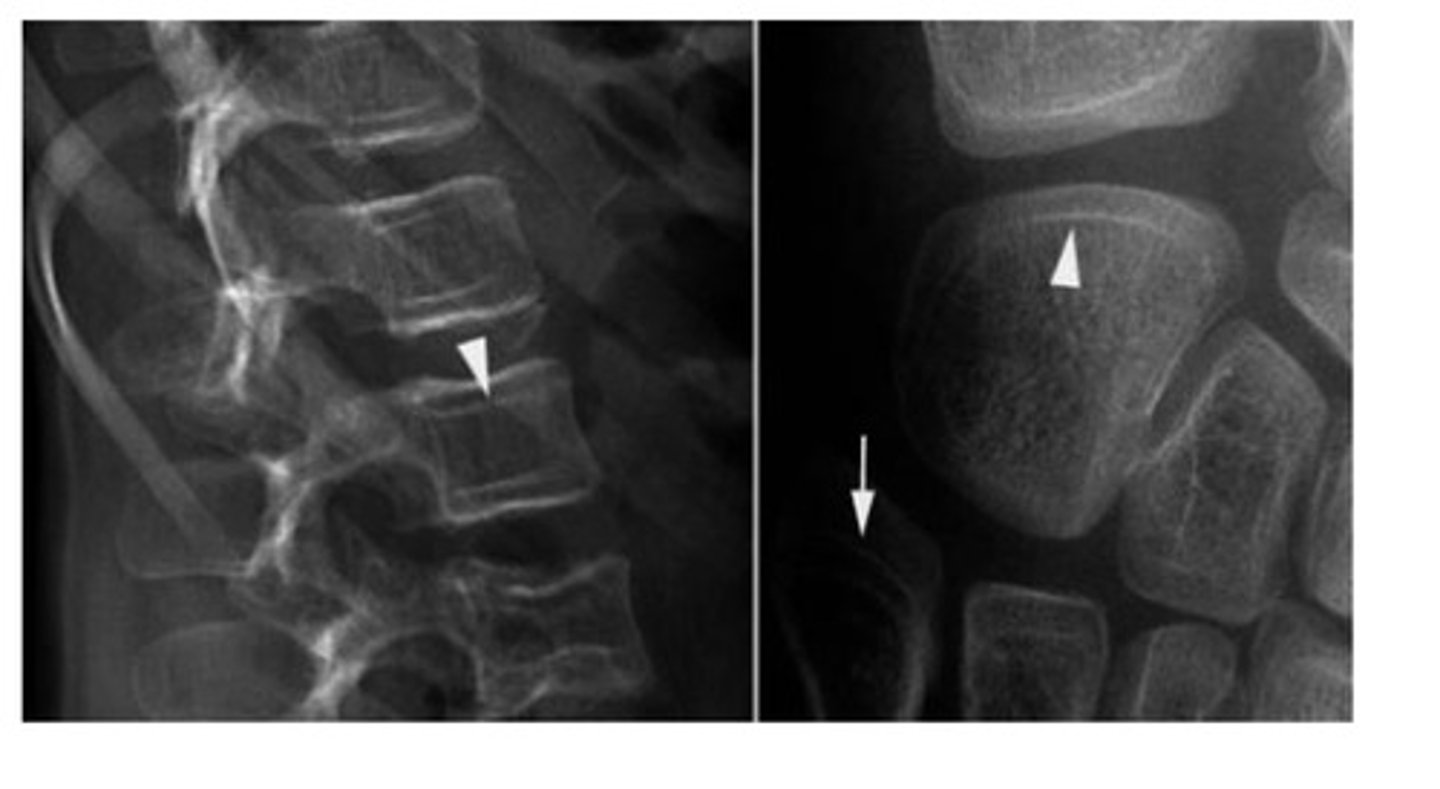
What is the main cause of osteogenesis imperfecta?
Mutated Type I collagen (inherited)
•α1 or α2 chains
• premature breakdown & structural weakness
• autosomal dominant
• 1 in 20,000
__________ is associated with normal bone strength, but frequently with stenosis of the foramen magnum and lumbar spinal stenosis
Achondroplasia
__________ frequently involves localized abnormalities in development of the clavicles and teeth
Cleidocranial dysplasia
Individuals born with ________ will be affected by an incomplete formation of one or more vertebral bodies.
type I congenital kyphosis
What does Radiolucent mean?
- Areas appearing darker on x-ray
- Due to lower density of structure
- Ex. Cartilage, foramen, gas in GI tract, bone destroying tumor, osteoporotic bone (with reduced density)
What does Radiopaque/Radiodensity mean?
- Areas appearing brighter/whiter on x-ray
- Due to higher density of structure
- Ex. Bone, metal
What is another name for osteopetrosis?
"marble bone disease"
What is osteopetrosis?
• Skeletal sclerosis (↑ density of bone)
• fractures: brittle
• Bony stenosis = cranial nerve palsies
• Deranged hematopoiesis
• fatigue & infections
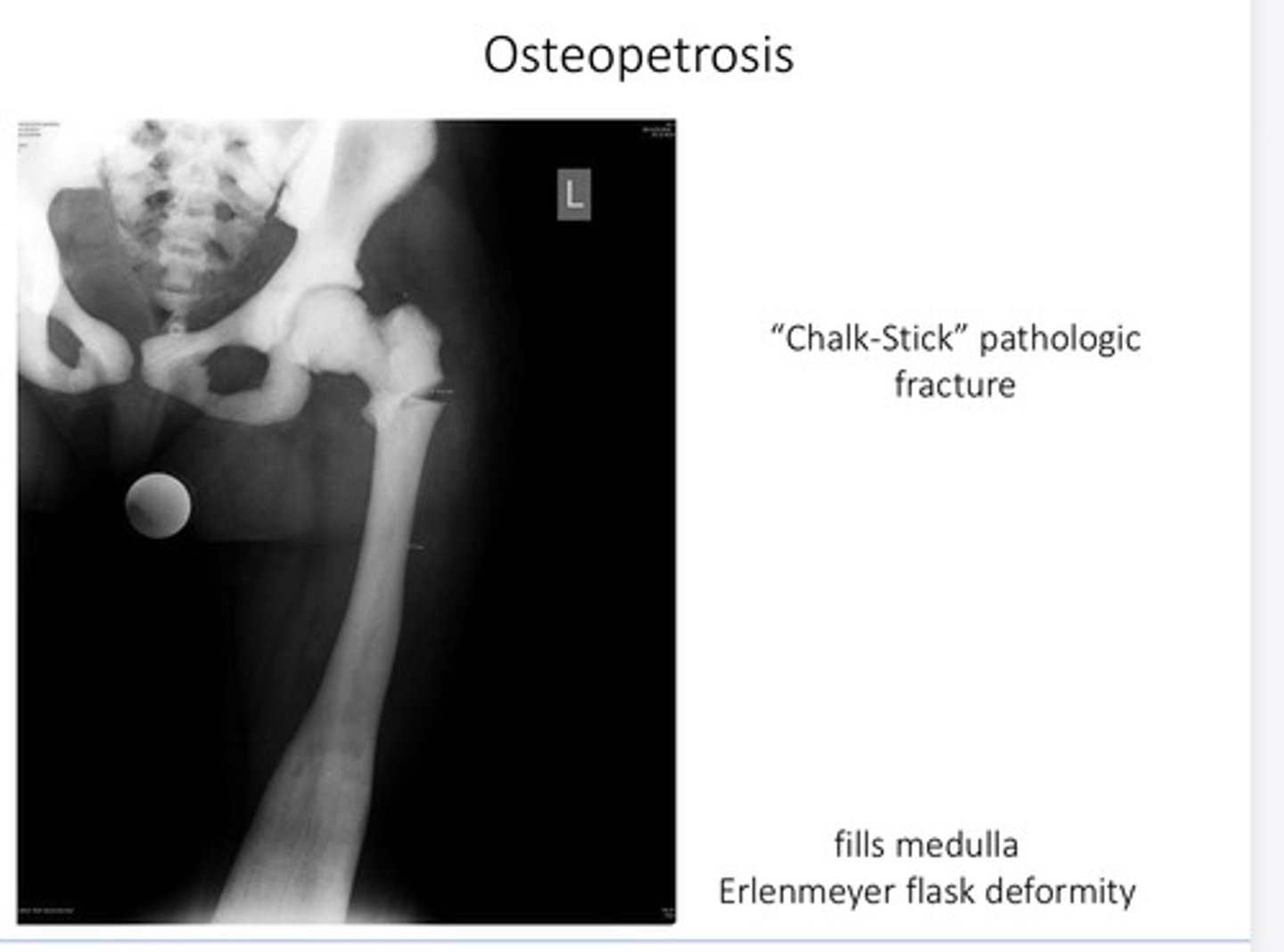
What is a chalk stick pathological fracture associated with?
Osteopetrosis
What is an Erlenmeyer flask deformity associated with?
Osteopetrosis
What is the root of the problem of Osteopetrosis?
- ↓ osteoclast activity
- loss of hematopoietic bone marrow
- ↓ Ca++ intake and/or stem cell transplant
What can a decrease in osteoclast activity?
- impaired acid production in osteoclasts
- Inability to remodel & resorb bone
- Leads to dense & thick, but brittle bone
True or false: osteopetrosis is an inherited condition.
True
What is used to measure bone mineral density and can determine risk of fracture?
DEXA scan
What is indicated if the DEXA scan is 2.5 standard deviations below?
Osteoporosis
What is indicated if the DEXA scan is between 1-2.5 standard deviations below?
Osteopenia
What type of osteoporosis comes after another disease or issue?
Secondary osteoporosis
What type of osteoporosis often affects the senile and those that are postmenopausal?
Primary osteoporosis
What often decreases osteoblast activity in people with osteoporosis?
Senile (old age)
True or false: osteoclast activity remains normal in individuals with osteoporosis?
True
What is linked to an increase in osteoclast activity with women that suffer from osteoporosis?
Postmenopausal (decrease in estrogen)
Women that have an increased age, that live a sedentary lifestyle are most at risk of what condition?
Osteoporosis
Distorted eating,malnutrition, and malabsorption can also lead to what?
Osteoporosis
Vertebral body compression Fx and Femoral neck fracture are all consequences of what condition?
Osteoporosis
True or false: x-ray is the best way to diagnosis a patient with osteoporosis.
False (nor sensitive enough)
Physical activity, Dietary calcium & Vitamin D, and Antiresorptive pharmacologic agents are all ways to prevent what condition?
Osteoporosis
What is the childhood vitamin D deficiency?
Rickets
What condition involve undermineralized bone, weak & bowing bones, and poor growth plates?
Rickets
What conditions if from failed osteoid formation and failed deposition of bone in the growth plates?
Rickets
Who is most affected by rickets?
Children
Deficiency (dietary or UV), malabsorption, and chronic renal disorders (↓ conversion to active vitamin D) all cause what condition?
Rickets and osteomalacia
What condion deals with Undermineralized bone and bone that is Weak & prone to fracture (in adults) ?
Osteomalacia
Failed remodeling and underminaralized matrix accumulation can cause what?
Osteomalacia
Who is most at risk for osteomalacia?
Adults (Less severe than in children)
Primary hyperparathyroidism is most common caused by a ________.
Adrenoma
Renal failure, which leads to hypocalcemia and a ↑ PTH all are associated with ______.
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
_____ osteoclast activity and _____ renal tubule resorption of Ca++ is caused from primary hyperparathyrodism.
Increase, increase
True or false: Hyperparathyroidism (Primary) is asymptomatic
True
Kidney stones (MC), bone pain, peptic ulcers,
depression, demineralization/pathologic Fx are all linked to ______.
Hyperparathyroidism (Primary)
unique skeletal changes and adiographic features are linked to what?
Hyperparathyroidism
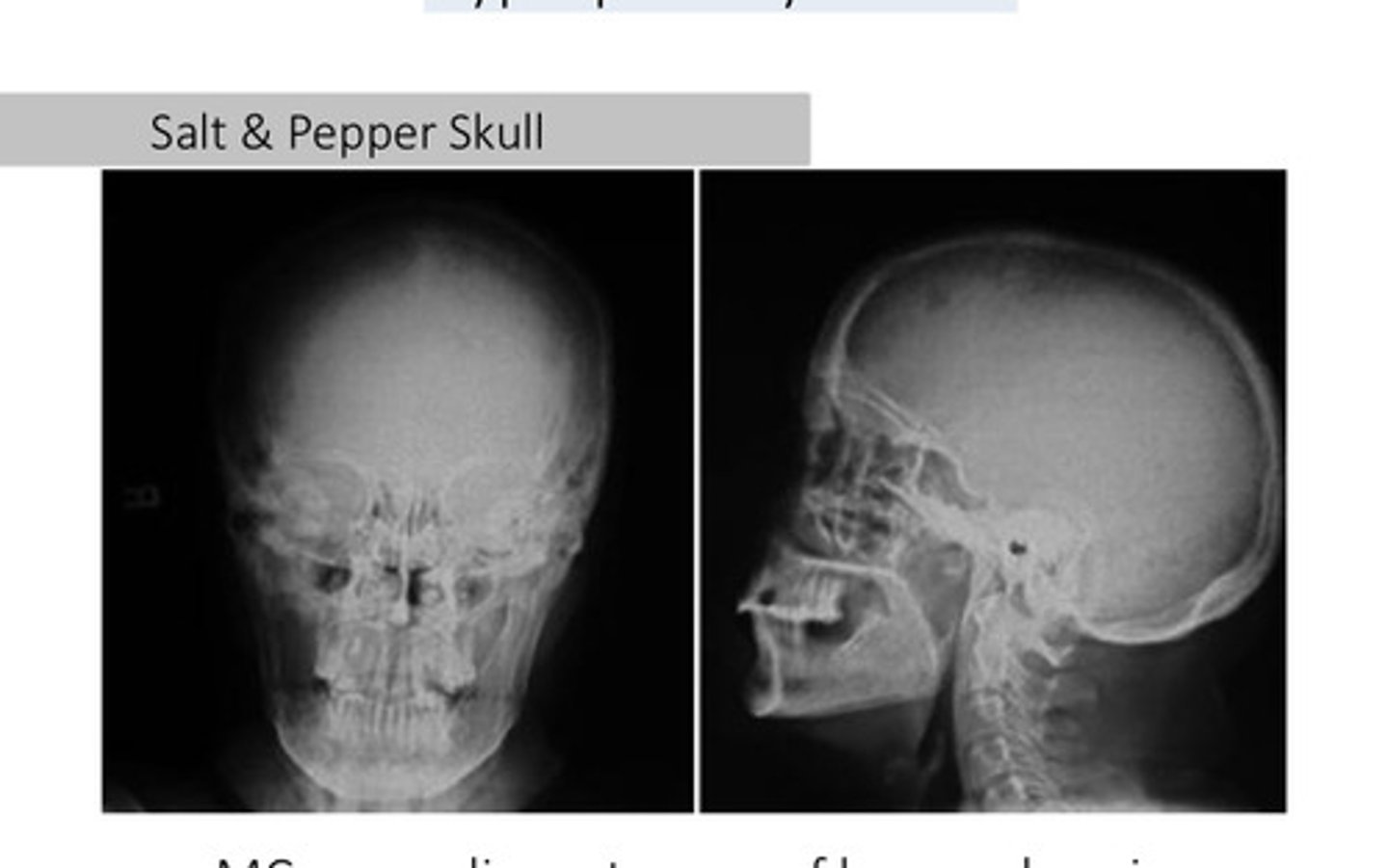
What is the most common non malignant cause of hypercalcemia?
Salt and pepper skull
Salt & Pepper Skull, rugger-jersey spine, and subperiosteal resorption is associated with what condition?
Hyperparathyroidism