Exam 1 Review
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What does this refer to
The degree to which a patient can obtain, communicate, process, and understand health information and services to make informed health decisions.
Health literacy
What does this refer to
Differences in the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and burden of diseases and other health conditions that exist among specific populations.
Infant mortality among non-Hispanic black patients when compared to non-Hispanic white patients.
Cancer rates among Asian and Pacific Islanders higher when compared to other populations
Health disparity
What does this refer to
A group of people (that make up our society) that can be thought of as individuals who possess special needs.
Make up every society
Special Populations
What does this refer to
Race
Gender
Education
Religion
Culture
Diet
Income
Others?
What defines a special population?
What does this refer to
: caused by an automatic association between two or more traits —a sterotype
Unfortunate influence on diagnoses and management
Stereotypes are based on unsubstantiated association of unrelated traits.
They are normal but can lead to bias
Ascertainment bias
What does this refer to
: a consistent shift (positive or negative) in thoughts and behavior that is not substantiated by facts.
Bias
What does this refer to
A framework for eliciting the patient’s understanding and cultural context
Series of questions a provider must use to obtain an understanding of the patient’s view of health and disease.
What do you think caused your problem?
What do you think your sickness does to you?
What are the most important results you hope to receive from this treatment?
What do you fear most about your sickness?
Kleinman explanatory model
What does this refer to
Another model for cross-cultural communication
LEARN model
What does this refer to
Listen to the patient’s perspective
L from Learn model
What does this refer to
Explain and share one’s own perspective
E from LEARN model
What does this refer to
Acknowledge differences between the two perspectives
A from LEARN model
What does this refer to
Recommend a treatment plan
R from LEARN model
What does this refer to
Negotiate a mutually agreed upon treatment plan
N from LEARN model
What does this refer to
Major factor in overcoming health
Family prayer group necessary at hospital
Strong desire for nature
Room with a view of trees, flowers etc…
Health is a result of chance
God’s will
Healing is a sign of forgiveness
Predestined life events
Feeling of having a little control or no control over events and life
Patient may have the choice not adhere to medications for conditions
Diabetes
Hypertension
Religious Beliefs
What does this refer to
Respect “Personal Bubble”
Eye contact included
Social beliefs
What does this refer to
Men tend to make decisions for the household
Elders are valued, honored, and respected
Strong sense of family
Care for the elderly rather than put in a home
Delay treatment until all members of the family present
Family often accompanies to visits
Large number of visitors
Allow family presence as much as possible
Involve family in the patient’s care as much as possible.
Go slow and allow for the patient to feel comfortable with you
Continuity of care important
Listen well and try not to interrupt
Social beliefs, Gender relationships
What does this refer to
When obtaining clinical history from a pediatric patient who can you collect them from?
The patient or a guardian
What does this refer to
Normal function of human development
Human sexuality
What does this refer to
Delayed sexual activity
Protected sex
Promiscuity
Concept of responsible sexuality is important for public health
What does this refer to
_________ : targets at-risk healthy population to prevent a health condition
Promotion of regular exercise to prevent development of chronic disease, such as hypertension or cardiovascular disease
Primary preventative medicine
What does this refer to
_________ : identification and treatment of an individual who has a risk factor for a disease or are with a disease and unaware
Routine screenings in women for breast cancer
Secondary preventative medicine
What does this refer to
______: Prevention of additional complications for a person with a disease
Podiatric and ophthalmologic exams for diabetics to prevent further complications
Tertiary preventative medicine
What does this refer to
Integrates a patient’s readiness to change by understanding the cycle/continuum of behavioral modification.
Prochaska’s Transtheoretical Model
What does this refer to
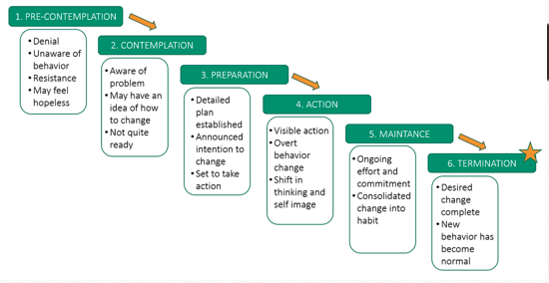
Prochaska’s Transtheoretical Model
What does this refer to
Standard Precautions
Personal Protective Equipment PPE
Do a chart check prior to room entry
Ways to prevent Blood Bourne pathogens BBP
What does this refer to
Uncontrolled chronic stress leads to ______
Consists of emotional exhaustion, a decreased perception of personal accomplishments, and the loss of empathetic connections, (depersonalization and detachment).
Negative outcomes-decreased productivity, decreased job satisfaction, depression, relationship problems, substance abuse, and suicide.
Contributors-excessive workload*, financial and economic factors, administrative responsibilities, low autonomy, work-life balance, lack of boundaries.
Burnout
What does this refer to
Emergency Medicine
Primary Care
Oncology
Palliative Care/Hospice
High Level Burnout Specialties
What does this refer to
Learning/Practice Environment
Society and Culture
Rules and Regulations
Health Care Responsibilities
Organizational Factors
External Factors Affecting Clinician Well-being
What does this refer to
Personal Characteristics
One’s own self-care plan and resilience, individual skills
Practice Characteristics
Workload, hours, patient contact v. administrative, teamwork, autonomy
Cultural Characteristics
Organizational factors, certification requirements, support, practice acts
Wellness model
What does this refer to
Book longer visits for new provider or new patient
Make an impression
Don’t look into your computer only
Know when and when not to interrupt a patient.
Overcoming time constraints
What does this refer to
Approach to medicine that addresses the socioeconomic and neighborhood/environmental factors that pose obstacles to making healthy decisions and attaining optimal health
Population-health approach
What does this refer to
Counseling and education
Clinical interventions
Long-lasting protective interventions
Changing the context to make individuals’ default decisions healthy
Socioeconomic factors
Population health impact pyramid
What does this refer to
Assessment
Monitor health
Diagnose & investigate
Policy development
Inform, educate empower
Mobilize community partnership
Develop policies
Assurance
Enforce laws
Link to/provide care
Assure competent workforce
Evaluate
Core functions of public health
What does this refer to
Physical environment
air & water quality
housing & transit
Social & economic factors
education
empolyment
income
family & social support
community safety
Clinical care
access to care
quality of care
Health behaviors
tobacco use
diet & exercise
alcohol & drug use
sexual activity
Factors that Affect Population Health
What does this refer to
Good __________ lets us have good decisions, ______ based medicine and tests
Do not use aromatherapy
Research
What does this refer to
An independent panel of experts in primary care and prevention that systematically reviews the evidence of effectiveness and develops recommendations for clinical preventive services
Talks to people about their weight, glucose levels, etc.
U.S Preventative Task Force
What does this refer to
Preventative screenings
Vaccination schedules
Travel health
Surveillance
Slows the onset and progression of chronic disease
Ways to increase the improved health care of the population
What is the number 1 reason for the high cost of insulin
The need for a lifesaving product
What does this refer to
Denial
Anger
Bargaining
Depression
Acceptance
Elisabeth Kubler-Ross’s stages of grief
What does this refer to
In the case of an emergency, a provider does not need _________
Consent
Can a specialist provide a referral to a PCP (True or False)
True
Asthma may be acquired from a work related injury (True or False)
True
What are methods to improve joints
ergonomics
Can social networking (ex: email) from a patient to a provider reduce healthcare cost?
Yes
What does this refer to
Age
Gender
Population
Household composition (like presence of children)
Demographic factors that affect disease transmission
Occupational injury may require worker compensation, reporting to OSHA, and contacting poison control (True or False)
True
The vast majority of state laws mandate physician supervision or collaboration. (True or False)
True
What type of supervision and collaboration is the following
Agreements made at the time of employment that delineate the duties and responsibilities of both parties, based on the anticipated scope of PA practice. Formal agreements are required in many states.
Prospective
What type of supervision and collaboration is the following
The oversight and availability of the physician that occurs on a daily basis forms the bulk of the element of concurrent collaboration General supervision means the physician must be available to the PA at all times. Direct supervision means the physician must be physically present at all times. Personal supervision (the most restrictive) means the physician must of present in the room when the PA provides care.
Concurrent
What type of supervision and collaboration is the following
Process of evaluating the performance, clinical activities and quality of care provided by the PA.
Retrospective
If you see a question with primary prevention, think
what the patient can do (you are trying to encourage the patient to do something)
What does this refer to
Careful, systematic, patient study and investigation of some field of knowledge, undertaken to discover or establish facts or principles” Webster’s
“A systematic, organized process that goes through a number of sequential (or near sequential steps). (Forister & Blessing text p 7)
Basic science, pure, experimental, applied, descriptive, survey, clinical, policy, epidemiological, anthropological, educational, sociological, psychological, workforce
Research
What does this refer to
Patient demographic information
Reason for referral/goals of therapy
Consultation only vs. consultation and management
What concerns do you as a referring provider have? What concerns does the patient have that need addressed?
What elements of care are needed
Emotional/Patient violence
mental health/substance use
Physical health- assigned gender at birth and present gender health concerns
Elements for providing a referral