Brain and Behavior Exam 1
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What are the 4 zones of a neuron?
Input zone, integration zone, conduction zone, and output zone
What are the 3 parts of the cell or neuron?
Dendrites, soma, axon
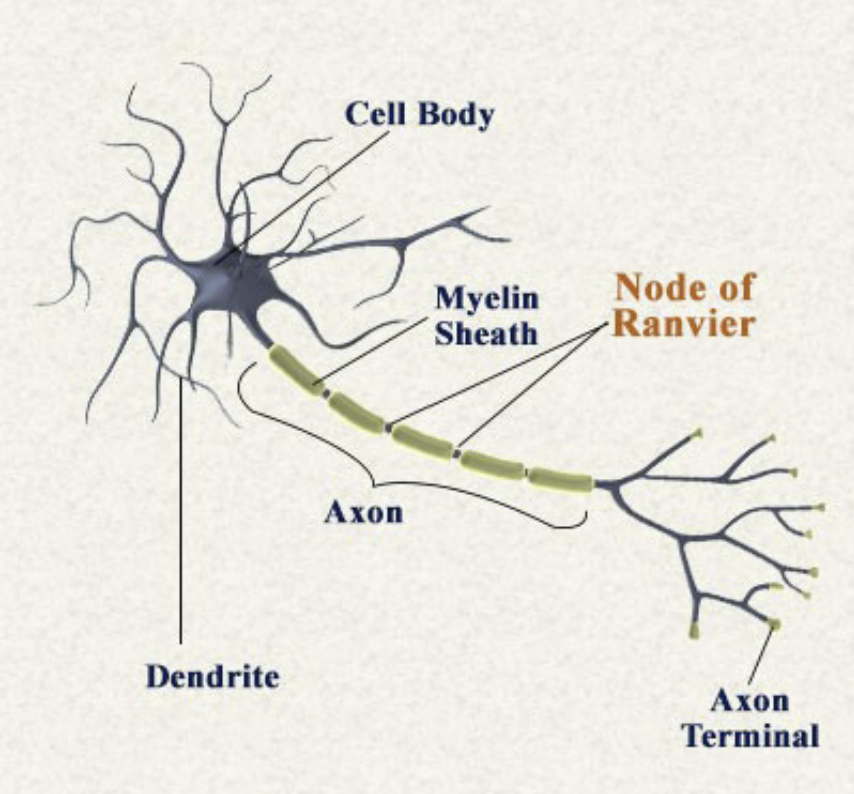
Soma
Cell body, includes organelles, nucleus, and fluid inside the cell
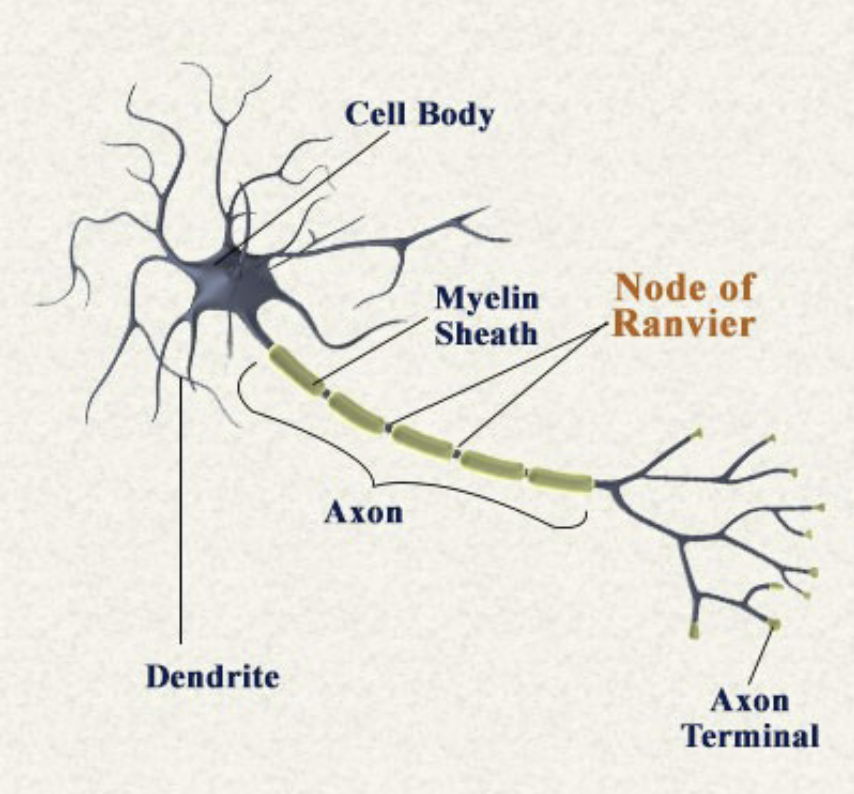
Axon
Transmit electrical signal to axon terminal, which causes neurotransmitter release. Includes axon hillock, axon, axon terminal. Made of Myelin and nodes of Ranvier
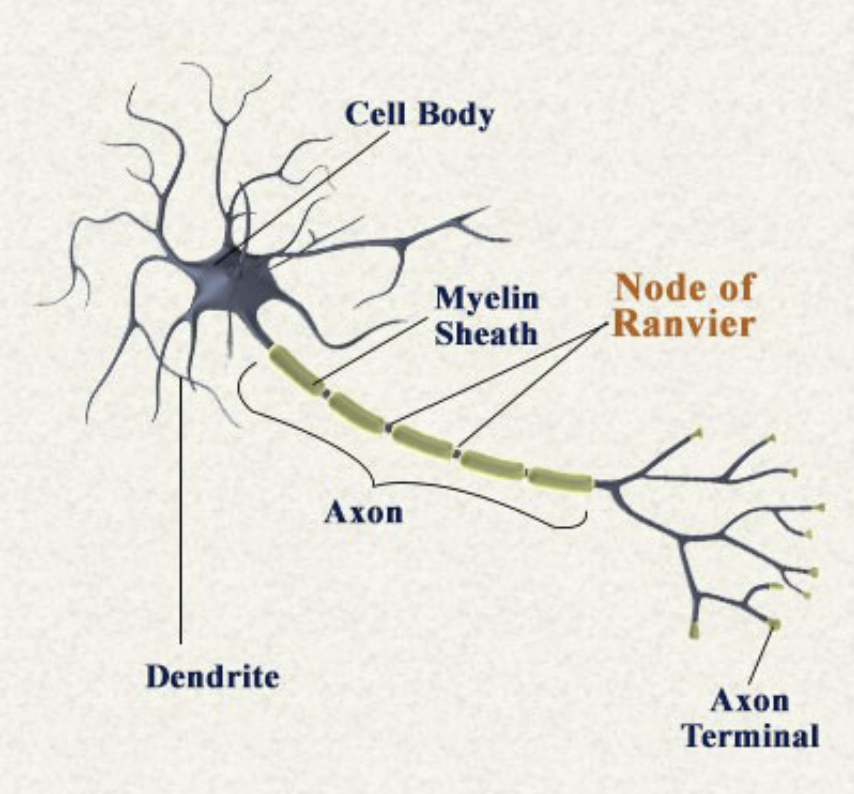
Dendrites
Collects information from the other cells
What are the four types of glia cells?
Astrocytes, Oligodendrocyte, Schwann cells, Microglia
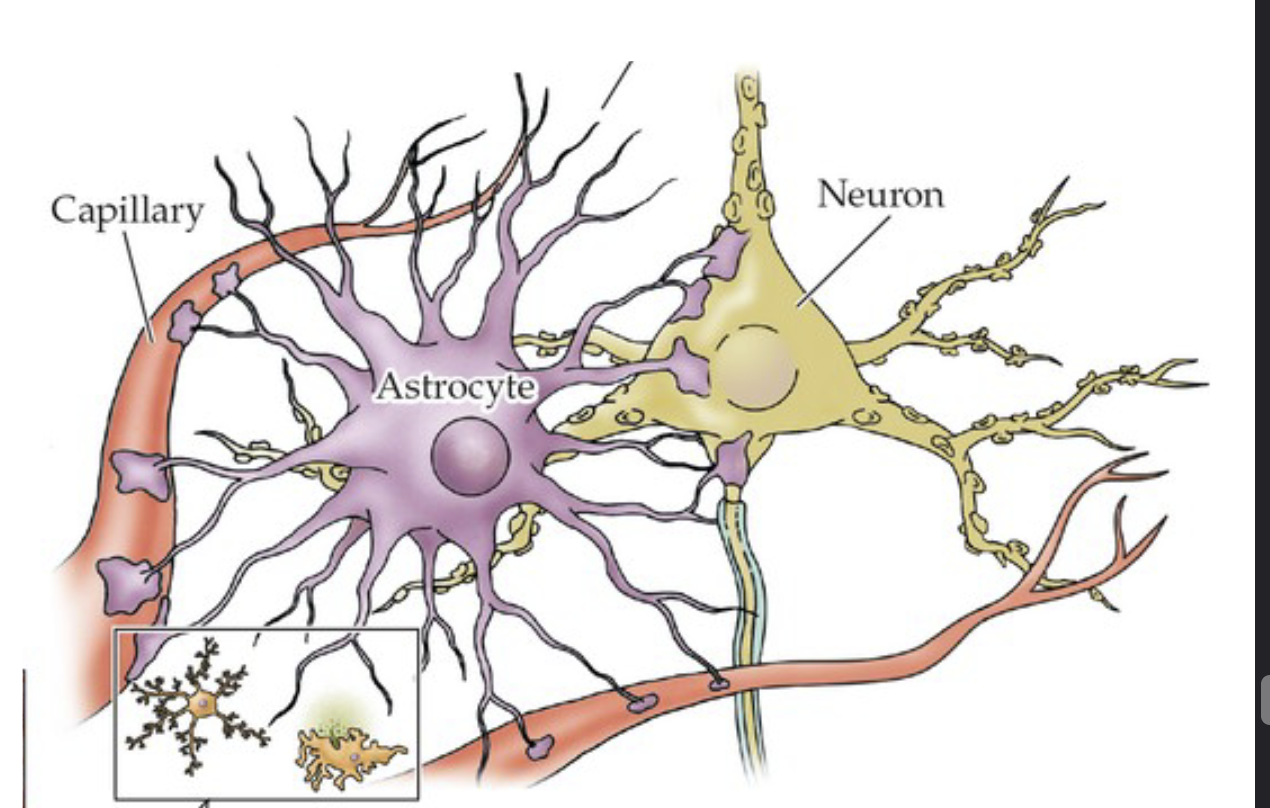
Astrocyte
Physical support, takes up excess neurotransmitter molecules (siphoning) and take waste from neurons and dump into blood vessels
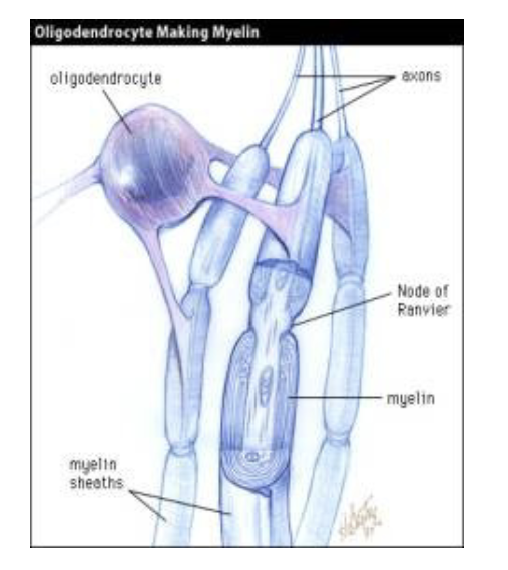
Oligodendrocyte
CNS, 50 axons for each cell
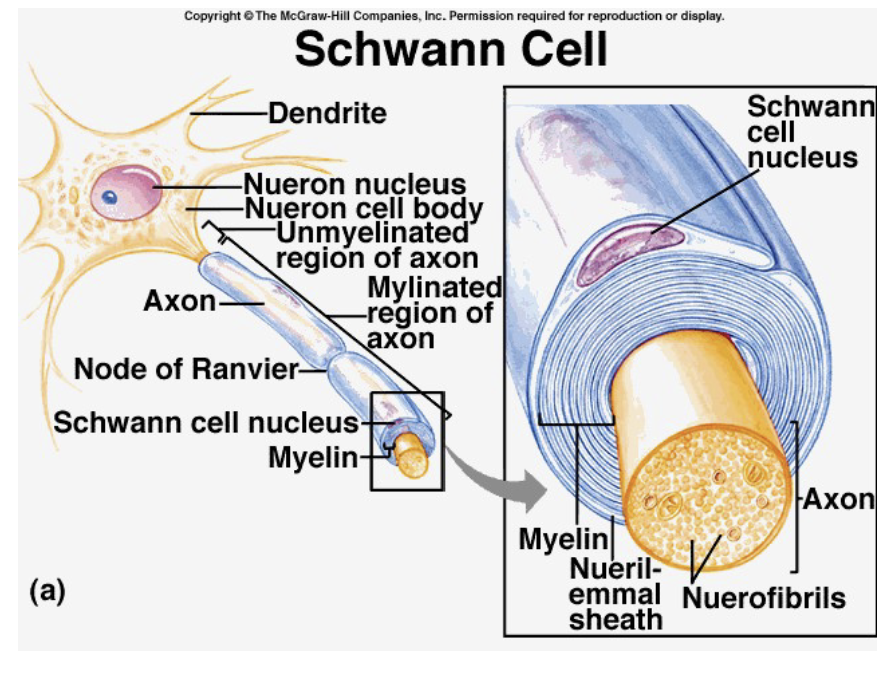
Schwann cell
PNS, one axon segment for cell
Microglia
First responders, immune defense
Who were the 3 people who received Nobel Prizes?
Sherrington, Ramon y Cajal and Golgi
Sherrington (1857-1952)
Proposed the concept of the synapse
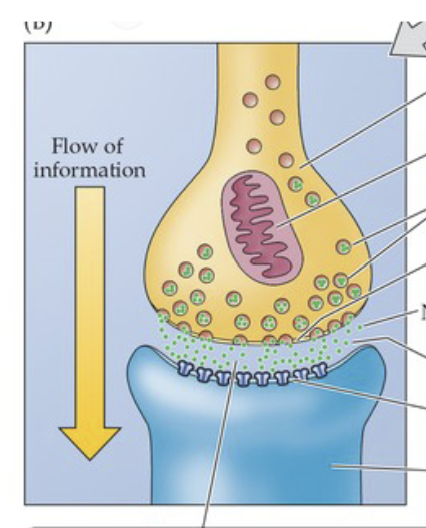
The Synapse
Space between two communicating cells, chemical signals get released across the synapse
Ramon y Cajal and Golgi (1906)
Stained neurons to visualize them
What are the 3 organelles of the soma?
Mitochondria , Rough Endoplasmic reticulum, Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
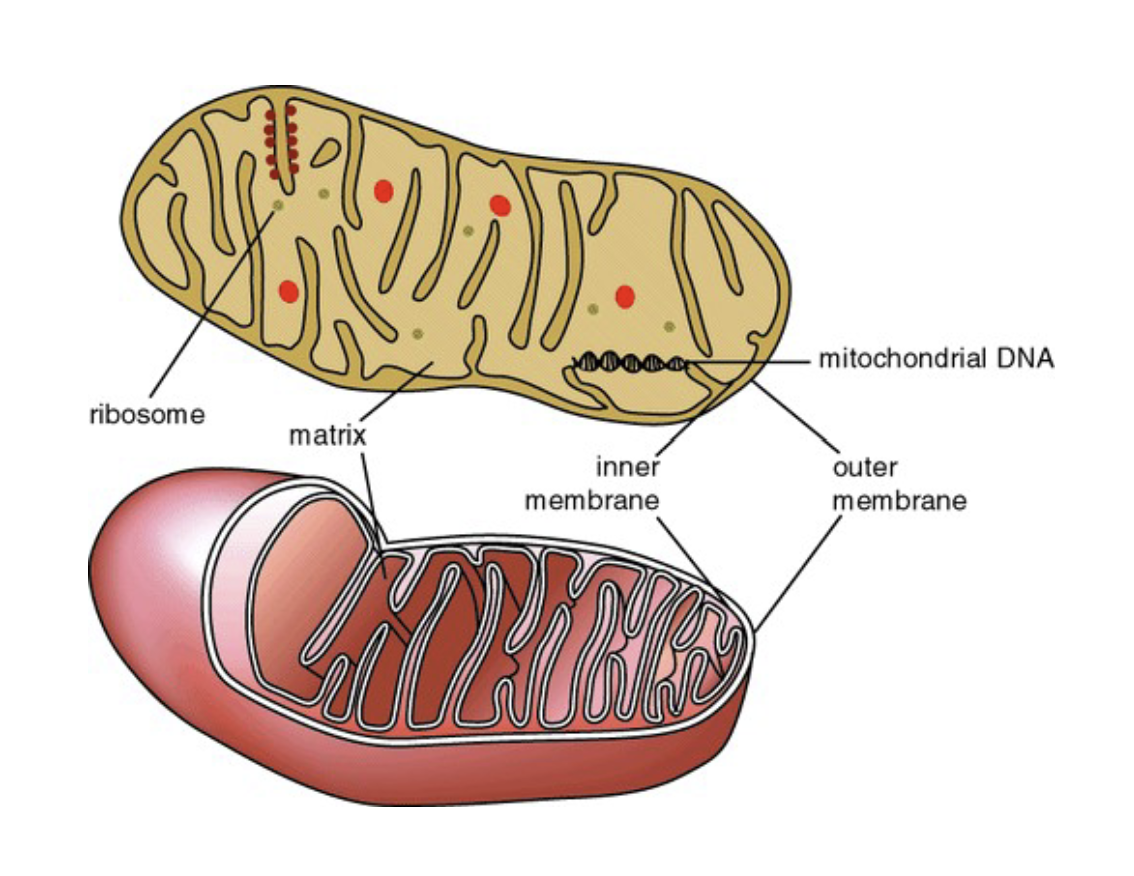
Mitochondria
supplies ATP to cell, makes energy
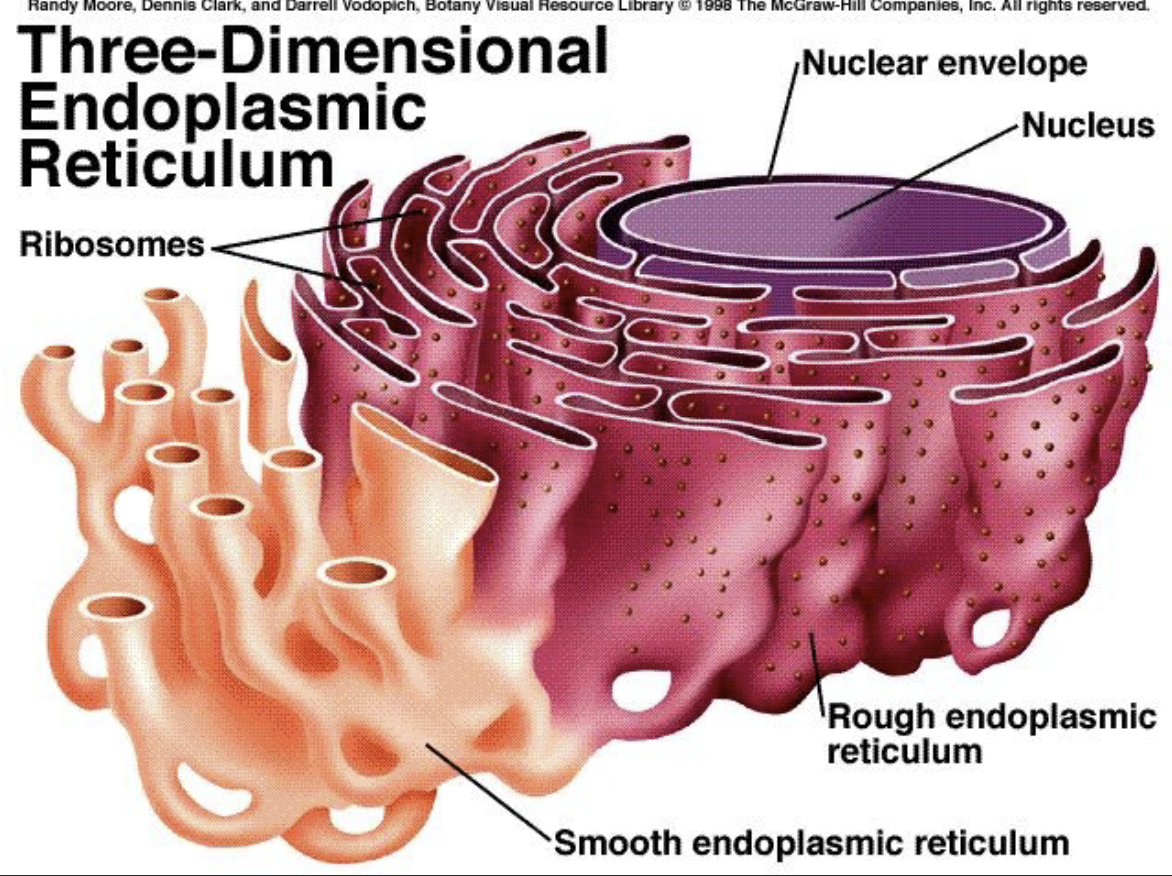
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
Has ribosomes which makes protein for the Golgi bodies and cell membrane
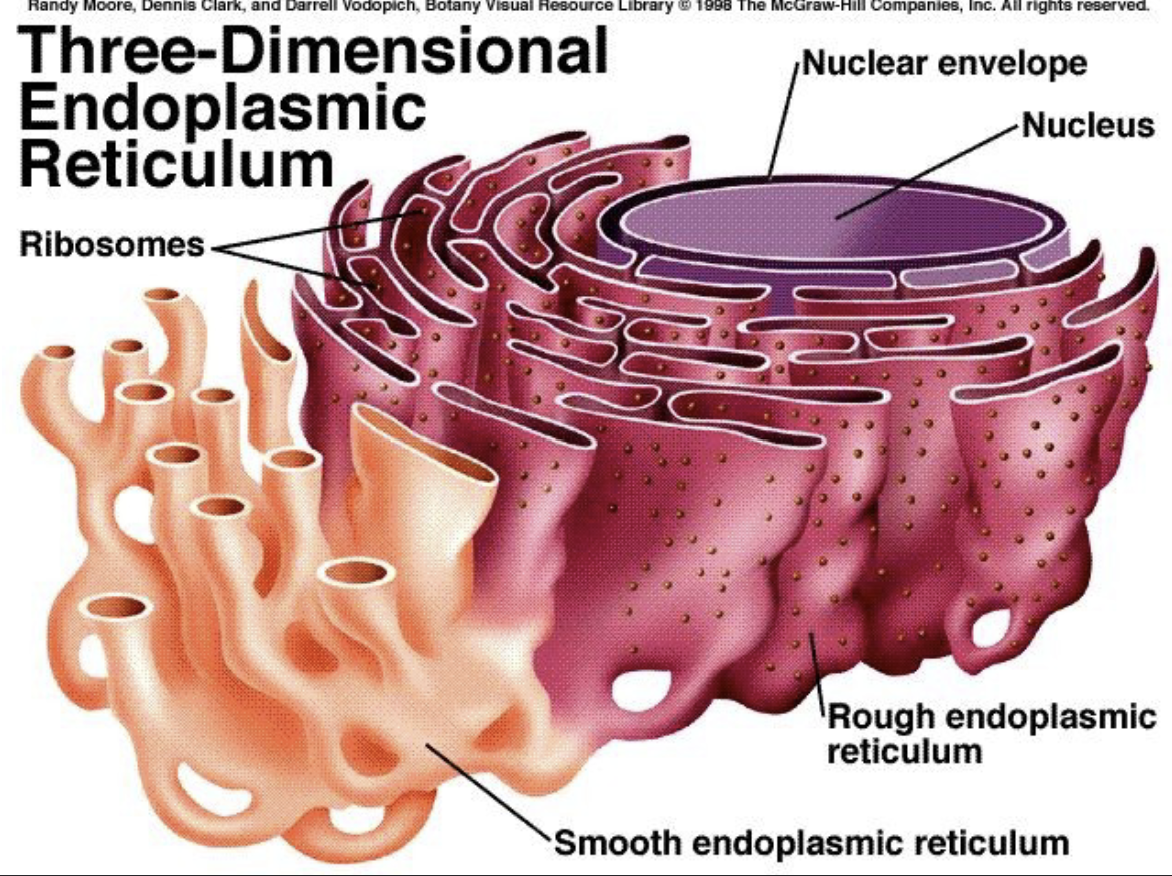
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
Makes lipids
Input zone
where neurons collect and process information either from the environment or from the other cell
integration zone
where the decisions to produce a neural signal is made
Conduction zone
where information can be electrically transmitted over great distance
Output zone
where the neuron transfers information to other cell
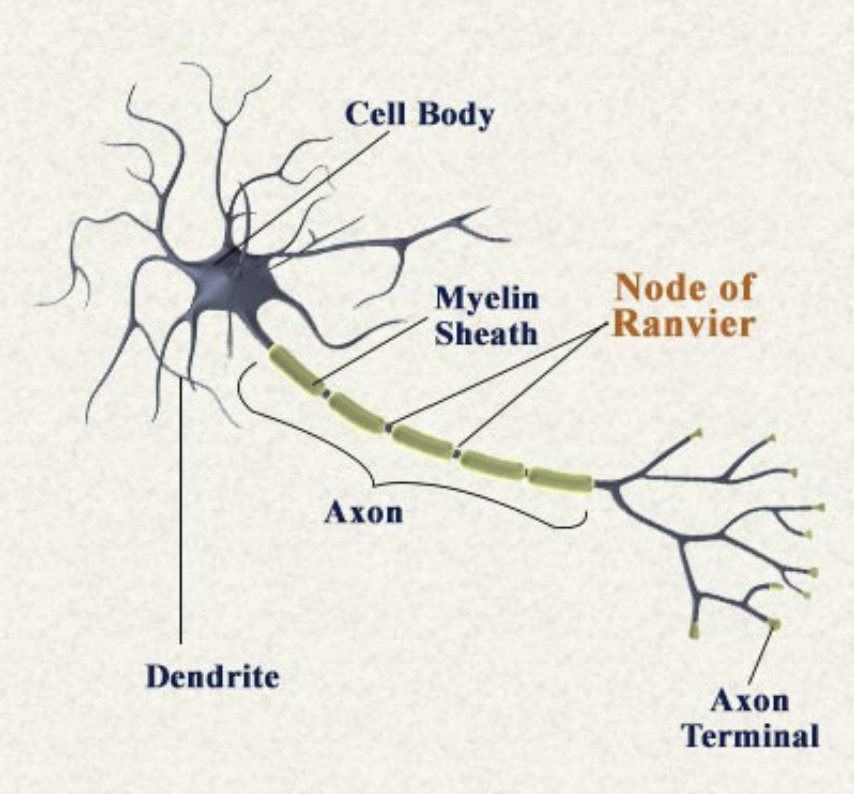
Myelin
A white fatty substance that insulates some axons and speeds transmission
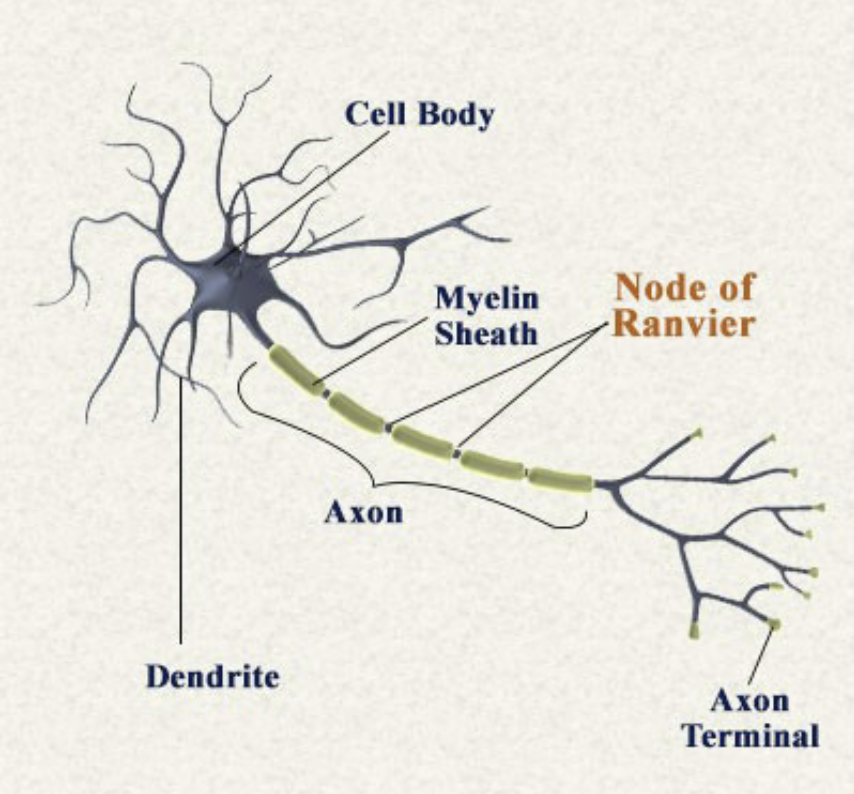
Nodes of Ranvier
The gaps between myelinated segments
Neuroscience
The study of the brain and explores how we interpret and react to our world
Hippocrates 400 BCE
Brain was seat of intelligence
Aristotle 350 BCE
Heart was the center of intellect
Descartes 1650 AD
Promoted dualism that the brain and mind were somehow separate entities
Localization of Function
Functions are localized to different parts of the brain, discovered by Galen
The Pineal gland
Descartes believed that the pineal gland was the seat of the soul, that is, the mind
Galen 150 AD
Physician to the gladiators in Greece, notices that people who sustained damage to a particular part of the head frequently had the same deficits
Localization of function
Franz Joseph Gall 1800-1850
Studied cranioscopy/ Phrenology
Cranioscopy/ Phrenology
Studying the bumps on the head to determine mental and moral faculties
Equipotentiality
Different parts of the brain have an equal potential to do given functions
Fluorens 1824
Founder of experimental brain science
Found that the cortex is equipotential. He took a pigeon and destroyed 10 percent of its cortex. He took another pigeon and destroyed a different 10 percent of the cortex. So on until he had 10 pigeons each with a different portion of the cortex removed. He could’’t find any deficits in the pigeons, so he conclude by stating that all the cortex has an equal potential to do things
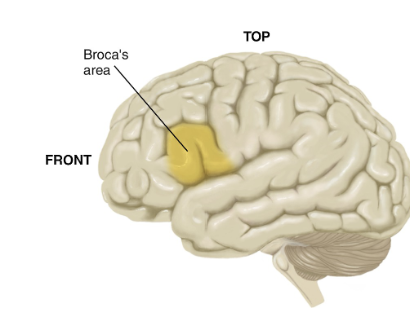
Paul Broca 1861
Patient “Tan” showed major speech deficit following a stroke and could only say the word tan. Could understand things fine, damage to the left hemisphere to broca’s area
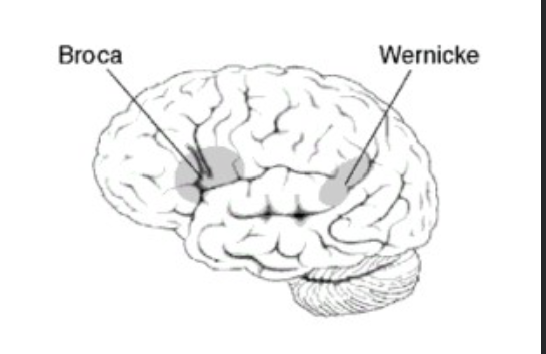
Wernicke 1874
Had patients who could speak just fine, but couldn’t understand language, damage to left hemisphere Wernicke areas
Lashley’s integrated theory
Memories are distributed, Cortex can function as a whole, higher intellect is generally mediated as a whole, any brain injury can impair higher functioning, one area can substitute for another, at least to some degree in many cases.
Neuropsychology
The study of the relationship between behavior and brain function. Involves testing and making a plan for them to succeed.

Phineas Gage
Railroad worker who accidentally had a hollow rod explode and pass through his brain in 1848. Against odds, he recovered and was studied. They staid his personality changed as a result of his injury to his frontal lobe.
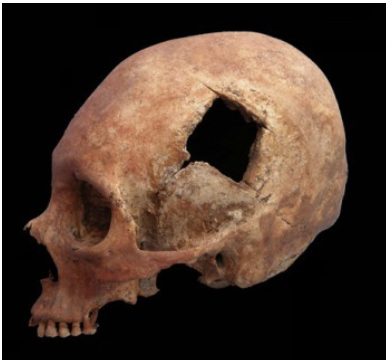
Trepanation 6500 BCE
Made holes in the head to release evil spirts or to relieve the brain of pain
Peripheral nervous system
Includes the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
This is our flight or fight response
Parasympathetic nervous system
This is our rest and digest response
Somatic nervous system
This includes the 12 cranial nerves
What are the 6 cranial nerves?
Olfactory, Optic, Trigeminal, Facial, Auditory, and Vagus nerve. They are all the motor and sensory information from the head
What are the four areas of the spinal cord?
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, and Sacral
Olfactory nerve (1)
Smell
Optic nerve (2)
Vision
Trigeminal nerve (5)
Touch and pain on face
Facial nerve (7)
Facial muscles
Auditory nerve (8)
Auditory vestibular nerve , hearing and balance
Vagus nerve (10)
Internal organs
Cervical
Neck
Thoracic
Upper back
Lumbar
Lower back
Sacral
Closest to the tailbone
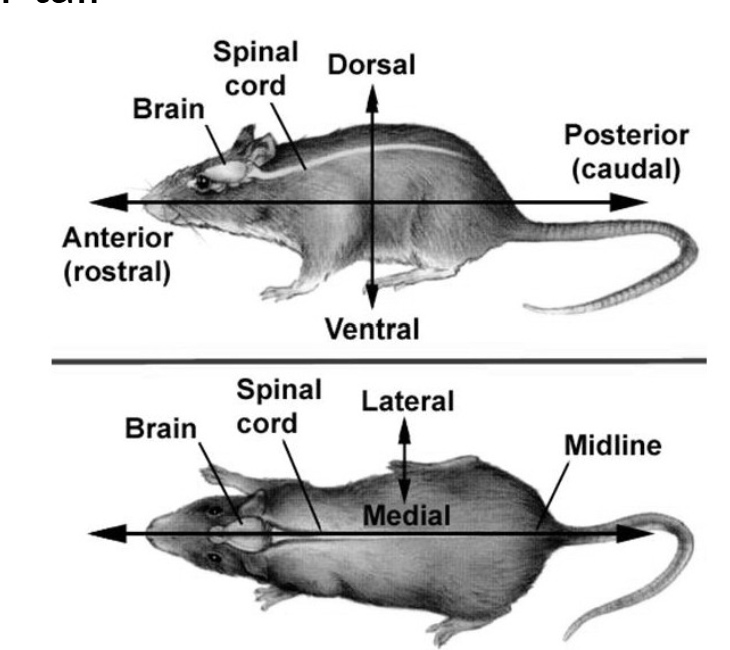
Neuraxis
An imaginary line from the tip of an animal's nose to the tip of their tail
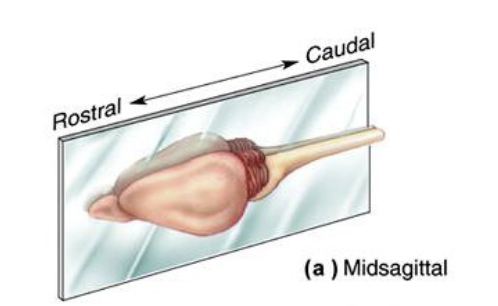
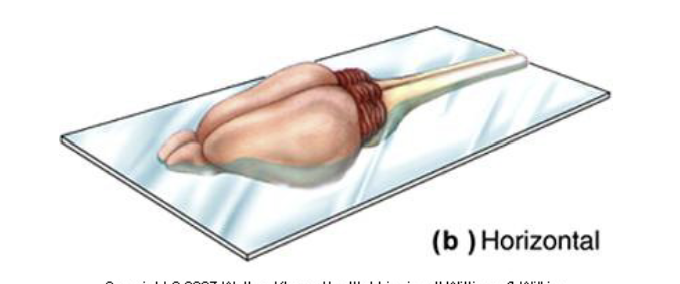
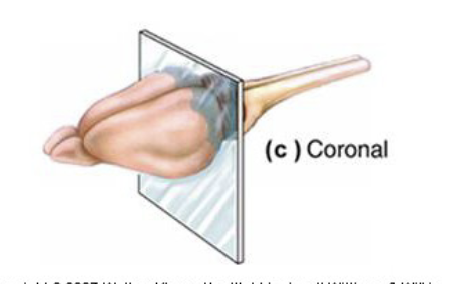
What are the 3 directional terms for sectioning the brain?
The midsagittal, Horizontal, and the Coronal
What is the covering around the brain?
Meninges
What is the white matter?
Cell bodies in the brain
What is grey matter?
The connections between cells (the myelin)
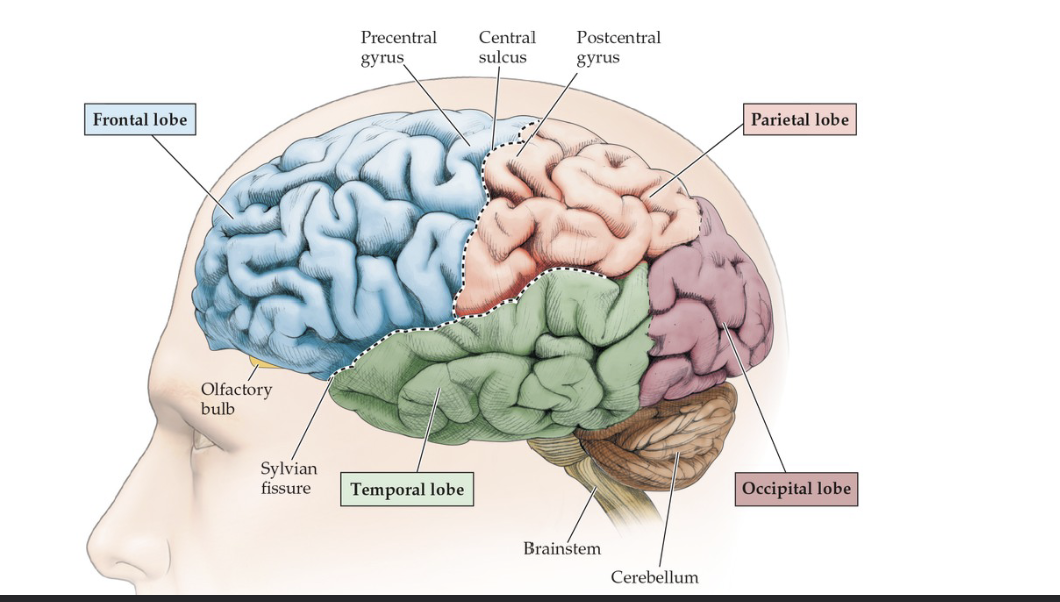
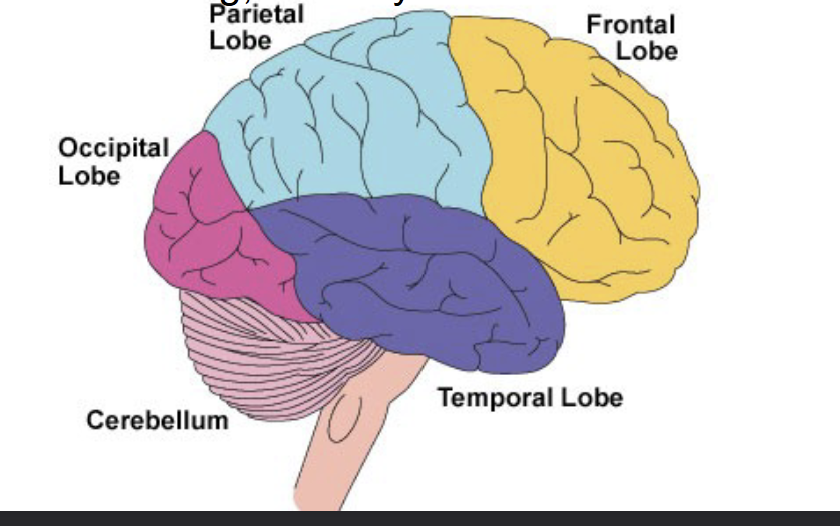
What are the four different lobes of the brain?
Frontal, Parietal lobe, Occipital lob, Temporal lobe
Which lobes doe the central sulcus separate?
This is the longest sulcus in the brain and is separates the primary motor cortex in the frontal lobe and the primary somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe
What is the function of the hindbrain
Has the medulla oblongata that is for breathing and sustaining the heartbeat and the cerebellum that is for balance and coordination
What is the function of the midbrain?
Has the reticular formation that is arousal/alertness and the pineal gland that produces melatonin
What is the function of the forebrain?
Forebrain includes the Thalamus (sensory system processing), hypothalamus (flight, fight, feeding, thirst , sex drive), amygdala (emotions), hippocampus (memory), corpus callosum (relays signals between the hemispheres)
What are the 3 systems?
The limbic, the movement, and the visual
Meninges
A covers that is 4 paper thick that protects the brain
Thalamus
Sensory system processing, in forebrain
Hippocampus
Memory, in forebrain
Hypothalamus
Fight, Flight, Feeding, Thirst and sex drive, in forebrain
Corpus callosum
Relays signals between the hemisphere, in forebrain
Amygdala
Emotions, in forebrain
Reticular formation
Arousal/alertness in the midbrain
Pineal gland
produces melatonin, in midbrain
Medulla oblongata
Breathing, sustaining the heartbeat, in the hindbrain
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
Midsagittal
A cut like a hotdog bun
Horizontal
A cut like a hamburger bun
Coronal
A cut like a loaf of bread
Dorsal
Means up
Ventral
Means down
Anterior
Or Rostral is front
Posterior
Or caudal means back
Central nervous system
This includes the brain and spinal cord
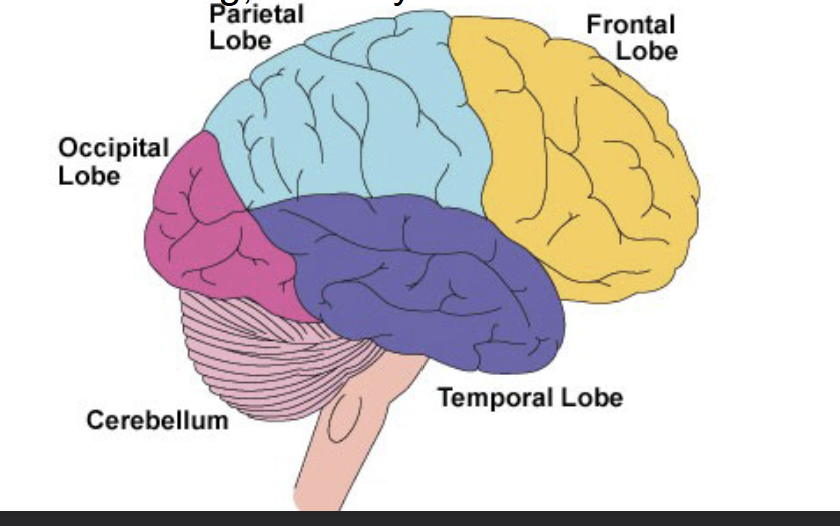
Frontal lobe
Higher thought, personality, motor control. This includes the primary motor cortex
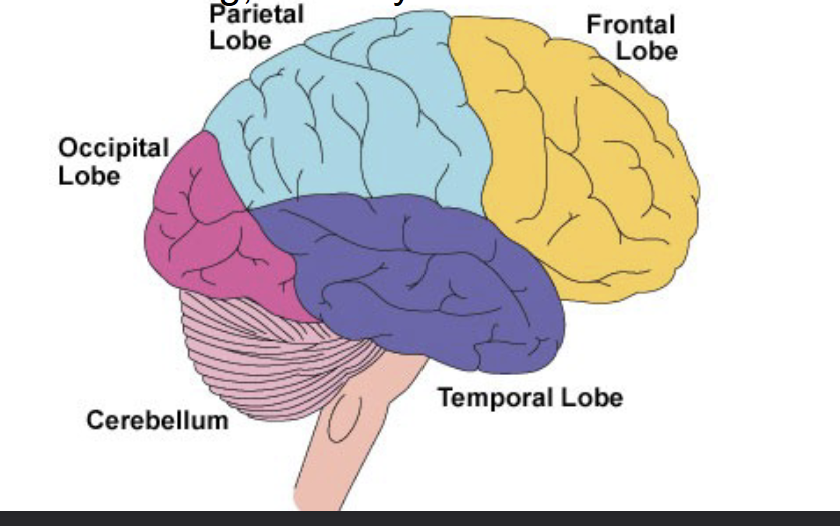
Parietal lobe
Touch and includes the somatosensory cortex
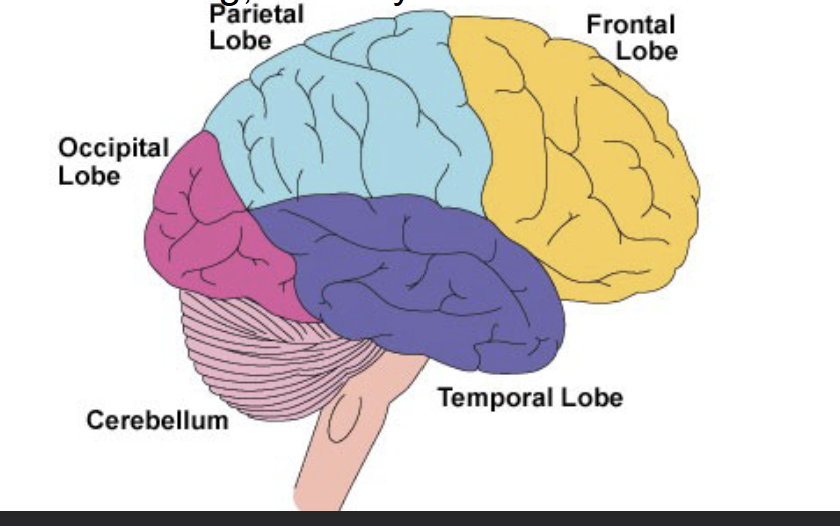
Occipital lobe
Vison
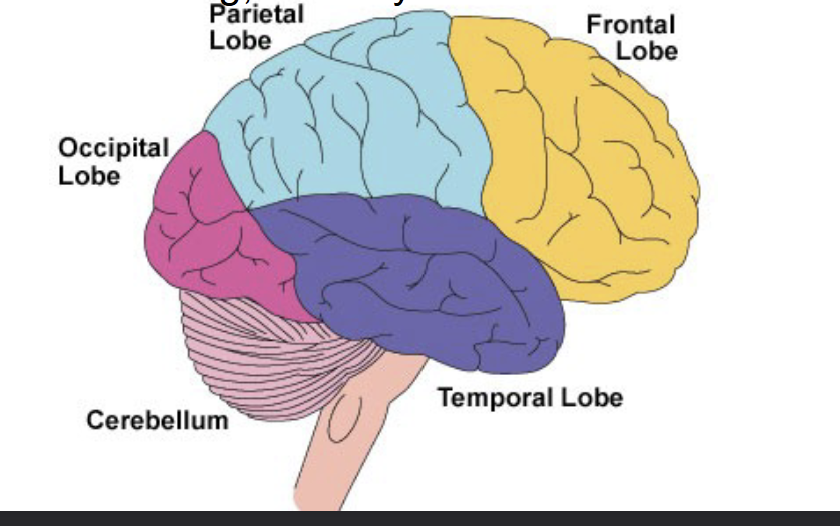
Temporal lobe
Hearing and memory
What is a tissue?
The bumps and folds on the surface of the brain
What are the two types of tissues?
Gyrus and Sulcus
Gyrus
The bumps
Sulcus
The folds
The limbic system
This is involved in emotions, it includes the amygdala (fear), hippocampus (memory), hypothalamus (sex), and thalamus (sensory system processing)
Movement system
This includes the primary motor cortex (motor control), cerebellum (balance and coordination), and the Basal ganglia (fine motor control)
Visual system
This includes the dorsal system (perceives motion) and the ventral stream (perceives individual components)
What gyrus is anterior to the central sulcus?
The primary motor cortex
What gyrus is posterior to the central sulus?
The somatosensory cortex
Ipsilateral
Same side