351 Test #1: Psych
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
anxiety and grief are
responses to stress and if they go unresolved, they can become psychiatric disorders
2
New cards
The concepts of mental health and mental illness are
culturally defined
3
New cards
Individuals experience
both physical and psychological responses to stress.
4
New cards
how we treat mental illness is also
culturally defined and impacted by stigma
5
New cards
maslow based his mental health theory on
\-A “hierarchy of needs”
\-Self-actualization as fulfillment of one’s highest potential
\-Self-actualization as fulfillment of one’s highest potential
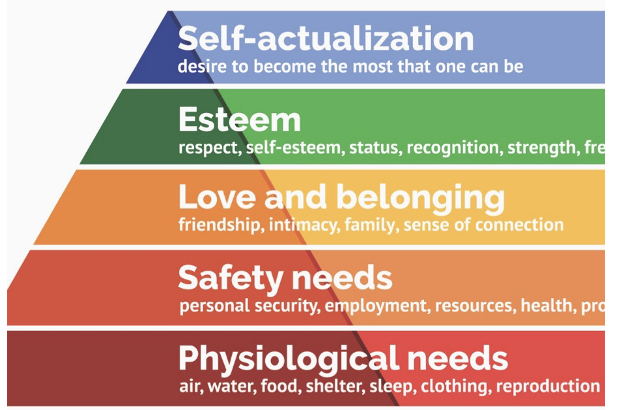
6
New cards
mental health clients often don’t have
their safety and physiological needs met (homeless, no access to food)
7
New cards
mental health is the
Successful adaptation to stressors from the internal or external environment, evidenced by thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that are age-appropriate and congruent with local and cultural norms
8
New cards
mental illness is
maladaptive (DSM5) responses to stressors from the internal or external environment, evidenced by thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that are incongruent with the local and cultural norms, and interfere with the individual’s social, occupational, and/or physical functioning.
9
New cards
Hans Selye defined stress as
\-the state manifested by a specific syndrome which consists of all the nonspecifically induced changes within a biologic system
\-fight or flight syndrome
\-fight or flight syndrome
10
New cards
Selye’s general adaptation syndrome had three stages
alarm reaction stage, stage of resistance, and stage of exhaustion
11
New cards
alarm stage
fight or flight, physiological effects and response to stress
12
New cards
resistance (adaptation stage)
becomes harder to adapt, body may rebound but there are still emotional and cognitive factors that get worse
13
New cards
exhaustion stage
resistance level decreases, medical therapy needed, death (can no longer adapt to stress)
14
New cards
physical responses to stress
\-Sustained physical responses to stress occur after a prolonged period of stress and promote susceptibility to many diseases of adaptation
\-fluid retention, increased BP, cardiac problems
\-decreased vulnerability to GAD due to adaptations like a support system
\-increased vulnerability to GAD with body’s inability to adapt
\-fluid retention, increased BP, cardiac problems
\-decreased vulnerability to GAD due to adaptations like a support system
\-increased vulnerability to GAD with body’s inability to adapt
15
New cards
there are 2 primary psychological response patterns to stress:
anxiety and grief
16
New cards
A variety of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are associated
with anxiety and grief, are experienced differently
17
New cards
Adaptation is determined by the extent to which the
thoughts, feelings, and behaviors interfere with an individual’s functioning, when they interfere this leads to a disorder/inability to adapt to stressors
18
New cards
anxiety
A feeling of discomfort and apprehension related to fear of impending danger. The individual may be unaware of the source of their anxiety, but it is often accompanied by feelings of uncertainty and helplessness
19
New cards
anxiety is
extremely common in our society
20
New cards
mild anxiety is
adaptive and can provide motivation for survival
21
New cards
Peplau has 4 levels of
anxiety
22
New cards
mild anxiety
special attention; increased sensory stimulation; motivational (increased productivity and perceptual field); can function at optimal level but not sustainable
23
New cards
moderate anxiety
something is wrong; nervousness/agitation; difficulty concentrating; able to be redirected; less alert; assistance with problem solving is needed
24
New cards
severe anxiety
trouble thinking/reasoning; tightened muscles; increased vital signs; restless; irritable, angry; centering on one thing; difficulty completing simple tasks; confusion, dread, horror
25
New cards
panic
fight, flight, freeze; increased vital signs; pupils dilate; cognitive processes focusing on defense; defenses slowly wear down; hallucinations/delusions; wild/desperate or withdrawn; convinced they are going crazy/losing control; life-threatening; reaches exhaustion phase quickly
26
New cards
At the __mild level__, individuals employ various coping mechanisms to deal with stress. A few of these include:
eating, sleeping, drinking, physical exercise
27
New cards
coping skills are coping behaviors that
enhance one’s adaption
28
New cards
At the __mild to moderate level of anxiety__, the strength of the ego is
tested
29
New cards
ego defense mechanisms are employed for
protection; are a response to anxiety
30
New cards
displacement
transference of feelings from one target to another that is considered less threatening or neutral
31
New cards
undoing
symbolic negation or cancellation of a previous action or experience that one finds intolerable
32
New cards
isolation
separating a thought or a memory from the feeling, tone, or emotions associated with it
33
New cards
denial
refusal to acknowledge the existence of a real situation or the feelings associated with it
34
New cards
introjection
internalization of the beliefs and values of another person, which symbolically become part of the self, to the extent that the feeling of separateness or distinctness is lost
35
New cards
identification
an attempt to increase self-worth by acquiring certain attributes and characteristics of a person one admires
36
New cards
regression
retreat to an earlier level of development and the comfort measures associated with that level of functioning
37
New cards
compensation
the act of covering up a real or perceived weakness by emphasizing a trait one considers more desirable
38
New cards
repression
the involuntary blocking of unpleasant feelings and experiences from one’s awareness
39
New cards
projection
the attribution to another person’s feelings or impulses that are unacceptable to one’s self
40
New cards
suppression
the voluntary blockage of unpleasant feelings and experiences from one’s awareness
41
New cards
rationalization
the attempt to make excuses or formulate logical reasons to justify unacceptable feelings or behaviors
42
New cards
reaction formation
preventing unacceptable or undesirable thoughts or behaviors from being expressed by exaggerating opposite thoughts or types of behaviors
43
New cards
sublimation
rechanneling of drives or impulses that are personally or socially unacceptable into activities that are constructive
44
New cards
intellectualization
an attempt to avoid expressing actual emotions associated with a stressful situation by using the intellectual processes of logic, reasoning, and analysis
45
New cards
Anxiety at the moderate to severe level that remains unresolved over an extended period can contribute to a number of
physiological disorders
46
New cards
Extended periods of repressed severe anxiety can result in
psychoneurotic patterns of behaving
(anxiety, dissociative disorders, somatic disorders, neuroses, still in touch with reality)
(anxiety, dissociative disorders, somatic disorders, neuroses, still in touch with reality)
47
New cards
Extended periods of functioning at the __panic level__ of anxiety may result in
psychosis (losing touch with reality)
48
New cards
examples of psychotic disorders
schizophrenia, schizoaffective, and delusional disorders
49
New cards
grief
\-Subjective state of emotional, physical, and social responses to the loss of a valued entity
\-Loss may be real or perceived
\-Loss may be real or perceived
50
New cards
patients can move backward or get stuck in stages for prolonged periods, which causes
mental disorders
51
New cards
five stages of grief
denial, anger, bargaining, sadness, happiness
52
New cards
grief
\-The experience of guilt for having had a “love-hate” relationship with the lost entity.
\-Guilt often lengthens the grieving process.
\-Guilt often lengthens the grieving process.
53
New cards
Anticipatory grieving is thought to
shorten the grief response when the loss actually occurs
54
New cards
Resolution
Length of the grief process is entirely individual. It can last from a few weeks to years and is influenced by a number of factors
\-triggers like an anniversary can cause a person to go back into grief stages
\-triggers like an anniversary can cause a person to go back into grief stages
55
New cards
The length of the grief response is often extended when an individual has experienced a number of
recent losses and when he or she is unable to complete one grieving process before another one begins
56
New cards
Resolution of the grief response is thought to occur when an individual can
look back on the relationship with the lost entity and accept both the pleasures and the disappointments of the association.
\-regains organization, hobbies again
\-regains organization, hobbies again
57
New cards
maladaptive grief responses
prolonged response, delayed/inhibited response; distorted response
58
New cards
prolonged response
preoccupation with loss many yrs after
59
New cards
delayed/inhibited response
\-can stay there for many years
\-stuck in denial stage
\-development of anxiety, somatic, eating, sleeping disorders
\-stuck in denial stage
\-development of anxiety, somatic, eating, sleeping disorders
60
New cards
distorted response
person stuck in a stage (anger), exaggerated response, can turn inward to depression
61
New cards
legislation determines what is
right or good in society
62
New cards
ethics
A branch of philosophy that deals with distinguishing right from wrong
63
New cards
bioethics
Term applied to ethics when referring to concepts within the scope of medicine, nursing, and allied health
64
New cards
moral behavior
Conduct that results from serious critical thinking about how individuals should treat others
65
New cards
values
Personal beliefs about what is important and desirable
66
New cards
values clarification
A process of self-exploration by which people identify and rank their own personal values
67
New cards
right
A valid, legally recognized claim or entitlement, encompassing both freedom from government interference or discriminatory treatment and entitlement to a benefit or service
68
New cards
absolute right
when there is no restriction whatsoever on a person’s entitlement
69
New cards
legal right
right that society has agreed upon and formalized into low
70
New cards
utilitarianism
An ethical theory that promotes action based on the end result that produces the most good (happiness) for the most people
71
New cards
kantianism
Suggests that decisions and actions are bound by a sense of duty, morality of right and wrong to do the greater good
72
New cards
Christian ethics
do unto others as you would have them do onto you, love forgiveness,
73
New cards
natural law theories
\-Do good and avoid evil. Human knowledge of the difference between good and evil directs decision-making.
\-self-evident and determined by human nature
\-self-evident and determined by human nature
74
New cards
ethical egoism
decisions are based on what is best for the person making the decision
75
New cards
ethical dilemma
\-are situations that require individuals to make a choice between two equally unfavorable alternatives.
\-taking no action is considered an action
\-no clear right or wrong
\-no clear reason to choose one over the other
\-taking no action is considered an action
\-no clear right or wrong
\-no clear reason to choose one over the other
76
New cards
autonomy
people are always capable of making independent choices for themselves
77
New cards
beneficience
one’s duty to benefit or promote the good of others
78
New cards
advocacy
acting in another’s behalf, being a supporter or defender
79
New cards
nonmaleficence
the requirement that healthcare workers don’t harm their patients, intentionally or unintentionally
80
New cards
justice
the right of people to be treated equally and fairly regardless of race, gender, sexual orientation, marital status, medical diagnosis, social standing, economic level, or religious beliefs
81
New cards
veracity
one’s duty to be truthful
82
New cards
model for making ethical decisions
assessment (objective/subjective data), problem identification, planning (benefits and consequences of theories), implementation (act on decision made, communicate with others), evaluation
83
New cards
all clients whom a nurse attends to have the following rights:
•The right to treatment
•The right to refuse treatment (including medication)
•The right to the least restrictive treatment alternative (restraints can cause isolation and seclusion)
•The right to refuse treatment (including medication)
•The right to the least restrictive treatment alternative (restraints can cause isolation and seclusion)
84
New cards
the Nurse Practice Act defines the legal parameters of professional and practical nursing with types of laws such as
statuary law and common law
85
New cards
civil law
•Protects the private and property rights of individuals and businesses
• Torts
• Contracts
• Torts
• Contracts
86
New cards
criminal law
Provides protection from conduct deemed injurious to the public welfare
87
New cards
legal issue: confidentiality/right to privacy
•Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (H I P A A)
•Doctrine of privileged communication
•Exceptions: A duty to warn; suspected child or elder abuse
•Doctrine of privileged communication
•Exceptions: A duty to warn; suspected child or elder abuse
88
New cards
informed consent
a client’s permission granted to a provider to perform a therapeutic procedure after information about the procedure has been presented to the client with adequate time given for consideration of pros and cons
89
New cards
restraints and seclusion: false imprisonment
the deliberate and unauthorized confinement of a competent person with the intent to prevent them from leaving the hospital; this includes use of threats or medications that interfere with the client’s ability to leave the facility
90
New cards
statutory law
law that has been enacted by a legislative body, such as a county or city council, state legislature, or U.S. Congress
91
New cards
common law
derived from decisions made in previous cases, may differ from state to state
92
New cards
tort
violation of civil law in which a person has been wronged
93
New cards
hospitalization: voluntary admission
patient seeks ER commitment, is a threat to themselves or others and admits themselves
94
New cards
hospitalization: involuntary commitment
•Emergency commitments (kept for 72 hrs, have a hearing, may need more treatment for 14, 90, or 180 days)-gov law
•A mentally ill person in need of treatment
•Involuntary outpatient commitment
•A gravely disabled client
•A mentally ill person in need of treatment
•Involuntary outpatient commitment
•A gravely disabled client
95
New cards
negligence
Failure to exercise the care toward others that a reasonable or prudent person would do in the circumstances.
96
New cards
malpractice
Act or continuing conduct of a professional that does not meet the standard of competence and results in provable damages to the patient
97
New cards
breach of confidentiality
revealing aspects about a client’s case or even for revealing that a person has been hospitalized which results in harm
98
New cards
defamation of character: libel and slander
when shared information is detrimental to the client’s reputation, the person sharing the information is liable for this
99
New cards
libel
written shared information that is detrimental to the client’s reputation
100
New cards
slander
oral defamation