1.4 competitive and concentrated markets
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
what are the four market structures
perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly and monopoly
which market structure is the most competitive
perfect competition
what are market structures characterised by
number of firms, product differentiation, barriers to entry, barriers to exit
what is a concentration ratio and what does a higher concentration mean
a concentration ratio is a combined share of a specified number of firms. a higher concentration ratio means fewer competitors and reduced competition
what is the typical CR of a monopoly
25%
how to calculate a CR
adding the top 5 market share percentages
what is a HHI
used by regulators to evaluate the effects of mergers on market competition
how to calculate HHI
summing the squares of the firm shares
what is an incumbent firm
firm that already operates in a market
what is an entrant
a firm that is trying to enter a market
are costs higher for incumbents or entrants
higher for entrants
what does homogeneity mean to price
entrants must compete on a price
examples of barriers to exit
high sunk costs like advertising, closure costs, redundancy costs
link between perfect competition and price
firms have no influence on price
what types of profits are earned
supernormal and normal
how do you calculate a firms profit
the difference between total revenue and total costs
where does profit maximisation occur
marginal cost (mc) = marginal revenue (mr)
what does profit maximisation mean
each extra unit produced gives no extra loss or revenue. net zero
graph for tc and tr
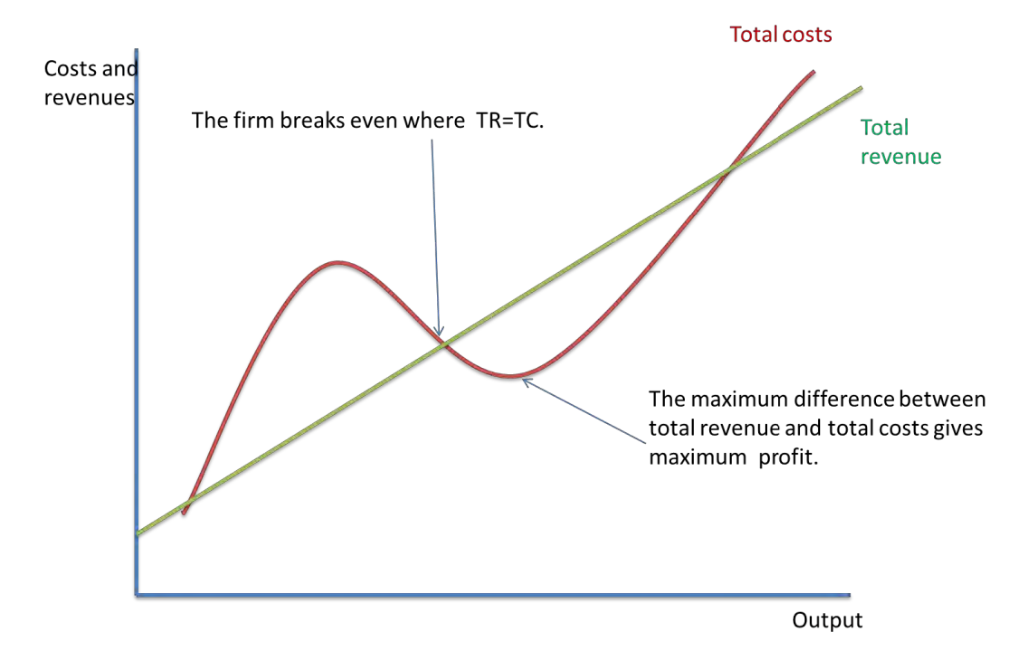
when does profits increase
when mr is less than mc
why do firms profit maximise
greater wages, retained profits which saves paying high interest rates
why do firms profit maximise in the short run
the interests of the owners and shareholders are most important since they aim to maximise their gain from the company
why do firms profit maximise in the long run
consumers do not like rapid changes in the short run, so it provides a stable price and output
what is the principal agent problem
theory of asymmetric information-the agent makes decisions for the principal, but the agent is inclined to act in their own interests rather than the principal’s
consequences of a divorce of ownership from control
when an owner of a firm sells shares, they lose some of the control they had over the firm
other objectives of a firm
survival, growth, increasing their market share, quality
when does revenue maximisation occur
when MR=0
what is sales maximisation
when a firm aims to sell as much of their goods and services without making a loss
what is the satisficing principle
when a firm is earning just enough profits to keep its shareholders happy
when does the satisficing principle occur
when there is a divorce of ownership and control
characteristics of perfect competition
sellers are price takers, free entry to enter and exit the market, perfect knowledge, many buyers and sellers
how is price determined in perfect competition
by the interaction of demand and supply
profits in a competitive market
lower with only a few large firms because each firm has a very small market share
what is the effect of a new entrant in a perfectly competitive market
enter due to low barriers and an increase in supply, which lowers the average price. Existing firms will be competed away
what profits are made in the short run/long run in perfectly competitive markets
SR- supernormal profits
LR- normal profits
what is a price taker
a firm that has no control over the market price
what is a price maker
firms that set the market price
what profit is made in the long run in competitive markets and why
normal profits- supernormal profits have been competed away
advantages of a perfectly competitive market
in the long run there is a lower price, productive efficiency and increased dynamic efficiency in the short run
disadvantages of a perfectly competitive market
LR dynamic efficiency is limited, few or no economies of scale, model rarely applies in real life (often competition is imperfect)
characteristics of a monopoly
profit maximisation
sole seller in a market
high barriers to entry
price maker
price discrimination
what is monopoly power influenced by
barriers to entry- high
number of competitors- fewer firms= lower barriers to entry
advertising- increases consumer loyalty
product differentiation- more unique= more the product can be differentiated
when do monopolies earn supernormal profits
in the long and short run
at what point is the profit maximisng equllibrium in a monopoly
when MC= MR
diagram for profit maximisation- monoplies

disadvantages of a monopoly
higher prices and profits and inefficiency may lead to a misallocation of resources
can exploit consumers by charging high prices = leads to good being under consumed
no incentive to become more efficient
loss of consumer surplus and a gain of producer surplus
advantages of a monopoly
earn significant supernormal profits - more dynamically efficient in the long run so more innovation
more likely to innovate
generate export revenue
high profits could be a source of government revenue through taxation
what is dynamic efficiency
a firm’s ability to adapt and improve its productivity over time
what is productive efficiency
ability of a firm to produce goods or services at the lowest possible cost
what is a price mechanism
determines the market price
referred to as ‘the invisible hand of the market’
resources are allocated through the price mechanism in a free market economy
price moves resources to where they are demanded or where there is a shortage and removes from a surplus
functions of a price mechanism
signalling, incentive, rationing, allocating resources
what is rationing in the price mechanism
there are scarce resources so prices increase die to the excess of demand
increase in price discourages demand and rations resources
what is incentive in the price mechanism
encourages a change in behaviour of a consumer or producer
e.g. a high price would encourage firms to supply more to the market
what is signalling in the price mechanism
price acts as a signal to consumers and new firms entering the market
price changes show where resources are needed in the market
a higher price signals to firms to enter the market because it is profitable
how are market structures characterised
number of firms in the market
degree of product differentiation
ease of entry into the market
how does the number of firms affect markets
the more firms there are, the more competitive the market is. this also includes the extent of competition from abroad
how does product differentiation affect markets
The more differentiated the products, the less competitive the market
In a perfectly competitive market, products are homogenous where products can be differentiated using price, branding and quality.
this affects cross price elasticity of demand.
how does ease of entry into a market affect markets
this is the number and degree of barriers to entry
barriers to entry are designed to prevent new firms entering the market profitably
how do barriers affect markets
Barriers to entry are designed to prevent new firms entering the market profitably.
This increases producer surplus.
The higher the barriers to entry, the less competitive the market
examples of entry into a market
economies of scale
brand loyalty
controlling technologies
reputation
backwards vertical integration
how does brand loyalty affect demand
demand becomes more inelastic as it is hard for new firms to gain consumer loyalty with a more known brand name
what is backwards vertical integration
this controls supply and means firms can control the price they pay suppliers. this makes it hard for new firms to compete on price which is a barrier to entry
what are the different types of barriers to entry
structural- different production costs
strategic- firms use different pricing policies
statutory- patents protect a franchise
what is a main objective of firms
profit
calculation for profit
difference between total revenue and total cost
what is profit to firms
the reward that entrepreneurs yield when they take risks
when does profit maximisation occur
when marginal cost = marginal revenue
what does profit maximisation result in
employees having higher wages
shareholders holding larger dividends
how can retained profits be useful
cheap source of finance
if firms want to invest in the future, they can use their profits rather than taking out a loan, which could potentially be expensive and have high interest rates
what is a plc
private limited company
why do PLCs profit maximise
they could lose their shareholders if they do not receive a high dividend
more likely to have short run profit maximisation as an object to keep shareholders happy
what are other objectives of firms
survival, growth and increasing their market share
what is survival as an objective
short term- survive in the market especially if they are a new firm entering a market
firms might have survival as their objective until there is economic growth again
firms might aim to sell as much as possible to keep their market position
what is growth as an objective
some firms may aim to increase the size of their firm
This could be to take advantage of economies of scale, such as risk-bearing or technological
this would lower average costs in the long run and make them more profitable
how can firms grow as an objective
expanding their product range
merging or taking over existing firms
large firms may participate more in research and devlopment
how do market shares affect a firms objective
helps to increase their chance of surviving in the market to maximise sales
how do objectives affect a firm
influence the firm’s behaviour
characteristics of a perfectly competitive market
many buyers and sellers
sellers are price takers
free entry to and exit the market
perfect knowledge
homogenous goods
firms are short run profit maximisers
how is price determined in a perfectly competitive market
determined by the interaction of demand and supply
how are profits in a competitive market
likely to be lower than a market with a few large firms
each firm has a small market share
market power is small
how do new firms affect competitive markets
If the firms make a profit, new firms will enter the market, due to low barriers to entry, because the market seems profitable.
new firms will increase supply in the market, which lowers the average price.
existing firms’ profits will be competed away
In the short run, firms will be able to make a lot more profit, than in the long run where profits are competed away.
what is a pure monopoly
there is one seller in the market
what is monopoly power
when one firm has a market share of over 25%
when can monopoly power be gained
when there are multiple suppliers
can also refer to two large firms in an oligoboly having over 25% market share
factors that influence monopoly power
Some Naughty Boys Always Eat Large Oreo Packs
sunk costs
number of competitors
brand loyalty
advertising
economies of scale
limit pricing
owning a resource
product differentiation
how do economies of scale affect monopoly power
As firms grow larger, the average cost of production falls because of economies of scale.
existing large firms have a cost advantage over new entrants to the market, which maintains their monopoly power.
It deters new firms from entering the market, because they are not able to compete with existing firms
how does limit pricing affect monopoly power
involves the existing firm setting the price of their good below the production costs of new entrants, to make sure new firms cannot enter profitably
what are sunk costs
unrecoverable costs such as advertising
how does product differentiation affect monopoly power
The more the product can be differentiated, through quality, pricing and branding, the easier it is to gain market share. This is because the more unique the product seems, the fewer competitors the firm faces
what is a concentration ratio
the combined market share of the top few firms in a market
what are some drawbacks of monopoly power
higher prices and profits and inefficiency may result in a misallocation of resources
monopolies can exploit consumers by charging higher prices
this means the good is under-consumed so consumer needs and wants are not fully met
the loss of allocative efficiency is a form of market failure
monopolies have no incentive to become more efficient, because they have few or no competitors so production costs are high
loss of consumer surplus and gain of producer surplus
what are benefits of a monopoly
they can exploit economies of scale so they have lower average costs of production
high profits results in more investment in research and development
yields positive externalities making it more dynamically efficient in the long run
more invention and innovation
how is price controlled in a competitive market
firms do not compete on price
firms try to distinguish their products and gain market share using non-price competition
what are ways firms try to stand out in a competitive market
improve products
reduce costs
improve quality of the service provided
why are consumers charged more in a monopoly
consumers have little choice where to purchase their goods and services since there are few firms in the market
consumer surplus falls