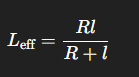Oscillations
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are oscillations
Periodic to-and-fro motions of a body about its mean (or equilibrium) position
What is a time period (for pendulums and NOT for circles;defination)
It is the amount of time required by the body to complete 1 oscillation
What is a time period (for circles and NOT for pendulums)
It is the amount of time required by the body to complete 1 revolution
What is the formula for angular frequency, and what are its units?
k/m
were,
k → Stiffness of the spring (From Hooke’s law)
m→ mass

What is the formula for finding out the time of oscillation
t = (T/2⊼)*ʘ
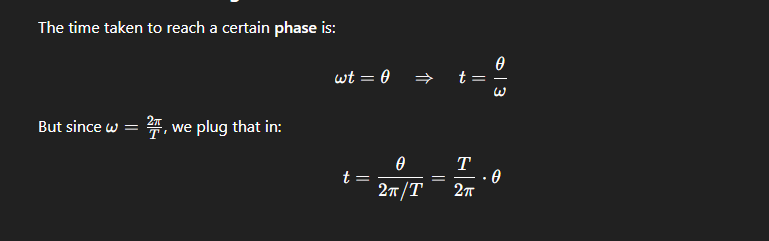
How can you write pi in time period’s terms?
T/2 = ⊼
When a particle is moving clockwise and anticlockwise, what happens to its angle?
Anticlockwise :- +ve
Clockwise :- -ve
What is the formula for the relation between velociy and distance in SHM?
V = w * √A²-x²
where,
w → Angular velocity
A → Amplitude
x → Distance
What is the formula for acceleration (w.r.t. position for SHM)?
a = -w²x
What is a second’s pendulum
It is a pendulum whose length is 1 meter and has a time period of 2 sec
What is the formula for the time period if the simple pendulum is very large compared to the radius of the Earth; What is it’s value?
It’s value is 84.6 minutes
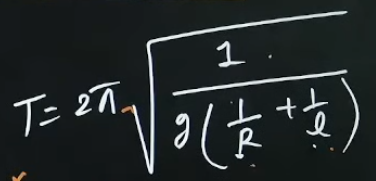
What is the changes in cos and sin as you change the phase between them by ⊼/2
cos(θ+π/2)= −sin(θ)
sin(θ+π/2)= cos(θ)
What is the formula that will be used to find the time period when the friction of the surface is sufficient to cause a body to roll when it is attached to a string

What is the formula that we will use when damping is occurring in oscillations?
k = b/2m
where,
where:
b: damping constant
m: mass
k: the damping coefficient (not the same as decay constant in general exponential decay)
If k is big → fast decay 😱
If k is small → slow decay 🐢
What is the formula that we will use to represent exponential decay?
At = A e-kt
Where:
A(t): Amount left after time t
A0: Initial amount (at time 0)
k: decay constant (positive value)
t: time
e: Euler's number (~2.718)
What is the formula we will use for length when the distance of the object > radius of the earth?