SOCIAL SCIENCE Q2
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Summary
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Demand
Quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase.
Law of Demand
Price increase, Quantity demanded decreases, assuming ceteris paribus
Demand Schedule
Table showing Qd at different prices
Demand Curve
Graphical representation of the demand schedule
Demand Function
Qd = a - bP
Factors affecting demand (shift)
Price of the Good
Income of Consumers
Prices of Related Goods
Tastes and Preferences
Expectations
Supply
Quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell
Law of Supply
As price increases, quantity supplied also increases, assuming ceteris paribus
Supply Schedule
Table showing Qs at different prices
Supply Curve
Graphical representation of Supply schedule
Supply Function
Qs = a - bP
Factors affecting supply (shift)
Input prices
Technology
Taxes and Subsidies
Number of Sellers
Price Expectations
Market Equilibrium
Point where Qd = Qs
Surplus (Excess Supply)
Occurs when price is set above equilibrium price
Qs > Qd
Shortage (Excess Demand)
Occurs when price is set below equilibrium price
Qd > Qs
Government interventions
Price Ceilings
Price Floor
Price Ceiling
Maximum legal price that sellers can charge
Set below equilibrium
Leads to shortage
Price Floor
Minimum legal price that sellers must charge
Set above equilibrium
Leads to surplus
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Measures how much Qd responds to change in price
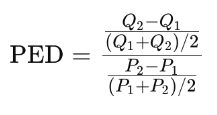
Elastic Demand
There are more available substitutes
Consumers react strongly to price changes
Ep > 1
Inelastic Demand
Price change cause only small change in quantity
Ep < 1
Perfectly Inelastic
People buy the same amount no matter the price
Ep = 0
Unit Elastic
The percentage change in price equals the change in demand
Ep = 0
Perfectly Elastic
Tiny price increase makes demand drop to zero
Ep = infinity
Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand
Availability to Substitutes
Necessity vs. Luxury
Proportion of Income
Time Period
Total Revenue and Elasticity
TR = P x Qty
TR | Elastic Demand
Price decrease = TR increases
TR | Inelastic Demand
Price increase = TR increase
TR | Unit Elastic
Changes in price do not affect TR
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED)
Measures the responsiveness of Qd of one good to a change in the price of the other good
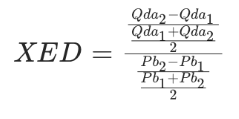
Goods are non-related
= 0
Goods are Substitutes
> 0 | positive
Goods are Complements
< 0 | negative
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Measures how much Qs changes when price changes
Focuses on how suppliers respond to changes in price
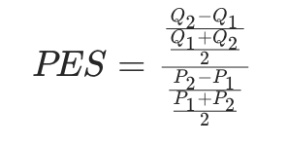
Unit Elastic
= 1
Elastic
> 1
Inelastic
< 1
Perfectly Elastic
= infinity
Perfectly Inelastic
= 0
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
Measures how quantity demanded responds to changes in consumer income
Normal Luxury
> 1
Normal Necessity
0 < Ey < 1
Inferior Goods
< 0
Theory of Choice | Consumer Theory
Interaction of preferences and constraints that guide purchasing decisions
Utility
The satisfaction or pleasure derived from economic activity or consuming goods and services
Total Utility
Overall satisfaction from consuming a specified qty
Marginal Utility
The additional satisfaction (increment) received from consuming an extra unti of a good
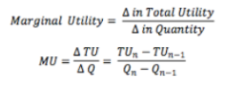
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
As the amount of a good consumed increases, MU decreases
Saturation Point
MU = 0
Maximum point of consumer satisfaction
Production Theory
Transforming production inputs into goods or services Sh
Short-run
At least one production input is fixed
Long-run
All production inputs are fixed
Total Product
Total amount of output produced
Marginal Product
Additional product per unit of labor hired
Average Product
Describes the average productivity of each worker
AP = TP/L
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
Adding additional units of a variable input while holding other inputs fixed, a firm eventually gets less and less extra output
Cost
All the opportunity costs in production
Total costs = explicit + implicit costs
Explicit Costs
Input costs that involve a direct disbursement of money
Implicit Costs
Input costs that do not require a disbursement of money
Economic Profit
TR - implict + explicit costs
Cost Components
Total Costs
Fixed Costs
Variable Costs
Fixed Costs
Expenses paid even at zero output
Variable Costs
Expenditures that depend on output
Total Cost
FC + VC
Marginal Costs
Additional cost incurred when producing a extra unit of output
Average Costs
Used to estimate profits by comparing price to cost
Curve is U shaped
MC and AC/AVC relationship
MC curve intersects AC and AVC at their lower points
MC > AC ; MC is falling
MC < AC; MC is rising
Total Revenue
measures qty sold by the price per unit
Marginal Revenue
The change in total revenue resulting from a one-unit change in output
Maximization
TR reaches max point when MR = 0
Profit
Financial gain when TR > TC
Normal Profit
Economic profit is zero
Break Even Point (BEP)
TR = TC; resulting in zero profits
Market Structures
Differentiated based on
Number of Sellers
Barriers to Entry
Price Control
Product Differentiation
Market Structure Types
Pure Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Pure Competition
No. of sellers: No limit
Barriers to Entry: None
Price Control: No price controls
Product Differentiation: Products are identical
Monopolistic competition
No. of sellers: Many buyers and sellers
Barriers to Entry: Few to none
Price Control: Some Control
Product Differentiation: Products are identical
Oligopoly
No. of sellers: Few
Barriers to Entry: High
Price Control: High
Product Differentiation: Can be differentiated or identical
Monopoly
No. of sellers: Only one
Barriers to Entry: High
Price Control: High
Product Differentiation: No product differentiation