ib business - finance 3.1,3.2,3.3
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
what is capital expenditure
money spent on fixed assets that a business will use for a long time
key features of capital expenditure
helps the business in the long term, long term investement, high cost equipment , collatoral for loans, helps the business grow and expand
examples of capital expenditure
buildings, machinery, computers, printers
revenue expenditure
money spent on the day to day running of the business
key features of revenue expenditure
short term, keeps the buisness operating, needs to be paid immediately w working capital
examples of revenue expenditure
stock/raw materials, delivery costs, wages and salaries, rent, insurance
why does revenue expenditure matter
impacts profit levels, poor control levels of revenue expenditure can conclude to irregular cash flow
why does capital expenditure matter
often serves as collatoral, influence deppreciation and invesement decisions
why does a business need finance
launch the business
required for day to day operations
expansion and growth
purchased fixed assets
dealing w a crisis
research
marketing + promotion
3.2
next slide
what is the definiton of sources of finance
refers to where or how businesses obtain their funds
Personal funds
Personal funds (owner's capital), business start-ups, short term
Retained profit
Retained profit is the value of profits that a business keeps after paying taxes and dividends
used for capital expenditure
kept in a contingency fund in case of emergencies
both long and short term
The sale of assets
Existing businesses can sell their dormant assets (unused assets), obsolete machinery
sale of land and buildings
selling subsidiaries due to a major liquidity threat short term
what are external sources of finance
external sources of finance refer to money that come from outside the busine
Share capital
Share capital is the money raised from selling shares, main source of finance for most
can provide a huge amount of finance.
ownership becomes diluted
involves many legalities and administrative procedures
loss of ownership
best for expansion and long term
Loan capital
money borrowed from a bank or financial insitiutions and repaid over time w interest
large sums available
predictable repayment schedule
interest increases cost
requires collateral
risk if cash flow is weak
best for buying machinery, equipment, long term
overdraft
a short term arrangement where a bank allows a buisness to withdraw more money than it has in its account.
very flexible + quick access to cash
ideal for temporary cash flow problems
high interest rates
can be withdrawn at any time
short term, buying stock before sales revenue arrives
trade credit
suppliers allow the business to receive goods now and pay later
imrpoves cash flow
no interest if paid on time + helps businesses
late fees for missed payments
best for retailers, cafes/restaurants both short and long term
crowdfunding
raising finance from a large number of small investors via online platforms (gofundme)
good for start ups
no trad loan/interest
builds a community + customers
not guaranteed to succeed
strong marketing
time consuming
best for start up products, creative projects and tech innovations both long and short term
leasing
renting an asset
low upfront cost
asset maintenance often included
keeps cash flow healthy
more expensive long term
business over owns the asset
best for expensive machinery, vehicle, equipment for start ups, long term
microfinance providers
organizations provide very small loans to entrepeuners who cannot access trad bank loans
helps invids w no collateral
encourages entrepreneurships
flexible and accessible
small loans amounts
higher interest rates
not suitable for large investements
best for small start up business w low capital needs
business angels
wealthy individuals who invest their own money into start ups in exchange for equity
investor brings expertise and industry contacts
no interest
useful when banks refuse loans
loss of ownerships
potential for investor influence over decisions
best for: high growth potential start ups long term
what is dilution of control means
loss of ownership percentage when new shares are issued
cost of debt
interest payment on loans or bonds
ownership remains
mandatory repayments
cost of equity
dividends payed to shareholders
no repayments obligatory
cost of dividends
3.3
next slide
fixed cost
cost a business pays regaardless of output. it does not change w output in the short run. eg rent,insurance, salaries, adv, security, matters bc of break even and long term planning, impact on business

variable cost
costs that change in proportion with the level of output or sales eg hourly wages, raw materials, packaging utilities
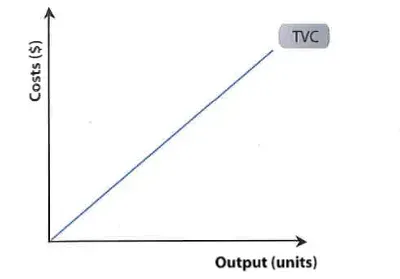
formula for tvc
vc per unit x quantity or vc also is tc - fc
total costs
sum of variable and fixed
determines profit and break even

formula fixed costs
fixed costs and variable costs
Direct costs
direct cost is related to an individual project or the output of a particular product; without which the costs would not be incurred- Not necessarily related to the level of output
For example, the direct costs of purchasing a commercial building include consultancy costs, solicitor's fees, telephone bills
Indirect costs (overheads)
Indirect costs cannot be clearly traced to the production or sale of any single product- Not necessarily related to the level of output
For example, rent and lighting costs can be associated with all areas of a business rather than being directly related to the output of a particular product
revenue
Revenue refers to the money coming into a business, usually from the sales
revenue streams
revenue streams are the sources of revenue from the sale of goods and services and others
revenue streams examples
advertising revenue - Google, Twitter and Facebook
Transactions fees - credit card commission
Franchise costs and royalties - McDonald's, Burger King and KFC
Sponsorship revenue - Sponsorship whereby the sponsor financially supports an organization in return for prominent promotional display
Subscription fees - charges on customers who use or access a good or service
Merchandise - entertainment industry
Interest earnings - positive cash balance can earn interest on their cash deposits
Dividends - a share of the net profits distributed to shareholders
Donations - financial gifts from individuals or other organizations
Subventions - subsidies offered from the government to certain businesses to help reduce their costs of production
average cost formula + what
total cost divided by quantity shows cost per unit helps managers compare efficiecny low ac = economies of scale
break even
where total revenue = total costs shows minimum output to prevent losses helps in financial planning and pricing
total revenue formula
price x quantity sold
margincal cost
the change in total production costs that comes from making or producing 1 additonal unit important for profit maximisation