Neuro Surgery
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
Lumbar disc herniation
Impingement of nerve exiting the spinal canal by herniating disc
2
New cards
S/S of radiculopathy in lumbar disc herniation
Pain radiating down LE
Motor weakness
Dermatomal sensory changes
Reflex changes
Nerve root tension signs (straight leg raise)
Tenderness over sciatic notch
Motor weakness
Dermatomal sensory changes
Reflex changes
Nerve root tension signs (straight leg raise)
Tenderness over sciatic notch
3
New cards
Sciatica
Pain along the course of sciatic nerve, usually from nerve root compromise- L1 through L5
4
New cards
Cauda equina syndrome s/s
-Saddle anesthesia
-Urinary retention
-Lower extremity weakness
-Foot drop
-->Go to ER/ immediate referral
-Urinary retention
-Lower extremity weakness
-Foot drop
-->Go to ER/ immediate referral
5
New cards
Lumbar disc herniation is mostly treated by ______
Conservative tx (85% resolve within 6 weeks)
PT/ exercise, steroid injections, spinal manipulations, NSAIDs/ APAP
PT/ exercise, steroid injections, spinal manipulations, NSAIDs/ APAP
6
New cards
Surgical indications for lumbar disc herniation
-Cauda equina syndrome
-Progression of sx despite conservative tx
-Severe radicular pain > 6 weeks
-Progression of sx despite conservative tx
-Severe radicular pain > 6 weeks
7
New cards
Cauda equina- what is it?
Terminates at....
Terminates at....
Nerve roots distal to conus medullaris
Terminates at L1/2
Terminates at L1/2
8
New cards
Dermatomal map
Esp look at lower extremities
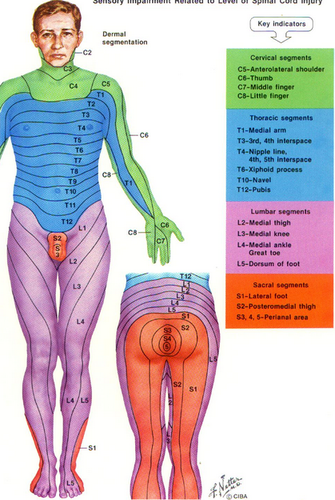
9
New cards
Disectomy
Removal of disc
10
New cards
Interbody
Between vertebral bodies
11
New cards
Fusion
Encouraging growth between vertebral bodies
12
New cards
Corpectomy
Removal of vertebral body
13
New cards
ALIF
OLIF/ATP
XLIF/LLIF/DLIF
TLIF
PLIF
OLIF/ATP
XLIF/LLIF/DLIF
TLIF
PLIF
Anterior lumber interbody fusion
Oblique lateral interbody fusion
Trans-psoas lumbar interbody fusion
Transforaminal lumbar interbdoy fusion
Posterior lumber interobody fusion
Oblique lateral interbody fusion
Trans-psoas lumbar interbody fusion
Transforaminal lumbar interbdoy fusion
Posterior lumber interobody fusion
14
New cards
ALIF is a spinal fusion procedure usually performed at....
What is it?
What is it?
L5/S1 or L4/L5
Disectomy performed, interbody spacer introduced and fixed into place with screws/ plates
Disectomy performed, interbody spacer introduced and fixed into place with screws/ plates
15
New cards
PLIF procedure
Partial laminectomy to gain access to spinal canal. Theca (and cauda equina) retracted to enable a disectomy. Interbody cage introduced with bone, and screws are placed connecting rods posteriorly

16
New cards
Woman comes in with left sided LE sensory deficits and numbness. Left buttock, posterior left thigh, under left foot for the past 3 weeks. No weakness, no urinary/ bowel problems. Pain 4/10 throbbing and constant, no history of trauma. MRI reveals a disc herniation at L5/S1. What's your approach
First start her on conservative therapy since she doesn't have sx of cauda equina/ alarm sx.
17
New cards
Back pain red flags and presentation of cord compression
History of malignancy
Violent trauma (fall from height, MVA)
Thoracic or radicular pain
Constant, progressive, non-mechanical pain
Systemically unwell
Widespread neuro s/s
Power reduction
Saddle anesthesia
Urinary retention
Violent trauma (fall from height, MVA)
Thoracic or radicular pain
Constant, progressive, non-mechanical pain
Systemically unwell
Widespread neuro s/s
Power reduction
Saddle anesthesia
Urinary retention
18
New cards
If you suspect cord compression, what imaging do you order?
MRI
19
New cards
Treatment of cord compression
High dose IV steroids reduces edema
Can be surgical emergency- decompression may be needed to prevent permanent disability
Radiotherapy for malignancy
Can be surgical emergency- decompression may be needed to prevent permanent disability
Radiotherapy for malignancy
20
New cards
You don't have as many problems in the thoracic region because...
Joints don't move bc they're stabilized by ribs
21
New cards
Head trauma stats
10% fatal
5-10% suffer serious neurological disorder
20-40% moderate disability
5-10% suffer serious neurological disorder
20-40% moderate disability
22
New cards
What's more damaging? High velocity or low velocity wounds?
High velocity
23
New cards
Leading cause of TBI
Ground level falls (GLF)
24
New cards
GCS is highly predictive of...
mortality
25
New cards
GCS scale
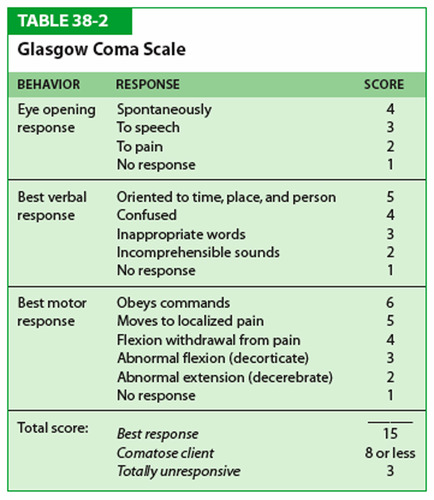
26
New cards
GCS mild
13-15
27
New cards
GCS moderate
9-12
28
New cards
GCS severe
3-8
29
New cards
GCS below 8 = _____% mortality
GCS above 8 = _____% chance of survival
GCS above 8 = _____% chance of survival
70%
90%
90%
30
New cards
Secondary head trauma
Herniation syndromes
Cerebral edema
Cerebral ischemia
Vascular injury (can be primary or secondary)
Cerebral edema
Cerebral ischemia
Vascular injury (can be primary or secondary)
31
New cards
Skull radiography obtained soley for the purpose of...
identifying prescence of skull fracture- no appropriate role in current management of head injured patient
32
New cards
THE screenign tool for imaging acute head trauma
Head CT
33
New cards
CT depicts both ___ and ___ injuries
Bone and soft tissue
34
New cards
NECT
Non-contrast enhanced CT
35
New cards
Head truama patients with acute intracranial lesions on CT have a higher risk for ______ _compared with patients with a CT negative head injury
Cervical spine fractures
36
New cards
_____ of patients with moderate to severe head injury (GCS) also have a spine injury
1/3
37
New cards
Repeat CT should be obtained if there is....
sudden unexplained clinical deterioration, regardless of initial imaging findings
38
New cards
CTA- CT angiography
Noninvasive imaging of vascular system - examines blood vessels and the organs supplied by them
39
New cards
______ is the procedure of choice in the initial evaluation of brain truama
CT without contrast
40
New cards
Who and when to image?
GCS of 3-8 (severe) or 9-12 (moderate)- obtain NECT
41
New cards
CT indicated if GCS = 15 plus any of the following...
HA
Vomiting
Patient > 60 yrs old
Intoxication (drugs/ alcohol)
Short term memory deficits (antegrade amnesia)
Visible trauma above clavicles
Seizure
Vomiting
Patient > 60 yrs old
Intoxication (drugs/ alcohol)
Short term memory deficits (antegrade amnesia)
Visible trauma above clavicles
Seizure
42
New cards
Canadian had CT rule for minor head injury: CT if GCS = 13-15 and....
witnessed LOC, amnesia, or confusion
43
New cards
High risk for neurological intervention (Canadian head CT)
GCS < 15 hours at 2 hours
Suspected open/ depressed skull fx
-Clinical sign of skull base fracture
->2 vomiting episodes
Age >65
Suspected open/ depressed skull fx
-Clinical sign of skull base fracture
->2 vomiting episodes
Age >65
44
New cards
Medium risk for brain injury detected by head CT (Canadian head CT rule)
Antegrade amnesia >30 minutes
"Dangerous mechanism" (auto-pedestrian, ejection from vehicle
"Dangerous mechanism" (auto-pedestrian, ejection from vehicle
45
New cards
NECT is first line in patient with...
sudden onset of unexplained neurological deficit
46
New cards
Emergent NECT imaging is also often obtained in patients with ______ to screen for suspected SAH, hydrocephlus, intracranial mass, etc
Headache
47
New cards
_____ is indicated in patients with sudden clinical deterioration and mixed-density hematoma (indicating rapid bleeding or coagulopathy)
CTA
48
New cards
______ in spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage predicts hematoma expansion and poor clinical outcome
Contrast extravasation
49
New cards
_______ is the most common underlying etiology in younger age groups
Vascular malformations
50
New cards
In elderly patients, ______ and ______ are the two most common etiologies of unexplained sICH (spontaneous ICH)- vascular
Hypertensive hemorrhage and amyloid angiopathy
51
New cards
Intracranial hemorrhages can either be...
intra-axial (intracerebral) or extra-axial (epidural/subdural/subarachnoid)
52
New cards
Epidural, subdural, suabrachnoid, intraventricular hemorrhages are examples of...
Extra-axial hemorrhages
53
New cards
MC type of stroke
Ischemic
2nd is hemorrhagic
2nd is hemorrhagic
54
New cards
Intracerebral hemorrahge facts
Onset?
Onset?
Most deadly
Unlike ischemic, onset is progressive over minutes to hours
Unlike ischemic, onset is progressive over minutes to hours
55
New cards
Intracerebral hemorrhage presentation
Severe HA, vomiting, altered level of consciousness
At least 1/3 enlarge over first 3 hours
At least 1/3 enlarge over first 3 hours
56
New cards
Risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage
Age- increases w/ age (esp after 55 and doubles each decade therafter)
Male> female
Greater in blacks
hx of stroke
Alcohol
Street drugs
Liver dysfunction
Male> female
Greater in blacks
hx of stroke
Alcohol
Street drugs
Liver dysfunction
57
New cards
In an intracerebral hemorrhage, ____ of hematoma correlates with morbidity/ mortality
Volume
58
New cards
Management of intracerebral hemorrhage
ICU
Tight blood pressure control
Euglycemia/ normothermia
Anticonvulsants
Correct coagulopathies
Tight blood pressure control
Euglycemia/ normothermia
Anticonvulsants
Correct coagulopathies
59
New cards
MC cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage
Trauma
60
New cards
Most spontaneous SAH are due to..
aneurysmal rupture
61
New cards
Peak age for aneurysmal rupture
55-60
62
New cards
Sentinal HA for 2-8 weeks prior to SAH in 10-50% of patients
True
63
New cards
SAH presentation
Sudden onset severe HA (thundreclap)
64
New cards
_____ will detect 95% of SAH
If you're suspicious and CT is negative....
If you're suspicious and CT is negative....
-NECT
-Get Lumbar puncture
-Get Lumbar puncture
65
New cards
Risk factors of SAH
HTN
SMoking
Alcohol abuse
Symptothomimetic drugs
Women> men
Hx / family hx of aneurysms
Pregnancy
SMoking
Alcohol abuse
Symptothomimetic drugs
Women> men
Hx / family hx of aneurysms
Pregnancy
66
New cards
Managment of SAH
ICU
Q1 neuro checks
Consider anticonvulsants
Oral nimodipine (Ca channel blocker)
Euvolemia
Prevent hydrocephalus
Q1 neuro checks
Consider anticonvulsants
Oral nimodipine (Ca channel blocker)
Euvolemia
Prevent hydrocephalus
67
New cards
Epidural hemorrhage etiology
Almost always traumatic
Arise from lacerated meningeal arteries, fractures, or torn dural venous sinuses
Arise from lacerated meningeal arteries, fractures, or torn dural venous sinuses
68
New cards
Most spontaneous epidural bleeds are found in the ______ epidural space and are emergenct
Spinal (not cranial)
69
New cards
Classic presentation of epidural hemorrhage (only about 40%)
Brief posttraumatic LOC from initial impact followed by a "Lucid" interval for several hours
Then obtunded, contralateral hemiparesis, ipsilateral pupillary dilation
Deterioration may take hours to weeks
May have HA, vomiting, seizure, hemi-hyperreflexia, unilateral Babinski, elevated CSF
Then obtunded, contralateral hemiparesis, ipsilateral pupillary dilation
Deterioration may take hours to weeks
May have HA, vomiting, seizure, hemi-hyperreflexia, unilateral Babinski, elevated CSF
70
New cards
CT findings for epidural hemorrhage
Biconvex (lens shaped) density
71
New cards
Management of epidural hemorrhage
Craniotomy
May medically manage if small, no midline shift, GCS > 8 and no focal neuro deficit
May medically manage if small, no midline shift, GCS > 8 and no focal neuro deficit
72
New cards
_____ causes most of subdural hemorrhages
More or less lethal than epidural?
More or less lethal than epidural?
Trauma
More lethal
More lethal
73
New cards
Subdural hemorrahges may result from torn _______
surface or bridging vessels
74
New cards
Nontraumatic subdural hemorrhages reported in association with a number of other conditions including...
hyponatremic dehydration
Inherited or acquired coagulation disorders
Dural venous sinus thrombosis
Meningitis
Inherited or acquired coagulation disorders
Dural venous sinus thrombosis
Meningitis
75
New cards
Burr holes are created for..
evacuation of extracerebral clots or in prep for a craniotomy
76
New cards
AV malformations
Dilated arteries and veins with dysplastic vessels- arterial blood flows directly from arteries and veins with no capillary bed or parenchyma
77
New cards
MC site of AV malformation
Intraparenchymal
78
New cards
Hemorrhage of AV malformations are related to...
Size (smaller are more lethal dt higher pressure)
79
New cards
Treatment of choice for AV malformations
Surgery
80
New cards
Coil embolization
Catheter-based procedure that allows precise occlusion of abnormal blood flow in a blood vessel
81
New cards
Normal flow of CSF
Made in choroid plexus of lateral ventricles --> foramen of monro --> 3rd ventricle --> cerebral aqueduct --> 4th ventricle --> cisterna magna, reabsorbed into arachnoid granulations
82
New cards
Types of congenital hydrocephalus
Chiari Type 1 malformation: 4th ventricle outlet obstruction
Chiari type 2
Dandy walker: Atresia of foramina of 4th ventricle
Chiari type 2
Dandy walker: Atresia of foramina of 4th ventricle
83
New cards
Most common etiology of hydrocephalus
Infectious (Post meningitis, TB, crytpococcus
84
New cards
S/S of hydrocephalus in children
Abnormal head circumference
Irritability, poor head control, N/V
Fontanels full an dbulging
"Setting sun sign"
Blindness
Irritability, poor head control, N/V
Fontanels full an dbulging
"Setting sun sign"
Blindness
85
New cards
VP shunt
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt:
Used to treat swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid by draining fluid into the peritoneal cavity.
Used to treat swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid by draining fluid into the peritoneal cavity.
86
New cards
Cerebral blood flow depens on ______ which is related to ICP
If ICP goes up, CCP goes ______ which means....
If ICP goes up, CCP goes ______ which means....
CPP- cerebral perfusion pressure
If ICP goes up, CPP goes down, which means less blood flow to the brain
If ICP goes up, CPP goes down, which means less blood flow to the brain
87
New cards
Normal ICP pressures
-Adults and older children:
-Young children
-Term infants
-Adults and older children:
-Young children
-Term infants
-
88
New cards
Types of ICP measuring monitors
Ventriculostomy
Intraparenchymal fibreoptic catheter
Epidural transducer
Subdural catheter
Subdral bolt
Intraparenchymal fibreoptic catheter
Epidural transducer
Subdural catheter
Subdral bolt
89
New cards
Epidural abscesses are most often in _____ spine and ____ to the spinal cord
Thoracic
Posterior
Posterior
90
New cards
Presentation and risk factors of epidural abscesses
-Back pain, fever, spine tenderness
-IV drug use, alcoholism, DM, CRF, skin infection (furuncle)
-IV drug use, alcoholism, DM, CRF, skin infection (furuncle)
91
New cards
Study of choice to test for epidural abscess
MRI
92
New cards
Surgical approach to epidural abscess
Laminectomy + antibiotics
93
New cards
MC oganism causing epidural abscess
S. aureus
94
New cards
What antibiotics would you prescribe for an epidural abscess caused by an unknown organism?
Ceftriaxone + Mentronidazole + Vancomycin until organism is ID'd
95
New cards
Risk factors for spinal osteomyelitis (infection of vertebrae)
Similar to epidural abscess
IV drug use
Alcoholism
Immunocompromised
DM
Hemodialysis
Post spinal surgery
IV drug use
Alcoholism
Immunocompromised
DM
Hemodialysis
Post spinal surgery
96
New cards
Diagnosis of spinal osteomyelitis
Percutaneous bone biopsy
97
New cards
Treatment of spinal osteomyelitis
Antibiotics (MC organism is S. aureus)
Surgery if instability in vertebrae
Pain meds
TLSO brace
Surgery if instability in vertebrae
Pain meds
TLSO brace
98
New cards
Presentation of discitis (which is what?)
Infection of nucleus pulposis
Back pain with any movement of spine
Fever/ chills
Radicular sx
Radiation to abdomen
Back pain with any movement of spine
Fever/ chills
Radicular sx
Radiation to abdomen
99
New cards
Diagnosis of discitis
MRI
WBC, cultures, ESR, CRP, percutaneous biopsy
WBC, cultures, ESR, CRP, percutaneous biopsy
100
New cards
Treatment of discitis
Antibiotics 4-6 weeks until ESR normalized
Possible surgery
Possible surgery