Week 3 - Recognizing Normal Skeletal Anatomy, Common causes of Back Pain and Non traumatic skeletal Abnormalities
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is the outer fibrous layer of the intervertebral disks called?
Annulus Fibrosus
What is the inner gel like layer of the intervertebral disc called?
Nucleus Pulposus
how many pair of nerves extends from the spinal cord
31 pairs
What is the conus medullaris?
end of spinal cord (L1/L2)
What are the branches of the cervical plexus?
C1-C4
What are the branches of the brachial plexus?
C5-T1
What are the branches of the lumbosacral plexus?
L1-S4
What percentage of all Americans will have some episode of back pain during their lifetime?
80%
What is degenerative disc disease?
- AKA DDD or Spondylosis
- Nucleus pulposus becomes degenerative and dehydrated, which leads to loss of height of IVD space
What is the vacuum disk phenomenon?
Desiccation of disks leading to the relase of nitrogen from tissues surrounding the disk resulting in the appearance of air density in disk space
What is the imaging study of choice for DDD?
Plain film X-Ray which may show:
- Disk space narrowing
- Sclerotic vertebral endplates w/ osteophyte formation
- Vacuum-disk phenomenon
What is Osteoarthritis of Facet Joints?
- Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
What are facet joints?
True synovial joints between superior and inferior articular facets
What are uncovertebral joints?
- Joints of Luschka
- Small joint-like structures at the lateral edges of C3-T1
What is the imaging study of choice of DJD? What will be present on imaging?
Plain film X-Ray
- Disk space narrowing w/ osteophyte formation
What is a herniated disc? + caused by what + where
ruptured intervertebral disc caused by degeneration or trauma that usually herniates posterolaterally
What is the gold standard for herniated disk?
MRI
What is the most common level for disherniation?
- C4-C7
- L4-S1
What is diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis?
DISH (AKA Forestier disease) that is characterized by bone or calcium excrescences at the site of ligamentous insertion
DISH mainly affects what population?
Males over 50
What is the imaging study of choice for DISH? What is present on imaging?
Plain Film X-Ray
- ossification of anterior longitudinal ligaments (OALL) at least 4 continguous vertebral bodies
- Normal SI joints
What is the imaging study for compression fractures? What is present on imaging?
X-Rays
- Wedge shaped deformity
- Loss of body height in anterior and central aspect of body
What is spinal stenosis? + caused by what
narrowing of the spinal canal or intervertebral foramen caused by degeneration, disk herniation, spondylolisthesis, Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum
What is the imaging study of choice for spinal stenosis
- MRI (gold standard)
- X-Ray often obtained first
What is malignancy involving spine? leads to what + associated with which cancers
Metastases that leads to compression fractures, involving both the anterior and posterior vertebral body, most commonly associated with lung, breast and prostate cancer
What is the imaging study of choice for Malignancy Involving Spine?
- Bone Scan (Gold Standard)
- MRI (early metastasis)
What is osteomyelitis of spine?
Infection of bone that is often associated with infection of disk
What is the imaging study of choice for osteomyelitis of spine?
-MRI (most sensitive)
- CT
What does CT imaging show in osteomyelitis of the spine?
Destruction of endplates
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
- AS is an inflammation and eventual fusion of sacroiliac joint (SI joint)
What gene is correlated with AS?
HLA-B27
What main population is affected by AS?
Young Males
What is the imaging study of choice for AS? What is seen on imaging?
- X-Rays
- Sacrioilitis
- Bamboo Spine
Why is MRI study useful?
- Soft tissue injury
- Marrow pathology
Most Exams of bone start with ________?
X-Rays
What is increase in bone density?
- Overall whiteness (=sclerosis)
- loss of distinction b/w normal cortico-medullary junction
What is decrease in bone density?
- Diffuse lose of bony trabeculae
- Accentuation of cortex (but thinner)
What is presentation of osteoblastic metastatic disease?
- Thickening of cortex
- Punctate sclerotic lesions in medulla
What is the MC of osteoblastic metastatic disease?
Carcinoma of prostate
Where are the MC osteoblastic lesion seen?
- Vertebrae
- Ribs
- Pelvis
- Humerus
- Femur
What is the imaging study of choice of osteoblastic metastatic disease?
Bone Scan
What is avascular necrosis?
- Ischemic necrosis/aseptic necrosis/osteonecrosis
- death of bone tissue due to lack of blood supply
What is a common x-ray finding of avascular necrosis?
- Crescent sign
- Snow capping
What is the most sensitive test for avascular necrosis (AVN)?
MRI
What is Paget Disease?
Chronic disease characterized by varying degrees of increased bone resorption and formation
What are the main sites of paget disease?
- Pelvis
- L/S
- T/S
- Femur
What x-ray findings are present in Paget Disease?
- Thickened cortex
- Coarsening + thicken trabeular pattern
- Increase in size of the bone involved
What are the X-ray findings for Osteoporosis?
- Thinning cortex
- Decrease in visible trabeculae in medullary cavity
- *Requires >50% of bone loss to be recognized*
What is the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis?
DEXA (dual energy x-ray absorptiometry) Scan
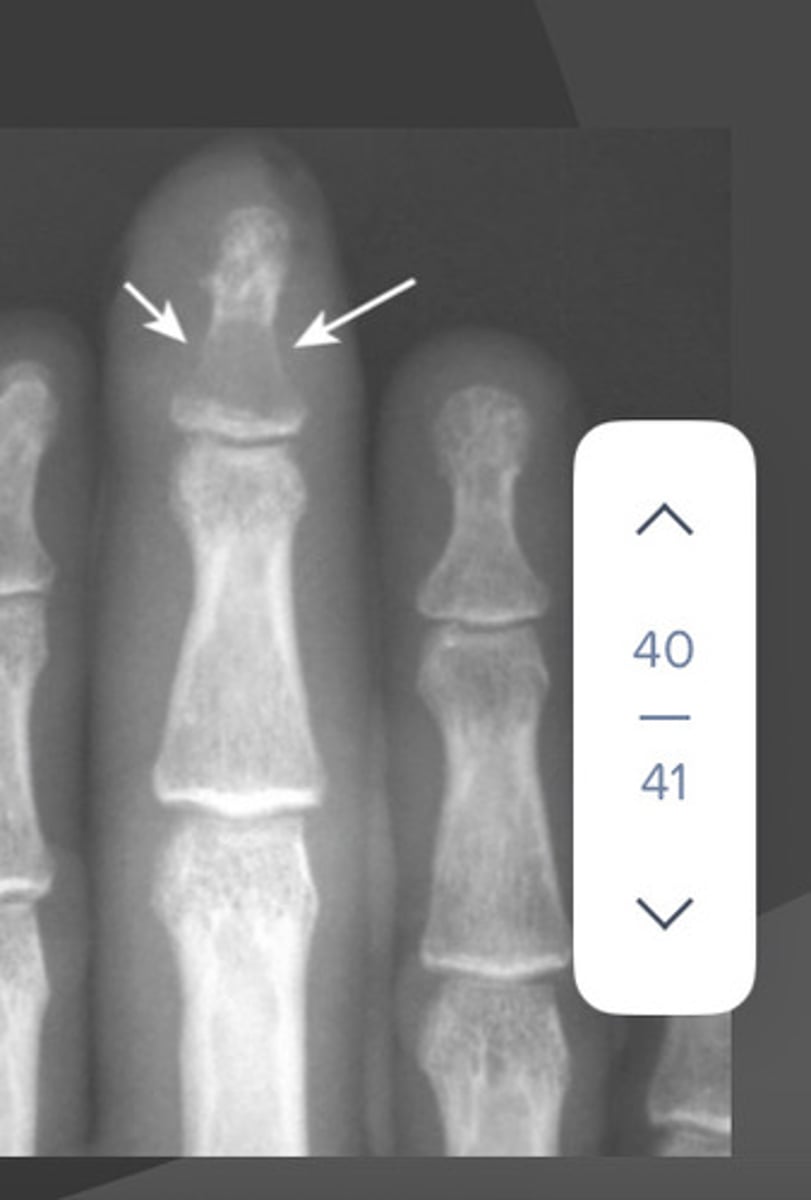
What are the x-ray findings in hyperparathyroidism?
- Subperiosteal bone resorption
- Erosion of distal clavicles
- Brown tumors - well-circumscribed lytic lesions
What are the X-ray findingss for osteolytic metastatic disease?
- Irregularly, shaped, lucent bone lesions
- Soap-bubbly appearance
- Pedicle sign (aka winking owl sign)
Which imaging studying is more sensitive for dx'Inguinal myeloma - X-ray or bone scans?
X-rays
What are the X-ray findings in Myeloma?
- Soap bubble expansile lesions (A)
- Punched out lytic lesions (B)

What are the x-ray findings in osteomyelitis?
- Focal cortical bone destruction
- Soft tissue inflammation