Marsupials/ hedgehogs/ skunks/ primates/ amphibia
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Marsupials:
Species (5)
Pouch/Marsupium and marsupial/epipubic bones (6)
GIT (4)
Dentition (3)
Torpor (5)
Sugar glider, opossums, kangaroos, wallabies, wallaroos
Abdominal pouch in females with four teats, holds 1-2 young, pouch skin infections and mastitis, have fully functional placent, young are born in embryonic state and develop outside of uterus in pouch attached to teat, bones serve as attachment surface for several muscles
Omnivorous, enlarged caecum for microbial fermentation, ends in cloaca (lower temp than body), variation dependent on diet
Diprotodonts (pair of large procumbent incisors on the lower jaw, variable size diastema, macropods koalas wombats and gliders), wombats have 1 pair of upper incisors and hypsodont teeth, Polyprotodonts (many incisors, opossums bandicoot)
A sate of decreased physiological activity often marked by reduced body temp and metabolic rate, 2 types: shallow dairy torpor (lasts 2-20hrs) or deep prolonged torpor (lasts 1-3 weeks), sugar gliders conserve energy by huddling in groups or going into a shallow shirt torpor, triggered by starvation and lack of forage and old and wet weather
Sugar gliders:
Patagium/ gliding membrane (3)
Eyes, ears, olfaction (4)
Androgen-sensitive scent glands (4)
Feet (3)
Cardiovascular (6)
Respiratory (2)
Repro (4, m4, f4)
Thin membrane between front and hind legs, wing-like extension which aids in gliding, careful handling and SC injection along dorsal midline of thorax
Nocturnal so widely spaces large protruding eyes, susceptible to ophthalmic trauma, thin mostly hairless relatively large independently moving ears, highly developed sense of smell
Frontal scent glands (males, forehead), Gular/sternal scent glands (males, ventral chest), Paracloacal scent glands (males and females), Pouch scent glands (females)
Opposable first digit on hind foot (clawless), syndactyly on second and thurs digits on hind foot (grooming claws, digits come together), longer digit four on front foot (get insects from crevices)
200-300bpm, blood collection 1% bodyweight, lateral saphenous vein, coccygeal vein, cephalic vein, jugular under GA
16-49bpm, variety of vocalisations which may impede thoracic auscultation
Seasonally polyoestrus, 15-17 day gestation, young in pouch for 70-74 days, weaned at 110-120 days, males (bifid/bificating penis with ruination at base before, pre-penile pendulous scrotum, large prostate, 2 pairs bulbourethral glands), females (2 uteri, 2 cervices, 2 long thin maternal vaginas that item to single coil-de-sac divided by septum 3 altogether, ureters run medically to lateral vaginas)
Macropods:
Species (4)
Skin (2)
Dentition (3)
Embryonic diapause in red kangaroos (3)
Kangaroos, wallabies, walaroos, quokkas
Thin skin (especially inner surface of limbs) with increased vascularity to aid thermoregulation
Molar progression, molars erupt causally and migrate forward throughout life, cheek teeth shed from front as worn and replaced by next tooth
Once joey attaches to teat mother immediately becomes pregnant again, presence of suckling young in pouch arrests development of new embryo, once joey leaves policy uterine embryo resumes development
Wombats (2)
Thicker in elastic skin
Hard sacral plate on rump used as defence mechanism and to compact burrow walls

Hedgehogs:
TPR (3)
Behaviours (3)
Integument (5)
Musculature (photos)
SC and IM injection sites (3) (5)
Vertebral formula and feet (3)
20-25 breathpm, 20l-289bpm, 33.5-36.8*C
Nocturnal/crepuscular, solitary, self anointing/anting (foamy saliva rubbed into spikes in response to nicer smell taste or texture)
Thin epidermis, thick fibrous dermis underlying spines, fat-filled subcutaneous layer beneath spines, keratin spines (defence mechanism and shock absorber), mantle (defence ball posture)
Spiny (longer to be absorbed) or furred (elastic and vascular) or junction between areas, orbicularis/ epaxial/ triceps/ quadriceps/ gluteal muscle
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cg13-15, European have 5 risen in each foot, African Pygmy have 5 on manus 4 on pes
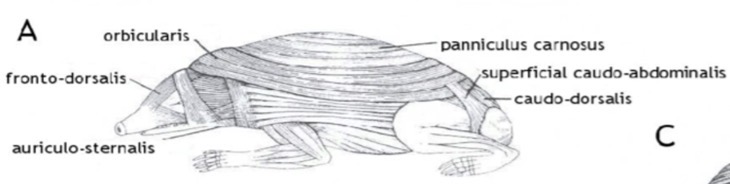
Hedgehogs:
Eyes, ears, olfaction (6)
GIT (7)
Dentition (4)
Eyes not well developed monochromatic prominent eyes with shallow orbit, sensitive hearing in ultrasonic range, highly developed sense of smell and prominent Jacobson/ vomeronasal organ
Predominantly insectivorous, opportunistic omnivorous, simple stomach, no caecum, smooth colon, vomit reflex, transit time 12-16hrs
Variation common, brachydont teeth, 36 teeth, I 3/2 C1/1 PM 3/2 M 3/3
Hedgehogs:
Cardiovascular (5)
Respiratory (3)
Hibernation (5)
Repro (8, m5, f6)
180-280bpm, veins collapse easily, lateral saphenous vein, cephalic vein, large vol from femoral vein or jugular under GA
25-59bpm, endotracheal intubation difficult as long soft palate and large tonsils, variety of vocalisation
Reduce energy needs and survive when food scarce, reduction in (overall metabolic rate, body temp, oxygen consumption, HR, RR), white fat provided long term energy supply, brown fat for thermoregulation, in European when temp below 6*C
Polyoestrous, gestation 34-37 days, delayed implantation can occur, 1-7 hogs per litter, spines already within hours for birth, infanticide and cannibalism, weaned 4-6 weeks, 5 pairs of teats (Eur) and 2-5 pairs (APH) in both sexes, males (long anogenital distance, testicles in para-anal recess, penis protrudes laterally into horn like structures, no defines scrotal sac, paired prostate gland/ seminal vesicles/ bulbourethral glands), females (short anogenital distance, bicornuate uterus, no uterine body, single cervix, long vagina, urethral opening in distal vagina)
Skunks (6)
Omnivores
Simulate stomach, no caecum
Winter dormancy in wild
Dental formulae I3/3 C1/1 PM3/3 M1/2 with flattened molars
Induced ovulators and os penis
Blood from jugular, cephalic, femoral veins
Primates:
Overview (4)
MSK (4)
Adaptations (8)
Repro (3)
Heterodont dentition, simple stomach elongated small intestines and variable caecum, complex cognitive abilities, extended parental care and prolonged development periods
Short snout and forward facing orbits, flexible s shaped spine, short broad pelvis, clavicles
Quadrupedalism, bipedalism, leaping, brachiation/ arm swinging, arboreal species/ hand and feet for grasping, binocular vision from forward facing eyes, highly developed facial muscles, well developed sensory systems with reliance on vision
Internal fertilisation, 2 nipples with pectoral mammary glands, long gestation periods
Amphibia (6)
Ectothermic
Immature larval/tadpole stage (gills, aquatic lifestyle)
Mature adult stage (lungs, terrestrial lifestyle)
Unscaled mucous skin
Some dermal resp
Primary nitrogenous waste as urea uric acid or ammonia depending on how aquatic the environment is (water dilutes)