Double stranded break repair and homologous recombination
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
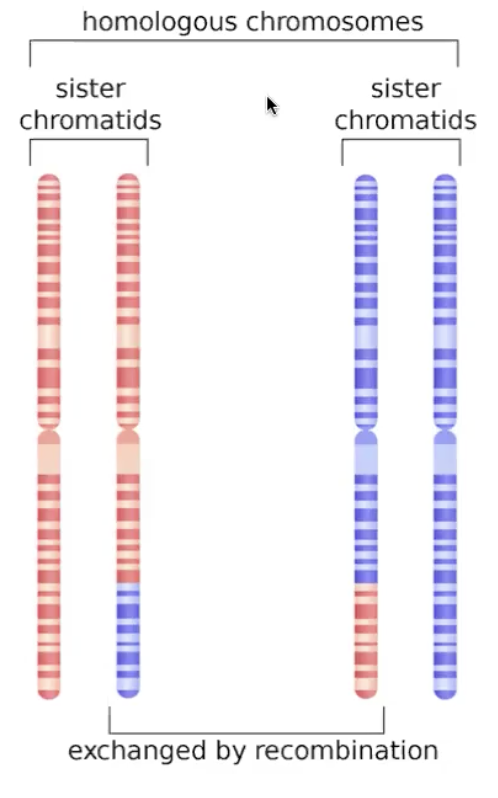
homologous chromosomes
similar
chromosome pair one from each parent
homologous recombination and homology directed repair involve
sequences that have high sequence identity (similarity)
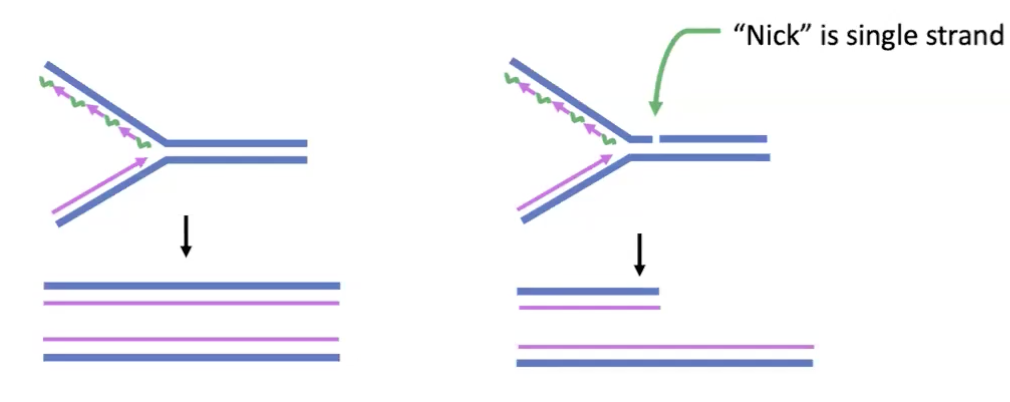
DNA double stranded breaks often results from
replication of template containing a nick
chemicals can make nicks
ionizing radiation such as X-rays can directly break dsDNA
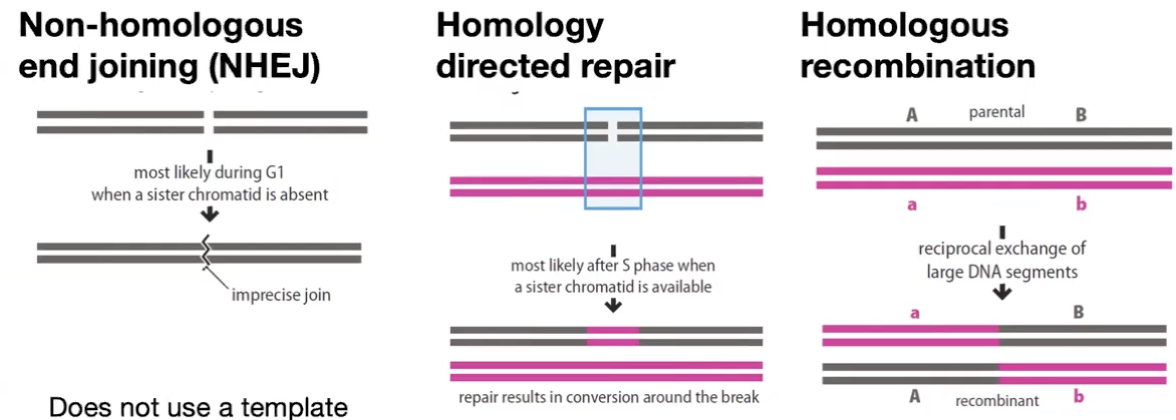
DS break repair types
-NHEJ Non-homologous end joining (rejoin ends w/o template)
-homology directed repair (use homologous DNA as template when sister chromatid is available)
-homologous recombination (mediates recombination crossing over of chromosomes in meiosis)
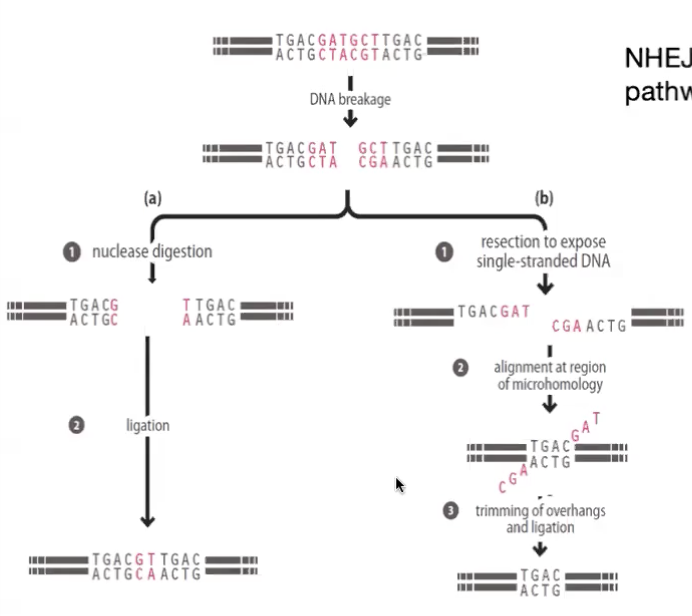
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
only available pathway in G1 phase, error prone aka mutagenic
occurs by simple ligation of ends
or
remove a few nucleotides to make overhangs to pair, loose some info
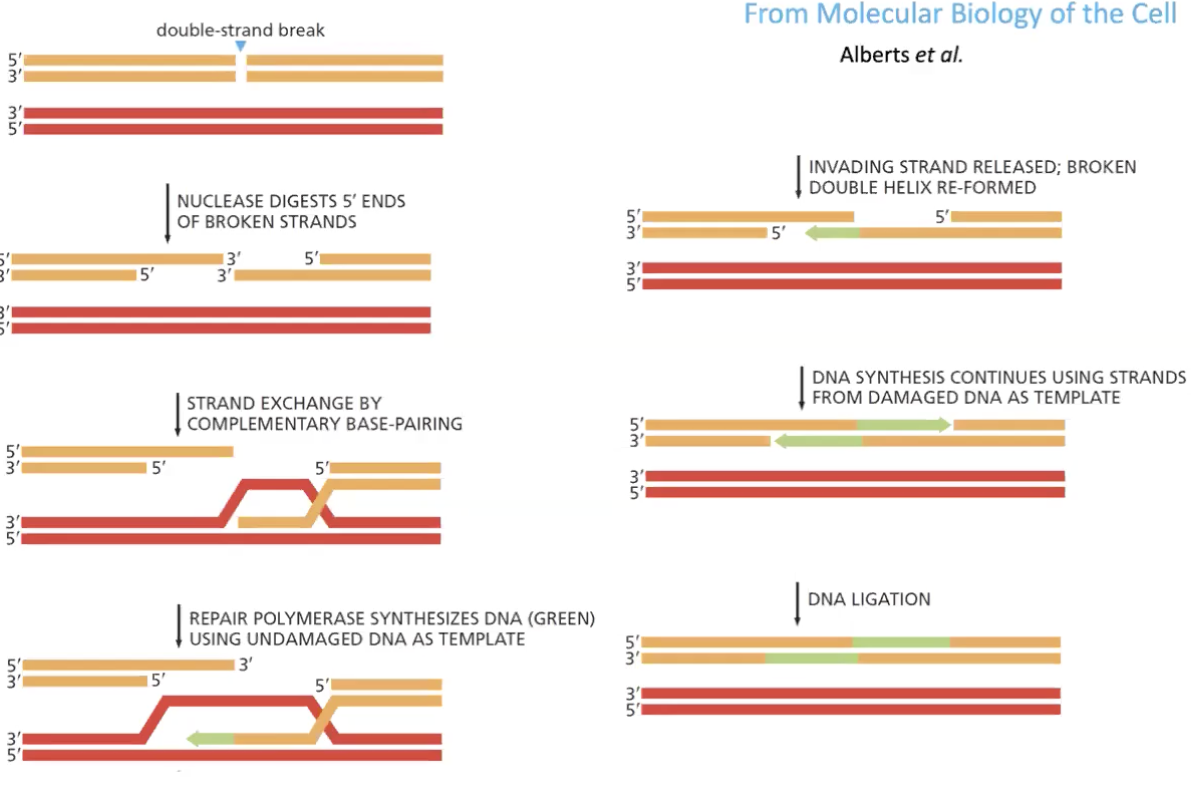
Homology-directed repair
begins with DNA resection to generate 3’ overhangs which find homology
creates d-loop in image 3
homologous recombination can result in
crossover or non crossover
starts with D-loop
DNA cut at junctions
double Holliday junction formed and cleaved
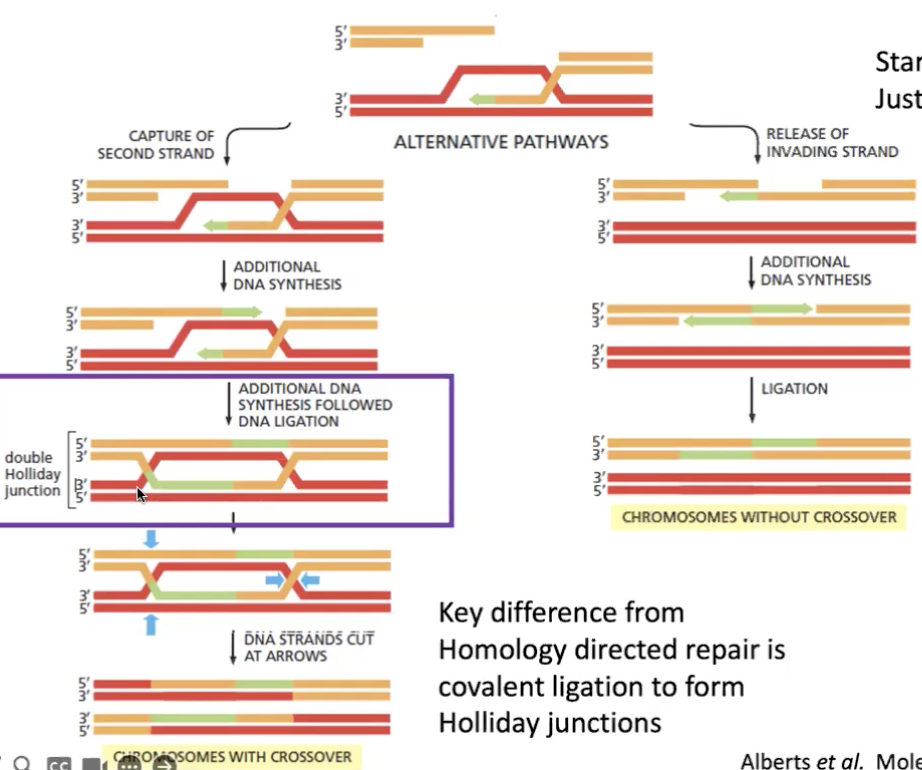
homologous recombination involves?
formation and cleavage of Holliday Junctions
can cut two ways
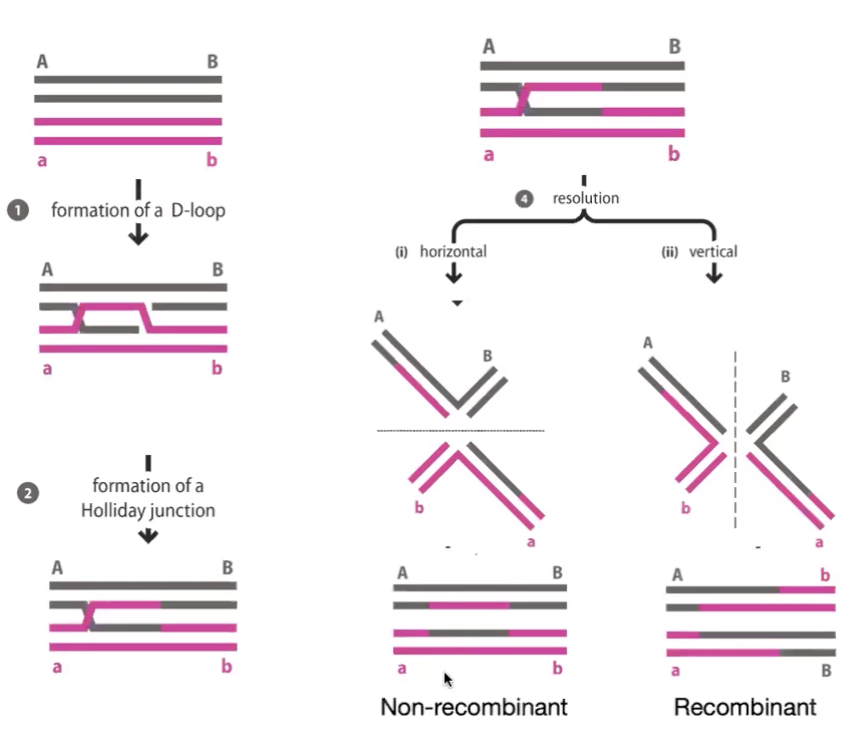
When homology directed repair uses homologous chromosome as a template what can happen?
gene conversion
when sister chromosomes are not available
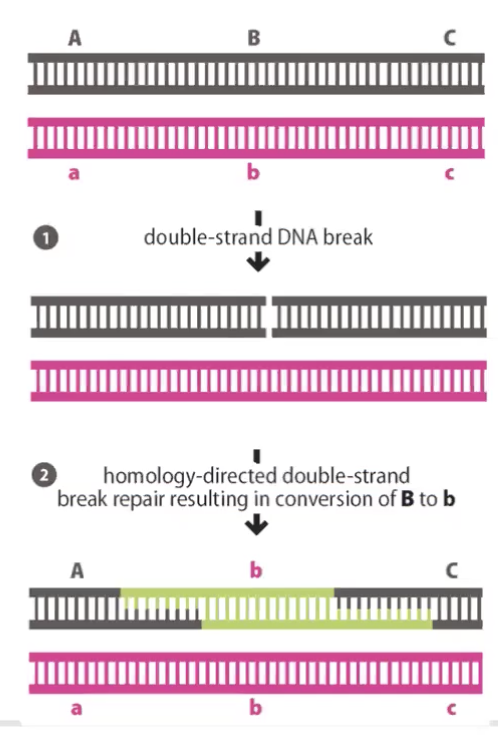
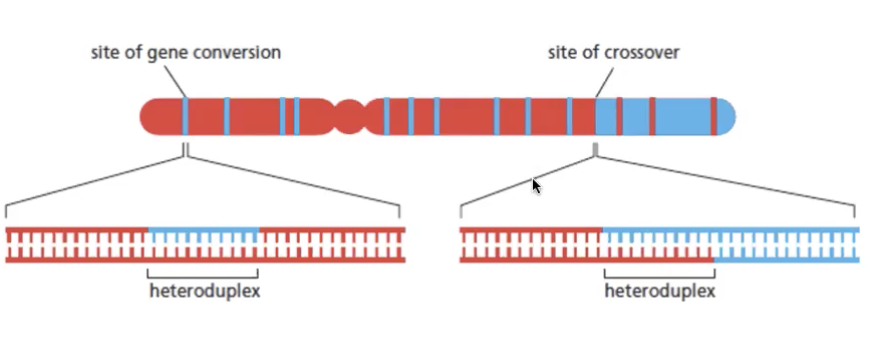
heteroduplexes
formed during recombination
can lead to gene conversion
have some bp mismatches
repaired o replicated to generate mother or father sequence
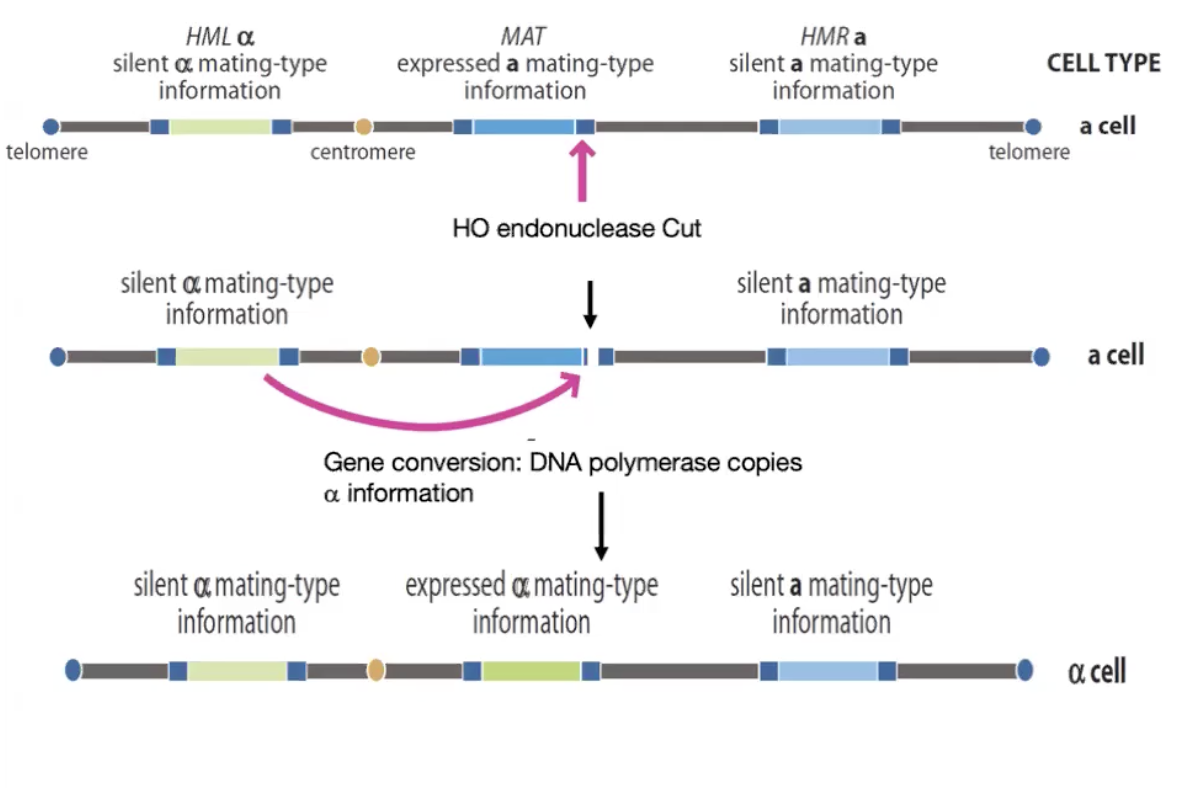
In yeast regulated gene conversion mediates
mating type determination
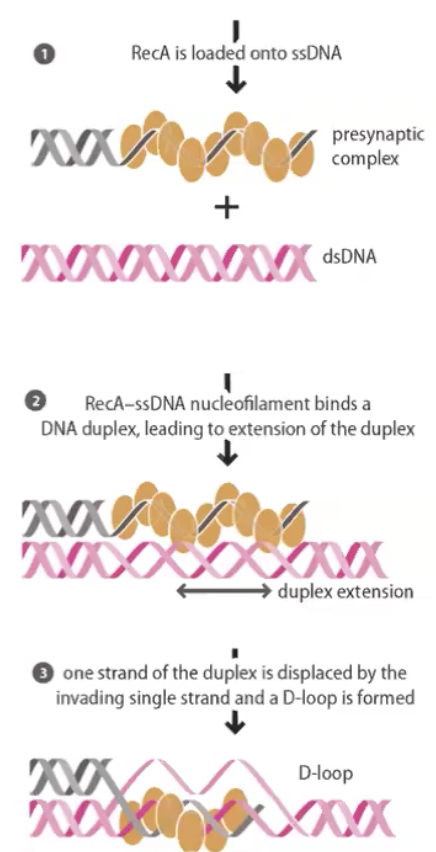
RecA and Rad1
RecA (bacteria) and Rad51 (eukaryotes) are critical for homologous-directed repair and homologous recombination
loaded on single stranded DNA to help pairing and forming D-loop
in vivo also need BRCA1 and BRCA2
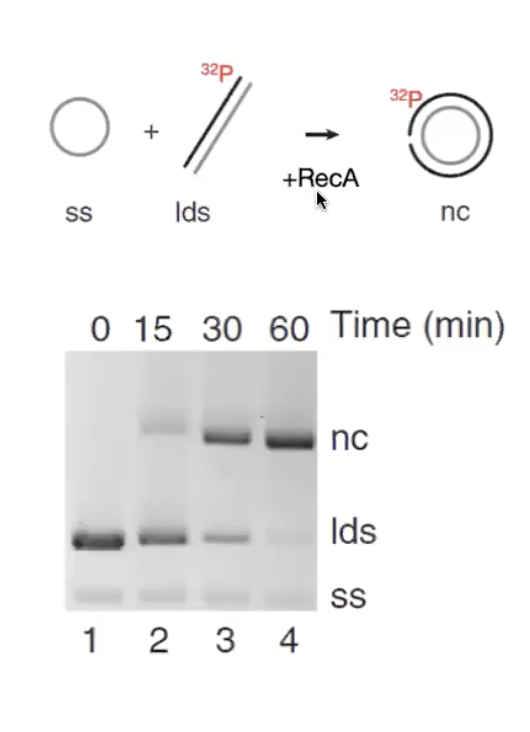
Strand exchange assay
same sequence single strand circular and linear double strand put together with Rec A and over time nicked circle accumulates
shows strand displacement activity in RecA
mitotic recombination leads to
genetic exchange between similar DNA sequences
usually in meiosis
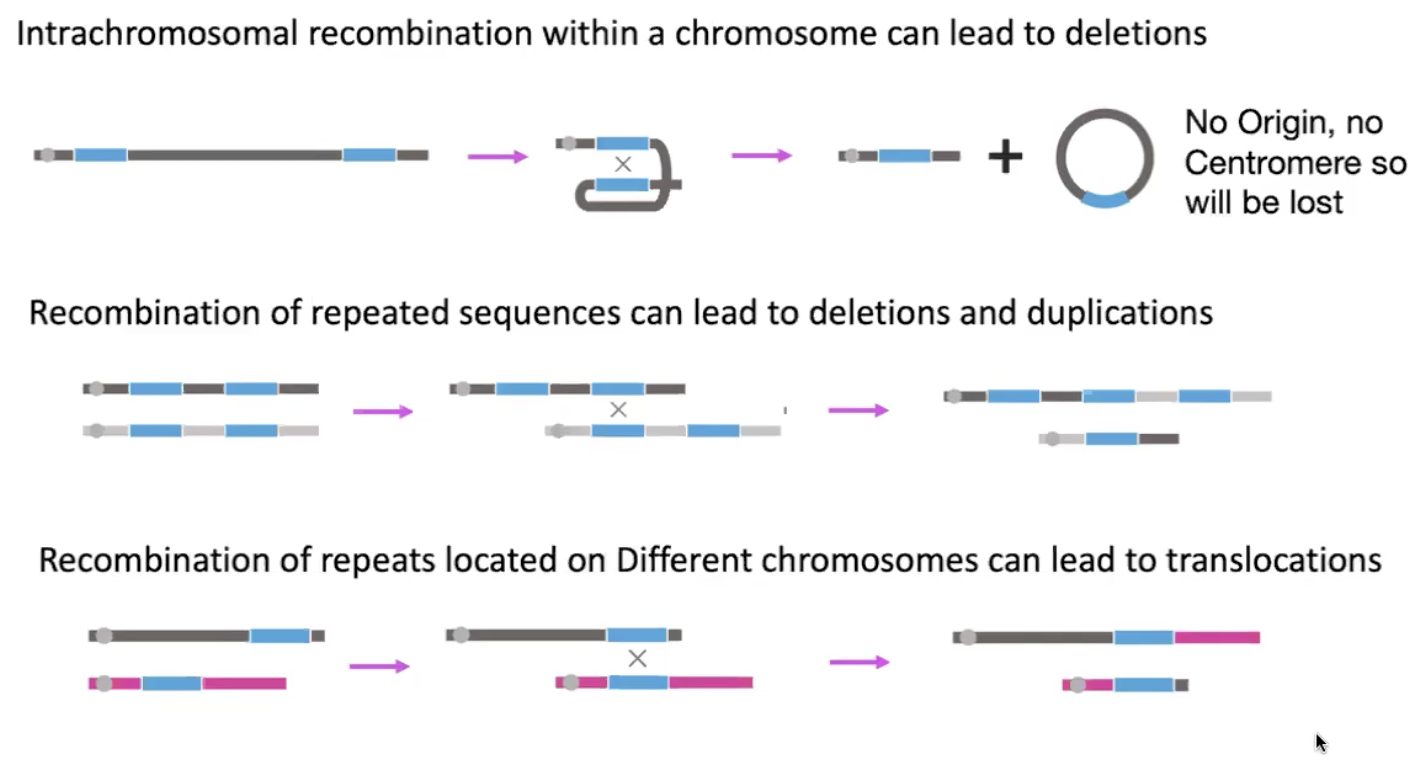
mitotic recombination between repeated sequences leads to
genome rearrangements
intrachromosomal recombination → deletions
repeated sequences → duplications and deletion
repeats on diff chromosomes can lead to translocations
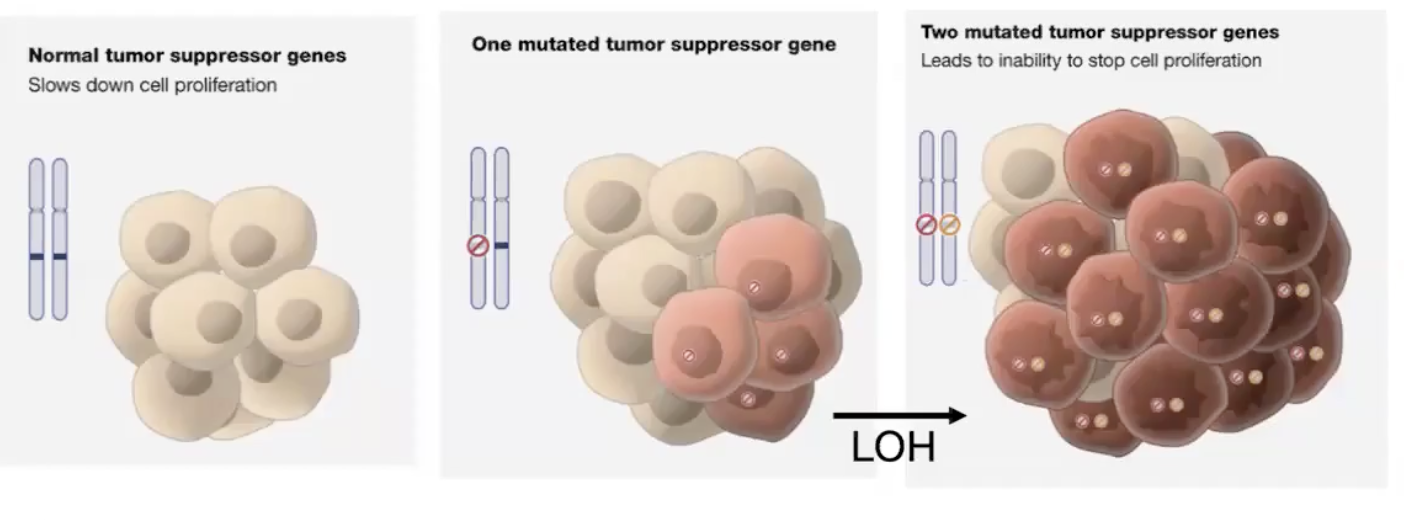
Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of tumor suppressor genes allows
growth of cancer, major driver of cancer
loosing checkpoint genes and DNA repair genes
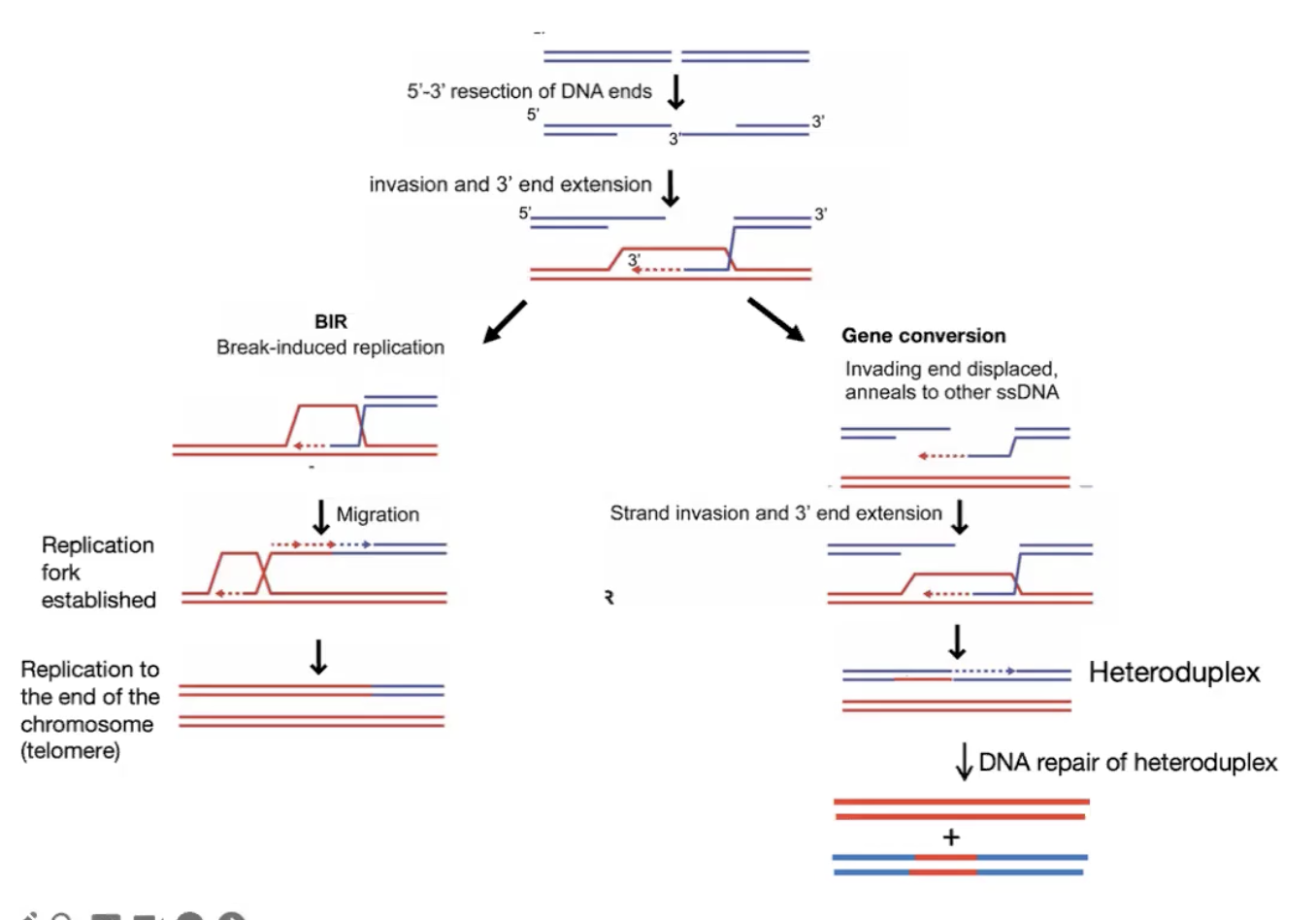
LOH can result from
repair of ds break through gene conversion or Break Induced Replication (BIR)
or mitotic recombination in diploids
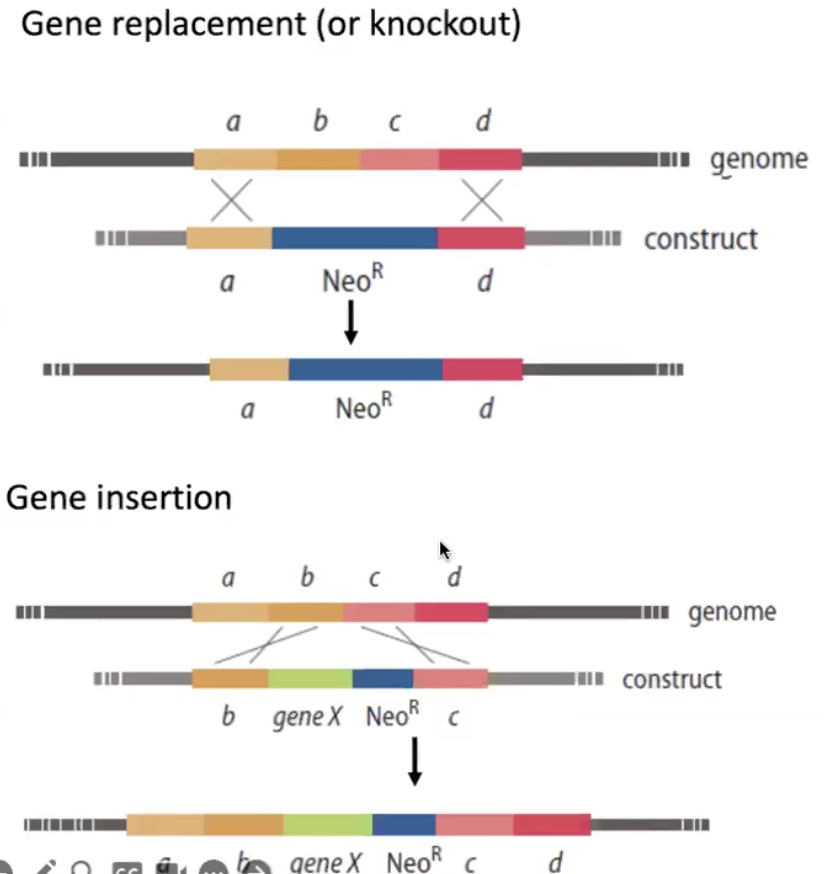
homologous recombination can be used to
knock out or alter specific genes