5.2.3 Redox & Electrode Potentials
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is oxidation in terms of electron transfer?
Loss of electrons
What is reduction in terms of electron transfer?
Gain of electrons
What is a redox reaction?
Reaction where both oxidation and reduction occurs
What is an oxidising agent?
Substance that is reduced, taking electrons from another species
What is a reducing agent?
Substance that is oxidised, giving electrons to another species
What does a half equation show?
Oxidation or reduction - shows electrons being lost or gained
How do you work out a half equation in acidic conditions?
•Balance element that changes oxidation state and any other non-H or O elements
•Work out oxidation states of element that is changing oxidation state
•Add electrons to balance oxidation states
•Add H⁺ to balance charges
•Balance atoms with H₂O
•Check that atoms and charges are balanced
How do you work out a half equation in alkaline conditions?
•Balance element that changes oxidation state and any other non-H or O elements
•Work out oxidation states of element that is changing oxidation state
•Add electrons to balance oxidation states
•Add OH⁻ to balance charges
•Balance atoms with H₂O
•Check that atoms and charges are balanced
How do you combine two half equations?
•Multiply up half equations to ensure that electrons are balanced
•Add them together
•Cancel any species that are on both sides until they only occur on one side of the equation
How do you balance a redox equation using oxidation numbers?
•Balance elements whose oxidation numbers are changing and any non-H and O elements
•Assign oxidation numbers to elements whose oxidation numbers are changing
•Identify electron transfer between elements
•Balance electron transfer
•Check atoms are balanced
How would you carry out a manganate (VII) titration?
1. Standard solution of KMnO₄ added to burette
2. Add measured volume of solution being analysed and excess of dilute sulfuric acid to conical flask
3. Add manganate (VII) solution until end point reached - colour change from colourless to pale pink
4. Repeat until concordant results reached
What is the role of manganate (VII)?
Oxidising agent
What is the half equation for manganate (VII) to manganese (II) ions?
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O
What is the half equation for iron (II) ions to iron (III) ions?
Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺ + e⁻
What is the overall equation in a manganate(VII)/iron titration?
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5Fe²⁺ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O + 5Fe³⁺
How do you read the meniscus in a manganate (VII) titration?
From the top due to deep purple colour
What is the end point for a manganate (VII) titration?
Colour change from colourless to pale pink
How would you carry out an iodine/thiosulfate titration?
1. Standard solution of Na₂S₂O₃ to burette
2. Add solution of oxidising agent to be analysed and excess of potassium iodide to conical flask. This forms a yellow-brown colour
3. Titrate solution with Na₂S₂O₃. As end point is reached/when colour faded to a pale straw colour, add starch indicator. Solution goes blue-black
4. Add Na₂S₂O₃ until end point reached
5. Repeat until concordant results are reached
What is the end point for an iodine/thiosulfate titration?
When blue/black colour disappears
What is the half equation for iodine to iodide ions?
I₂ + 2e⁻ → 2I⁻
What is the role of thiosulfate?
Reducing agent
What is the half equation for thiosulfate to tetrathionate?
2S₂O₃²⁻ → S₄O₆²⁻ + 2e⁻
What is the overall equation in an iodine/thiosulfate titration?
2S₂O₃²⁻+ I₂ → 2I⁻ + S₄O₆²⁻
What is the role of iodine?
Oxidising agent
How do you calculate numbers of moles of analyte?
•Find moles of a substance provided
•Use stoichiometric ratios to find moles of analyte
What is standard electrode potential?
The e.m.f. of a half cell compared to the standard hydrogen half cell, measured at 298K with solution concentrations of 1 moldm⁻³ and a gas pressure of 1 atmosphere
What is standard electrode potential a measure of?
Tendency of a species to gain electrons
What does a half cell contain?
All of the chemical species present in a redox half equation
What is a voltaic cell?
Converts chemical energy into electrical energy
How are half equations normally written?
Show reduction - electrons are on the left
How can you create a voltaic cell from half cells?
Connect together two different half cells - chemicals in the two half cells must be kept apart
What are two ways of making half cells?
•Metals or non-metals in contact with their ions in aqueous solution
•Ions of the same element in different oxidations states in contact with a Pt electrode
How do you draw a half cell if one of the species is a gas?
Tube with gas being pumped towards a platinum electrode
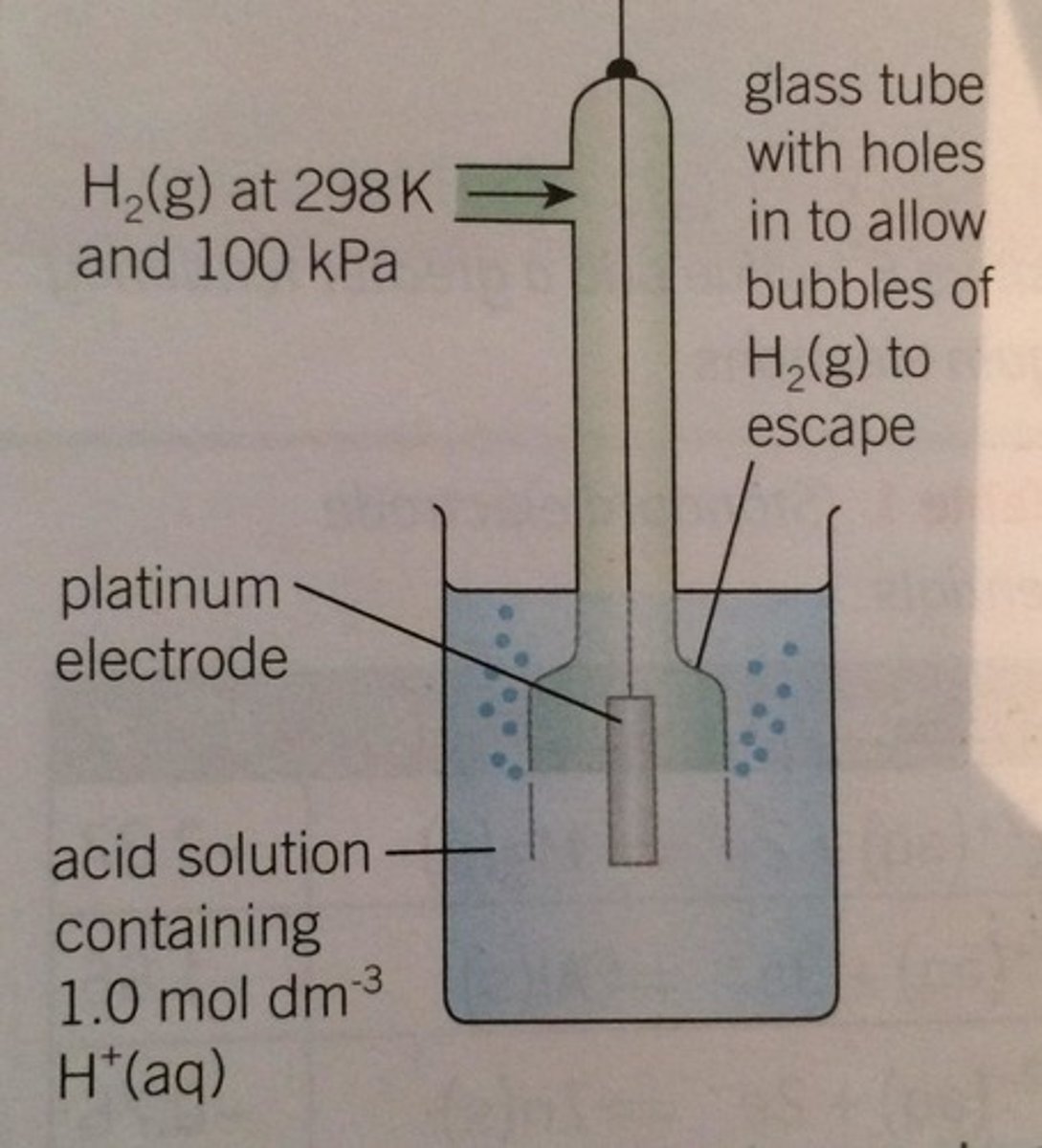
What is the electrode potential of a standard hydrogen half cell?
0 V
How do you draw two half cells connected?
•Electrodes joined by a wire with a voltmeter
•Solutions connected by a salt bridge which allows ions to flow
What is the negative electrode?
Where electrons are being lost
What is the positive electrode?
Where electrons are being gained
How does electricity flow through the wire?
From the negative electrode to the positive electrode
How do you calculate the cell potential of a voltaic cell?
Subtract less positive electrode potential from more positive electrode potential (if both half equations are written as reduction processes)
What is the condition for whether a redox reaction is feasible or not?
•One half equation must be reduction and the other must be oxidation
•Cell potential must be more than 0V
What are the limitations of using standard electrode potentials to predict feasibility of a redox reaction?
•Reaction rate may be slow due to high activation energy
•Conditions may be different such as concentration and temperature
•In reality redox reactions are only feasible if cell potential is more than +0.4V
What are the the three main types of cells?
•Primary
•Secondary
•Fuel
What is a primary cell?
•Non-rechargeable - designed to be used once only
•Redox reaction cannot be reversed
What is a secondary cell?
•Rechargeable
•Cell reactions producing electrical energy can be reversed during recharging - chemicals in cell are regenerated
How do fuel cells work?
They use the energy from the reaction of a fuel with oxygen to create a voltage