MCAT Essential Equations
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
linear motion
v = v0 + at
linear motion (terms of x/distance)
x = v0t + (at2)/2
linear motion (change in distance,time,velocity)
∆x = ∆t • 1/2(vi+vf)
y-component of force
Fg = mgsin𝜃
x-component of force
Fg = mgcosθ
parallel force on an incline
∥Fg = mgsin𝜃 (sin is sliding down)
perpendicular force on an incline
⟂Fg = mgcos𝜃
force between two objects
F=G(m1m2)/r2
center of mass
x = (m1x1 + m2x2 +… ) / (m1 + m2 + … )
kinetic energy
KE = 1/2mv2
average molecular speeds
K=1/2mv2=3/2KbT
elastic potential energy
U = 1/2kx2
efficiency
work out/work in
Efficiency
(load x load distance)/(effort x effort distance)
centripital force (Fc)
F = (mv2)/r
specific gravity
ρ(object)/ρ(water)
absolute pressure
P = Po + pgz
P(gauge) = P(absolute) - P(atm)
Archimedes' Principle
F(buoy) = ρ(fluid)V(fluid displaced)g = ρ(fluid)V(submerged)g
Bernoulli's Equation
P1+ ρgh1+ 1/2ρv12 = P2+ ρgh2+ 1/2ρv22
Poiseuille's equation
Q = (π)r4ΔP/8ηL
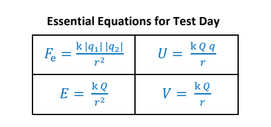
Electric field
E = kQ/r2 [N/C]
Left to Right: multiply by “r”; Top to Bottom: divide by “q”
magnetic field in a straight wire
B = uI/2(π)r [T]
F = ILBsinθ [T = 1Ns/Cm]
C = Q/V [Farad]
intensity of sound wave
I = Power/Area
Magnification
m = -di/do = hi/ho
total magnification
m1 x m2 x m3
Snell's Law
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
Energies of photons and frequencies (Rydberg Formula)
E = hf
c = fλ (light) OR v=fλ
% Yield
actual/theoretical x 100%
% Error
| actual - theoretical / actual | x 100%
Centripetal Acceleration
ac = v2/r
Michaelis-Menten Equation
V0 = Vmax x [S] / Km+[S]
Catalytic Efficiency
Kcat/Km
osmotic pressure
π =iMRT
Arrhenius Equation
k = A*e(Ea/RT)
Gibbs Free Energy (standard conditions)
ΔG˚ = −RT ln (Keq)
Potential Energy of a Capacitor
Ucap = 1/2CV2