Unit Two: Cell Structure and Function- essential knowledge
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What do ribosomes do
comprise ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and synthesize proteins based on mRNA sequences
Where are ribosomes found and what does this indicate
all forms of life reflecting common ancestry
How does the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) appear and what are its general functions
rough (membrane-bound ribosomes)- compartmentalizes cell
smooth- detoxification and lipid synthesis
How does the Golgi complex appear and what is its general function
flattened membrane sacs- folding of polypeptide chains and protein trafficking
What is the structure of mitochondria
double membraned (outer smooth, inner convoluted with folds)
What are lysosomes
membrane-enclosed sacs with hydrolytic enzymes
What are vacuole
membrane-bound sac with varying roles
What is the structure of chloroplasts and their functions
double outer membrane, used for photosynthesis processes
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do
provide mechanical support, carries out protein synthesis on, and intracellular transport
What does the mitochondrial double membrane do
provides compartments for different metabolic reactions
What do lysosomes do
with hydrolytic enzymes; intracellular digestion, recycling of organic matter, and apoptosis
What do vacuoles do
storage and release of macromolecules and cellular waste, water retention
Why does the inner cellular membrane fold
increases surface area allows more ATP synthesized
How are the thylakoids organized
into stacks called grana
What within chloroplast allows for energy usage
thylakoids and stroma
Where and what is the stroma
fluid within the inner chloroplast membrane and outside the thylakoid
Where does the Calvin-Benson cycle occur and what does it do
occurs in the stroma for photosynthesis
Where does the Kerbs Cycle occur and what does it do?
occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria for the citric acid cycle
Where does electron transport and ATP synthesis occur
occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
What do surface area-to-volume ratios affect
ability of biological systems to obtain necessary resources, eliminate waste products, acquire or dissipate thermal energy, and exchange chemicals and energy with the environment
Equation for the volume of a sphere
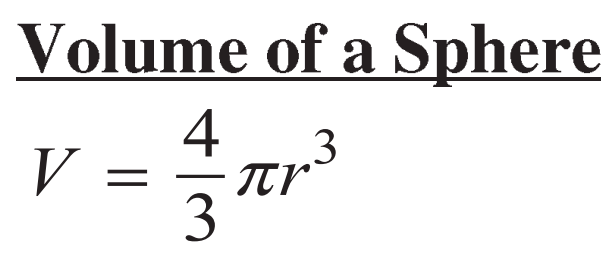
Equation for the volume of a cube
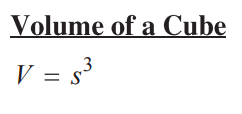
Equation for the volume of a rectangular solid

Equation for the volume of a cylinder
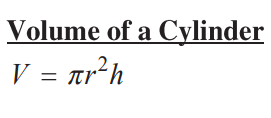
Equation for the surface area of a sphere
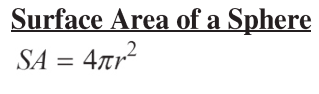
Equation for the surface area of a cube

Equation for the surface area of a rectangular solid
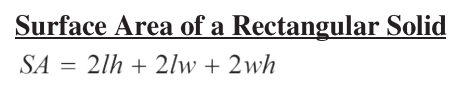
Equations for the surface area of a cylinder
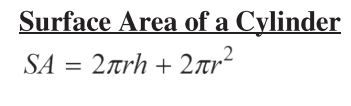
What is true about smaller cells
surface area-to-volume ratio is high with effective exchange of materials with the environment
What happens with volume increases
surface area decreases, demand for internal resources increases, and environment-cell exchange decreases
What is necessary for cell structures to exchange materials
complex structures (i.e membrane folds)
What two regions does a phospholipid have and what are their orientation
hydrophilic- toward aqueous external/internal environment
hydrophobic- toward each other within inner membrane
What can proteins be
hydrophilic- charged, polar side groups
hydrophobic- non-polar side groups
What do cell membranes contain
phospholipids, proteins, steroids, glycoproteins, glycolpids
What does the cell membrane structure result in as described by what model
selective permeability, fluid mosaic model
What do cell membranes do
separate internal and external environments
What can pass through the membrane freely
N2, O2, and CO2
What can pass through the membrane with embedded channels and transport proteins
hydrophilic substances, large polar molecules, and ions
How does H2O pass through the membrane
in small amounts
What do cell walls provided
structural boundaries and permeability barrier
What are cell walls composed of
complex carbohdrates
What does active transport require and what does it does passive transport do
import of materials and waste export
What does active transport require and what does it do
direct energy input for the movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentrations
What does selective permeability allow for
formation of concentration gradients of solutes across the membrane
What do the endocytosis and exocytosis process require
energy
What is the exocytosis process
internal vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and secrete large macromolecule out of the cell
What is the endocytosis process
cell takes in macromolecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles
Where does large water quantities pass through
aquaporins
Where do charged ions (i.e Na+ and K+) pass through
through membrane with channel proteins
How does water move
with osmosis from areas of high water potential/low osmolarity/low solute to areas of low water potential/high osmolarity/high solute
Equation for the water potential

how is growth and homeostasis maintained
constant movement of molecules across membranes
What does osmoregulation do
maintain water balance and allow organisms to control their internal solute composition/water potential
Equation for the solute potential of a solutions

What do membranes and membrane-bound organelles do in eukaryotic cells
compartmentalize intracellular metabolic processes and specific enzymatic reactions
How do internal membranes facilitate cellular processes
minimizing competing interactions and increasing surface area in reaction areas
Where did membrane-bound organelles evolve from
free-living prokaryotic cells via endosymbiosis