Anatomy of Renal system
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Function of urinary system
Filter blood, form urine & excretion of waste products
Regulate water, electrolyte & acid base balance
Produce some hormone & participate in metabolism of others
Rest; estimated 20% of cardiac output (~1000ml/min) flows through kidney where it's filtered & reconditioned
Kidney anatomical position
Lie on posterior abdominal wall, one on each side of vertebral column, behind peritoneum & below diaphragm
Located retroperitoneal of abdominal cavity
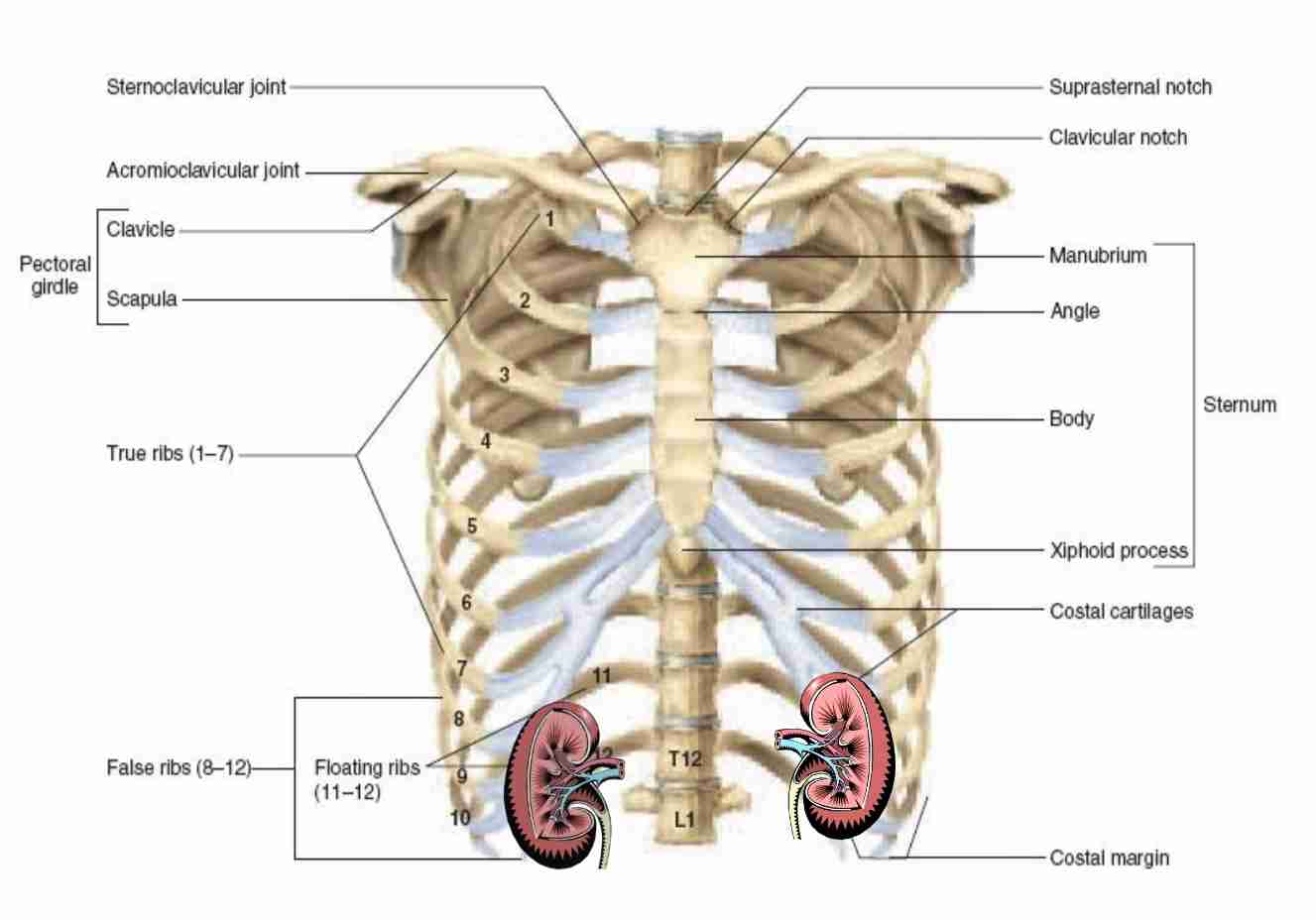
Partially protected by 11&12 pairs of rib
Right is slightly lower than left kidney (space occupied by liver)
Kidney gross anatomy
Shaped: bean-shaped, with medial concavity & lateral convecity
Weight: male,150-200g & female 120-135g
Size Adult: (12 × 6 × 2.5)cm long x wide x width
Near concave border is deep fissure called renal hilus
Blood vessel, lymphatic vessel & nerve enter & exit kidney through hilus
Kidney function
Urine formation by filtration & selective reabsorption processes
Receives 1.2 liter/min of blood
Anatomical position of Ureter
Starts at renal pelvis, located at hilum of kidney.
Runs down retroperitoneum, anterior to psoas major muscle & crosses under gonadal vein
Ureter then curves laterally into pelvis, crosses iliac vessels & enter base of bladder
Gross anatomy of Ureter
Length: muscular tube; 25-30 cm long & 0.3 cm wide in adults
Shape: S-shaped; travel from kidney to bladder
Segments: 3 segments - proximal, distal & intramural
Function of Ureter
Propel urine from kidney into bladder by peristaltic contraction of smooth muscle layer
Intrinsic property of smooth muscle & not under autonomic nerve control
Waves of contraction originate in pacemaker in minor calcyes
Peristaltic waves occur several times per minute, increasing in frequency with volume of urine produced & send little spurts of urine in bladder
Anatomical position of Urinary Bladder
Located in the pelvis, behind the pubic bones, and extends into the abdomen when full.
Located in the lower abdomen and pelvic cavity, and its position changes depending on how full it is
When empty: The bladder is in the lesser pelvis.
When full: The bladder extends into the abdominal cavity.
In children: The bladder is in the abdomen until puberty.
Gross anatomy of Urinary Bladder
Urinary bladder is a sac that stores urine before it's expelled through the urethra.
Apex or dome: The top-front part of the bladder that points toward the abdominal wall
Body: The large area between the apex and the fundus
Fundus or base: The bottom-back part of the bladder
Neck: The narrow group of muscles that connect to the urethra
Function of Urinary Bladder
Stores & release urine
Anatomical position of Urethra
In the pelvic region of the body that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The anatomical position of the urethra varies between males and females:
Female: about 4 cm long and starts at the bladder neck. It passes through the pelvic floor muscles and opens into the vestibule, the area between the labia minora. The urethral opening is in front of the vaginal opening and behind the clitoris.
Male: includes the prostatic urethra, which passes through the prostate gland. The prostatic urethra is surrounded by smooth muscle and is most commonly affected by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Gross anatomy of Urethra
Tube in the pelvic region that carries urine out of the body. It has several anatomical features, including:
Layers: three coats: a muscular layer, an erectile layer, and a mucous layer. The muscular layer is a continuation of the bladder's muscular layer.
Sphincters: 2 sphincters, or muscles that act as valves to open and close:
External xternal urethral sphincter: Located in the pelvic floor
Internal urethral sphincter: Located at the point where the urethra leaves the bladder.
Lining: varies by segment, but it's made up of epithelial tissue, smooth muscle cells, and connective tissue:
Prostatic urethra: Lined with transitional cell epithelium (urothelium)
Membranous urethra: Lined with stratified columnar and pseudostratified epithelium
Penile urethra: Lined with stratified columnar and pseudostratified epithelium, with stratified squamous epithelium distally
Glands: small mucus-secreting glands, as well as bulbo-urethral glands of Cowper, that secrete mucous to lubricate the urethra
Vascular submucosa: membranous urethra has a rich vascular submucosa that provides urethral occlusive pressure
Function of Urethra
Allows urine to pass out of the body and has other functions depending on the sex of the person:
Urination: The urethra allows urine to exit the body after the brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten and the sphincter muscles to relax.
Sperm and semen release: In males, the urethra is also used to release sperm and semen.