Chapter 2: Structure of the Atom
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the three fundamental components of the atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What charges are associated with protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons=Positive, Neutrons=Neutral, Electrons=Negative
Where are the components of an atom found?
Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus, while the electrons orbit around it
If an atom has _____ number of protons and electrons, it would have no ___ ______ making it electrically neutral.
equal, net charge
If an atom has an overall positive charge it is called a ________ ___
positive ion
If an atom has an overall negative charge it is called a ________ ___
negative ion
_______ ______ is a strong nuclear force that holds the nucleus together as well as the electrons in their orbit
Binding energy
What does the atomic number represent?
The number of protons it contains in its nucleus
What does the atomic mass represent?
The number of protons and neutrons it has in its nucleus
An _______ represents an element with the same number of protons but different number of _______, which would affect the ______ ____.
Isotope, neutrons, atomic mass
Changing the number of protons changes the....
atomic number
Changing the number of neutrons changes the ______ ____ and it is then called an _______
atomic mass, isotope
Changing the number of electrons produces an ____, either positive or negative
ion
When two or more atoms join together chemically it forms a ________
molecule
The two primary ways that atoms bond to form molecules are a _____ bond or a ________ bond
ionic, covalent
Ionic bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
Polyenergetic
consisting of a spectrum of different energies
Electron shells
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
Hydrogen
H 1
Iron
Fe 26
Nickel
Ni 28
Copper
Cu 29
Calcium
Ca 20
Carbon
C 6
Nitrogen
N 7
Oxygen
O 8
Molybdenum
Mo 42
Rhodium
Rh 45
Silver
Ag 47
Tin
Sn 50
Iodine
I 53
Barium
Ba 56
Tungstun
W 74
Rhenium
Re 75
Gold
Au 79
Lead
Pb 82
Thorium
Th 90
Mendelevium
Md 101
Columns on a periodic table have the same number of...
Valence electrons
Rows (periods) of the periodic table
Have the same number of orbital shells
Periodic table invented by...
Dimitri Mendeleev, 1869
Formula to tell maximum number of electrons a specific shell can hold?
2(n)^2, n being the shell's number
Principle quantum number indicates _____?
The amount of energy an electron has
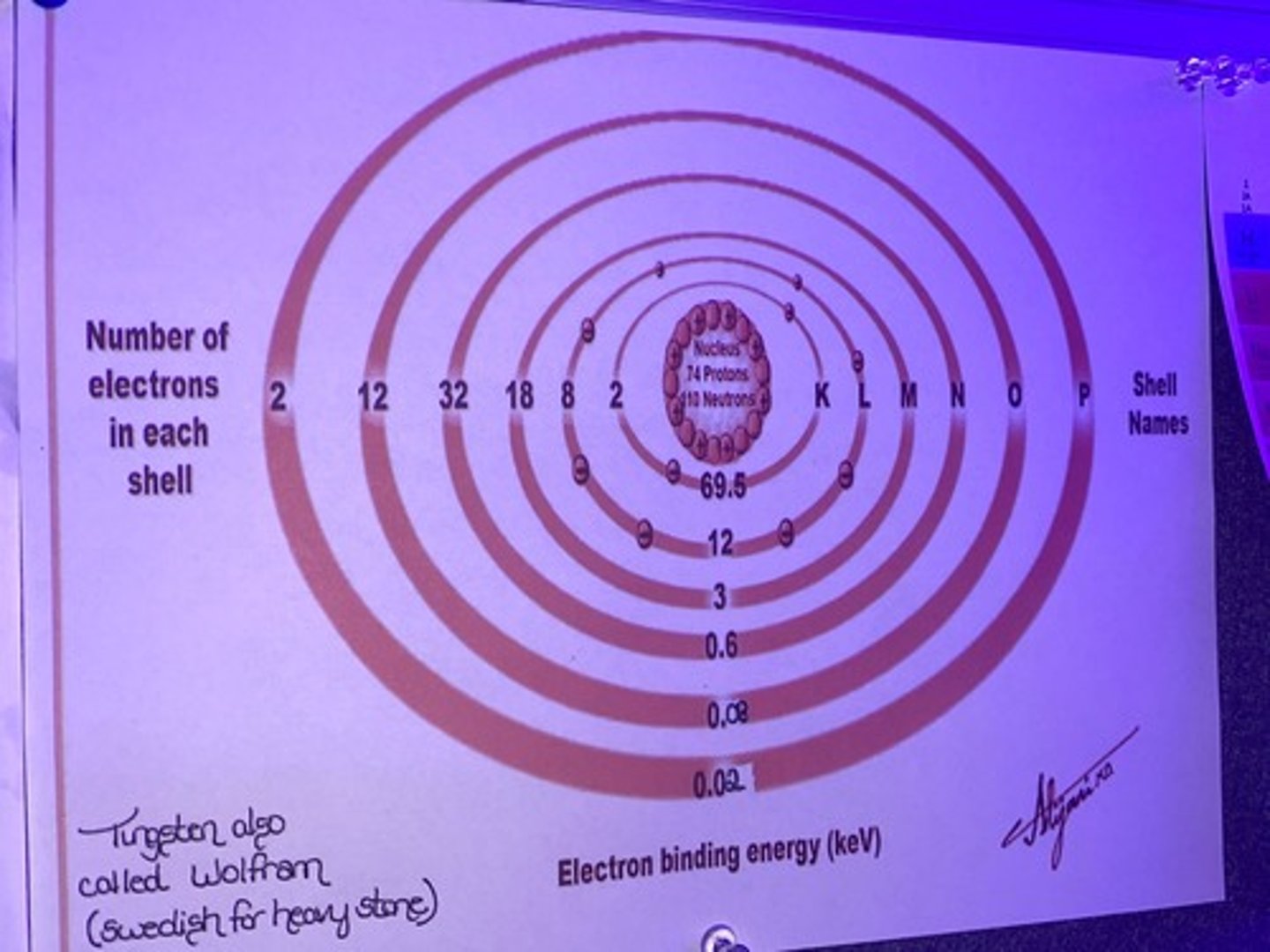
Describe the Tungsten Target
Six shells, labeled K-P.
From in to outer, the number of electrons goes from 2, 8, 18, 32, 12, then 2
Diagnostic range
30-150 kVp
kVp
kilovoltage peak