anatomy & physiology muscles
0.0(0)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:40 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
muscle tissue
muscle cells specialized for contraction
2
New cards
skeletal muscle
organ made of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels
3
New cards
skeletal muscle functions
1. produce body movement
2. maintain posture
3. support soft tissues
4. guard body entrances/exits
5. maintain body temp
6. store nutrients
4
New cards
skeletal muscle tissue
produce movement by pulling on bone
* voluntary
* voluntary
5
New cards
cardiac muscle tissue
pumps blood and circulates it in vessels
* involuntary
* involuntary
6
New cards
smooth muscle tissue
walls of hollow organs and small arteries
* involuntary
* involuntary
7
New cards
epimysium
dense sheath of collagen fibers around muscle that separates muscle from other tissues/organs
8
New cards
muscle fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
9
New cards
perimysium
fibrous layer dividing muscle into fascicles
10
New cards
skeletal muscle fibers
individual muscle cells
11
New cards
myofibrls
bundles of protein filaments
12
New cards
endomysium
thin layer of areolar connective tissue around each muscle fiber
13
New cards
myosatellite cells
stem cells that help repair damaged muscle tissue
14
New cards
tendon
attached muscle to specific point in a bone
15
New cards
aponeurosis
broad sheet with broad bone attachments
16
New cards
myoblasts
embryonic cells that fuse to form multinucleate cells that differentiate into skeletal muscle fibers
17
New cards
sarcolemma
plasma membrane
18
New cards
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm
19
New cards
myofibrl
small cylindrical structures arranged parallel inside muscle fiber
20
New cards
sarcomeres
repeating functional units of skeletal muscle fibers
21
New cards
striations
z lines, I band, A band, M line, H band
22
New cards
Z lines
junction of adjacent sarcomeres
* protein connect thin filaments of adjacent sarcomeres (actinins)
* protein connect thin filaments of adjacent sarcomeres (actinins)
23
New cards
I band
lighter band with only thin filaments (actin)
24
New cards
A band
dark/dense region containing thick filaments (myosin)
25
New cards
M line
center of A band where adjacent thick filaments connect
26
New cards
H band
lighter region on each side of M line with only thick filaments
27
New cards
zone of overlap
within A band, overlapping thick/thin filaments
28
New cards
myofilaments
bundles of protein filaments inside myofibrls
29
New cards
thin filament
mostly composed of actin
30
New cards
thick filaments
mostly composed of myosin
31
New cards
transverse tubules
form passageways through muscle fiber and encircle sarcolemma
32
New cards
sarcoplasmic reticulum
similar to smooth ER
33
New cards
terminal cisternae
enlarged sections on either side of T tubule
34
New cards
triad
pair of terminal cisternae and one T tubule
35
New cards
thin filaments structure
attached to z lines by actinin
36
New cards
F-actin
twisted double strand of G-actin
* G-actin molecules have active site for binding myosin
* G-actin molecules have active site for binding myosin
37
New cards
Nebulin
holds two strands of G-actin molecules together
38
New cards
tropomyosin
double stranded protein wrapped around F-actin
* blocks myosin binding sites on G-actin molecules
* prevents actin/mysoin interaction
* blocks muscle contractions
* blocks myosin binding sites on G-actin molecules
* prevents actin/mysoin interaction
* blocks muscle contractions
39
New cards
thick filaments structure
* contains \~300 myosin molecules
* titin core
* titin core
40
New cards
titin core
connects thick filaments to Z lines and recoils after stretching
41
New cards
sliding filament theory
when muscles contract, thin filaments slide over thick filaments
* H & I bands get smaller, zones of overlap get larger
* Z lines move closer together, A band is unchanged
* sliding occurs in all sarcomeres in each myofibrl
* H & I bands get smaller, zones of overlap get larger
* Z lines move closer together, A band is unchanged
* sliding occurs in all sarcomeres in each myofibrl
42
New cards
membrane potential
unequal distribution of changes on either side of plasma membrane = potential difference
* exists because plasma membrane contains leak channels that are always open (K+ & Na+)
* exists because plasma membrane contains leak channels that are always open (K+ & Na+)
43
New cards
chemical gradient
concentration gradient for an ion across the plasma mebrane
44
New cards
electrical gradient
created by the attraction between opposite charges and repulsion of like charges
45
New cards
electrochemical gradient
chemical & electrical gradient
46
New cards
action potential step 1
small increase in membrane permeability to Na+
* Na+ entering cell moves membrane potential positive to threshold -55mV
* Na+ entering cell moves membrane potential positive to threshold -55mV
47
New cards
action potential step 2
voltage gated Na+ channels open
* rush of positive Na+ ions into cell
* depolarization: change of membrane potential to positive
* rush of positive Na+ ions into cell
* depolarization: change of membrane potential to positive
48
New cards
action potential step 3
membrane potential reaches to +30 mV
* Na+ channels close
* K+ channels open & K+ leaves cells
* repolarization: membrane potential returns to polarized state
* Na+ channels close
* K+ channels open & K+ leaves cells
* repolarization: membrane potential returns to polarized state
49
New cards
action potential step 4
repolarization continues to hyperpolarization
50
New cards
action potential step 5
membrane potential stabilizes
* K+ channels close at resting potential
* Na+/K+ pump restores original distribution
* refractory period: time needed to reach original distribution
* membrane cannot respond to another stimulus until after refractory period
* K+ channels close at resting potential
* Na+/K+ pump restores original distribution
* refractory period: time needed to reach original distribution
* membrane cannot respond to another stimulus until after refractory period
51
New cards
neuromuscular junction
location where motor neuron controls a skeletal muscle fiber
* there’s one NMJ per muscle fiber
* a motor neuron may control multiple muscle fibers
* there’s one NMJ per muscle fiber
* a motor neuron may control multiple muscle fibers
52
New cards
axon terminal (synaptic terminal) of motor neuron
contains vesicles with Acetylcholine (ACh)
53
New cards
motor end plate of muscle fiber
* has junctional folds that increase # of ACh receptors
* contains Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
* breaks down ACh
* contains Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
* breaks down ACh
54
New cards
synaptic cleft
space between axon terminal and motor end plate
55
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 1
electrical impulse arrives at axon terminal
* change in membrane permeability causes ACh vesicles to fuse with neuron plasma membrane
* ACh released (exocytosis)
* change in membrane permeability causes ACh vesicles to fuse with neuron plasma membrane
* ACh released (exocytosis)
56
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 2
ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft
* binds ACh receptor membrane channels at motor end plate
* changes sarcolemma Na+ permeability\\
* Na+ enters muscle fiber sarcoplasm
* binds ACh receptor membrane channels at motor end plate
* changes sarcolemma Na+ permeability\\
* Na+ enters muscle fiber sarcoplasm
57
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 3
Na+ influx generates action potential in sarcolemma
* ACh diffuses away or breaks down (AChE)
* ACh receptor membrane channels close
* ACh diffuses away or breaks down (AChE)
* ACh receptor membrane channels close
58
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 4
action potential generated at motor end plate immediately spreads across sarcolemma
* ACh cleared from receptor
* no other stimulus occurs until AP occurs
* ACh cleared from receptor
* no other stimulus occurs until AP occurs
59
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 5
action potential moves down T tubules between terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum
* changes permeability of SR
* changes permeability of SR
60
New cards
neuromuscular junction action step 6
sarcoplasmic reticulum releases stored Ca2+ into sarcomeres and begins contractions
* excitation contraction coupling: action potential is coupled with contraction
* excitation contraction coupling: action potential is coupled with contraction
61
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 1
resting sarcomere
* myosin heads are energized or “cocked”
* cocking head requires breakdown of ATP
* myosin heads are energized or “cocked”
* cocking head requires breakdown of ATP
62
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 2
contraction cycle begins
* calcium ions arrive from sarcoplasmic reticulum
* calcium ions arrive from sarcoplasmic reticulum
63
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 3
active sites exposed
* calcium binds to troponin
* troponin changes position, moves tropomyosin and exposes active sites on actin
* calcium binds to troponin
* troponin changes position, moves tropomyosin and exposes active sites on actin
64
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 4
cross-bridges form
* myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin
* forms cross-bridges
* myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin
* forms cross-bridges
65
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 5
myosin heads pivot
* cross-bridge formation causes myosin heads to pivot toward M line (center of sarcomere)
* power stroke
* ADP and P release
* cross-bridge formation causes myosin heads to pivot toward M line (center of sarcomere)
* power stroke
* ADP and P release
66
New cards
muscle fiber contraction cycle step 6
cross-bridges detach
* a new ATP attaches to each myosin head, myosin releases from actin
* released energy used to recock myosin head
* a new ATP attaches to each myosin head, myosin releases from actin
* released energy used to recock myosin head
67
New cards
troponin
protein or protein complex that assists is skeletal muscle contractions
* promotes muscle contractions
* promotes muscle contractions
68
New cards
mV
threshold: -55 mV
depolarizatiom: +30 mV
resting: -85 mV
depolarizatiom: +30 mV
resting: -85 mV
69
New cards
muscle twitch
single stimulus contraction relaxation sequence in a muscle
70
New cards
fasciculation
involuntary muscle twitch under skin
71
New cards
motor unit
group of muscle fibers controlled by single motor neuron
72
New cards
myogram
shows development of muscle tension
73
New cards
muscle twitch phase 1
latent period
* action potential stimulates sarcolemma
* calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
* no tension yet
* action potential stimulates sarcolemma
* calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
* no tension yet
74
New cards
muscle twitch phase 2
contraction phase
* calcium binds to troponin
* cross-bridge cycling
* start of tension development to peak tension
* calcium binds to troponin
* cross-bridge cycling
* start of tension development to peak tension
75
New cards
muscle twitch phase 3
relaxation phase
* calcium drops; cross-bridges detach; active sites covered
* tension returns to resting level
* from peak tension to end of twitch
* calcium drops; cross-bridges detach; active sites covered
* tension returns to resting level
* from peak tension to end of twitch
76
New cards
peak tension
depends on the frequency of stimulation and the number of muscle fibers stimulated
77
New cards
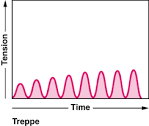
treppe
stimulation of muscle fiber immediately after relaxation phase produces increasing maximum tension
78
New cards
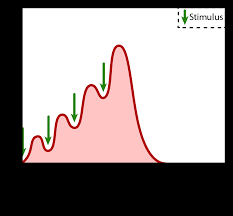
wave summation
addition of one twitch to another
* stimulation of muscle fiber before relaxation phase ends produces increasing maximum tension
* stimulation of muscle fiber before relaxation phase ends produces increasing maximum tension
79
New cards
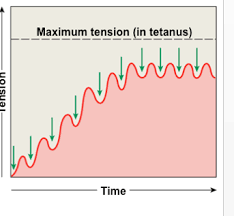
incomplete tetanus
rapid cycle of contraction/relaxation producing near peak tension
80
New cards
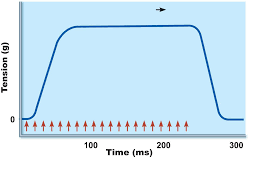
complete tetanus
higher stimulation frequency eliminates relaxation phase
* results in peak tension
* no calcium ions return to SR
* results in peak tension
* no calcium ions return to SR
81
New cards
motor unit recruitment
activation of more motor units to produce more tension
* smaller motor units activated first, then large motor units
* smooth, steady increase in muscle tension
* smaller motor units activated first, then large motor units
* smooth, steady increase in muscle tension
82
New cards
asynchronous motor unit summation
motor units activated on rotating basis to maintain sustained contractions
83
New cards
muscle tone
resting tension in skeletal muscle
84
New cards
isotonic contractions
tension rises and skeletal muscle length changes
* concentric contractions
* eccentric contractions
* concentric contractions
* eccentric contractions
85
New cards
concentric contraction
muscle tension rises until it exceeds load
* as muscle shortens, tension remains constant
* ex: flexing elbow while holding dumbell
* as muscle shortens, tension remains constant
* ex: flexing elbow while holding dumbell
86
New cards
eccentric contraction
peak tension produced is less than the load; muscle lengthens
* ex: returning dumbell from flexed position to extended
* ex: returning dumbell from flexed position to extended
87
New cards
glycolysis
anaerobic breakdown of glucose to pyruvate
* occurs in cytosol
* oxygen in cytosol
* produces 2 ATP & pyruvate molecules for each glucose
* occurs in cytosol
* oxygen in cytosol
* produces 2 ATP & pyruvate molecules for each glucose
88
New cards
aerobic metabolism
* produces 95% of ATP demands of resting cell
* occurs in mitochondria
* produces 15 ATP for each pyruvate
* ATP comes from electron transport chain
* occurs in mitochondria
* produces 15 ATP for each pyruvate
* ATP comes from electron transport chain
89
New cards
glycogen
the way most energy stored
90
New cards
free ATP
minimal, supports only \~10 twitches
91
New cards
creatine phosphate
* supplies energy for 15 seconds
* creatine assembled from amino acids
* creatine assembled from amino acids
92
New cards
muscle metabolism at rest
* low ATP demand
* mitochondria produces surplus ATP
* fatty acids & glucose absorbed from bloodstream
* make ATP to convert creatine to creatine phosphate & glucose to glycogen
* mitochondria produces surplus ATP
* fatty acids & glucose absorbed from bloodstream
* make ATP to convert creatine to creatine phosphate & glucose to glycogen
93
New cards
muscle metabolism at moderate activity levels
* ATP demand increases
* relies on anaerobic metabolism of pyruvate to make ATP
* increased oxygen consumption
* relies on anaerobic metabolism of pyruvate to make ATP
* increased oxygen consumption
94
New cards
muscle metabolism at peak activity levels
* enormous ATP demands
* mitochondria at max production produces 1/3 ATP needs
* most produced by glycolysis
* excess pyruvates to lactate
* lactate & H+ increase, drops pH (lactic acidosis) and causes muscle fatigue
* mitochondria at max production produces 1/3 ATP needs
* most produced by glycolysis
* excess pyruvates to lactate
* lactate & H+ increase, drops pH (lactic acidosis) and causes muscle fatigue
95
New cards
fatigue
muscle can no longer perform at required level
* major factor is decreased pH
* decreases calcium/troponin binding
* alters enzyme activity
* major factor is decreased pH
* decreases calcium/troponin binding
* alters enzyme activity
96
New cards
polio
virus that attacks CNS motor neurons causing atrophy and paralysis
97
New cards
tetanus
toxin from bacteria suppresses mechanism that inhibits motor neuron activity; causes sustained and powerful muscle contractions
98
New cards
botulism
toxins from bacteria blocks ACh release at neuromuscular junctions
* paralysis of skeletal muscles
* acquired through bacteria-contaminated food
* paralysis of skeletal muscles
* acquired through bacteria-contaminated food
99
New cards
myasthenia gravis
autoimmune disease causing loss of ACh receptors at neuromuscular junctions
100
New cards
rigor mortis
generalized muscle contractions shortly after death
Explore top notes
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)
Chp 14 Materality: Constructing Social Relationships and Meanings with Things
Updated 1265d ago0.0(0)