States of Matter
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Matter
Matter is anything that takes up space (i.e. has volume) and has a mass. Matter is also made up of tiny particles including atoms, molecules and ions.
3 states of matter
Solid, liquid, gas
Kinetic energy
The energy an object possesses during to its motion
What are the differences between the states (7)
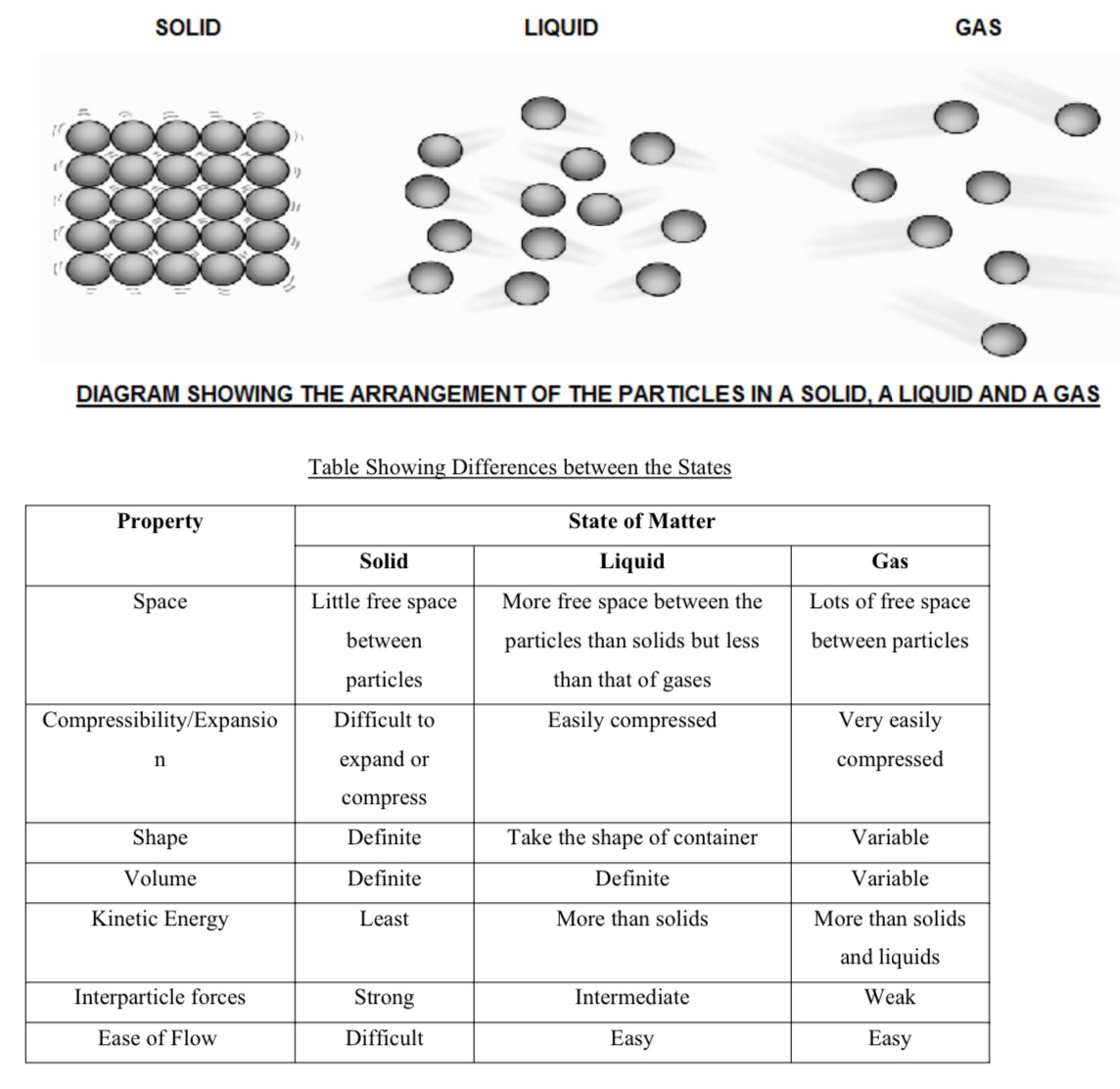
What does the particulate nature of matter suggest?
That particles are in constant motion
What phenomena provide evidence to support the theory of the particulate nature of matter
Diffusion
Osmosis
Brownian motion
Diffusion
The movement of fluid (liquid or gas) particles from and area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until both concentrations reach equilibrium
Describe the experiment to test for diffusion
Dip a cotton ball into a basic substance (ammonia) and place it into a litmus tube with red litmus paper. The litmus will turn from red to blue as the gas moves from the area of high concentration, the cotton ball, to the area of low concentration, the rest of the tube
What is osmosis
The movement of water particles from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a semipermeable membrane
What is Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid (liquid or gas) resulting from collisions with other fast-moving molecules of the fluid.
More solute, less solvent
Concentrated solution
Less solute, more solvent
Diluted solution
What determines the state a substance takes
Temperature and pressure
What is the effects of greater energy on a substance
The particles can break bonds and move about more vigorously
Show the interconversion of states

What’s the difference between boiling and evaporation
Boiling is a rapid change, while evaporation is a gradual change.
Draw a heating and cooling curve