Gastrointestinal System Assessment (ABDOMEN)
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Anatomy & Physiology of the Gastrointestinal (GI) System
Functions of the GI System
Ingestion: Intake of food.
Digestion: Breakdown of food (mechanical and chemical).
Absorption: Nutrient transfer to the bloodstream.
Excretion: Waste elimination via defecation.
Anatomy of the GI System
Upper GI Tract: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach.
Lower GI Tract: Small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine (colon, rectum, anus).
Accessory Organs: Liver, gallbladder, pancreas.
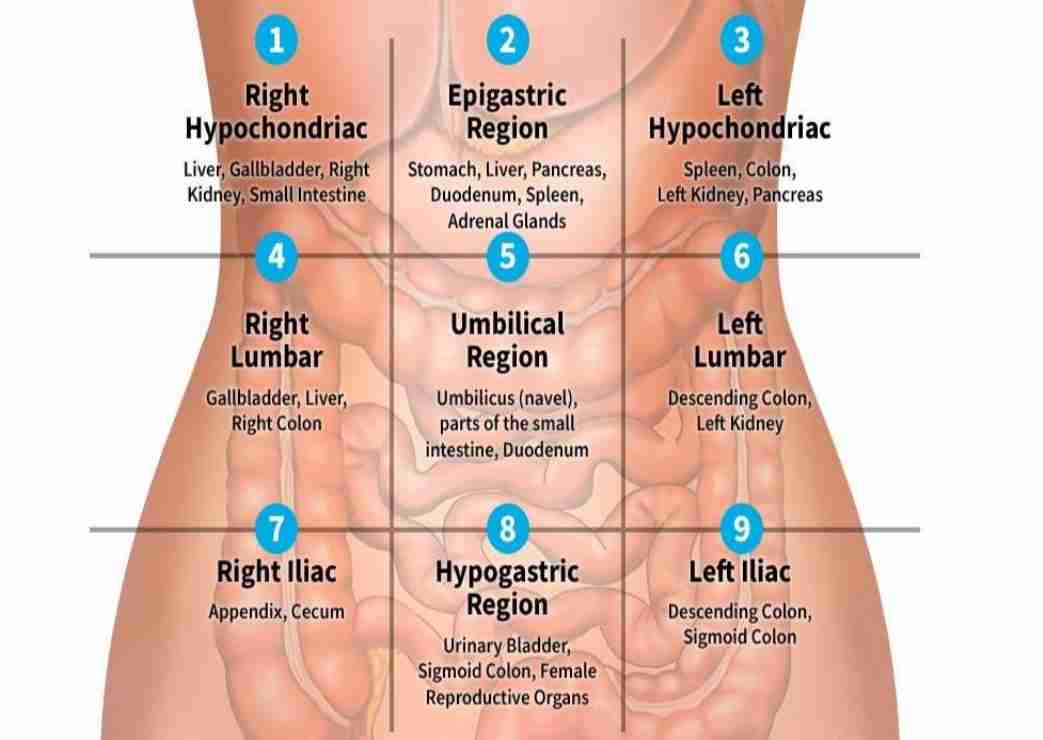
GI System Landmarks for Physical Assessment
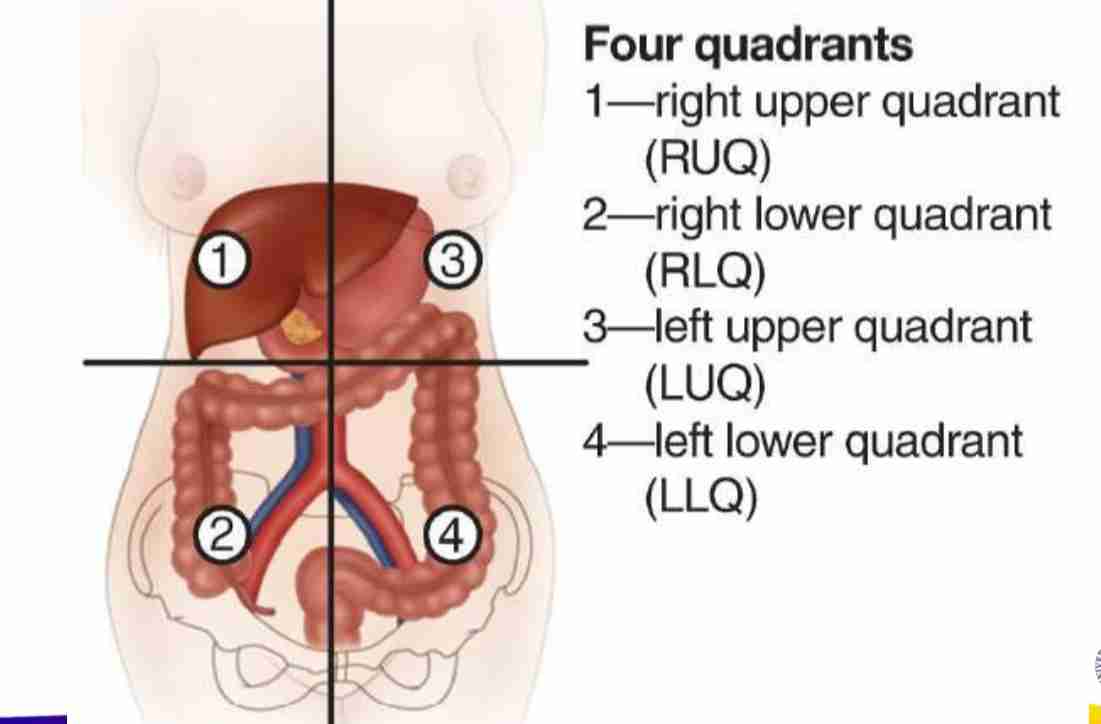
Four Quadrants:
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ): Liver, gallbladder, right kidney, pancreas head.
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ): Stomach, spleen, left kidney, pancreas body.
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ): Appendix, cecum, right ovary.
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ): Sigmoid colon, left ovary.
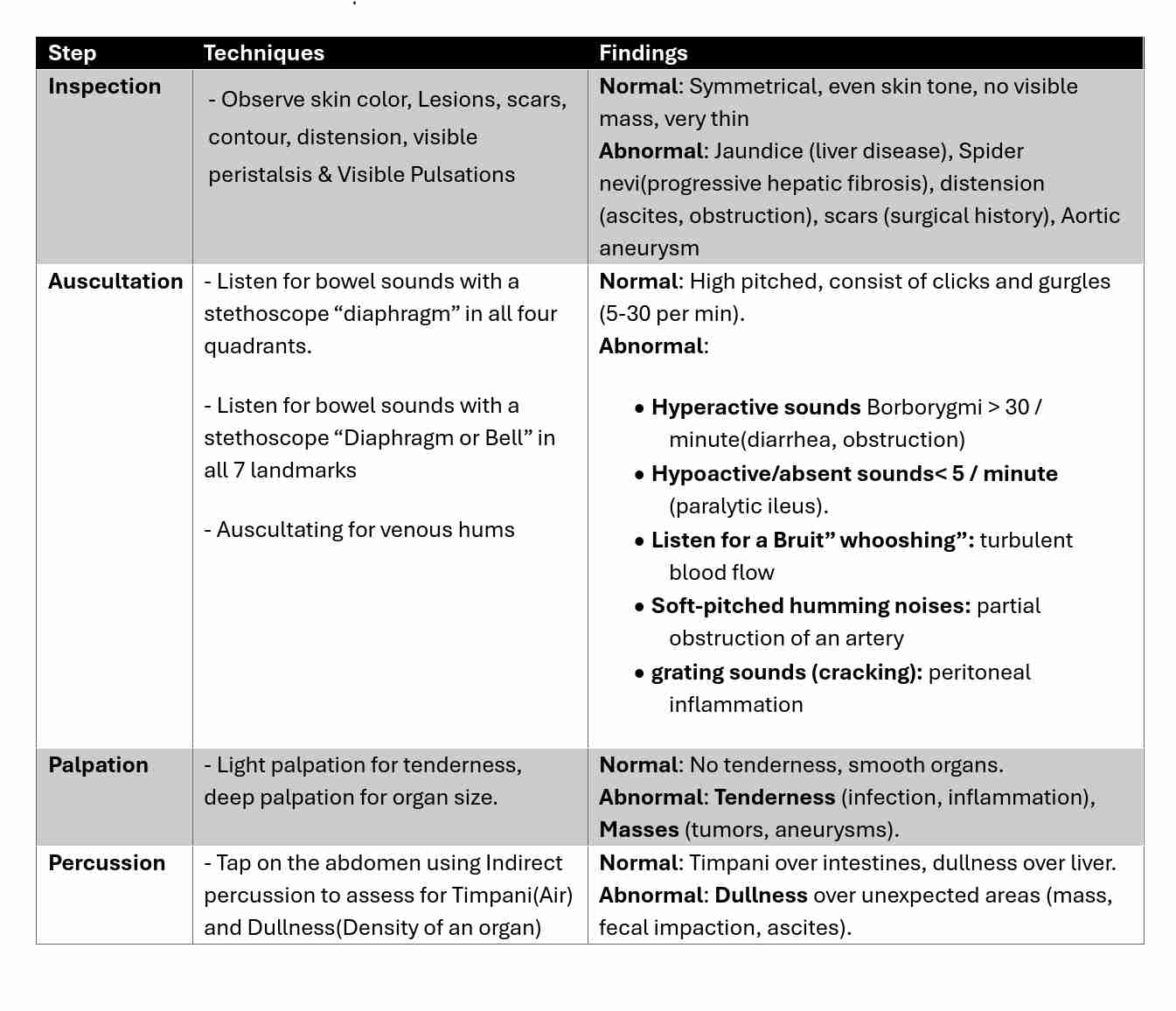
Physical Examination Techniques
Key Special Tests
Mc Burney’s Point Tenderness → Appendicitis (RLQ pain).
Rovsing’s Sign → RLQ pain with LLQ palpation (appendicitis).
Fluid Wave Test → Detects ascites.
Differentiating Normal & Abnormal Findings
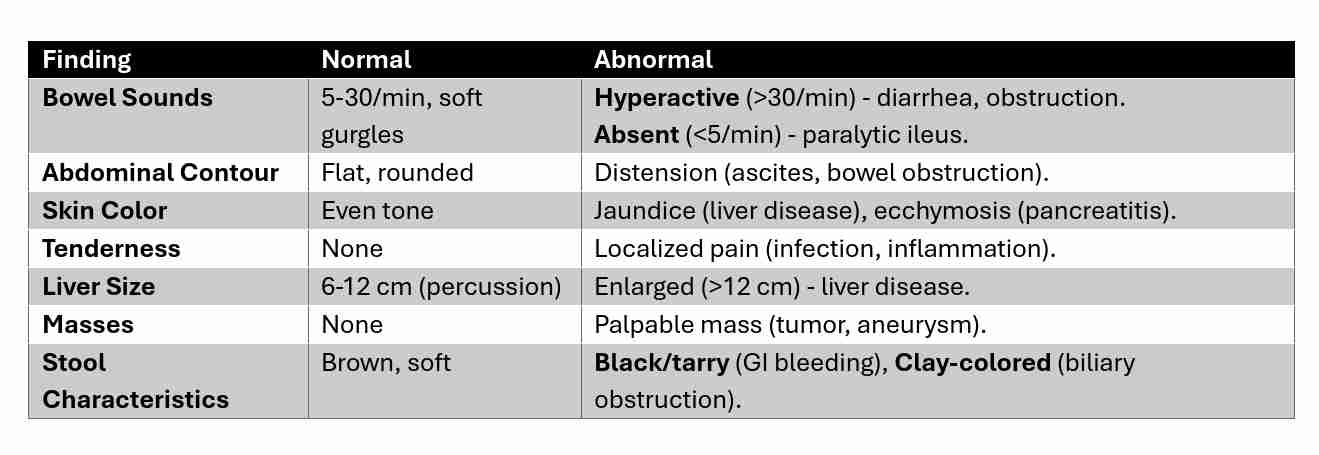
Analyzing Findings from Interviews, General Survey & Physical Exam
Interview Findings:
Chief complaints: Abdominal pain is often, bloating, nausea, vomiting, changes in bowel habits.
Past history: Surgery, ulcers, hepatitis, gallstones.
Dietary habits: High-fat diet, fiber intake.
Alcohol & smoking history: Risk for ulcers, liver disease.
General Survey:
Skin tone: Jaundice (liver dysfunction), pallor (anemia).
Weight loss/gain: Malabsorption (weight loss), fluid retention (ascites).
Physical Exam Analysis:
RUQ tenderness + Jaundice → Liver disease, gallbladder disease.
RLQ pain + Rebound tenderness → Appendicitis.
Distended abdomen + Absent bowel sounds → Bowel obstruction.
Black stools + Epigastric pain → GI bleeding, peptic ulcer.