TOPIC 2 - Mains electricity
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
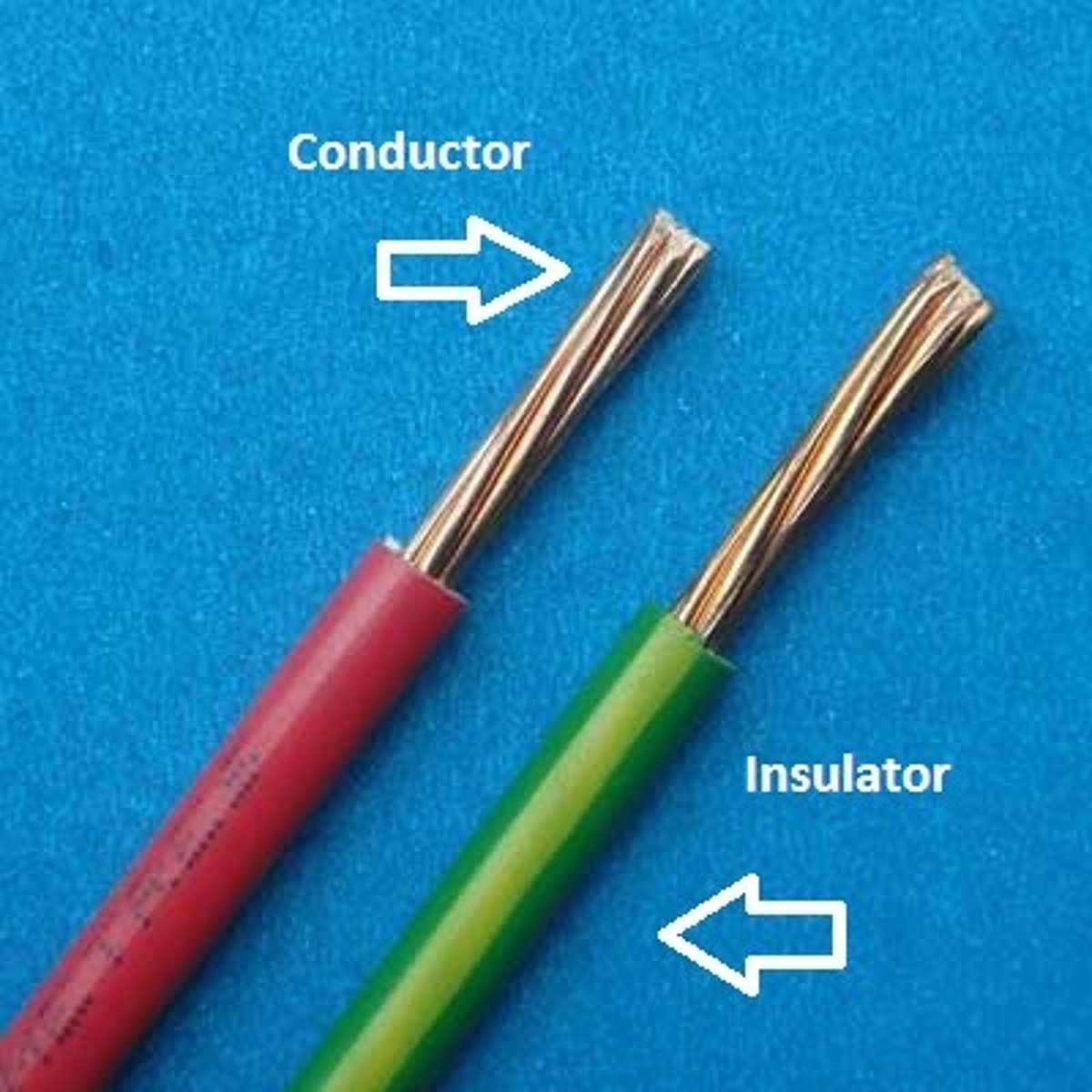
Electrical safety - INSULATION
- The conducting part of a wire is usually made of copper or some other metal. If this comes into contact with a person, this poses a risk of electrocution.
- Therefore, wires are covered with an insulating material, such as rubber.
Electrical safety - DOUBLE INSULATION
- Some appliances don't have metal cases and so there is no risk of them becoming electrified.
- Such appliances are said to be double insulated, as they have two layers of insulation:
1. Insulation around the wires themselves.
2. A non-metallic case that acts as a second layer of insulation.
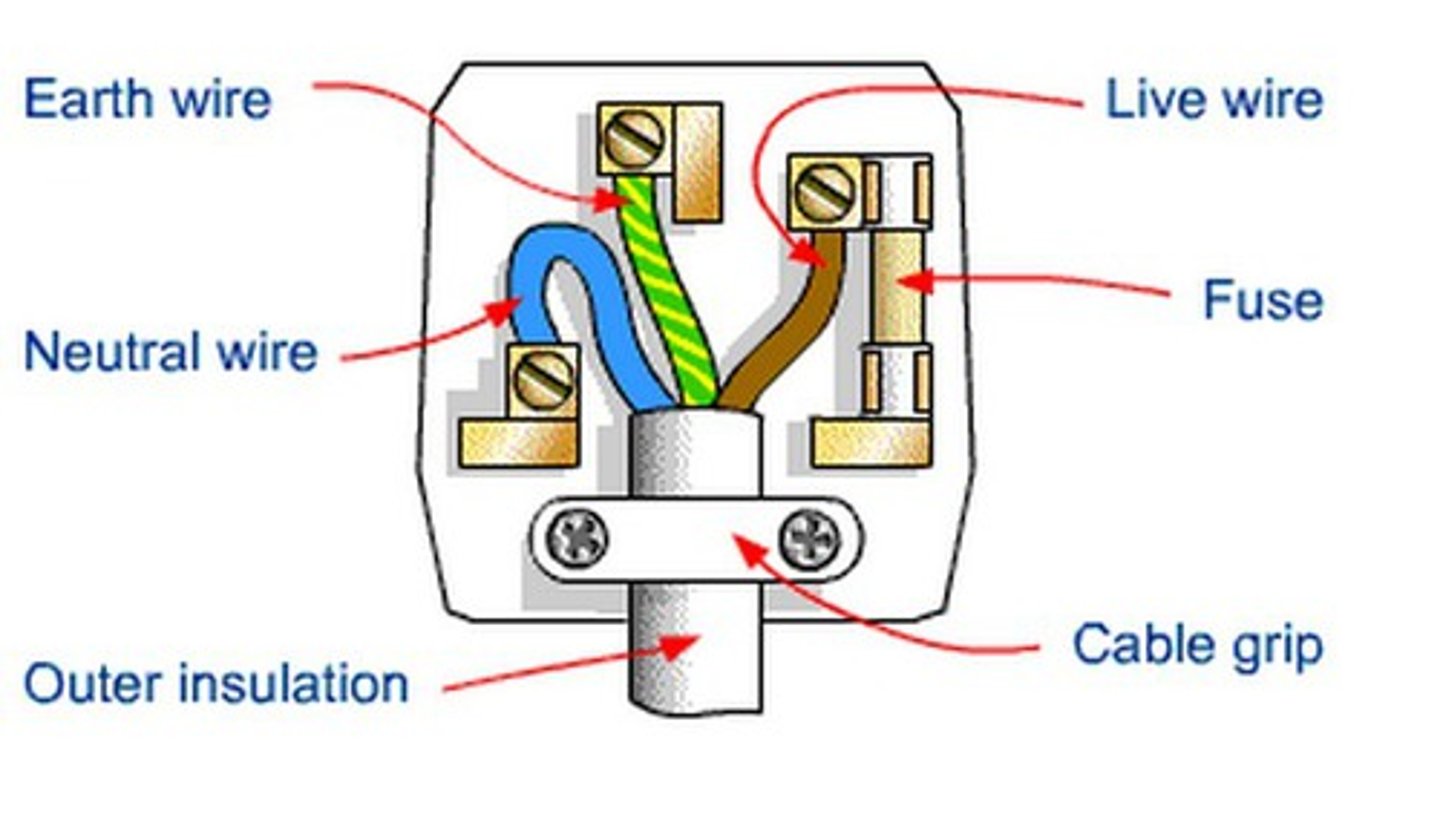
Electrical safety - EARTHING
- Many electrical appliances have metal cases: If a live wire (inside the appliance) came into contact with the case, the case would become electrified and anyone who touched it will risk being electrocuted.
- The earth wire is an additional safety wire that can reduce this risk:
1. The earth wire provides a low resistance path to the fuse.
2. It causes a surge of current in the earth wire and in the live wire.
3. The high current through the fuse causes it to melt and break.
4. This cuts off the supply of electricity to the appliance, making it safe.
Electrical safety - FUSE
- A fuse is designed to cut off the flow of electricity if the current becomes to large:
1. The wire heats up an melts.
2. This causes the wire to break, breaking the circuit and stopping the current.
Electrical safety - CIRCUIT BREAKER
- A circuit breaker consists of an automatic electromagnet switch that breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain value.
1. The main circuit breaker can quickly shut off electricity to the whole house.
2. The branch circuit breakers can shut off electricity to specific areas of the house.

Explain the benefits to using a circuit breaker over a fuse
- It doesn't melt and break, hence it can be reset and used again.
- It works much faster
Explain why current in a resistor results in the electrical transfer of energy, and an increase in temperature
- Energy is transferred as a result of collisions between:
1. ELECTRONS flowing in the conductor
2. and... the LATIC OF ATOMS within the metal conductor.
- When the electrons collide, they lose energy by transferring it to the ions, which start to vibrate more.
- As a result, the metal INCREASES in TEMPERATURE.
Name 5 domestic appliances that utilize this increase in temperature caused by current in a resistor
- Electric heaters
- Electric ovens
- Electric hob
- Toasters
- Kettles
Definition of alternating current
(a.c.)
A current that continuously changes its direction, going back and forth around a circuit.
- MAINS ELECTRICITY is supplied by an alternating current.
Definition of direct current
(d.c.)
A current that is steady, constantly flowing in the same direction in a circuit, from positive to negative.
- BATTERIES OR CELLS are supplied by direct current.
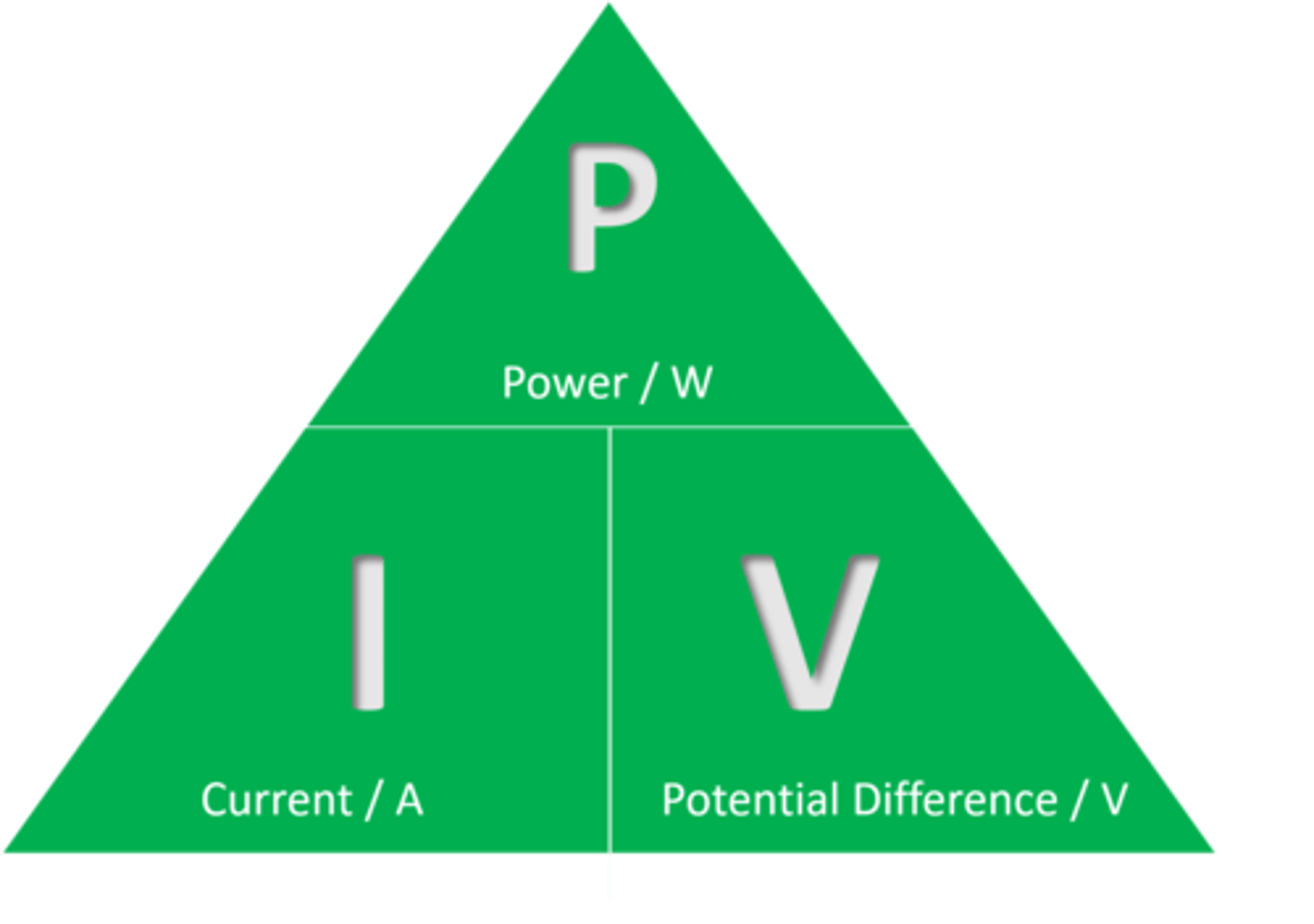
Equation linking power, current and voltage
power = current x voltage
(P = I X V)
Equation linking energy transferred, current, voltage and time
Energy transferred = current x voltage x time
(E = I x V x t)