Bio Midterm
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/74
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
bulk trasnport
Larger molecules and clumps of material can
also be actively transported across the cell membrane. Sometimes involves changes in the shape of the cell membrane.
also be actively transported across the cell membrane. Sometimes involves changes in the shape of the cell membrane.

2
New cards
Endocytosis
Vesicles from cell membrane moving particles inside cell, part of bulk transport

3
New cards
Excosytosis
Vesicles moving from inside a cell to outside, by bulk transport

4
New cards
Phagocytosis
process in which extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf large particles and take them into the cell.
EX: Bacteria in human cells taken in and destroyed through forming a vesicle
EX: Bacteria in human cells taken in and destroyed through forming a vesicle

5
New cards
3 types of passive transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
6
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, moves LOW solute concentration to HIGH solute concentration(Moves only water)

7
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.

8
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels

9
New cards
Does diffusion travel long or short distances
Really short distances
10
New cards
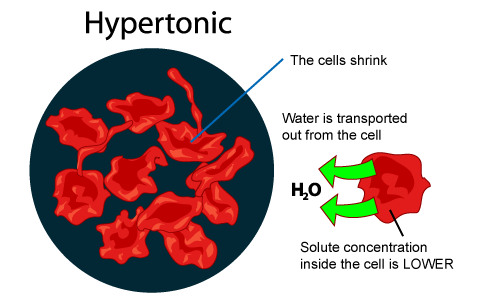
Hypertonic solution
Water will leave the cell to create equilibrium, higher solute concentration on outside
11
New cards
Isotonic solution
Equilibrium between inside and outside of cell, solute concentration equal on outside and inside

12
New cards
Hypotonic solution
Water will enter the cell to create equilibrium, higher solute concentration on inside of cell

13
New cards
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference, molecules moves against the concentration gradient(LOW concentration to and area of HIGH concentration)
14
New cards
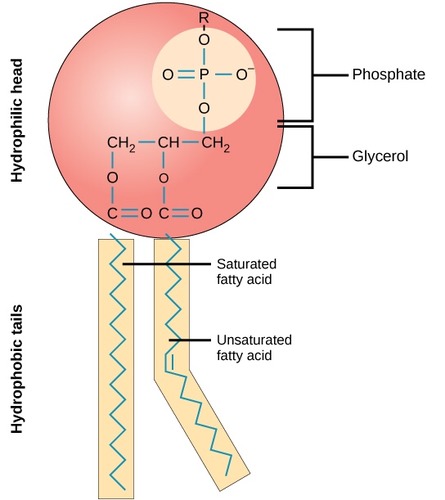
Phosopholipids
Primary structural component of cellular membrane. head is hydrophilic. tail is hydrophobic
15
New cards
channel proteins
proteins that provide passageways through the membrane(changes shape)

16
New cards
carrier proteins
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane(uses energy to change shape)

17
New cards
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.

18
New cards
glycoprotein
A protein with one or more carbohydrates covalently attached to it.

19
New cards
transmembrane protein
An integral membrane protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer.

20
New cards
cholesterol molecule
-helps stabilize the phospholipids
-prevents the fatty acid chains of the phospholipids from sticking together
-prevents the fatty acid chains of the phospholipids from sticking together

21
New cards
aquaporin
water channel protein in a cell
22
New cards
Macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
23
New cards
Sacharides are
carbs
24
New cards
Peptides are
proteins
25
New cards
Glycerides are
lipid esters
26
New cards
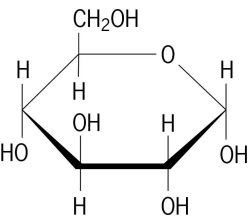
Carbohydrates
Found in starch, glucose main energy source, stored in liver and muscles, Quick energy.
27
New cards
elements found in carbohydrates
C, H, O
28
New cards
elements found in proteins
CHON
29
New cards
elements found in lipids
C, H, O
30
New cards
elements found in nucleic acid
C, H, O, N, P
31
New cards
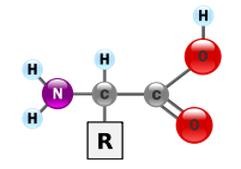
Proteins
amino acids, simplest form of amino acids, can wok as enzymes
32
New cards
protein primary structure

33
New cards
protein secondary structure

34
New cards
protein tertiary structure

35
New cards
protein quaternary structure

36
New cards
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats and oils, long term energy, highest amount of energy,

37
New cards
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA

38
New cards
dehydration synthesis
monomers are joined by removal of OH from one monomer and removal of H from the other at the site of bond formation
39
New cards
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
40
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
41
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
42
New cards
how to convert from calories to kilocalories
divide by 1,000
43
New cards
Nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.

44
New cards
Plasmids
small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome

45
New cards
Capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface

46
New cards
Flagellum
A long, hair like structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move.

47
New cards
Pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
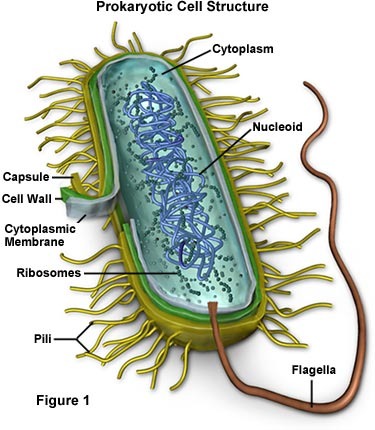
48
New cards
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction

49
New cards
Rough ER
That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes. Protein factory

50
New cards
Smooth ER
That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes. Lipid factory also Storage and removes harmful substances

51
New cards
Golgi apparatus
"Post office" of the cell Made from membranes Packages proteins in vesicles before sending it to its destination
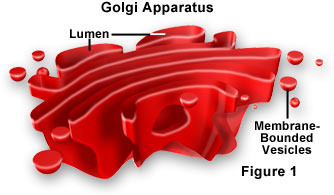
52
New cards
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production

53
New cards
Ribosomes
Makes proteins

54
New cards
Lysosomes
Uses chemicals to break down food and worn out cell parts(only in Animal cells)

55
New cards
Plasma membrane
Acts as a barrier between inside and outside. Provides structure/protection. Decides what comes in and goes out

56
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended

57
New cards
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell

58
New cards
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates

59
New cards
Cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.

60
New cards
Amyloplasts
Synthesizes starch

61
New cards
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
62
New cards
Eukaryote
an organism with cells characteristic of all life forms except primitive microorganisms such as bacteria
63
New cards
Cellular respiration
a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP
64
New cards
Denaturation
loses/changes shape
65
New cards
How does low temperature affect enzymes.
the substrate moves too slow and enzyme doesn’t work
66
New cards
How does high temperature affect enzymes.
the enzyme denatures
67
New cards
Co-Factors
Some enzymes need a co-factor, Helps the enzyme to do its job
68
New cards
Enzyme Inhibition
Enzymes can stop working or work slower when an inhibitor is present, Inhibitors are “impostors” that bind to the active site and stops the substrate from binding
69
New cards
Photosynthesis equation
CO2+H2O = C6H12O6 + O2
70
New cards
Where does Photosynthesis happen?
Happens in the chloroplast
71
New cards
Where does Cellular Respiration happen?
Happens in the mitochondria in between the “folds” of the inner and outer membrane
72
New cards
Opposite of Photosynthesis
Cellular Respiration
73
New cards
Where does most of the ATP in a leaf made?
electron transport chain
74
New cards
monomer Protein are called
Amino Acids
75
New cards
How does surface area and volume affect diffusion
As the surface area of the membrane increases, the rate of diffusion also increases, but a smaller cell will diffuse faster because it has less volume a larger surface area compared to larger cells