AP Pyschology unit 0
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
critical thinking
thinking that examines assumptions, evaluate evidence, assesses conclusions, discerns bias, and appraises the source
hindsight bias
tendency to believe after learning an outcome; one would have foreseen it
overconfidence
judgment from bias in seeking information rather than confirms them.
Gestalt perspective
perspective that is associated with “ the whole is greater than the sum of the parts”
confirmation bias
the tendency to favor info. that confirms beliefs/ biases, while downplaying contradictory evidence
psychodynamic perspective
the belief that the unconscious drives thoughts and behaviors; unconscious and repressed
behavioral perspective
consequences of a behavior will influence whether of not the behavior is repeated
humanistic perspective
belief that individuals choose their own destinies
cognitive perspective
focuses on how mental processes influence behavior
biological perspective
the understanding of the physiology of the human brain to better understand thoughts and behaviors
sociocultural perspective
examines the influence of cultural standards affecting one’s thoughts and behaviors
evolutionary perspective
examines human behaviors and though processes relating to Darwin’s theories of evolution and adaptation
peer reviewers
scientific experts who evaluate a research article’s theory, originality,, and accuracy
theory
explanation for behaviors; events offered by ideas that oragnize observations
hypothesis
testable predictions
falsifiability
the possibility that an idea, hypothesis, or theory can be disproven by experiments/ observations
operational definitions
statement of the exact (operations) used in a research study.
replication
repeating the essence of a research study
case study
in-depth analysis of individuals or groups
self-report bias
bias when people report their bias inaccurately
sampling bias
a flawed sampling process… produces an unrepresentative sample
random sample
fair sampling process… each member has an equal chance of inclusion
population
all those in a group being studied
non-experimental methods
method that shows us what can happen, and they offer ideas for future studies; case studies, naturalistic observations, and surveys
experimental methods
method which uses controlled experiments to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables
correlation
statistical measure that reflects the relationship between two variables
correlation coefficient
statistical index of the relationship b/w two things; to help figure out how closely two things vary together ( ranging from ( -1.00 to 1.00)
variable
anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure
illusory correlation
is a cognitive bias where poeple perceive a relationship b/w two variables when no such relationship exists
regression toward the mean
extremely high or low scores on a measurement will, on average, be followed by less extreme scores upon retesting
experiment
research method which is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables
experimental group
the group in the experiment where the participants receive special treatment
control group
group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment, serving as the comparison
random assignment
assigning participants randomly to either the experimental or control group, eliminating bias
single-blind procedure
experimental procedure in which the participants are ignorant about whether they have received the treatment v. placebo
double-blind procedure
experimental procedure where the participants AND the research staff are ignorant about whether the participants received placebo or not.
placebo effect
the participant experiences improvement within their symptoms/ conditions after receiving a fake treatment
placebo
imitation of a drug/remedy designed to trick people into thinking that they are receiving the genuine treatment
independent variable
the factor that is being manipulated
dependent variable
the outcome that is measured
cofounding variable
the factor other than the factor being studied that might influence a study’s result
validity
the extent to which a test/ experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
quantitative research
method that uses numerical data
qualitative research
methods that rely on in-depth, narrative data
Likert scales
psychometric scale used in surveys to measure attitudes or opinions.
institutional review
where academic research must propose a study the ethics board of the IRB at the institution in which was established to review an approve research subjects
debriefing
occurs after the study and is to educate participants about the true nature of the study
informed consent
participates are given info. on a study to see if they are willing to participate
informed assent
process where minors agree to participate in clinical research
descriptive statistics
methods used to organize, summarize, and present data using numerical data to describe the characteristics of a group
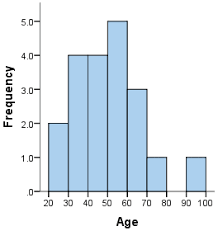
histogram
bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
mode
most frequent score in the data set
median
score that falls in the middle of the distribution
mean
arthmetic average of all scores; calculated by adding up all the scores/ by the total number of scores.
percentile rank
indicates the percentage of scores in a specific comparison group that fall below a particular score
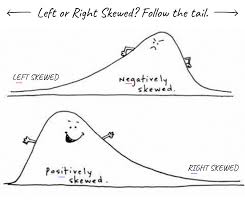
skewed distribution
The shape of a set of data in which the values are not evenly distributed around the mean.
range
the difference between the highest and lowest in distribution
standard deviation
measure used to quantify the amount of variation/dispersion in a set value
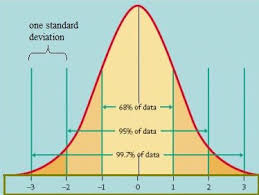
normal curve ( bell curve , Gaussian distribution)
represents the data that clusters around the mean or average.
inferential statistics
methods used to draw conclusions about a larger population based on data from a sample
meta-analysis
statistical technique used to combine and analyze the results from multiple independent studies on the same topic.
statistical significance
any differences observed between groups being studied are ‘real’
effect size
quantitative measure of the magnitude of the experimental effect.