Comprehensive Human Tissues: Histology, Epithelia, Connective, Muscle, Nervous, and Membranes
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Histology
Study of normal structures of tissues.
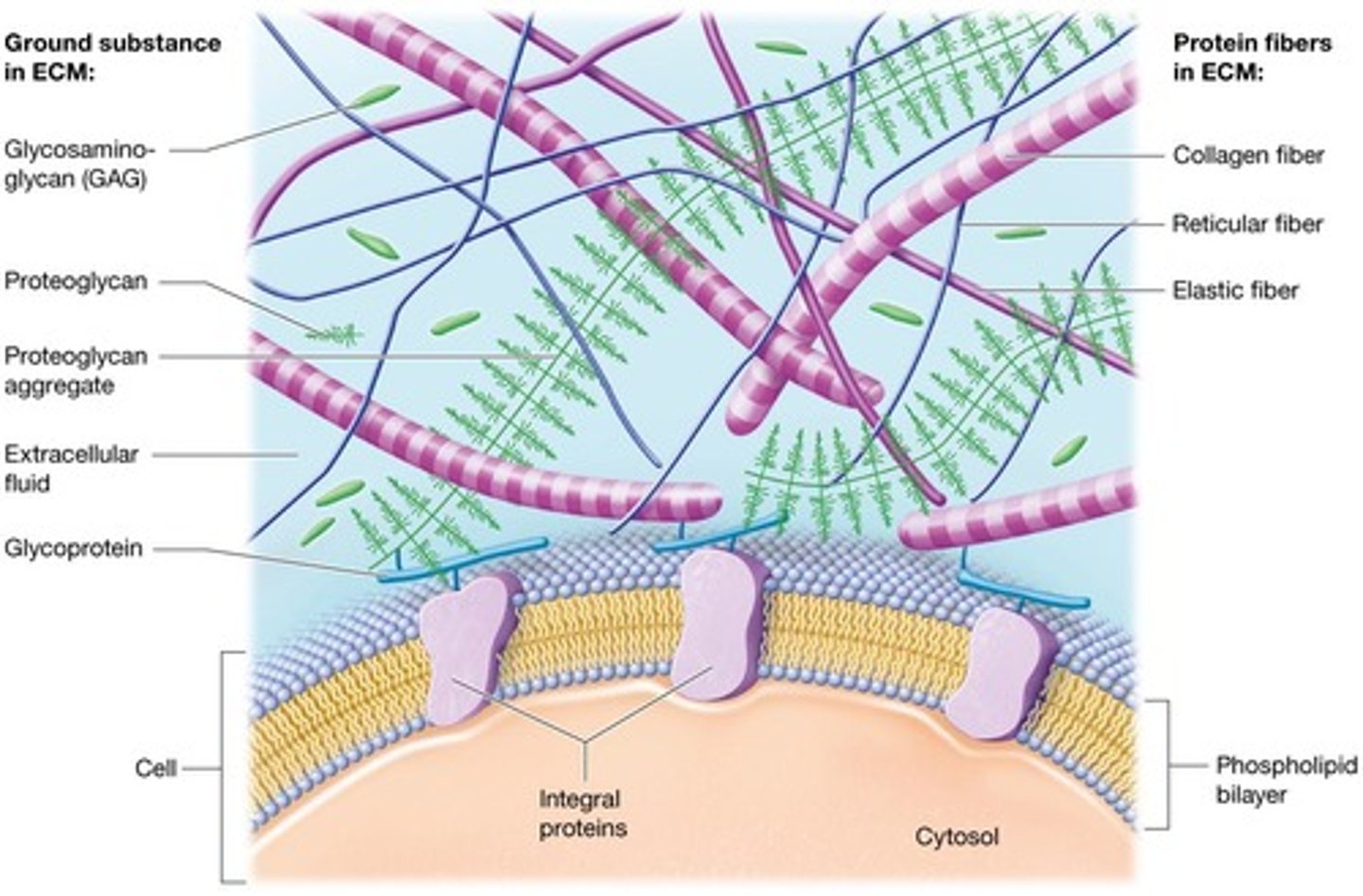
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
Surrounding material including the ECF.
Epithelial tissues (epithelia)
Tightly packed sheets of cells with no visible ECM that cover and line all body surfaces and cavities.
Connective tissues
Connect all other tissues to one another with ECM as a prominent feature.
Muscle tissues
Cells capable of generating force by contracting with little ECM between them.
Nervous tissues
Cells capable of generating, sending, and receiving messages in a unique ECM.
Ground substance
Makes up most of ECM containing the ECF or interstitial fluid with water, nutrients, ions, and three families of macromolecules.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Long, straight polysaccharide chains called chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid.
Proteoglycans
GAGs bound to protein core resembling a bottle brush.
Glycoproteins
Cluster of different types of glycoproteins called Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs).
Collagen fibers
Make up 20-25% of all proteins in body, resistant to tension and pressure.
Elastic fibers
Composed of protein elastin surrounded by glycoproteins, allowing fibers to stretch up to one and a half times resting length without breaking.
Reticular fibers
Thin, short collagen fibers that form a meshwork or scaffold supporting cells and ground substance.
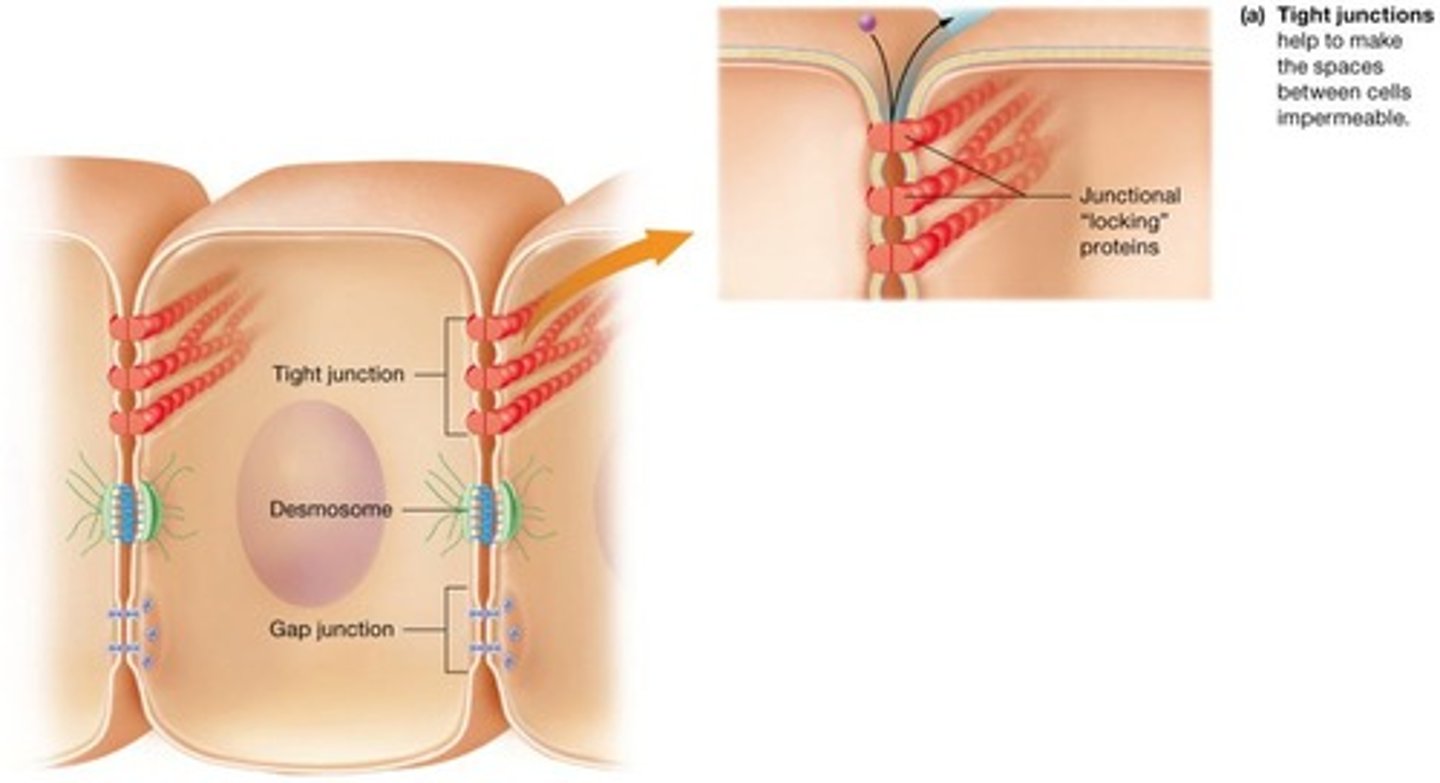
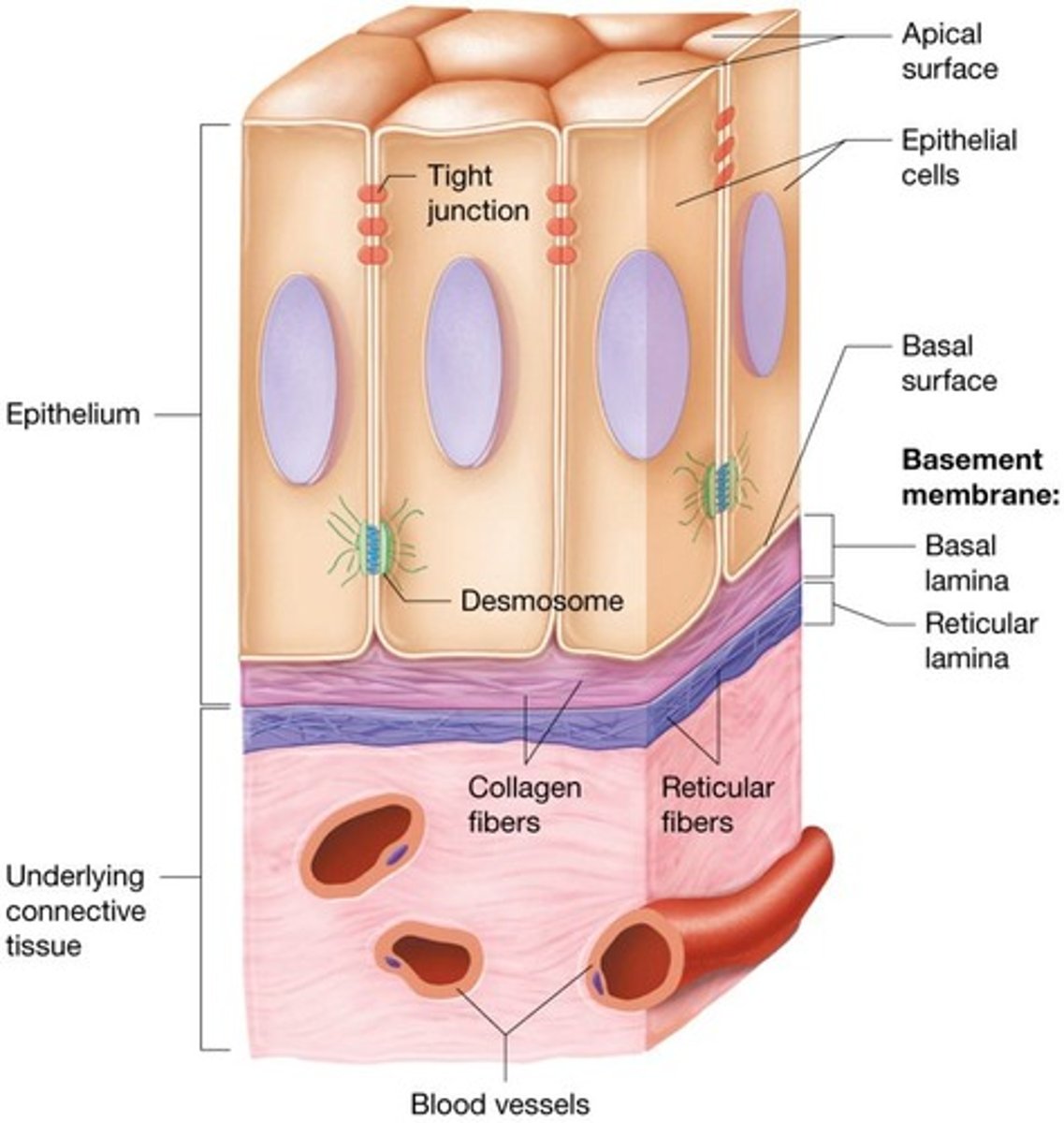
Cell junctions
Cells bind to one another through neighboring cell's plasma membranes linked by integral proteins.
Tight junctions
One of the three major types of cell junctions.
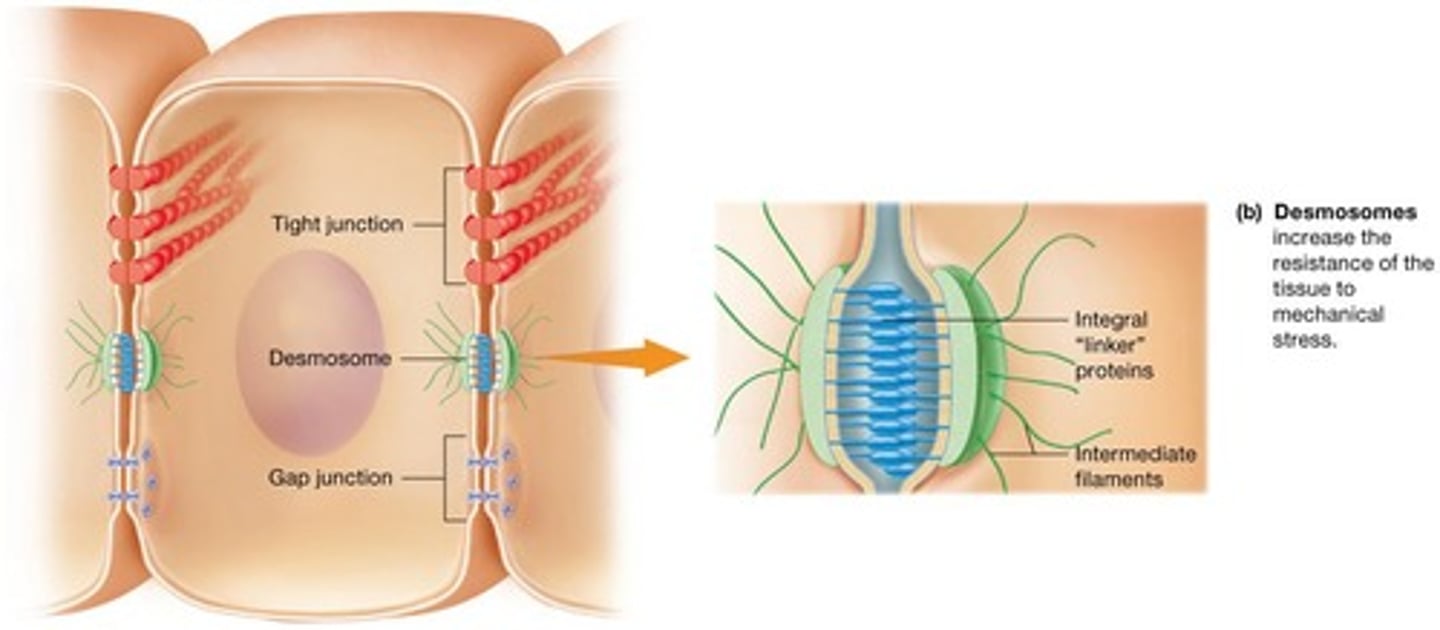
Desmosomes
One of the three major types of cell junctions.
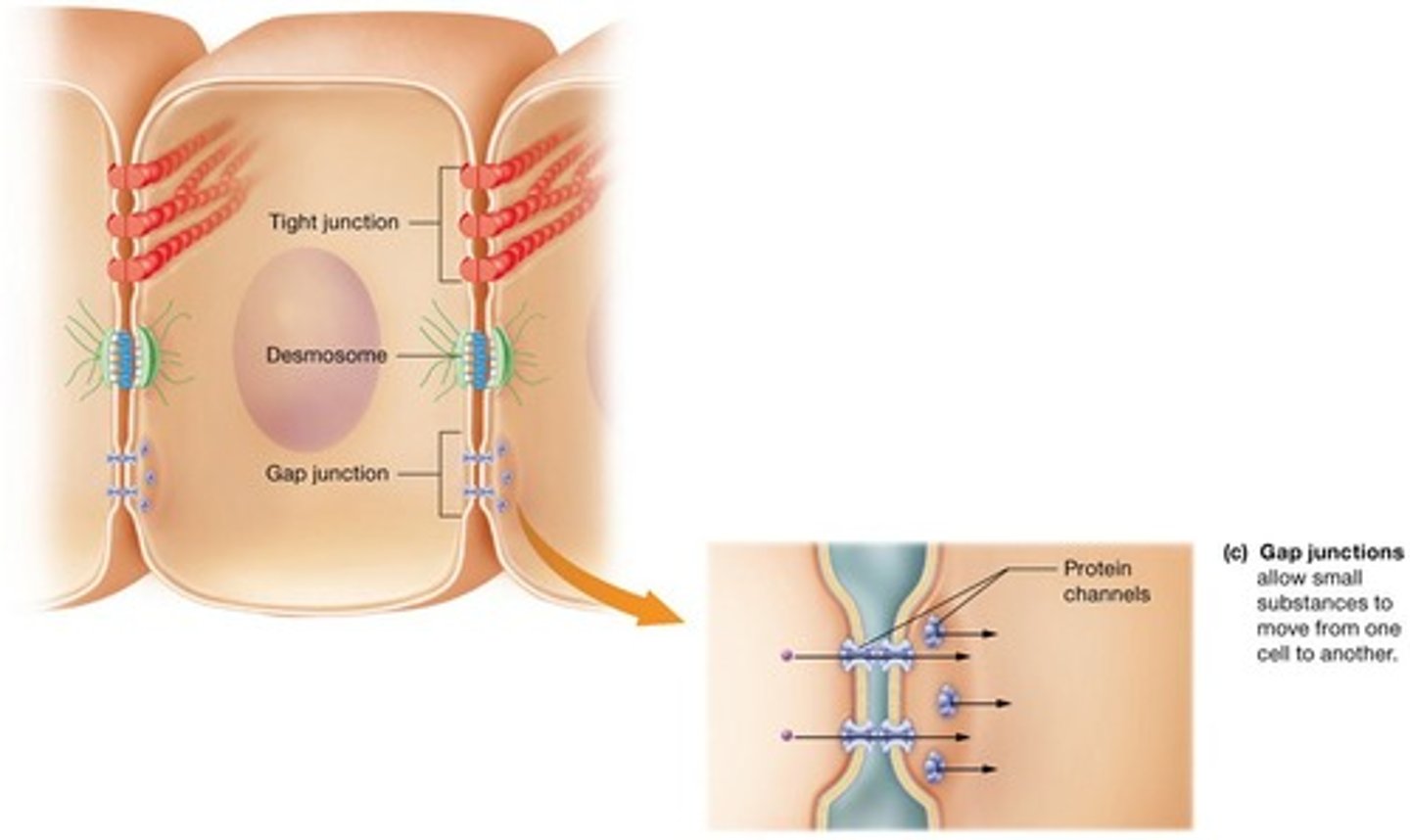
Gap junctions
One of the three major types of cell junctions.
ECF
Extracellular fluid surrounding cells.
Macromolecules
Large molecules including glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins.
Osmosis
Movement of water out of cells and blood vessels creating a concentration gradient.
Tensile strength
The ability of a material to resist tension or pulling forces.
Compression resistance
The ability of a material to withstand compressive forces.
Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Molecules that adhere cells to one another and to their surroundings.
Mitotic activity
The process of cell division and growth.
Epithelial tissues
On every internal and external body surface acting as a barrier between body and external environment as well as lining organs and fluid-filled cavities.
Protection
Shield underlying tissues from mechanical and thermal injury.
Immune defenses
Form physical barriers to prevent invasion by microorganisms; specialized cells of the immune system are also scattered throughout epithelial tissues.
Secretion
Form glands that produce substances like hormones and oils to be secreted into blood or through ducts.
Transport into other tissues
Selectively permeable membranes so certain substances can cross these barriers by passive or active transport and enter other tissues.
Sensation
Most epithelial tissues are associated with a rich nerve supply to detect changes in internal and external environments.
Basal lamina
ECM synthesized by epithelial cells consisting of collagen fibers and ground substance.
Reticular lamina
Synthesized by underlying connective tissue, consisting of reticular fibers and ground substance.
Simple epithelia
Epithelial tissue classified as a single cell layer.
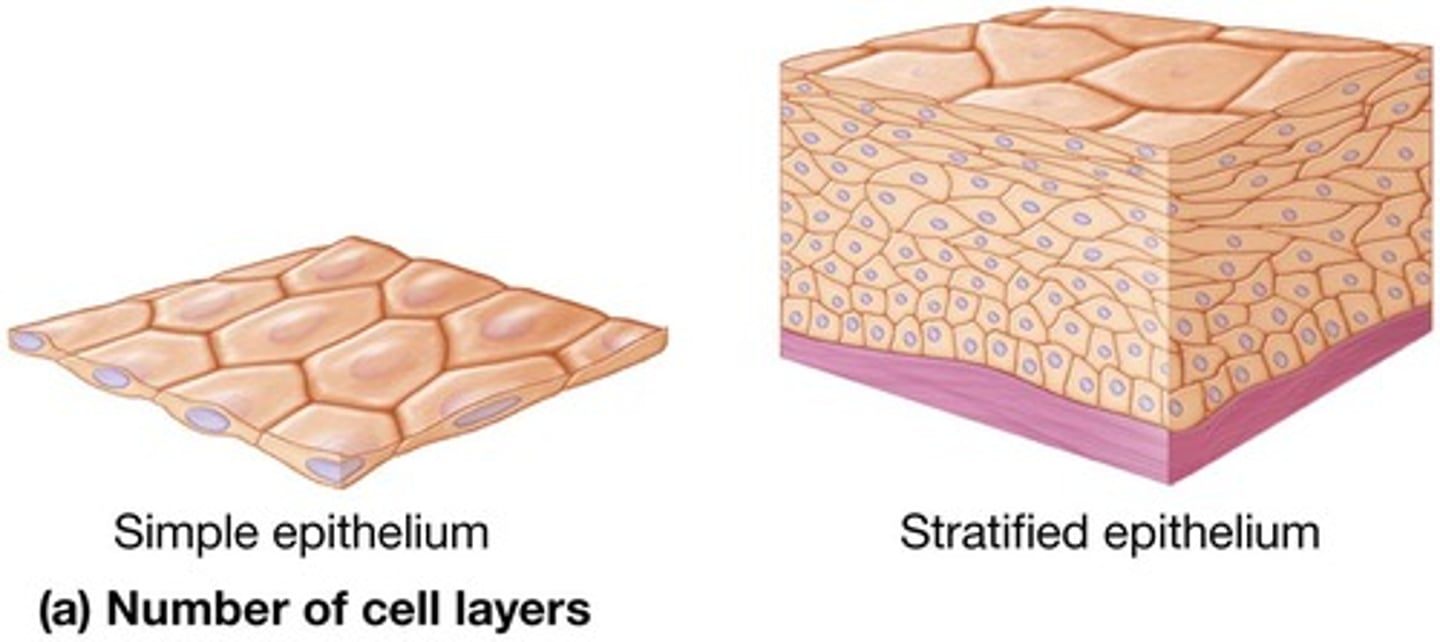
Stratified epithelia
Epithelial tissue classified as more than one cell layer.
Squamous cells
Flattened epithelial cells.
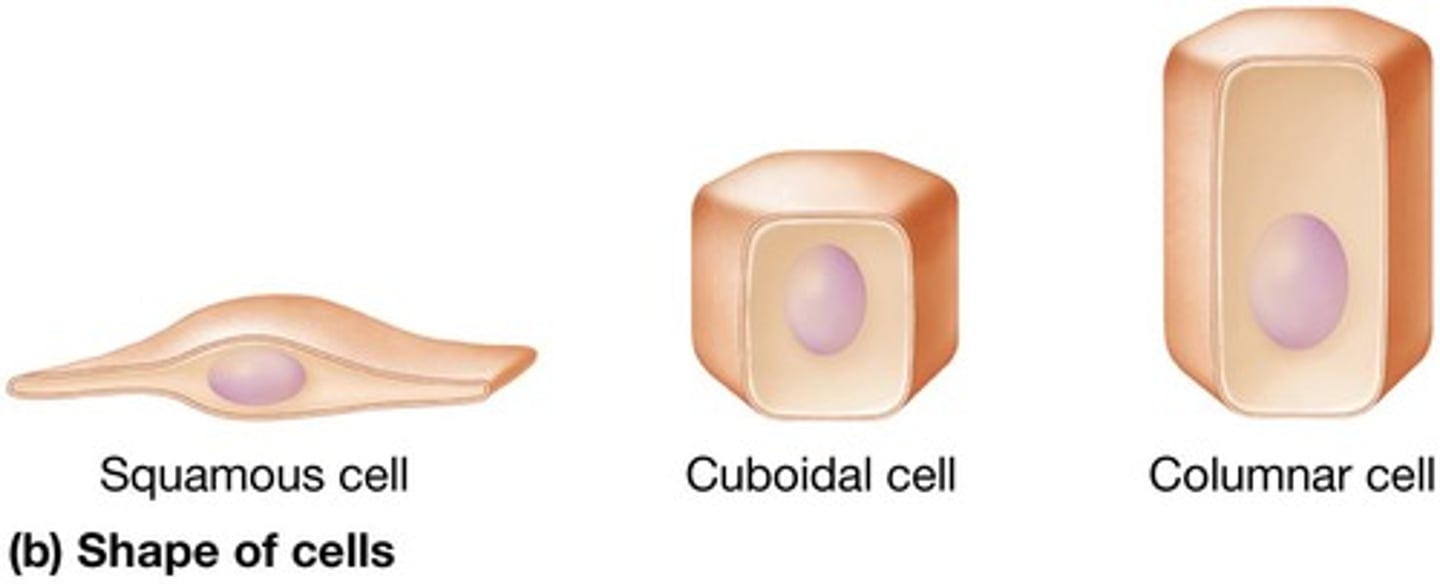
Cuboidal cells
Short epithelial cells.
Columnar cells
Tall and elongated epithelial cells.
Avascular
Epithelial tissues lack blood vessels and must obtain oxygen and nutrients by diffusion from deeper tissues.
Basement membrane
Anchors underlying blood vessels in place and provides a barrier between epithelia and underlying tissues.
ECM
Extracellular matrix found beneath cells rather than between them in a thin basement membrane.
Mechanical stress
Force applied to tissues that is distributed more evenly by desmosomes.
Electrical signals
Communication method between cardiac muscle cells facilitated by gap junctions.
Specialized sensory epithelial cells
Examples include taste buds that detect changes in the environment.
Covering and lining epithelia
Found on inner and outer body surfaces with cells of each shape knitted into broad, flat sheets of varying thickness called membranes.
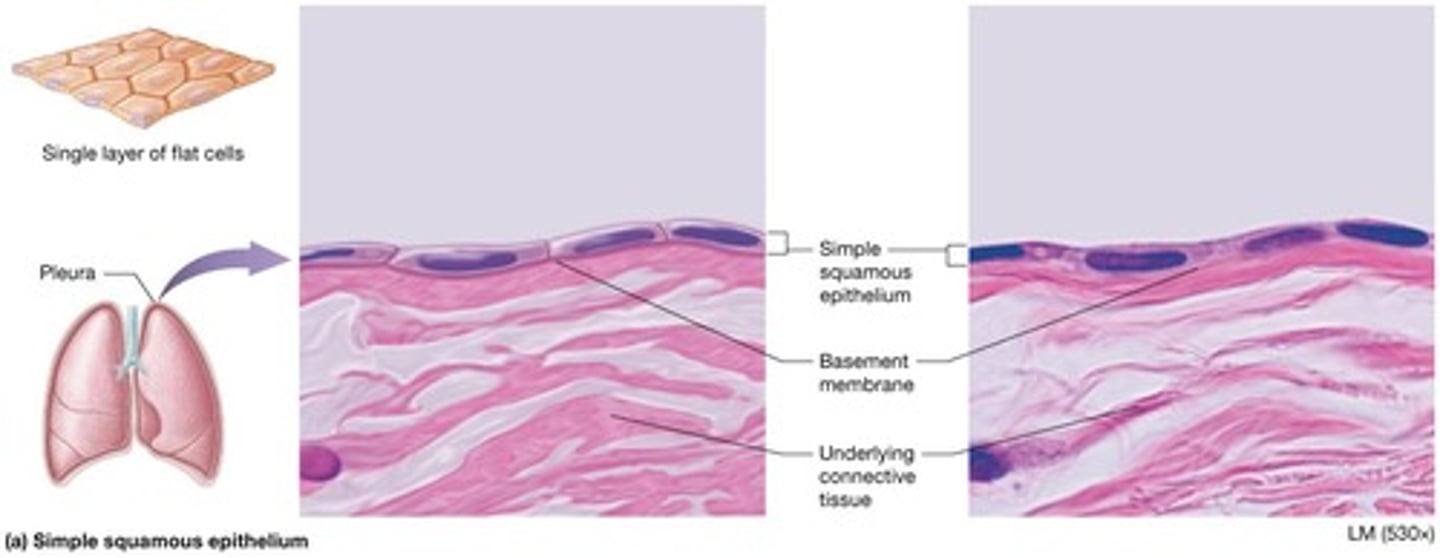
Simple squamous epithelium
Very thin single layer of cells with a 'fried egg' appearance, adapted for rapid diffusion of substances (oxygen, carbon dioxide, fluids, and ions).
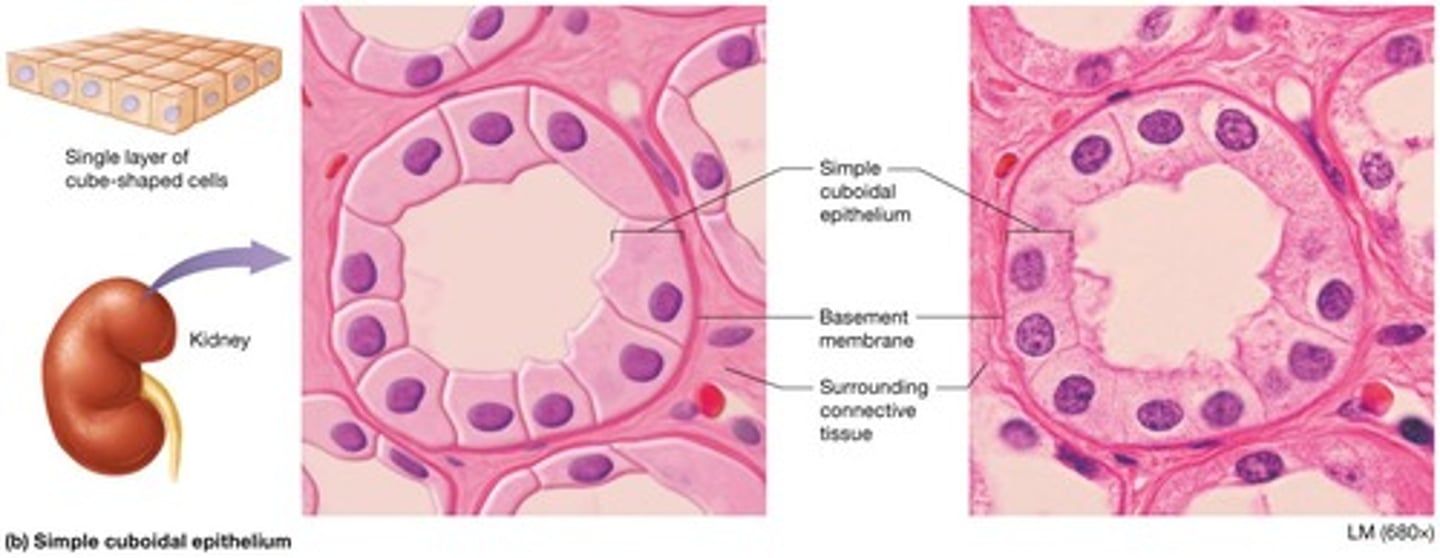
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cube-shaped cells with large central nucleus thin enough for rapid substance diffusion.
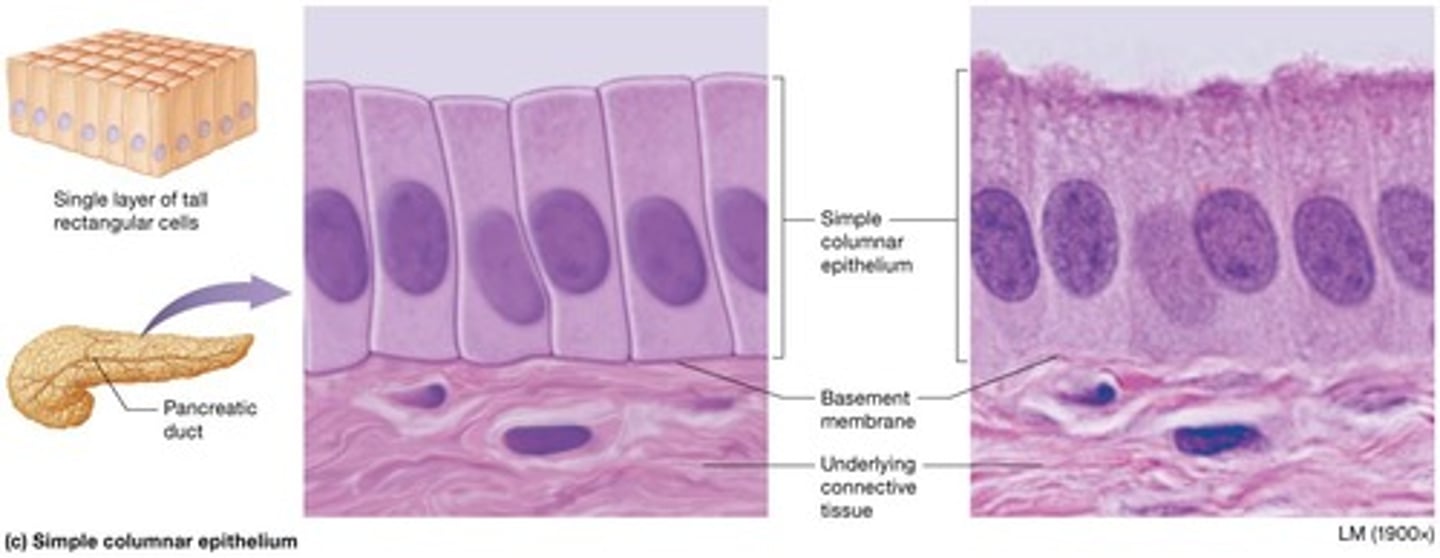
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of rectangular-shaped cells with nuclei in basal portion of cell.
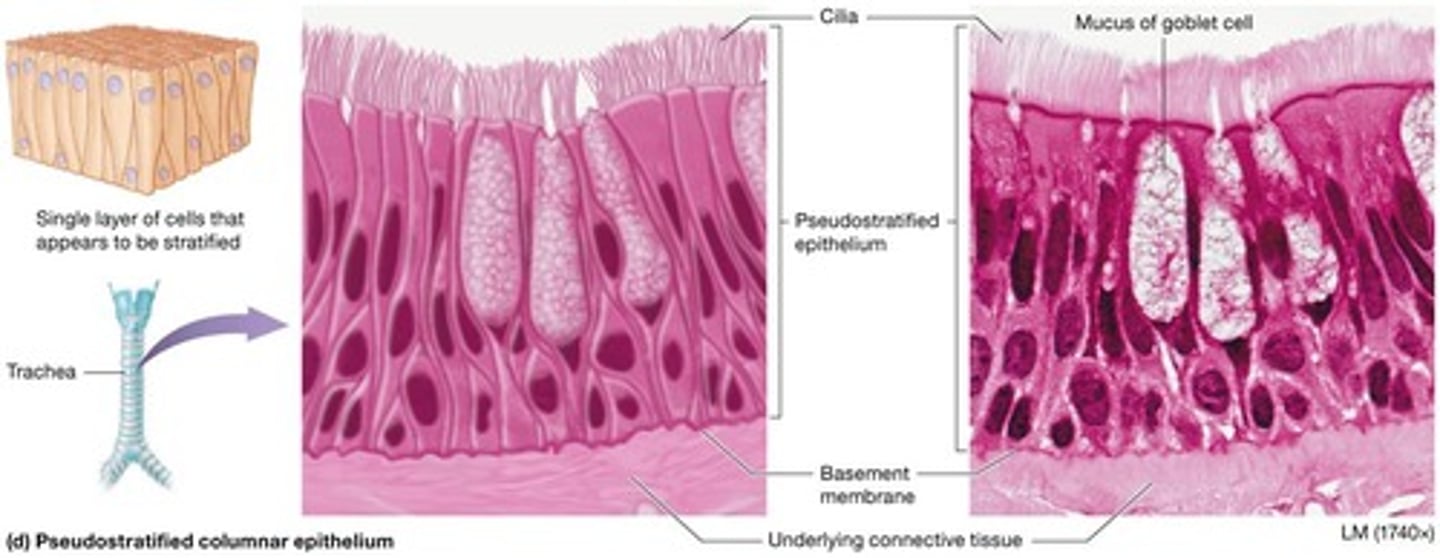
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Appears layered because nuclei are at various heights but only one cell-layer thick with basal plasma membranes firmly in contact with basement membrane.
Paracellular transportation
Substances leak between cells in epithelial membrane, although this is limited due to tight junctions that make spaces between cells nearly impermeable.
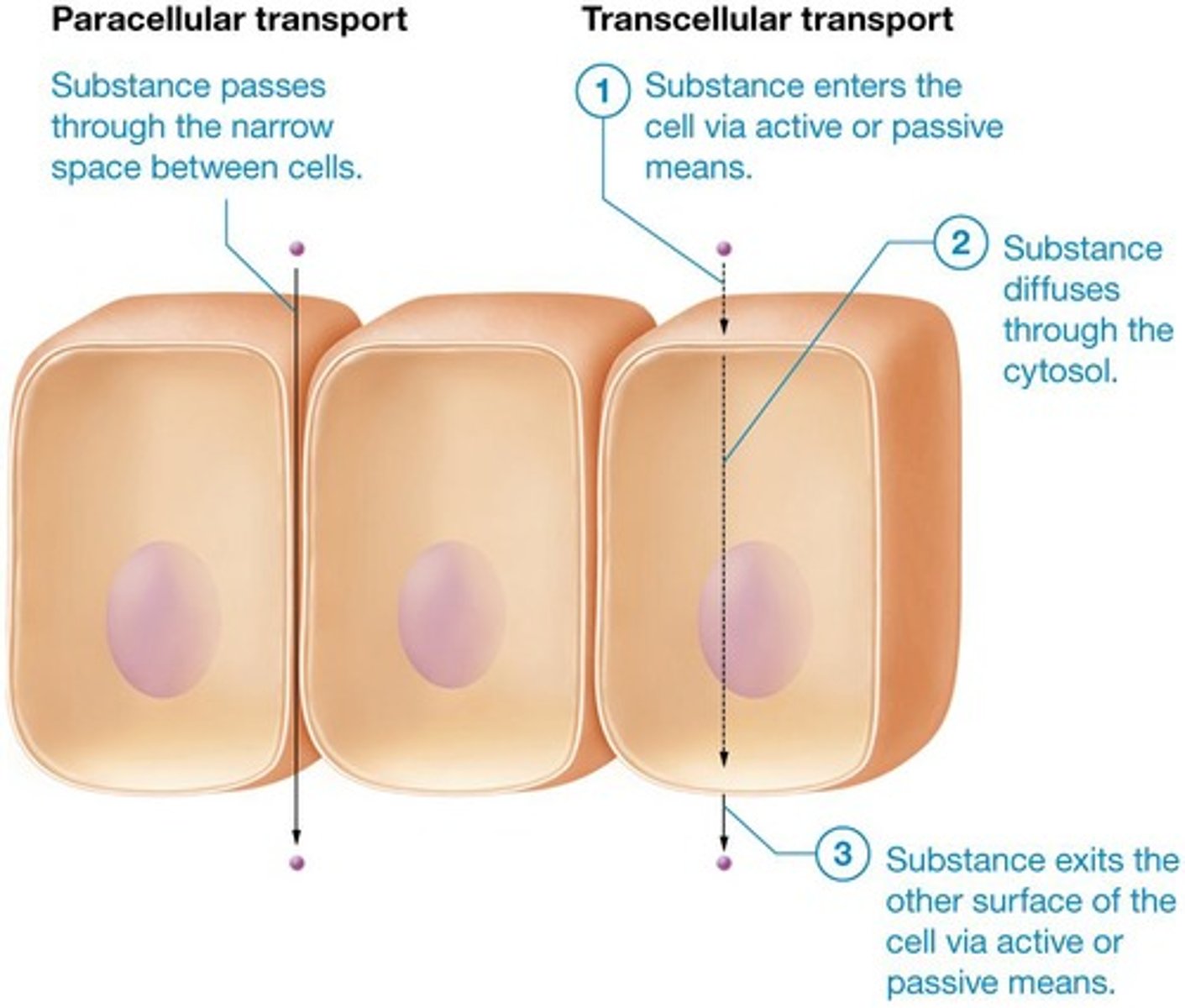
Transcellular transportation
Substance enters cell by crossing plasma membrane, diffusing across cytosol, and exiting cell through plasma membrane at opposite side.
Stratified squamous epithelium
Has 2 types: Keratinized and Nonkeratinized.
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Apical cellular layers are dead, lack nuclei and filled with protein keratin, making tissue tough and resistant to friction.
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
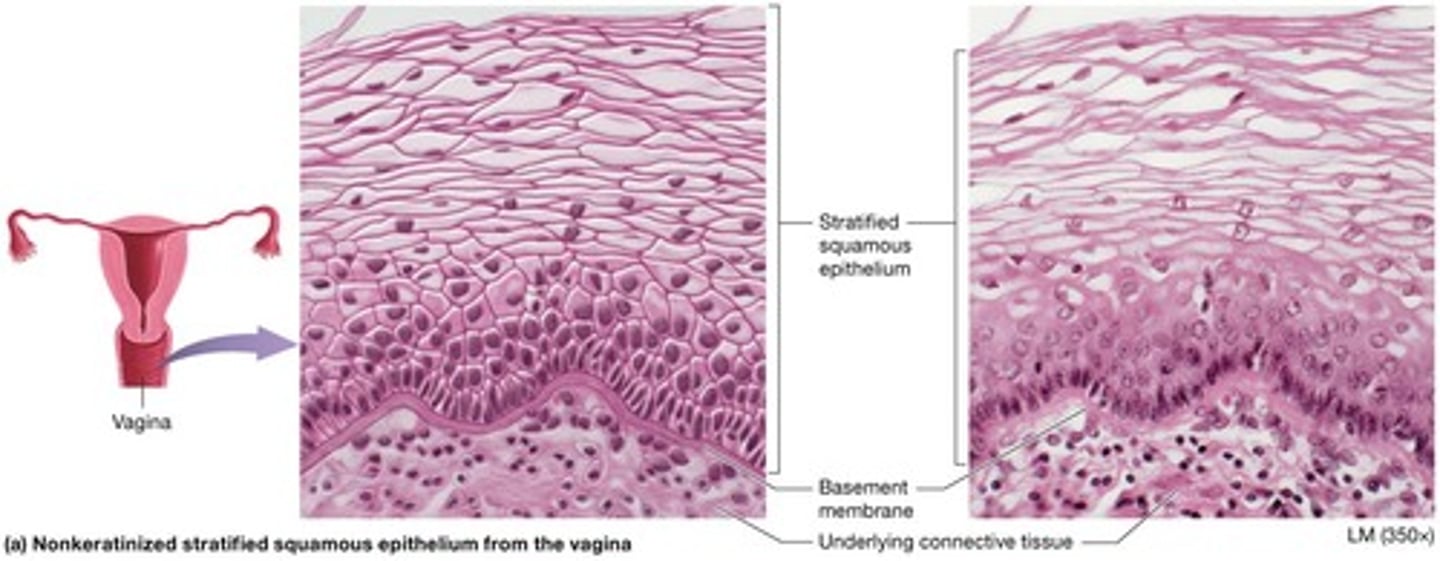
Apical cellular layers retain nuclei, are still alive and located in regions subjected to mechanical stress where surface must remain moist.
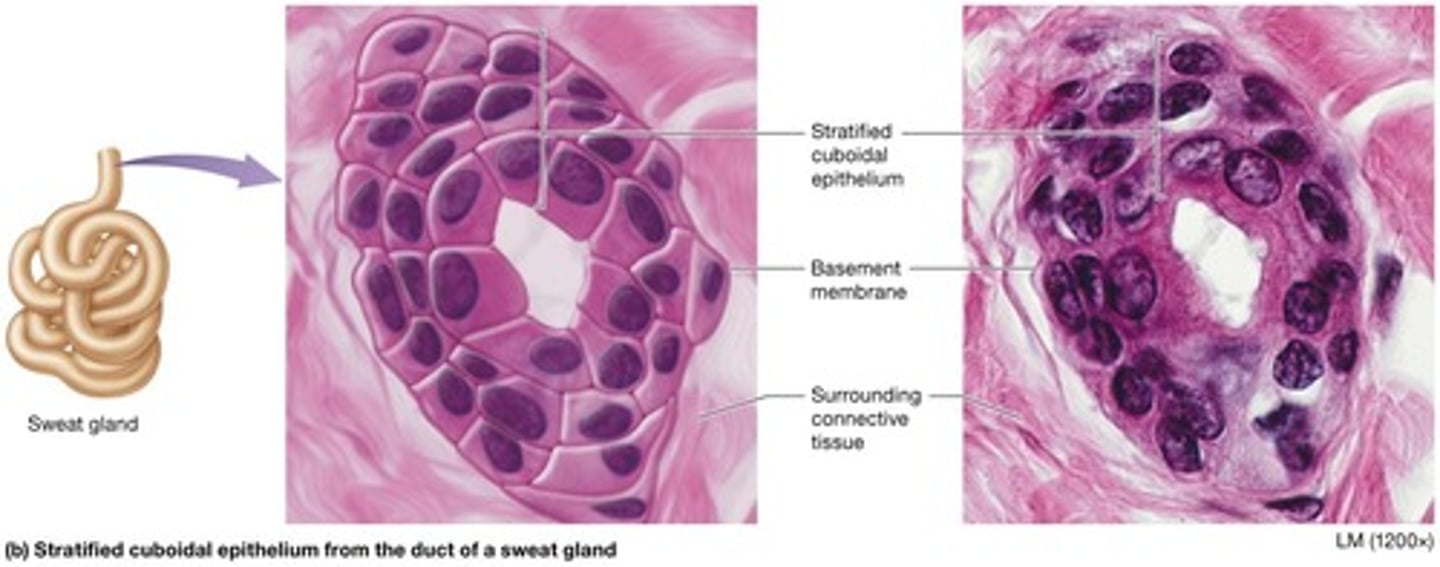
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two cell layers, lines ducts of sweat glands, and is rare in humans.
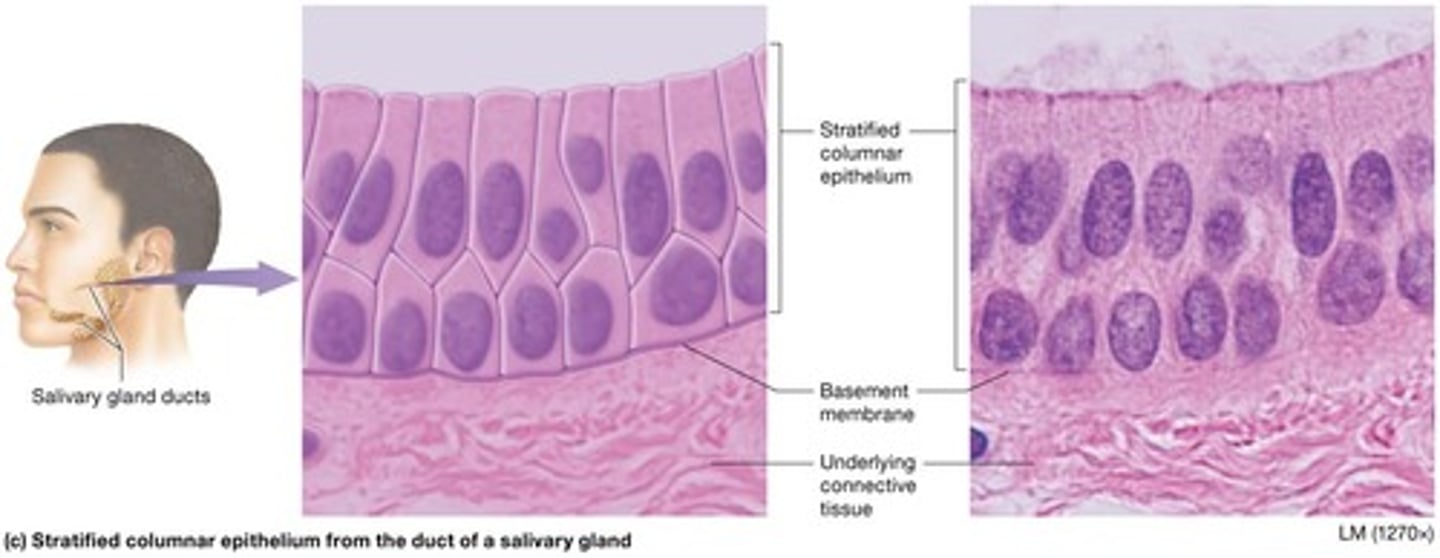
Stratified columnar epithelium
Very few layers with apical layer made of columnar cells and basal cell layer of cuboidal cells, also rare in humans.
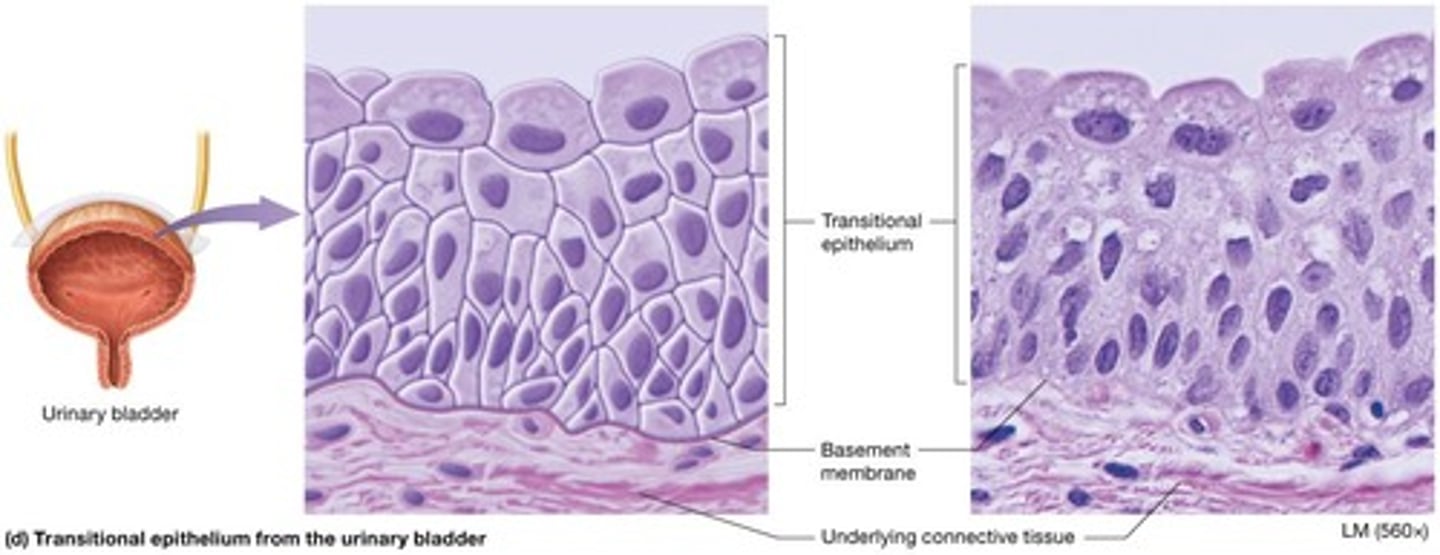
Transitional epithelium
Cuboidal basal cell layers and dome-shaped apical cell layers present in relaxed tissue, allowing tissues to stretch.
Simple epithelia types
Include Simple squamous, Simple cuboidal, Simple columnar, and Pseudostratified columnar.
Stratified tissue types
Include Stratified squamous, Stratified cuboidal, Stratified columnar, and Transitional.
Locations of Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Mouth, throat, esophagus, anus, and vagina.
Locations of Transitional epithelium
Lines interior of kidney, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Function of simple epithelia
Adapted for transportation of substances between different tissues.
Function of stratified epithelium
Best as protective barriers where subjected to high degrees of mechanical stress.
Appearance of Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Appears layered due to nuclei at various heights.
Structure of stratified cuboidal epithelium
Consists of two cell layers.
Structure of stratified columnar epithelium
Consists of very few layers with apical columnar cells.
Gland
Structure of epithelial origin that synthesizes and secretes product from designated secretory cells.
Endocrine glands
Secrete products, usually hormones, directly into bloodstream without use of ducts.
Exocrine glands
Release products onto apical surfaces of epithelium or lining hollow organ that opens to outside of body.
Goblet cells
Most common unicellular exocrine gland found in digestive and respiratory tracts where they secrete mucus.
Simple glands
Ducts that don't branch.
Compound glands
Glands with branched ducts.
Tubular
Cluster shape classification that is long and straight or coiled.
Acinar
Cluster shape classification that is spherical.
Tubuloacinar
Cluster shape classification that includes both tubular and acinar sections.
Merocrine secretion
Used by majority of exocrine glands, including salivary and sweat glands, with products packaged in secretory vesicles for release by exocytosis.
Holocrine secretion
Used by sebaceous glands in skin to secrete sebum, which accumulates in cytosol and is secreted with cell death.
Apocrine secretion
Rare type of secretion in which portions of cytoplasm are pinched off with product being secreted.
Connective tissue proper
Widely distributed in body, connecting tissues and organs to one another.
Fibroblasts
Most common resident cell in connective tissue proper that makes protein fibers, ground substance, and components of ECM.
Adipocytes
Resident cell found in connective tissues with cytoplasm filled with a single large inclusion containing lipids.
Mast cells
Cells in connective tissue that play a role in immune response.
Phagocytes
Cells in connective tissue that engulf and digest cellular debris and pathogens.
Immune system cells
Cells found throughout connective tissues that are involved in immune responses.
Blood
Fluid connective tissue that serves as the main transport medium in the body.
Shock absorption
Function provided by cartilage and fat in connective tissues to protect internal organs.
Loose connective tissue
Mostly ground substance containing all three types of protein fibers, fibroblasts, and occasionally adipocytes, found beneath the epithelium of skin and in membranes lining body cavities.
Dense connective tissue
Made primarily of protein fibers, grouped into three classes: dense irregular, dense regular collagenous, and dense regular elastic connective tissue.
Dense irregular connective tissue
Predominantly disorganized collagen bundles that resist tension in all three planes of movement, found in high tension areas such as the dermis.
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue
Organized into parallel collagen bundles, found in tendons and ligaments, and subject to tension in one plane of movement.
Dense regular elastic connective tissue
Mostly parallel-oriented elastic fibers with randomly oriented collagen fibers, found in walls of organs that must stretch, such as large blood vessels.
Reticular tissue
Mostly reticular fibers produced by fibroblasts, forming fine networks that support small structures like blood and lymphatic vessels.
Adipose tissue
Fat-storing tissue composed of adipocytes and their surrounding fibroblasts and ECM, serving functions such as fat storage, insulation, and shock absorption.
Adipocyte functions
Include fat storage as a major energy reserve, insulation to retain warmth, and shock absorption and protection.
Inflammatory mediators
Chemicals contained in granules of mast cells, such as histamine, that are released during inflammation.
Macrophages
A type of phagocyte that can be either resident or migrant, involved in ingesting foreign substances.
Neutrophils
Migrant phagocytes that ingest foreign substances and microorganisms.
Protein fibers
Fibers in connective tissue that include collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers.
Avascular epithelial tissues
Epithelial tissues that lack blood vessels and rely on connective tissue for nutrients and support.
Weblike nets
Structures formed by reticular tissue that trap old and foreign cells, found in lymph nodes and spleen.
Energy reserve of body
The primary function of adipose tissue, storing fat as a major source of energy.