SBI3U - U1 Origins, Prokaryotes, Viruses and Immune System Practice Test
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*SBI3U UNIT 1 feb. 2024 abx: antibiotics * M/C from feb. 2023 tests at the beginning of the knowt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
*Which of the following organisms first gave Earth it’s oxygen-containing atmosphere
a. | cyanobacteria |
b. | early protozoans |
c. | methanogens |
d. | plants |
e. | green algae |
a. | cyanobacteria |
*Which of the following is NOT true
a. | some scientists suggest that meteorites and comets seeded earth with organic molecules |
b. | from the time of the ancient Greeks until the nineteenth century, it was widely accepted that life are from non-living matter on a regular and continuing basis. |
c. | the earliest life was much simpler than anything living today |
d. | deep ocean vents seem to be the most likely candidates for where protocols first arose. |
e. | the first life on Earth likely appeared four million years ago. |
e. | the first life on Earth likely appeared four million years ago. |
*If the atmosphere of the early Earth had been oxidizes instead of reducing, life might never have arisen. What is the main reason for this?
a. | aerobic respiration is too complex to have been invented by the earliest organisms |
b. | the carbon dioxide to form carbon compounds would have been absent from an oxidizing atmosphere |
c. | oxygen is corrosive and tends to destroy organic compounds by stripping off electrons; a reducing atmosphere tends to add electrons and thus fosters the buildup of organic compounds |
d. | atmospheric oxygen would have created an ozone layer, which would blocked out the ultraviolet light essential for the prebiotic synthesis of organic molecules |
d. | atmospheric oxygen would have created an ozone layer, which would blocked out the ultraviolet light essential for the prebiotic synthesis of organic molecules |
*Which of the following is NOT true?
a. | bioremediation is the use of prokaryotes (and other organisms) to clean up pollution |
b. | prokaryotic decomposers are the mainstays of human sewage-treatment facilities |
c. | archaea convert nitrogen compounds from the atmosphere into nitrogen gas that plants can take up and use. |
d. | there are more beneficial bacteria than disease causing |
e. | bacteria can evolve antibiotic resistance within two weeks |
c. | archaea convert nitrogen compounds from the atmosphere into nitrogen gas that plants can take up and use. |
*the term for a closer association between two or more species is
a. | symbiosis |
b. | interdependence |
c. | associative living |
d. | colonialism |
e. | mutualism |
a. | symbiosis |
*normal bacterial inhabitants of the human body
a. | are naturally resistant to antibiotics |
b. | are able to outcompetes some invading pathogens and thus are one of the body’s defence mechanisms |
c. | can be transformed into pathogenic forms if a person’s resistance to disease is low |
d. | are unable to survive the human body’s defence mechanisms |
e. | none of the above |
b. | are able to outcompetes some invading pathogens and thus are one of the body’s defence mechanisms |
*which of the following organisms are targets for viruses ?
a. | animals |
b. | bacteria |
c. | plants |
d. | a) and c) |
e. | a) and b) |
d. | a) and c) |
*which of the following is false?
a. | all viruses have capsids made of proteins |
b. | the virus uses either DNA or RNA at its core, but not both |
c. | all viruses are phage viruses |
d. | viruses can be replicated only after they enter a living cell |
e. | an infected person will display visible symptoms |
c. | all viruses are phage viruses |
*the envelope of an enveloped virus
a. | is then made from the host cell membrane |
b. | is coded for by viral genes |
c. | helps the virus insert its DNA into the host cell genome |
d. | mutates rapidly, thereby helping the virus evade an immune response |
e. | accounts for viruses’ resistance to abx |
a. | is then made from the host cell membrane (I think) |
*mutant and cancerous cells are destroyed by which cells?
a. | helper T |
b. | memory |
c. | macrophages |
d. | cytotoxic T |
e. | plasma B |
d. | cytotoxic T (killer T) |
*successful inculcation against smallpox used
a. | scabs from smallpox sores |
b. | pus and exudates from open smallpox sores |
c. | blood from a person who had become immune to smallpox |
d. | material from a cowpox sore |
e. | all of the above |
d. | material from a cowpox sore |
*which statement is NOT true
a. | when an invading bacterium is destroyed by a macrophage, its antigens are preserved and presented on the macrophage’s cell membrane. |
b. | antibodies attack and destroy invading antigens |
c. | helper T cells recognize both the MHC and antigens on the surface of macrophages |
d. | self-cells have MHC markers |
e. | helper T cells help the cells of th immune system communicate with each other |
b. | antibodies attack and destroy invading antigens (they mark them for destruction) |
*which of the following can be effective in preventing viral infection in humans
a. | taking abx |
b. | getting vaccinated |
c. | applying antibacterial cream |
d. | both a) and b) |
e. | both a) and c) |
b. | getting vaccinated |
*gram positive bacteria react to which of the following whereas gram negative bacteria do not?
a. | presence of oxygen |
b. | presence of chemical stain |
c. | presence of light |
d. | absence of carbohydrates |
e. | presence of magnetic fields |
b. | presence of chemical stain |
*cyanobacteria
a. | are photosynthetic archaea |
b. | evolved from archaea |
c. | are chemoautotrophs |
d. | are of the same nutritional type as the earliest forms of life |
e. | bloom in lakes contaminated with organic wastes |
e. | bloom in lakes contaminated with organic wastes (no clue tbh) |
*a patient comes to a Kenora doctor because of a large, bull’s eye shaped, red rash that has a clear patch in the centre. originally there was an insect bite in the middle of the rash. which of the following diseases would the physician immediately suspect?
a. | influenza |
b. | smallpox |
c. | malaria |
d. | Lyme disease |
e. | c.diff |
d. | Lyme disease |
Which of the following groups are types of life in the order in which they are thought to have appeared on the Earth (from earliest to most recent)?
a. | heterotrophic organisms, photosynthetic organisms, organisms tolerant of oxygen, eukaryotic cells |
b. | organisms tolerant of oxygen, photosynthetic organisms, heterotrophic organisms, eukaryotic cells |
c. | organisms tolerant of oxygen, eukaryotic cells, photosynthetic organisms, heterotrophic organisms |
d. | photosynthetic organisms, organisms tolerant of oxygen, heterotrophic organisms, eukaryotic cells |
e. | eukaryotic cells, organisms tolerant of oxygen, autotrophic organisms, photosynthetic organisms |
a. | heterotrophic organisms, photosynthetic organisms, organisms tolerant of oxygen, eukaryotic cells |
A stromatolite is
a. | a fossilized bacterial mat probably formed mainly by ancient heterotrophic bacteria. |
b. | a fossilized bacterial mat probably formed mainly by ancient cyanobacteria. |
c. | a living bacterial mat formed mainly by cyanobacteria. |
d. | a living algal mat formed mainly by green algae. |
e. | a living algal mat formed mainly by slime molds. |
b. | a fossilized bacterial mat probably formed mainly by ancient cyanobacteria. |
Which of the following organisms first gave Earth its oxygen-containing atmosphere?
a. | cyanobacteria. | c. | early protozoans |
b. | methanogens | d. | Plants |
a. | cyanobacteria. |
Many of the organic compounds essential for life, such as amino acids and nucleotides, could NOT assemble spontaneously in the presence of
a. | hydrogen. | c. | CO2 | e. | argon. |
b. | free oxygen. | d. | nitrogen. |
|
|
b. | free oxygen. |
Fossil evidence of the earliest living organisms now dates back
a. | 570 million years. | d. | more than 5 billion years. |
b. | 1.4 billion years. | e. | to 4004 B.C. |
c. | about 3.8 billion yrs |
|
|
c. | about 3.8 billion yrs |
The primitive atmosphere did NOT contain
a. | water vapor. | d. | free oxygen. |
b. | free nitrogen. | e. | inert gases. |
c. | free hydrogen |
|
|
d. | free oxygen. |
The transition of the early earth's atmosphere from one rich in H2 to one rich in O2 may be attributed to
a. | photosynthesis. |
b. | photophosphorylation. |
c. | cyclic AMP. |
d. | chlorophyll breakdown. |
e. | all of these |
a. | photosynthesis. |
Experiments like those first performed by Miller and Urey in 1953 demonstrated that
a. | DNA forms readily and reproduces itself. |
b. | many of the lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleotides required for life can form under abiotic conditions. |
c. | complete, functioning prokaryotic cells are formed after approximately three months. |
d. | a lipid-protein film will eventually be formed by thermal convection. |
e. | all of these |
b. | many of the lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleotides required for life can form under abiotic conditions. |
The first organisms
a. | absorbed their food supplies from the organic molecules that surrounded them. |
b. | were eukaryotes. |
c. | utilized fermentation for energy production. |
d. | utilized ATP. |
e. | all of these except "were eukaryotes." |
e. | all of these except "were eukaryotes." |
The presence of free oxygen in the atmosphere
a. | was a result of the accumulation of the by-products of photosynthesis. |
b. | prevented the further spontaneous generation of life. |
c. | provided the opportunity to extract more energy through aerobic respiration. |
d. | did not occur immediately after the earth was formed. |
e. | all of these |
e. | all of these |
The conversion of solar energy to chemical energy occurs during
a. | glycolysis. | c. |
| respiration. | e. | chemosynthesis. |
b. | photosynthesis. | d. |
| fermentation. |
|
|
b. | photosynthesis. |
Chemosynthetic forms of life
a. | derive energy from sunlight. |
b. | derive energy by stripping hydrogen from inorganic compounds such as sulfur compounds. |
c. | are anaerobic forms that live in the dark. |
d. | are one form of heterotrophic life. |
e. | are unable to generate enough energy to synthesize complex food-storage molecules. |
b. | derive energy by stripping hydrogen from inorganic compounds such as sulfur compounds. |
Heterotrophs are
a. | self-feeding. |
b. | independent of other forms of life for sustenance. |
c. | unable to participate in the web of life. |
d. | animals only. |
e. | none of these |
e. | none of these |
When molecules are broken apart in respiration,
a. | the heat produced is used to drive biological reactions. |
b. | the oxygen in the compounds that are broken apart is used as an energy source. |
c. | the energy released in respiration is channeled into molecules of ATP. |
d. | ATP is converted into ADP. |
e. | ADP is released as a waste product. |
c. | the energy released in respiration is channeled into molecules of ATP. |
C6H12O6 is the chemical formula for
a. | glucose.. | c. | protein. |
b. | starch. | d. | adenosine triphosphate. |
a. | glucose.. |
Which of the following liberates the most energy in the form of ATP?
a. | aerobic respiration |
b. | anaerobic respiration |
c. | alcoholic fermentation |
d. | lactate fermentation |
e. | All liberate the same amount, but through different means. |
a. | aerobic respiration |
Under anaerobic conditions, muscle cells produce
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fermentation
a. | may occur in a muscle under anaerobic conditions. |
b. | produces more ATP than is liberated in the hydrogen transfer series. |
c. | breaks down glucose in reaction with oxygen. |
d. | is restricted to yeasts. |
e. | None of these. |
a. | may occur in a muscle under anaerobic conditions. |
Energy released during cellular respiration is stored in a compound called
a. | glucose. | c. |
| ATP. | e. | RNA. |
b. | ADP. | d. |
| DNA. |
|
|
c. |
| ATP. |
The process of using sunlight to convert low-energy compounds into higher-energy compounds is known as
a. | fermentation. | d. | chemosynthesis. |
b. | respiration. | e. | phosphorylation. |
c. | photosynthesis. |
|
|
c. | photosynthesis. |
Identify the products of photosynthesis
a. | carbon dioxide and water. |
b. | glucose and oxygen. |
c. | glucose and carbon dioxide. |
d. | water and sunlight. |
e. | carbon dioxide and oxygen. |
b. | glucose and oxygen. |
What are the disadvantages of anaerobic respiration in the human body?
a. | Less energy is released from glucose. |
b. | The product of the reaction is potentially harmful. |
c. | Both a) and b) are disadvantages. |
d. | There are no disadvantages. |
e. | Anaerobic respiration is advantageous because oxygen is not needed. |
c. | Both a) and b) are disadvantages. |
Which of the following are of the smallest size?
a. | viruses | c. |
| fungi | e. | plants |
b. | bacteria | d. |
| protistans |
|
|
a. | viruses |
The short, thin appendages that help prokaryotes adhere to surfaces, such as rocks or cells, are called
a. | flagella. | c. |
| cilia. | e. | plasmids. |
b. | pili. | d. |
| mesosomes. |
|
|
b. | pili. |
Which of the following is NOT an environment in which you would find Archaea?
a. | salt marshes | d. | ocean vents |
b. | hot springs | e. | swamps |
c. | active volcanoes |
|
|
c. | active volcanoes |
Bacterial cell walls contain a unique substance called
a. | cellulose. | d. | glycogen. |
b. | peptidoglycan. | e. | proteinoid |
c. | phospholipid. |
|
|
b. | peptidoglycan. |
Evidence for the closer relationship of archaea to eukaryotes than to bacteria includes all of the following except
a. | similar RNA. |
b. | similar DNA. |
c. | the presence of peptidoglycan in the cell wall. |
d. | similar organelles. |
c. | the presence of peptidoglycan in the cell wall. |
In bacteria, DNA is found
a. | in the nucleus alone. |
b. | in organelles alone. |
c. | in both the nucleus and organelles. |
d. | attached to the cell wall as a single circular thread. |
e. | as particles scattered throughout the bacterial cell. |
d. | attached to the cell wall as a single circular thread. |
Which one of the following statements is NOT true?
a. | Archaea are one of the most abundant cell types below 1,000 meters in the oceans. |
b. | Archaea that thrive in extremely hot places are known as thermophiles. |
c. | Archaea that thrive in anaerobic places are known as anaerophiles. |
d. | Archaea that thrive in extremely salty places are known as halophiles. |
e. | Human intestinal gas is largely produced by archaea in our intestines that are referred to as methanogens. |
c. | Archaea that thrive in anaerobic places are known as anaerophiles. |
Bacteria
a. | have cell walls composed of cellulose. |
b. | reproduce primarily by conjugation. |
c. | have a single chromosome. |
d. | are eukaryotic. |
c. | have a single chromosome. |
Which of the following concerning bacteria is true?
a. | They have multiple chromosomes. |
b. | They produce gametes. |
c. | They possess circular DNA molecules. |
d. | They are eukaryotic. |
c. | They possess circular DNA molecules. (plasmids!) |
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of bacterial cells?
a. | they are prokaryotic and single celled |
b. | contain no membrane-bound organelles |
c. | have a single chromosome |
d. | majority are pathogens |
e. | reproduce asexually |
d. | majority are pathogens |
Three of the four answers listed below are descriptions of bacterial shape. Select the exception.
a. | coccus | b. | bacillus | c. | pili | d. | spiral |
c. | pili |
Pairs of rod-shaped bacteria are called
a. | cocci. | c. |
| diplobacilli. | e. | vibrios. |
b. | bacilli. | d. |
| spirochetes. |
|
|
c. |
| diplobacilli. |
Spherical bacteria are called
a. | bacilli. | c. |
| cocci. | e. | all of these |
b. | spirilla. | d. |
| bacteriophages. |
|
|
c. |
| cocci. |
A helical or spiral bacterium is called a
a. | spirillum. | c. | coccus. |
b. | bacillus. | d. | bacillus or coccus. |
a. | spirillum. |
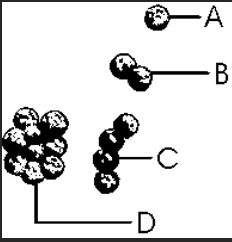
Which label is pointing to a sample of staphylococcus?
a. | A | b. | B | c. | C | d. | D |
d. | D |
A bacterial colony that is observed to survive and reproduce only when no air is around would be classified as which of the following?
a. | obligate aerobe | d. | facultative anaerobe |
b. | obligate anaerobe | e. | none of the above |
c. | facultative aerobe |
|
|
b. | obligate anaerobe |
Small circular extrachromosomal molecules of DNA in bacteria are called
a. | plasmids. | c. |
| pili. | e. | transferins. |
b. | desmids. | d. |
| F particles. |
|
|
a. | plasmids. |
The pseudosex process by which one bacterial cell transfers DNA to another is
a. | fission. | c. |
| conjugation | e. | none of these |
b. | gamete fusion. | d. |
| lysis. |
|
|
c. |
| conjugation |
Which of the following allow the bacteria to join together to transfer genes?
a. | flagella |
b. | pores |
c. | connecting channels |
d. | pili |
e. | stylets |
d. | pili |
During conjugation between two E. coli cells, which of the following would most likely occur?
a. | Transfer of an antibiotic. |
b. | Transfer of a plasmid. |
c. | Transfer of viral genes. |
d. | Lysogeny. |
e. | Ttransfer of a plasmid and transfer of viral genes. |
b. | Transfer of a plasmid. |
Which of the following is the basis for determining the causative agent of most infectious diseases?
a. | Koch's postulates |
b. | Pasteur's laws |
c. | trial and error |
d. | process of elimination |
e. | None of the choices are correct. |
a. | Koch's postulates |
The term for a close association between two or more species is
a. | symbiosis. | d. | colonialism. |
b. | obligate anaerobe | e. | mutualism. |
c. | associative living. |
|
|
a. | symbiosis. |
Which statement is inaccurate?
a. | Viruses are not able to move by themselves. |
b. | Viruses are not able to reproduce by themselves. |
c. | Viruses are not structurally organized. |
d. | Some biologists consider viruses to be forms of life and other biologists consider them to be nonlife. |
e. | Viruses contain instructions to make themselves. |
c. | Viruses are not structurally organized. |
Which of the following statements is FALSE? Antibiotics
a. | serve as an agent of natural selection in pathogenic bacteria. |
b. | are effective against viruses. |
c. | may produce potent side effects. |
d. | are normal metabolic by-products of certain microorganisms. |
e. | when used by women often have to be accompanied by antifungal drugs to control yeast infections. |
b. | are effective against viruses. |
Which of the following is FALSE?
a. | The outer coats of all viruses are alike. |
b. | The virus uses either DNA or RNA at its core, but not both. |
c. | Viruses can be replicated only after they enter a living cell. |
d. | Most viruses have a protein coat or covering. |
e. | A virus may not kill a host cell but may become inactive for a period of latency. |
a. | The outer coats of all viruses are alike. |
When a virus takes over the machinery of a cell, it forces the cell to manufacture
a. | more mitochondria for energy for the virus. |
b. | more liposomes to isolate themselves from water. |
c. | more food particles. |
d. | more viral particles. |
d. | more viral particles. |
Four of the five answers listed below are found in viruses. Select the exception.
a. | coat | c. |
| DNA | e. | envelope |
b. | prions | d. |
| tail fibers |
|
|
b. | prions |
Which of the these diseases is NOT caused by a virus?
a. | common cold | c. |
| influenza | e. | tuberculosis |
b. | smallpox | d. |
| polio |
|
|
e. | tuberculosis |
Which of the following represents the correct stages of viral replication?
a. | synthesis, assembly, release, attachment |
b. | assembly, release, attachment, synthesis |
c. | release, attachment, synthesis, assembly |
d. | attachment, synthesis, assembly, release |
e. | none of the above |
d. | attachment, synthesis, assembly, release |
Which of the following statements concerning viruses and human health is FALSE?
a. | In many diseases caused by viruses, the virus attacks cells as it reproduces. |
b. | Most viral infections are difficult to treat but they can be finally destroyed by antibiotics. |
c. | Some viruses can remain dormant in the body for years before disease symptoms appear. |
d. | Oncogenic viruses can add genes to a cell and turn it into a cancer cell. |
e. | Many viral diseases can be controlled through vaccinations. |
b. | Most viral infections are difficult to treat but they can be finally destroyed by antibiotics. |
Which of the following is one of the body's first lines of defense against infection?
a. | several nonspecific antibodies |
b. | several nonspecific amino acid toxins |
c. | nonspecific obstacles such as skin and mucus |
d. | increased production of certain hormones and changes in microcirculation |
e. | None of the choices are correct. |
c. | nonspecific obstacles such as skin and mucus |
The major result of the inflammatory response is to
a. | initiate the production of antibodies. |
b. | recruit white blood cells to disinfect and clean damaged tissues. |
c. | initiate cell-mediated immune responses. |
d. | initiate humoral-mediated immune responses. |
e. | initiate the production of killer cells. |
b. | recruit white blood cells to disinfect and clean damaged tissues. |
Why do diseases involving widespread infection usually result in a fever?
a. | because the rapid multiplication of the invading microorganisms results in extra heat production |
b. | because the inflammatory and immune responses result in extra heat production |
c. | because the microorganisms trick the brain's temperature control center into creating a hot environment that favors their growth |
d. | because the brain's temperature control center responds to systemic inflammation by creating a hot environment unfavorable to microorganisms |
e. | None of the choices are correct. |
d. | because the brain's temperature control center responds to systemic inflammation by creating a hot environment unfavorable to microorganisms |
The two main functions of the lymphatic system are
a. | coagulating blood and fighting infections. |
b. | producing hormones that regulate the immune system and coagulating blood. |
c. | producing hormones that regulate the immune system and fighting infections. |
d. | returning tissue fluid to the circulatory system and coagulating blood. |
e. | returning tissue fluid to the circulatory system and fighting infections. |
e. | returning tissue fluid to the circulatory system and fighting infections. |
Antibodies are
a. | amino acids. | c. |
| carbohydrates. | e. | nucleic acids |
b. | lipids. | d. |
| proteins. |
|
|
d. |
| proteins. |
A substance that can elicit an immune response is a(n)
a. | complement. | c. |
| histamine. | e. | antigen. |
b. | interferon. | d. |
| antibody. |
|
|
e. | antigen. |
The host range of a virus is determined by
a. | the proteins on its surface and that of the host. |
b. | whether its nucleic acid is DNA or RNA. |
c. | the proteins in the host's cytoplasm. |
d. | the enzymes produced by the virus before it infects the cell. |
e. | the enzymes carried by the virus. |
a. | the proteins on its surface and that of the host. |
Which cells are divided into two groups: T cells and B cells?
a. | macrophages | d. | platelets |
b. | lymphocytes | e. | all of these |
c. | complement cells |
|
|
b. | lymphocytes |
Which cells produce and secrete antibodies that set up bacterial invaders for subsequent destruction by other white blood cells?
a. | phagocytes | d. | T cells |
b. | macrophages | e. | all of these |
c. | plasma B cells |
|
|
c. | plasma B cells |
Body cells have proteins that are self-markers located
a. | in their nuclei. |
b. | in the endoplasmic reticulum. |
c. | in the mitochondria. |
d. | on the cell membrane. |
e. | inside the Golgi bodies. |
d. | on the cell membrane. |
The purpose of a vaccine is to
a. | produce a mild case of the disease. |
b. | stimulate the immune response. |
c. | cause memory cells to be formed. |
d. e. | stimulate the immune response and cause memory cells to be formed. all of the above |
e. all of the above
All but which of the following are good barriers to invasion by microbes?
a. | mucous membranes | d. | urine |
b. | eye secretions | e. | gut bacteria |
c. | broken skin |
|
|
c. | broken skin |
Normal bacterial inhabitants of the human body
a. | are naturally resistant to antibiotics. |
b. | are able to outcompete some invading pathogens and thus are one of the body's defense mechanisms. |
c. | can be transformed into pathogenic forms if a person's resistance to disease is low. |
d. | are unable to survive the human body's defense mechanisms. |
e. | None of these. |
b. | are able to outcompete some invading pathogens and thus are one of the body's defense mechanisms. |
Phagocytes perform their services in
a. | the blood. |
b. | tissue spaces. |
c. | the lymph system. |
d. | a) and b) only. |
e. | All of a), b) and c).. |
e. | All of a), b) and c).. |
The accumulation of fluid at the site of a wound is the result of the secretion of
a. | antibodies. | c. |
| neutrophils. | e. | leukocytes. |
b. | histamines. | d. |
| interferons |
|
|
b. | histamines. |
Which cells produce antibodies?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Which cells are held in reserve to be used for a rapid response to subsequent intruders of the same type?
a. | helper T | c. |
| cytotoxic T | e. | naïve B-cells |
b. | macrophages | d. |
| memory cells |
|
|
d. |
| memory cells |
Which cells are the longest lasting in the body?
a. | helper T | c. |
| cytotoxic T | e. | naïve B-cells |
b. | macrophages | d. |
| memory cells |
|
|
d. |
| memory cells |
Which cells directly destroy body cells infected by viral or fungal parasites?
a. | helper T | c. |
| cytotoxic T | e. | naïve B-cells |
b. | macrophages | d. |
| memory cells |
|
|
c. |
| cytotoxic T |
All of the cells involved in the immune response are
a. | leukocytes. |
b. | erythrocytes. |
c. | white blood cells. |
d. | Both a) and c). |
e. | Both b) and c). |
d. | Both a) and c). |
Body cells have self-markers located
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The markers that identify "self" are actually
a. | genes. | c. | phospholipids (fats). |
b. | proteins. | d. | small surface bumps. |
b. | proteins. |
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Only B cells and their progeny make antibodies. |
b. | The primary immune response is faster and more complete than a secondary immune response. |
c. | Virgin B cells already have antibodies but have not yet encountered an antigen. |
d. | Macrophages will digest invading bacterial cells but do not destroy the antigens that eventually become mounted on the surface of the macrophages. |
e. | Some B cell progeny differentiate into memory cells. |
b. | The primary immune response is faster and more complete than a secondary immune response. |
Antibodies are shaped like the letter
a. | C | b. | E | c. | H | d. | K | e. | Y |
e. | Y |
Which of the following is false regarding an antigen?
a. | It can lead to the generation of an antibody. |
b. | It identifies a pathogen as "foreign" to the body. |
c. | It can be an oligosaccharide (a sugar). |
d. | It passes directly between the plasma membranes of the pathogen and macrophage. |
e. | It forms complexes with the MHC markers. |
d. | It passes directly between the plasma membranes of the pathogen and macrophage. |
Which statement is NOT true?
a. | When an invading bacterium is destroyed by a macrophage, its antigens are preserved. |
b. | Antibodies attack and destroy invading antigens. |
c. | Helper T cells recognize the major histocompatibility complex and antigens on the surface of macrophages. |
d. | Self cells have major histocompatibility complex markers or antigens. |
b. | Antibodies attack and destroy invading antigens. |
antibodies mark/attack antigens for destruction via Cytotoxic T-cells | I think lol |
A vaccine contains
a. | killed pathogen. |
b. | weakened pathogen. |
c. | noninfective fragments of a pathogen. |
d. | full-strength pathogen. |
e. | All except "full-strength pathogen" may be used. |
e. | All except "full-strength pathogen" may be used. |
CTBA: The purpose of a vaccine is to
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When the body's defenses turn against its own cells, the disorder is called
a. | an autoimmune response. |
b. | anaphylactic shock. |
c. | acquired immune deficiency syndrome. |
d. | passive immunity. |
e. | an inflammatory response. |
a. | an autoimmune response. |
Match each term with their appropriate description.
a. | halophiles | c. | thermophiles |
b. | cyanobacteria | d. | methanogens |
__1. Live in temperatures that don’t usually allow life.
__2. These produce "swamp gas."
___3. Live in water of very high salt concentration.
___4. These perform photosynthesis.
C
D
A
B
Match each of the chemical processes with their products.
a. | anaerobic respiration in animals | d. | aerobic cellular respiration |
b. | photosynthesis | e. | anaerobic cellular respiration in yeast cells |
c. | product of respiration |
|
|
_5. alcohol (and carbon dioxide)
__6. lactic acid
__7. adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
___8. water and carbon dioxide
___9. oxygen and glucose
E
A
C
D
B
Match an item with the correct statement below. Not all items will be used.
a. | viruses | f. | vaccines |
b. | capsid | g. | HIV |
c. | bacteriophages | h. | capsule |
d. | host range | i. | adenovirus |
e. | lysis |
|
|
10. microscopic particles capable of reproducing only within living cells
__11. a category of viruses that infect and destroy bacterial cells
__12. the destruction or bursting open of a cell
__13. the limited number of host species, tissues, or cells that a virus or other parasite can infect
___14. the protective protein coat of viruses
___15. an example of a retrovirus: forces host cell to make DNA that codes for building the virus; can lead to AIDS
___16. solutions that are prepared from viral components or inactivated viruses
A
C
E
D
B
G
F