chapter 8 gases part 2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
kinetic theory of gases postulates
gas particle volume is zero, gas particles are in constant random directional motion in straight lines, change direction when colliding with other molecules or container walls, obey newton’s laws, elastic particle collisions
what conversion factor should i always remember
g to kg(SI)
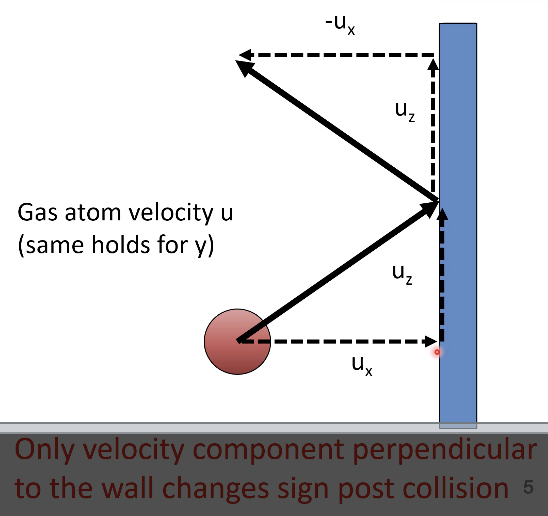
when gas atom collides with wall
only velocity component perpendicular to the wall changes sign
P =
1/3 * N/V * m * mean(u²) where N is number of particles, m is mass of a particle, and mean square velocity
PV =
2/3 * avg kinetic energy (1/2 m u² avg) = 1/3 * N m u²avg
T =
1/3 * NA/R * m u²avg, shows that temperature depends on velocity
average KE of a gas molecule
3/2 RT/NA
with root mean square velocity we can see that
as temperature increases, so does rms
as molar mass increases, rms decreases
root mean square velocity =
√3RT/M
effusion
process by which a gas escapes through a tiny hole into a vacuum
law of effusion and diffusion
RateA/RateB = √MB/MA
diffusion
random movement of one gas through another e.g. drop of ink into water
mean free path
average distance a gas molecule travels between collision
collision frequency
the average number of collisions per second per gas molecule
real/non-ideal gases
gas molecules are not compressible, results in higher pressures than under ideal gas law - excluded volume starts playing a role
real gas molecules will
attract each other at short distances
van der waals equation
(P + n²/V² a)(V - nb) = nRT, where first term accounts for intermolecular attraction and second accounts for excluded volume. a and b are vdw constants
ideal gas behaviour observed at
high temperatures and low pressures
non-ideal gas behaviour observed at
low temperatures and high pressures
compressibility factor
Z = PV/nRT
if z = 1, >1, or <1
ideal gas, excluded volume dominates, attractive forces dominate