III : Innate Immunology
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Innate / Natural Immunity
• Non-specific Pathogens
Innate / Natural Immunity
• 1st & 2nd line of Defense
Innate / Natural Immunity
- the effect gear towards to non-specific pathogen.
- Our skin will protect us against any other pathogen.
Adaptive / Acquired Immunity
• Specific Immunity
Adaptive / Acquired Immunity
• 3rd line of Defense
Adaptive / Acquired Immunity
- Acquire when exposed (to vaccines)
Adaptive / Acquired Immunity
- We have the Lymphocytes – T cells (Cell Immunity) & B cells (Humoral Immunity) both of them can produce a memory cells therefore they can participate to anamnestic response.
Innate Immune System
- Defense against infection that immediately act when a host is attacked by a pathogen.
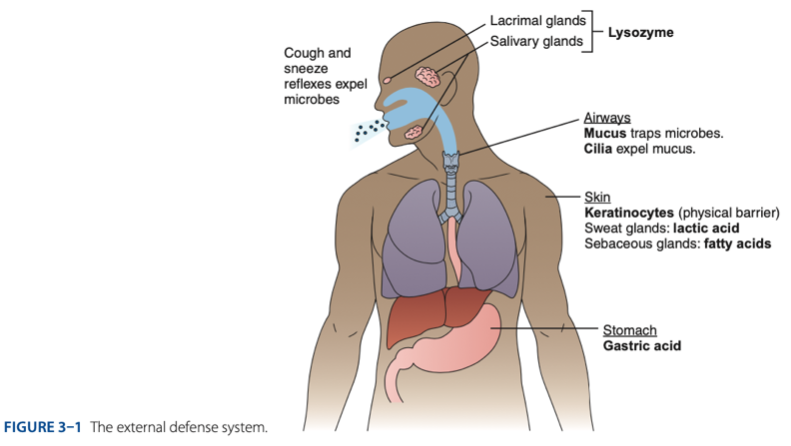
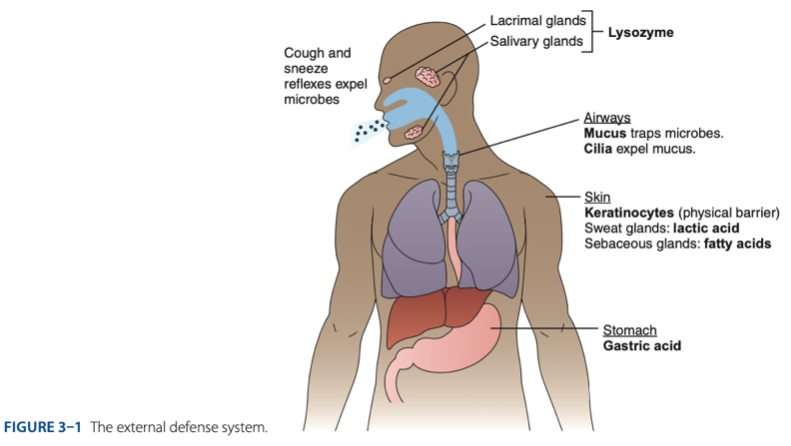
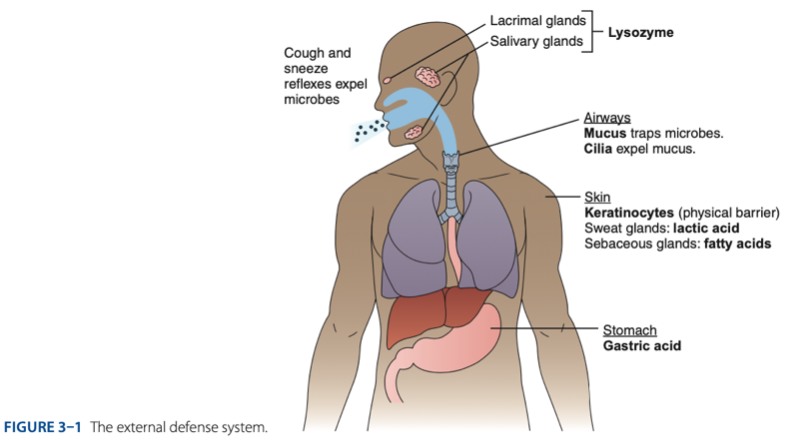
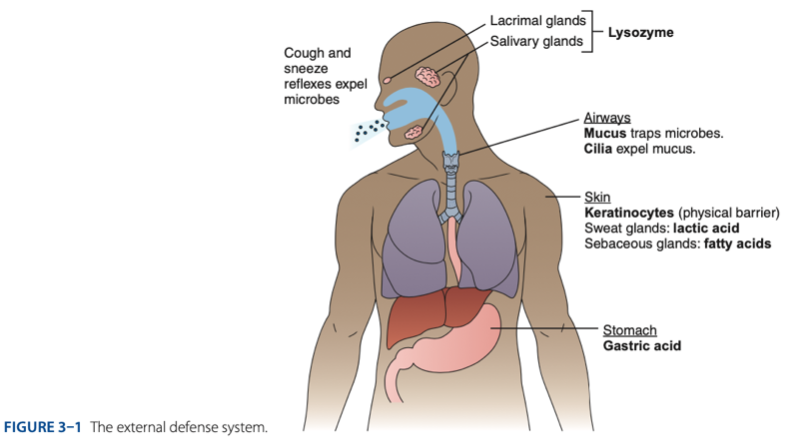
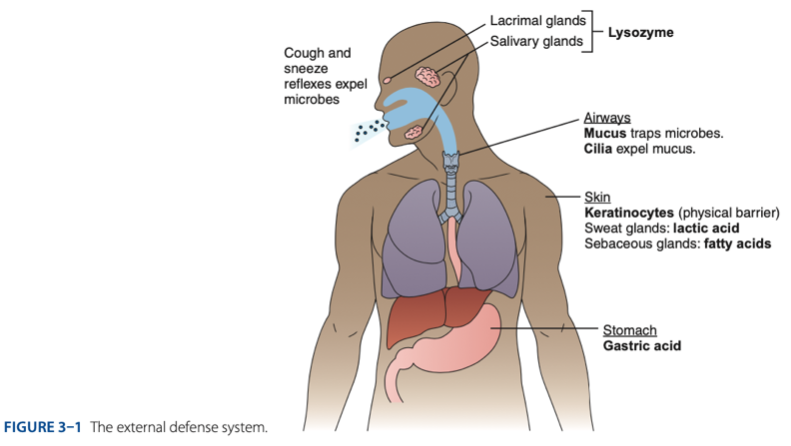
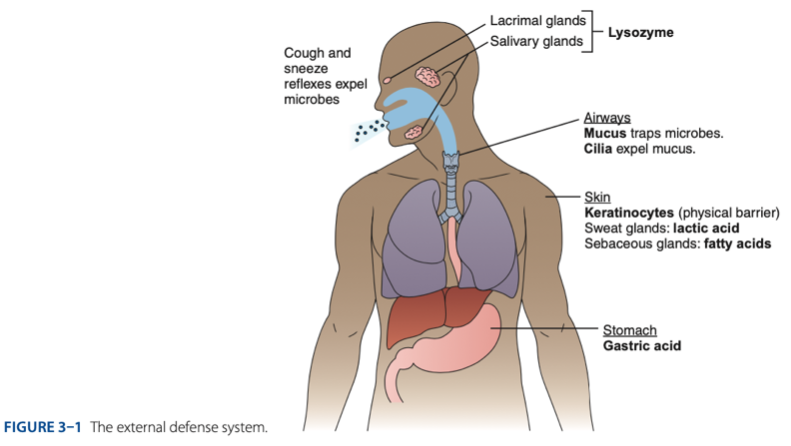
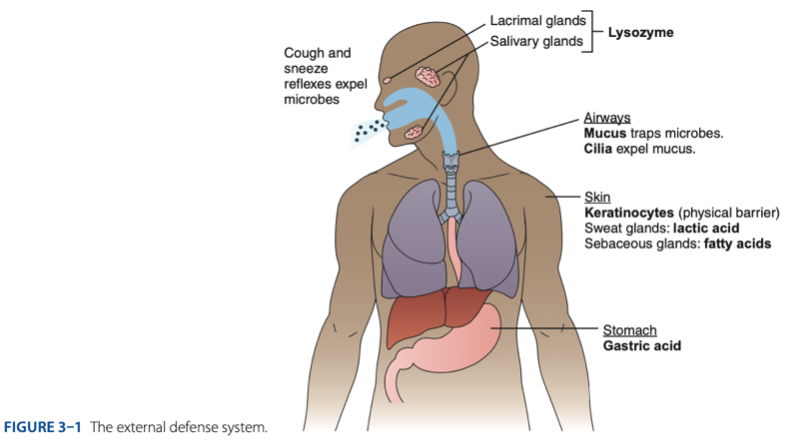
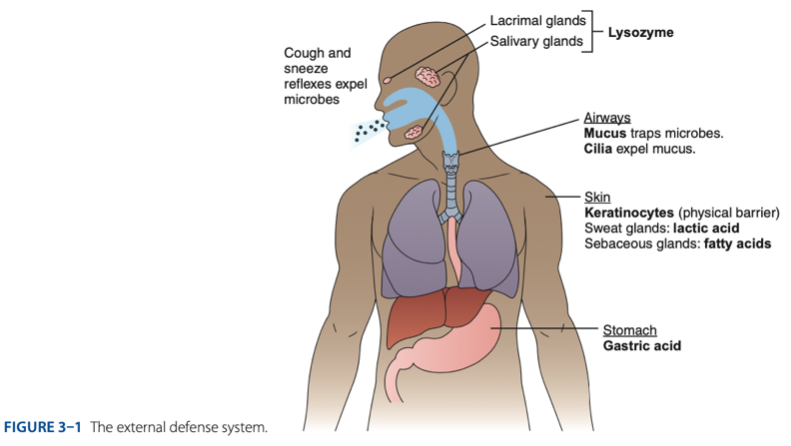
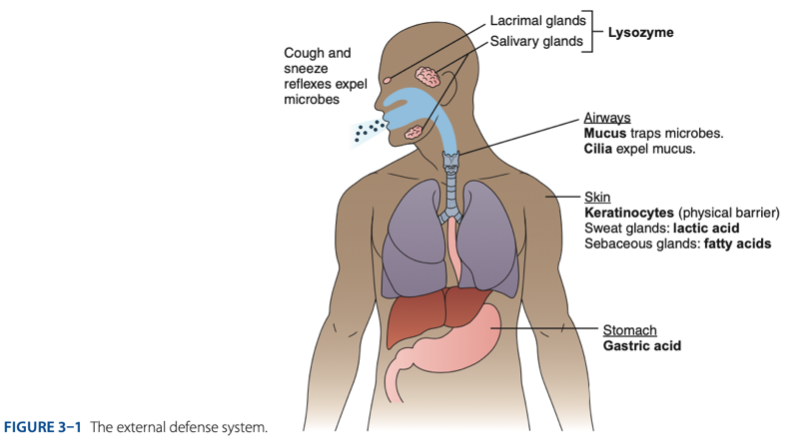
External Defense System
Internal Defense System
Innate IS is composed of 2 systems that work to promote phagocytosis which are
physical, chemical, & biological barriers
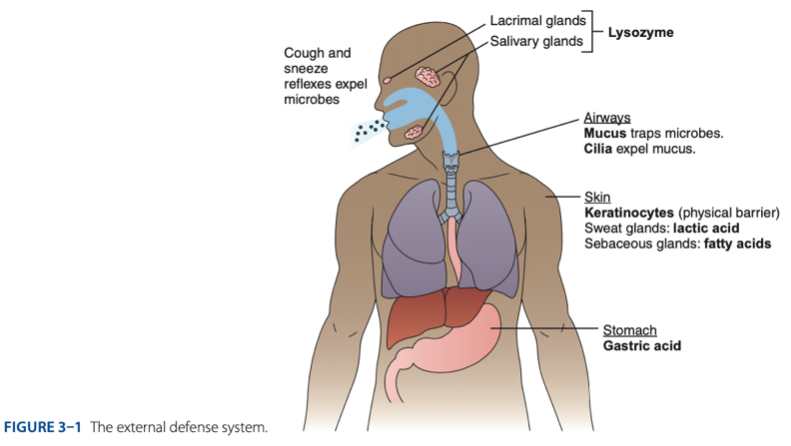
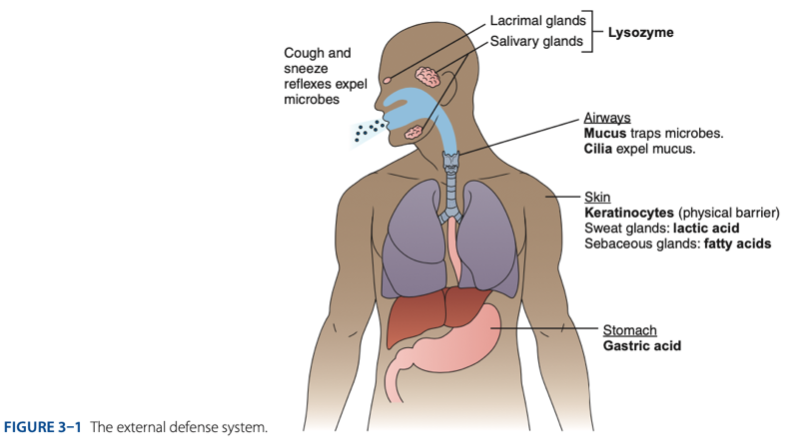
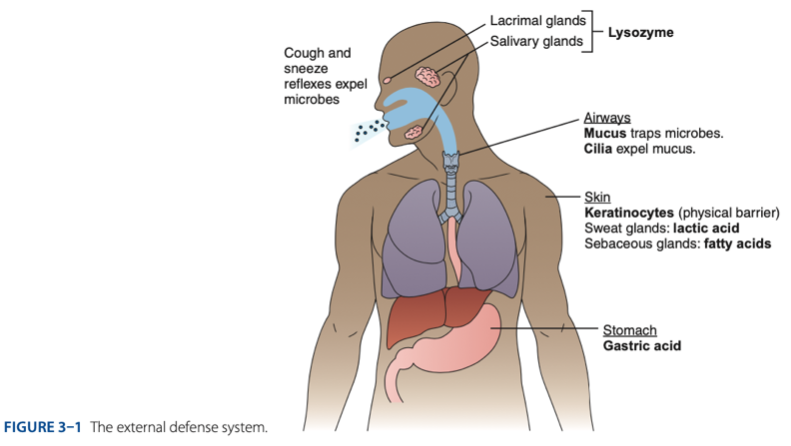
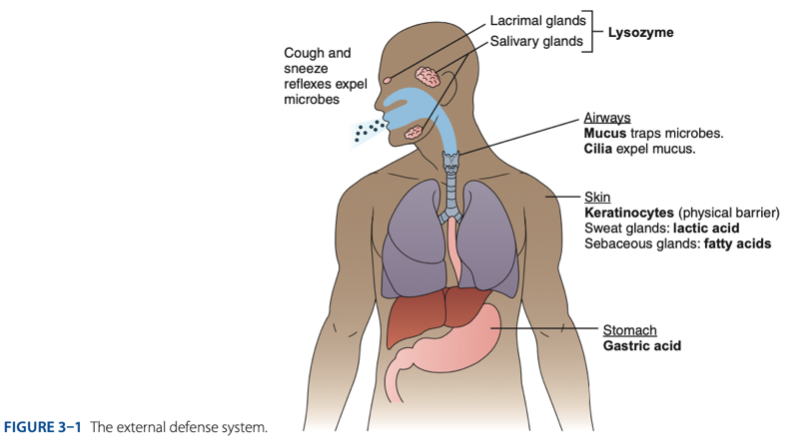
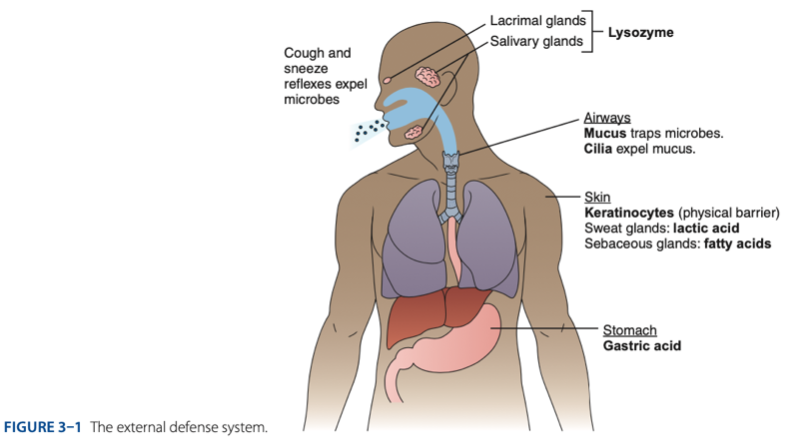
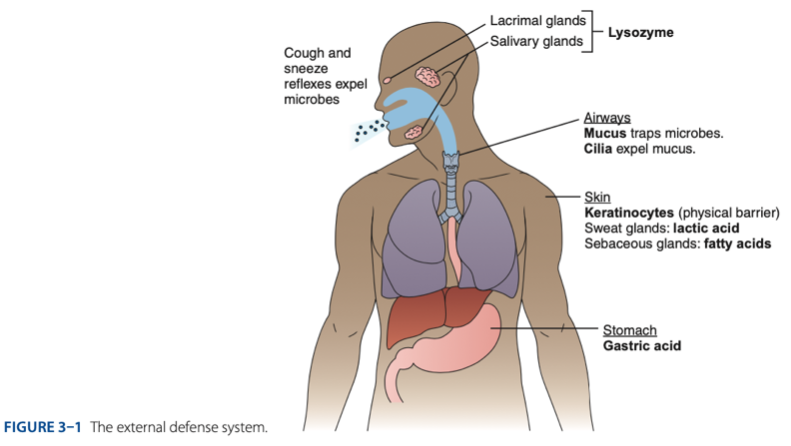
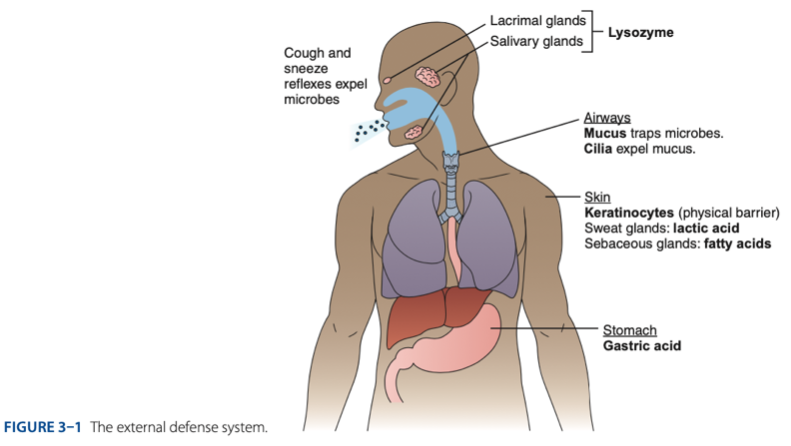
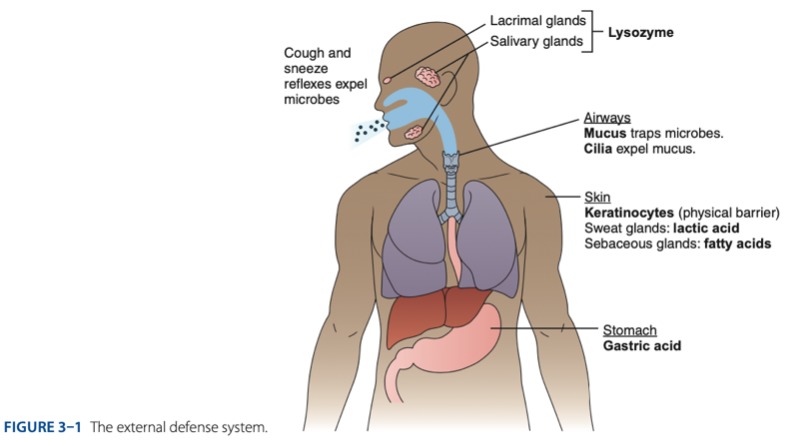
External Defense System is composed of what barriers that work together to prevent infection from entering the body.
External Defense System
- Anatomical barriers designed to keep microorganisms from entering the body.
External Defense System
- Refers to the anatomical barriers represents the epithelial barriers (skin).
Urine
helps remove potential pathogens from the genitourinary tract.
keratinocytes
External Defense System
The physical barrier refers to the skin particularly
Physical Barrier
refers to the skin particularly keratinocytes that is important for the keratin to make our skin dry.
Physical Barrier refers to the skin particularly keratinocytes that is important for the keratin to make our skin dry.
Physical Barrier refers to the skin particularly - that is important for the keratin to make our skin dry.
Physical Barrier
Another is respiratory (mucus and cilia) cilia e.g., pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium smoker more risk in getting covid 19 due to damaged cilia.
F
Another is respiratory (mucus and cilia) cilia e.g., pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium smoker more risk in getting covid 19 due to damaged cilia.
Physical Barrier (t/f)
Another is respiratory (mucus and cilia) cilia
e.g., pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium smoker is at low risk in getting covid 19 due to damaged cilia.
Gastric Acid
External Defense System
Chemical Barrier is composed of
coughing
sneezing
External Defense System
Biological barrier is composed of what mechanisms that is helping us to expel the microbes.
Internal Defense System
- Includes cellular responses that recognize specific molecular components of pathogens.
inflammation
Internal Defense System
Another internal defense system that will allow localization of infection is -.
Phagocytosis & inflammation
Internal Defense System
What are important mechanisms as part of our body defense.
• P - Pathogen – recognition Receptors
• P - Phagocytosis
• A - Acute-phase Reactants
• I - Inflammation
• N - Natural Killer (NK) Cells
Internal Defense System is composed of
Cellular Response
Internal Defense System
– appearance of phagocytosis
Skin
External Defense System
- Physical barriers with secretions that discourage microorganism growth
5.6
External Defense System
- Lactic acid & fatty acids maintain the skin at a pH of approximately - (maasim).
Psoriasisn
External Defense System
– a small protein produced by skin cells, has antibacterial effects.
Epidermis
External Defense System
– tightly packed epithelial cells coated in keratin.
Dermis
External Defense System
– connective tissue with blood vessels, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, & WBCs.
1 stratum cornium
External Defense System
- Skin layer: - (dead skin) composed of microorganism
sebum & fatty acids
External Defense System
Sebaceous Glands is composed of
sweat
External Defense System
- Sweat Glands is composed of
Keratin
External Defense System
– keeps our skin dry.
F
External Defense System
- Severely burn skin is at high risk from getting infected.
External Defense System (t/f)
- Severely burn skin is at low risk from getting infected.
Respiratory Tract
- Mucous secretion block bacteria from adhering to epithelial cells
Respiratory Tract
what block bacteria from adhering to epithelial cells
Coughing/sneezing
Respiratory Tract
what moves pathogens out of tract
pseudostratisfied ciliated columnar epithelium
Respiratory Tract
- The lining of our trachea is made up of - .
Goblet cells
Respiratory Tract
- The lining of our trachea is made up of pseudostratisfied ciliated columnar epithelium. This pseudo stratified has - this cells produced mucus that block & trap bacteria.
hydrochloric acid
Digestive Tract
What acid in the stomach keeps the pH as low as 1, prohibiting microorganism growth.
pH 1
Digestive Tract
- Stomach’s hydrochloric acid keeps the pH as low as -, prohibiting microorganism growth.
Normal Flora / Microbiota
Digestive Tract
– Helps to keep pathogens from establishing themselves in these areas.
E. coli
Digestive Tract
can produce bacteriocins (prevent bacteria from growing) on the mouth
bacteriocins
Digestive Tract
o E. coli can produce - (prevent bacteria from growing) on the mouth
Clostridium defficile
Digestive Tract
o – associated with antibiotic diarrhea
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
- Recognize molecules unique to infectious organisms. (has marked in order to identify)
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
- Encoded by host’s DNA to sense extracellular infection.
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
- Recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on microorganisms
phagocytic cells.
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
- When bound to a pathogen, activate -
• Macrophages
• Dendritic cells
• Neutrophils
• Eosinophils
• Monocytes
• Mast cells
• T cells
• Epithelial Cells
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs) is found on
• Neutrophils
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
– cannot attack/phagocytize by neutrophil because they are too big.
• Eosinophils
Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
– attack large microorganisms like parasites.
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
example of Pathogen-Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
10 types
How many types of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) are found in humans
cell surface & in cytoplasm
Majority of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) are found on the
phagocytosis
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Glycoproteins that bind to particular substances, activating cytokine & chemokine production & other processes to enhance -.
T
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) (t/f)
- Can destroy most pathogens that humans are exposed to before disease sets in.
phagocytosis
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
- Most important in promoting & enhancing -.
• C-type Lectin Receptor (CLR)
• Retinoic Acid
• Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) Receptor
Other Receptors in Internal Defense System
C-type Lectin Receptor (CLR)
binds to mannan & β-glucans found in fungal cell walls to activate cytokine & chemokine production. The outcome is to minimize/prevent fungal infection.
minimize/prevent fungal infection.
C-type Lectin Receptor (CLR) binds to mannan & β-glucans found in fungal cell walls to activate cytokine & chemokine production. The outcome is to -
Retinoic Acid
– inducible gene-l like receptor (RLR)
Acute-Phase Reactants
- Soluble factors found in serum.
Acute-Phase Reactants
- Increase rapidly in response to infection, injury, or tissue trauma.
Acute-Phase Reactants
- Facilitate contact between microbes & phagocytic cells.
Acute-Phase Reactants
- Mop up & recycle important proteins after phagocytosis
C-rp
example of Acute-Phase Reactants
C-rp
indicator for infection & inflammation
C-reactive Protein
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Response Time (hours) : 4 – 6
Normal Concentration (MG/DL): 0.5
Increase: 1000x
• Opsonization
• Complement Activation
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of C-reactive Protein
Serum amyloid A
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Response Time (hours) : 24
Normal Concentration (MG/DL): 5
Increase: 1000x
Activates monocytes & macrophages
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of Serum amyloid A
Alpha1-antitrypsin & Fibrinogen
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Response Time (hours) : 24
Normal Concentration (MG/DL): 200 – 400
Increase: 2 – 5x
Protease inhibitor
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of Alpha1-antitrypsin
Clot formation
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of Fibrinogen
Ceruloplasmin
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Response Time (hours) : 48 – 72
Normal Concentration (MG/DL): 20 – 40
Increase: 2x
Binds copper & oxidizes iron
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of Ceruloplasmin
Complement C3
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Response Time (hours) : 48 – 72
Normal Concentration (MG/DL): 60 – 140
Increase: 2x
• Opsonization
• Lysis
Association of HLA Alleles & Disease
Function of Complement C3
Opsonization
an immune response process which uses opsnonin’s to tag foreign pathogens for elimination by phagocytes. Without an opsonin, such as an antibody, the negatively-charged cell walls of the pathogen & phagocyte repel each other.
Crp
is the most common nonspecific indicator for inflammation/infection.
Ceruloplasmin
copper transport protein & can oxidize iron.
C3
most abundant/dominant form of complement.
Process of Inflammation
body’s overall reaction to injury/invasion by an infectious agent.
• Redness/ Erythema – Rubor
• Swelling / Edema – Tumor
• Heat – Calor
• Pain – Dolor
• Funciolasse – loss of function, 5th cardinal sign
Cardinal Signs & Symptoms of Process of Inflammation
Rubor
Redness/ Erythema
Tumor
Swelling / Edema
Calor
Heat
Dolor
Pain
Funciolasse
loss of function, 5th cardinal sign
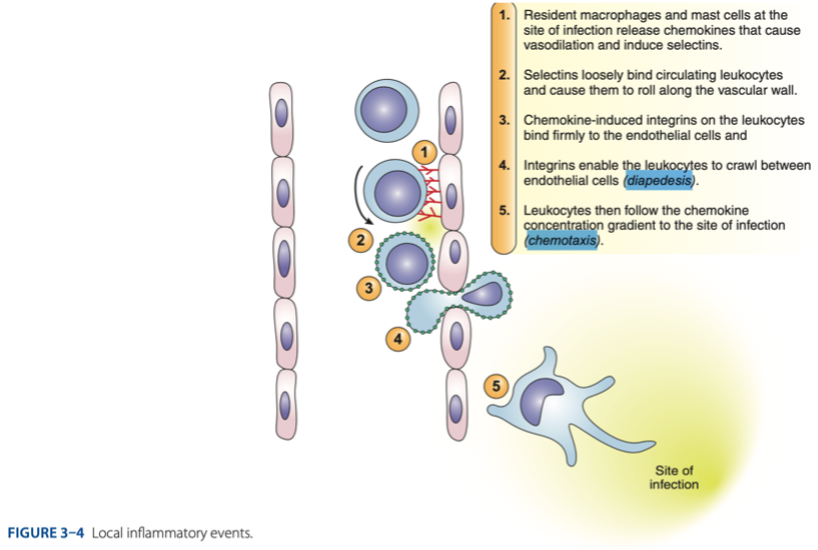
simple squamous epithelium
Process of Inflammation
- Our blood vessels is made up of endothelial cells (-)
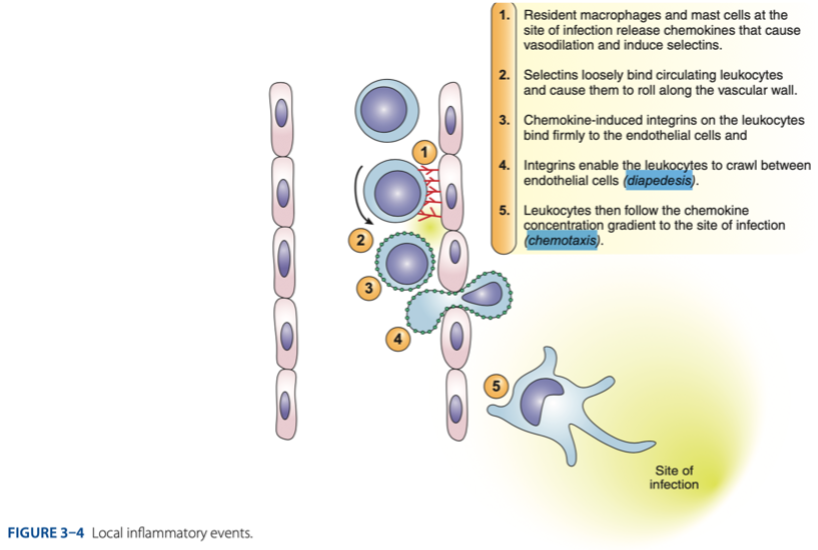
diapedesis
Process of Inflammation
- Process called _ – the leukocytes can crawl between endothelial cells
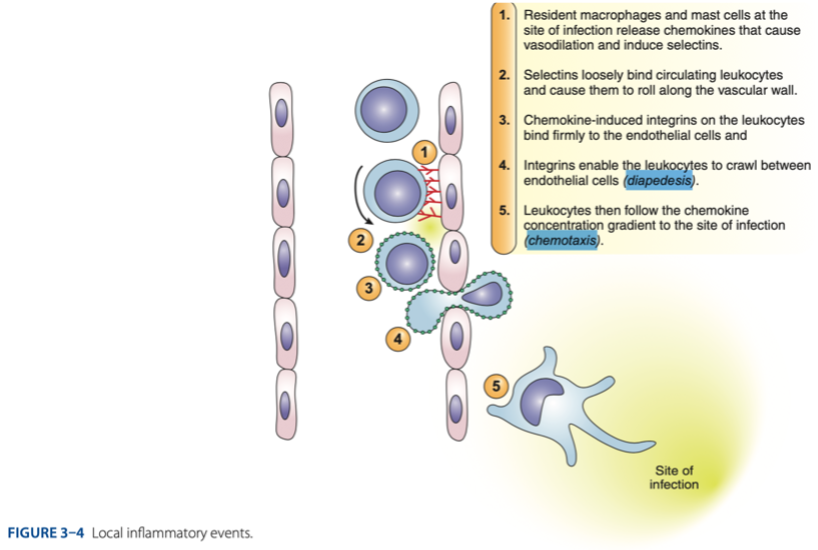
T
Process of Inflammation (t/f)
• Localize the infection which means there is no systemic infection, because when it is already systemic this will be hard to control.
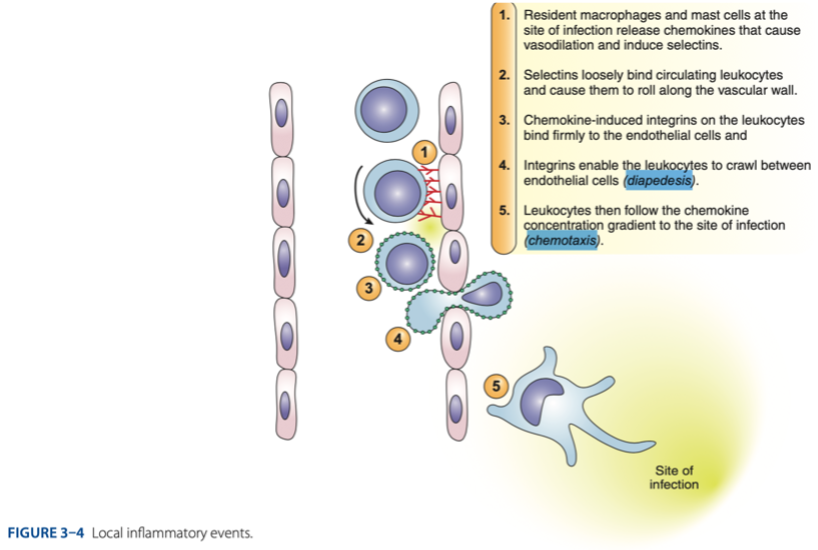
T
Process of Inflammation (t/f)
• Important for tissue repair (healing)
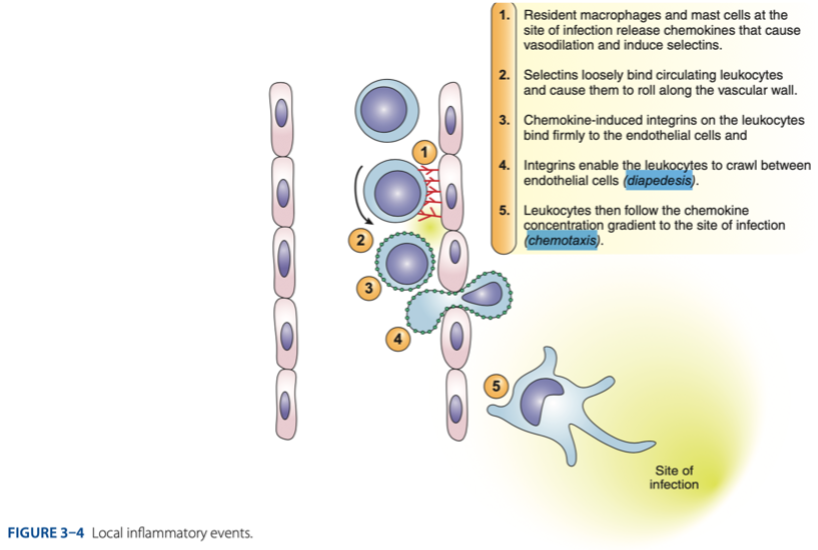
T
Process of Inflammation (t/f)
- Pimples may pus cells. This pus cells will protect then and localize the infection.
Neutrophils
– #1 cell to attack due to their small size.
Phagosome
characterized by the presence of vacuole in the cytoplasm.
Lysosome
granulated (acid hydrolase) then they are released/emptied
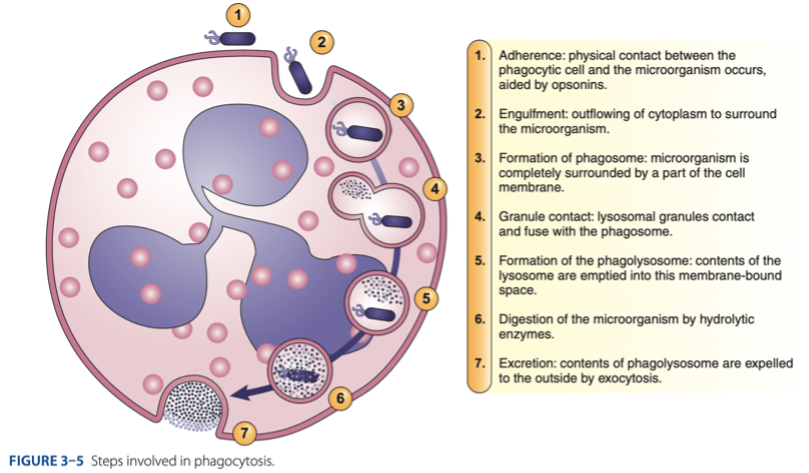
I - Initiation
C - Chemotaxis
E - Engulfment
D - Diapedesis
Phagocytosis
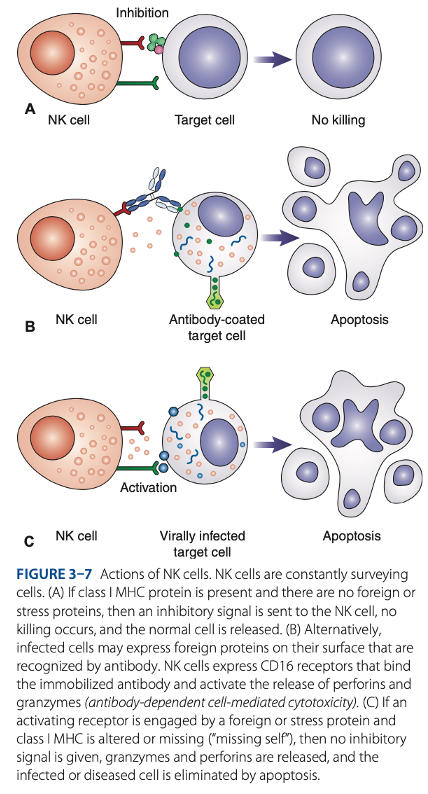
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
- 1st line of defense against:
• Cells that are virally infected