Psych 3501 Exam 3: Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Historical Development of DBT
Developed by Marsha Linehan in 1970s-1980s
Originally created to treat individuals at high-risk for dying by suicide
- Borderline personality disorder
Heavily inspired by:
- Radical behaviorism: treats everything as a behavior
- Zen contemplative practices
- Personal experience
- Dialectics
What are dialectics?
a concept of synthesizing or integrating seemingly opposing truths or ideas to achieve a more balanced and nuanced understanding of oneself and the world
A closer look at dialectics
Walking the middle path
Typically, psychological well-being rarely exists when we exist rigidly at the extremes
Fundamental dialectical dilemma in DBT
Acceptance vs. change
Cognitive therapy (focuses on change): invalidating
Acceptance and commitment therapy: don’t have to change anything
Therapist at middle point too, ready to adjust depending on the circumstances
Who was DBT originally designed for? characteristics
Emotional vulnerability: Difficulties with emotion regulation
Self-invalidation: Intense shame, self-hate, self-directed anger
Unrelenting crises: Frequent negative environmental events
Inhibited grieving: Inhibit or overcontrol negative emotions (not showing)
Active passivity: Looking to environment for problem solving/emotion regulation
Apparent competence: Appear more competent at handling life stressors than one truly is; Difficulty with generalizing competencies to new situations
How do these behavioral patterns emerge?: Biosocial theory of emotions
Biological vulnerability to emotions:
1. Higher emotional sensitivity
2. Higher emotional reactivity
3. Slower than average return to emotional baseline
Along with Social environment with high
1. Invalidation of private experiences
2. Ignored or punished emotional displays
3. Oversimplification of emotions or experiences
What does DBT treatment look like? (four components)
Individual psychotherapy
Skills training
- Group or individual therapy
- Learn the skills to address each barrier
Phone coaching
- therapists providing brief, real-time guidance to clients via phone calls to help them apply skills learned in therapy to everyday situations
Therapist consultation team
These four components are necessary to consider the therapy full protocol
Primary goal of DBT
Goal: to identify and run towards life worth living
Identify barriers along the way
Teach skills to address each one
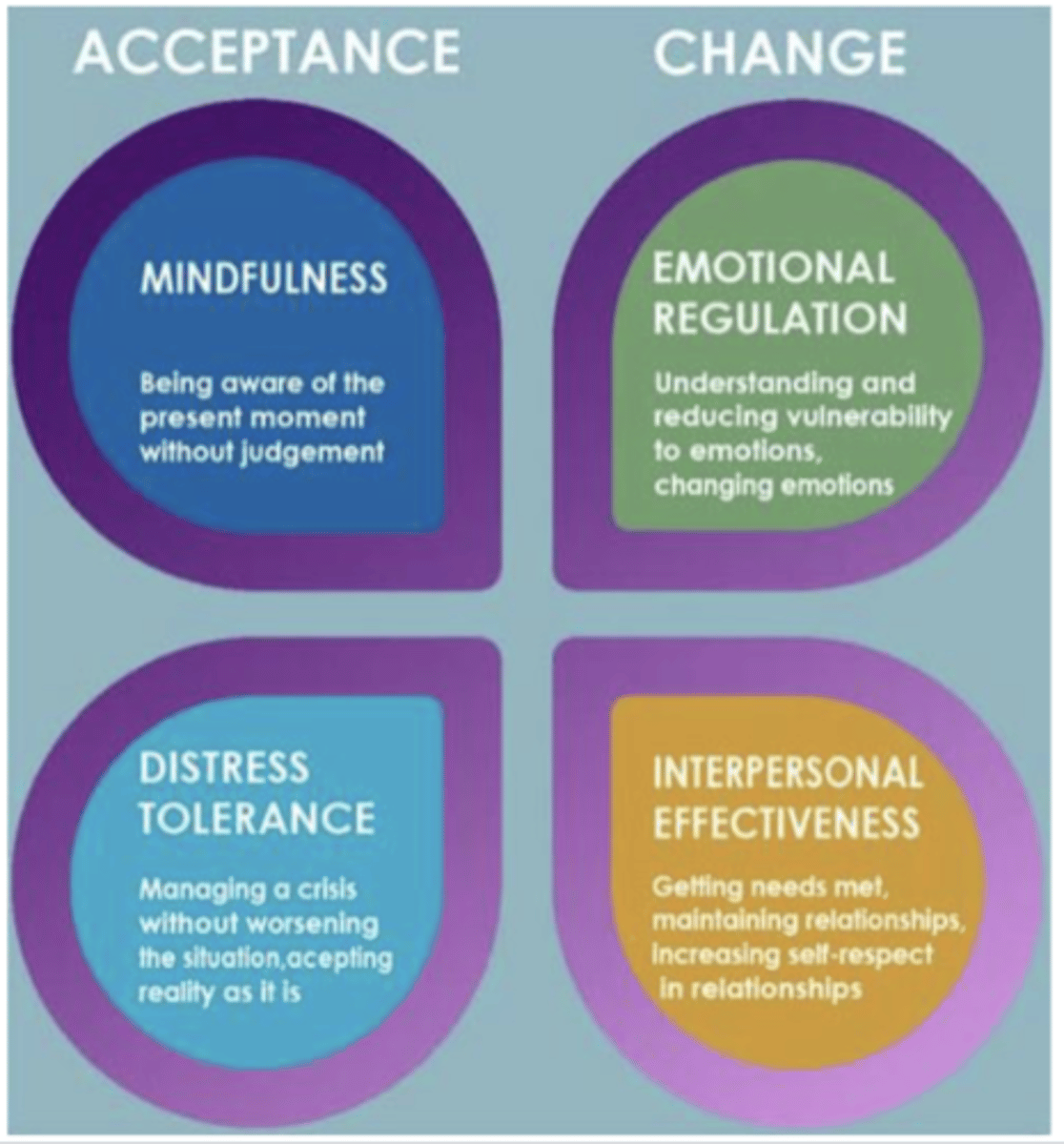
Skills training
Mindfulness
Distress tolerance
Emotion regulation
Interpersonal effectiveness
Mindfulness
Paying attention, on purpose, to the present moment without judgment
The core piece of DBT
Why:
- Slowing down
- Increase control of your mind
Emotion regulation: 3 categories
1. Skills for identifying and understanding emotions
2. Skills to decrease emotional sensitivity
3. Skills to decrease emotional suffering
Decreasing emotional sensitivity
We all have an emotional gas tank
When it is depleted, it can be difficult to manage what life throws at you
Can refill the tank in many different ways
Skills taught in DBT: Accumulating positives in the short- and long-term
Label and (actually) do things that help us recharge
Distress tolerance skills
Survive crisis situation without making them worse
Crisis situation = highly stressful situations
Crisis: High stress, possibility of very bad outcomes, short-term, strong urge for immediate resolution
How do you know they worked?
Helped you not make the situation worse
Only meant to get through the crisis
Temperature skill
Takes advantage of the body's dive reflex
Cover face in ice cold water for 30+ seconds
Reduces heart rate, helps get through anxious/fearful situations without acting on a urge
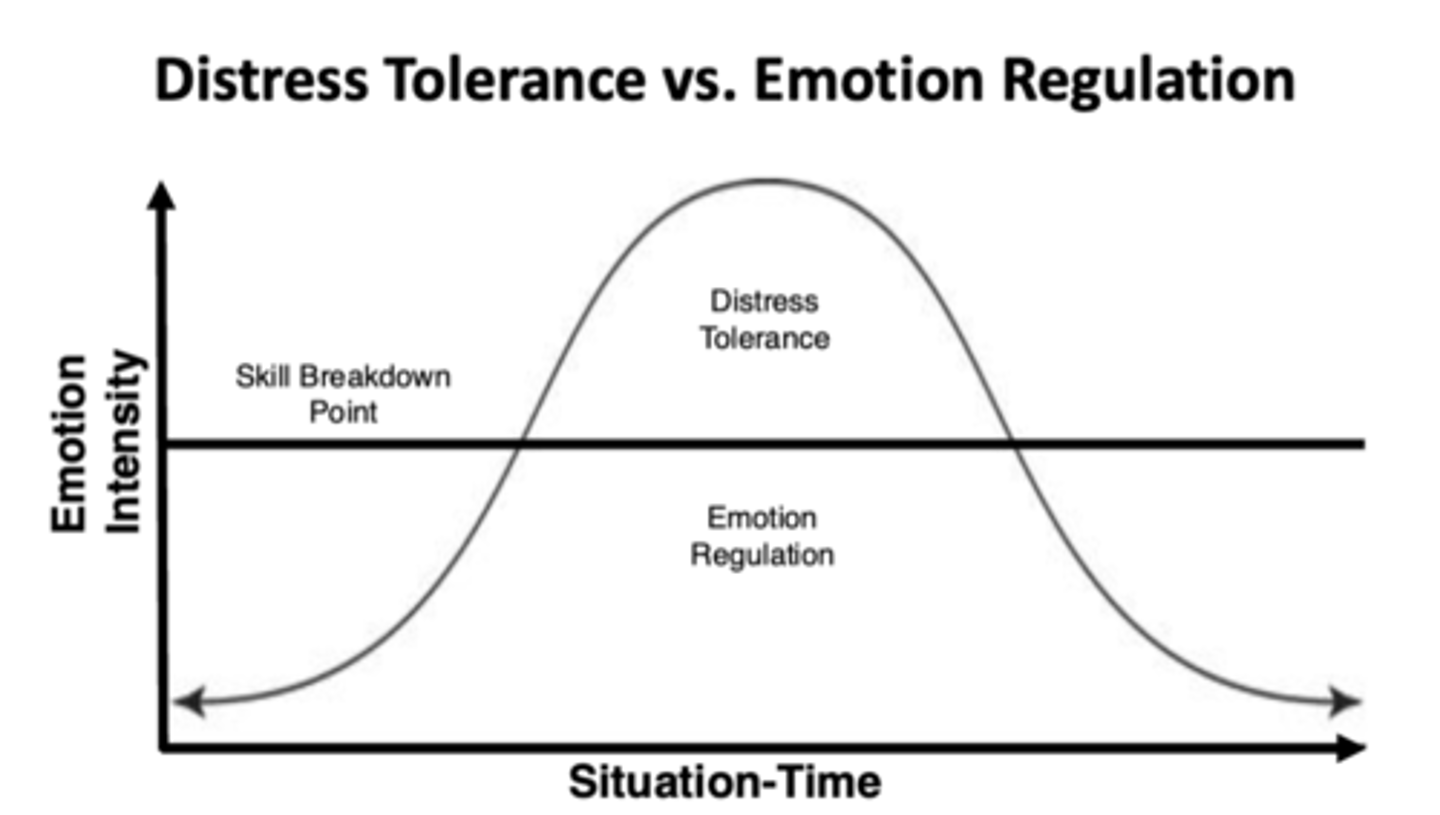
Distress tolerance vs. emotion regulation
Start: an event that triggers an emotional response
Rapidly go up on emotional intensity
To skill breakdown point: can't talk yourself out of it, hard to do emotion regulation skills (mindfulness, etc.)
After going down: go back to problem-solving and emotion regulation
Interpersonal effectiveness skills
Learn skills to be effective in interactions with others, so you are able to get what you want from these interactions
Effectiveness is "doing what works"
- Not getting caught up in what's "fair" or "right"
Balancing objective effectiveness, connection effectiveness, self respect effectiveness
DEAR MAN
Describe the situation without judgment
Express your feelings about the situation
Assert yourself by stating what you want or need
Reinforce the other person if they respond well
Mindful: keep your focus on what you want, don’t get sidetracked
Appear confident
Negotiate: open to negotiation
Individual therapy for DBT
Mindfulness
Diary card
Chain analysis
Solution analysis
Diary card
Develop priority list
Behaviorally specific
For clients to build awareness of their goals
Track behaviors, urges, emotions
Life threatening behaviors -> therapy interfering behaviors -> life barriers
Chain analysis
Used to figure out the "chain of events" that led to the target behavior
Vulnerability
Prompting event
Links
Problem behavior
Short-term consequence
Long-term consequence
Solution analysis
What skills can help reduce the likelihood of the target behavior?
Where in the chain can we intervene to reduce likelihood?
Pick solutions from
- Mindfulness
- Distress tolerance
- Emotion regulation
- Interpersonal effectiveness