ANSC FINAL
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Your mouth produces what enzymes
amylase, mucin, bicarb
HCl
Activates pepsinogen (makes stomach acidic)
Mucin
protects the stomach linging
Gastric Lipase
in tummy
digests fat
but not well bc its not emulsified yet
Pepsinogen
in tummy
digests fat
Intrinsic Factor
in tummy
Faciliatates B12 absorption
helps big molecules get across membranes
Bile
liver-gall bladder
emulsifies fat
Trypsin
pancreas
digests protein
Chymotrypsin
pancreas
digests protein
Carboxypeptidase
pancreas
digests protein
Bicarbonate
pancreas
buffers pH
Sucrase
small intestine
digests sucrose
maltase
small intestine
digests maltose
Lactase
small intestine
digests lactose
aminopeptidases
digest polypeptides (protein fragments)
small intestine
Gibberella Zea (F. roseum)
Deoxynivalenol (feed refusal in pigs)
Zearalenone (estrogenic)
Aspergillus Flavus
Aflatoxin (carcinogenic)
Fusarium moniliforme
Fumonison (kills Horses)
Claviceps purpurea
Ergot, in Rye (unpalatable —> LSD and dry gangrene)
Hammer Mills
most common
portable
steel shaft with hammers that swing battering the feed
Roller Mills
rollers flatten grain with precise tolerance
vry good feed prep
Digestible Energy
Gross energy - feces
how much energy doesn’t end up in poop/what did animal absorb
Metabolizable Energy
Gross energy - feces - urine&gas
still not all available for animal to use
Net Energy
Gross energy - feces - urine&gas - heat increment
heat increment (energy lost in fermentation)
actually available for the animal to use
TDN
total digestible nutrients
an energy index on a carb equivalent basis
TDN Formula
sum of products of:
%CP x digestibiltiy
%EE x 2.25 x digestibility
% CF x digestibility
%NFE x digestibility
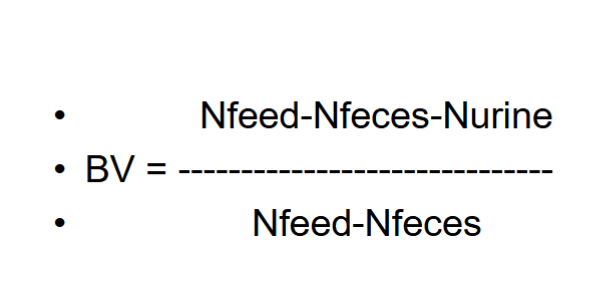
Biological Value
amino acid balance of the digestible part of the protein (which in turn effects the digestibility)
% N Digestibility (apparent)
(N in feed - N in feces)/ N in feed x 100

Nitrogen Balance
N in feed - N in feces - N in urine

% Nitrogen Retention
[(N in feed - N in feces -N in urine)/ N in feed] x 100
![<p>[(N in feed - N in feces -N in urine)/ N in feed] x 100</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0722e835-f149-44b2-aeba-b3d03ef56eb8.png)
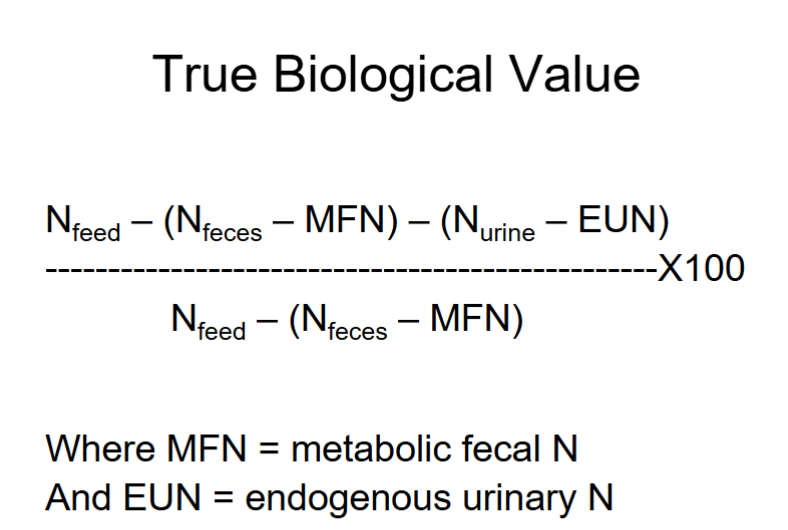
True N Digestibility
[N in feed - (N in feces - MFN)/n in feed] x 100
MFN = metabolic fecal nitrogen
![<p>[N in feed - (N in feces - MFN)/n in feed] x 100</p><p>MFN = metabolic fecal nitrogen</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb0088bc-57bd-4d3e-9107-23e687b1c8d6.png)
Apparent Biological Value
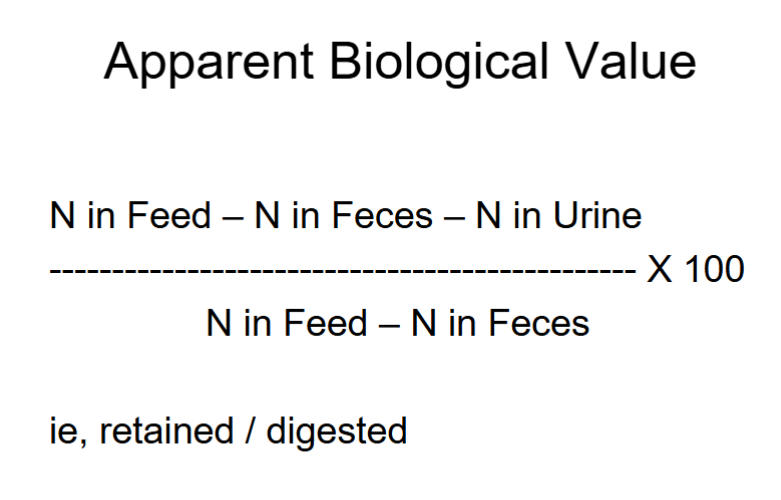
True Biological Value
BIological Value formula
Corn
56 lbs/buschel
low lysine
Wheat
Esophagus for Birds
Crop
Tummy in poultry
Proventriculus (after crop)
has gizzards > teeth
Metabolism Carbs
used by the body of nutrients and metabolites
carbs —> convert to a lil bit of glycogen —> use for blood sugar, ATP or goes to fat
Metabolism (FAT)
liver —> fat storage/ energy usage
Metabolism (Protein)
amino acids enter blood stream —> give cells a acids for protein synthesis
Amino acid not quickly used are deaminated + used for energy
Ruminant Stomach
Rumen (fermentation vat)
Reticulum (hardware stomach)
Omasum (holding space)
Abomasum (true stomach)
What do bacteria do in the Rumen
digest CHO —> VFAs
remodel proteins, manufacture essential amino acids + utilize NPN
Make B vitamins
6 classes of nutrients
Water
Carbs
Fats
Proteins
Vitamins
Minerals
Lipids different to carbs how
way less oxygen —> higher ration of Carbon to hydrogen= energy
Function of protein in the diet
suppy amino acids to the body so cells can make protein
in excess —> make energy
10 amino acids (essential)
Phenylalanine
Valine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Isoleucine
Methionine
Histidine
Arginine
Lysine
Leucine
Triglyceride
1 glycerol
3 fatty acids
What are the 3 essential fatty acids
Linoleic
Linolenic
Arachidonic
2 long chain saturated fatty acids
palmitic acid
stearic acid
what has the most influence on the biological value of a feed
amino acid pattern
Biological value and digestibility
are independent variables
DIP
gets broken up in the rumen and rearranged by bacteria
UIP
left alone by bacteria —> animal will absorb its amino acids so the amino acid balance is important
NIRS is used in animal nutrition
to rapidly estimate the components in feed
Opaque-2-corn
Corn with more Lysine
Why is fat used more efficiently than carbs in the summer
heat increment of fat is lower
How could 2 feeds have the same TDN value, and even the same DE value, but still be of different use to the animal due to energy?
they could have different heat increments
6-8 grass forages
fat cow syndrome
too much fat in the liver —> caused by too much grain in the diet
Characteristics of good hay
cut early
green and leafy
soft pliable stems
freee of mold
palatable
little foreign matter
Legume examples
Alfalfa (problems with bloat)
Clavoer
Soybeans
Lespedeze
Birdsfoot trefoil
Sweet Clover (anti coagulant)
Grases
Timothy
Big Bluestem
Indian Grass
Switch grass
Orchardgrass (deterrent to bloat)
Acidosis
too much lactic acid
rumen ferm is too much that buffers won’t work
ketosis
cows + sheep
too many ketone bodies in blood
not enough pyruvate (form oxaloacetate to make citrate)
treat with glucose
prevent by keeping energy intake levels up and avoiding too much grain in advance
Bloat
failure of eructation mechanisms *Wet Summers, rapidly growing clover, treat with movement and poloxalene)
Feedlot Bloat
high concentrate diets —> slime produced by bacteria
frothy bloat assocaited with wheat and legume more roughage in diet
Nitrate poisoning
can be toxic from conversions of nitrate to nitrite in the rumen
happens in stressed Plants
Fat Cow Syndrome
fat accumulates in the lvier
too much concentrate fed to dry cows
can occur rapidly
Founder
comes from overeating grain