Anti-Platelets and Anti-Coagulants
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Common NSAIDs
-Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Naproxen sodium, Indomethacin
Ketorolaac (parenteral NSAID)
(COX-2 agents are kinda in their own bracket)
-all increase risk of heart attack
primary vs secondary prophylaxis
1: given to prevent a stroke/MI
2: given to prevent ANOTHER stroke/MI
What was the first NSAID (the protypical agent)
Aspirin
What is the only NSAID with cardiac protection? Why?
Aspirin (primary vs secondary)
it is an irreversible inhibitor of platelet aggregation
the others are reversible inhibitors
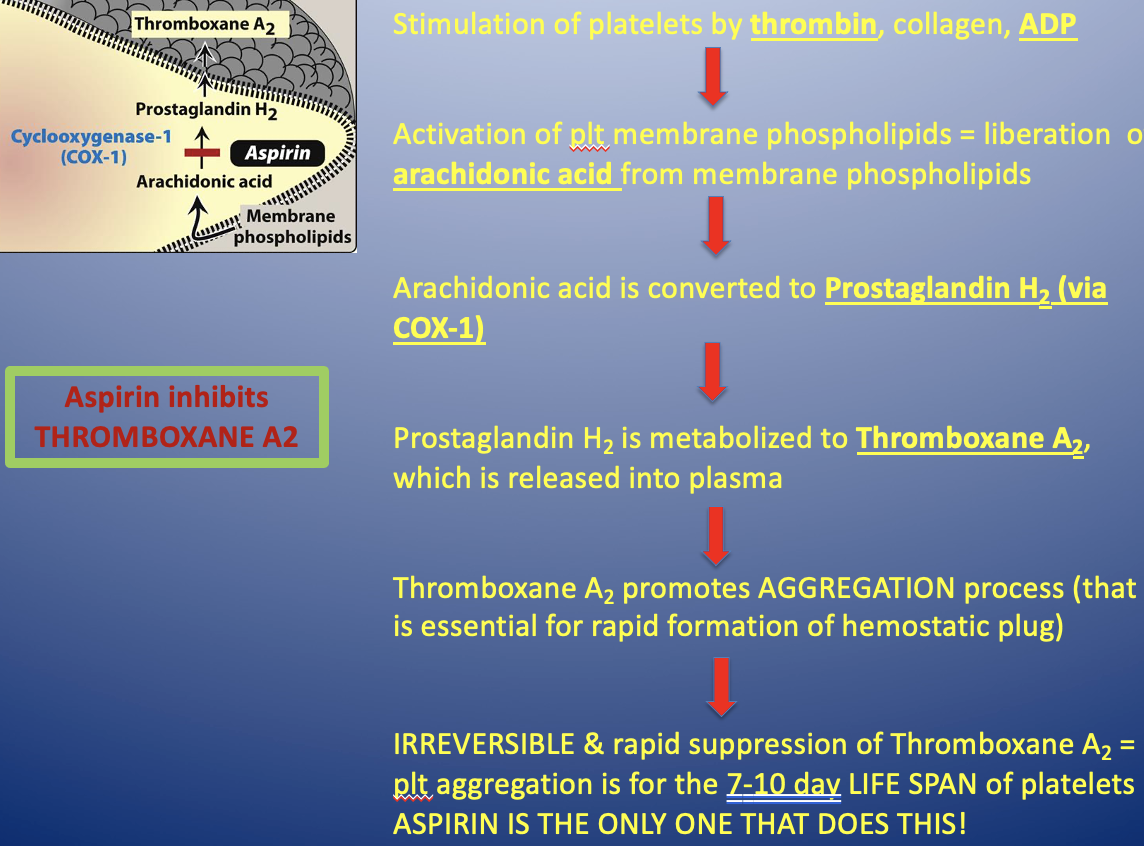
Aspirin MOA
-stimulates platelets by thrombin, collagen, ADP
-activation of platelet membrane phospholipids=liberation of arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids
-arachidonic acid is converted to prostaglandin H2 (via COX-1)
-prostaglandin H2 is metabolized to thromboxane A2, which is released into plasma
-Thromboxane A2 promotes AGGREGATION process
-IRREVERSIBLE and rapid suppression of thromboxane A2 = plt aggregation is inhibited for the 7-10 days LIFE SPAN of platelets
ONLY ASPIRIN DOES THIS
Aspirin inhibits Thromboxane A2
Aspirin: Use/PK
-to prevent arteriolar clots (anti-coags prevent venous clots)
PK: after absorption it is hydrolyzed to salicylic acid via liver (reye syndrome: exposure to salicyclic acid)
Aspirin: dosing and indications
Dosing: 81-325mg EC TAKE WITH FOOD (nsaids and steroids)
Men: 45-79 to prevent AMI
Women: 55-79 to prevent ischemic stroke
Unisex: >80 only for hihg CV risks and no additional GI bleedings
Aspirin: adverse effects
Prolonged bleeding time: (increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke and GI Bleeding)
ibuprofen: take within 2hrs before aspirin: antogonism for aspirins platelet inhibition (Take aspirin 1 hr BEFORE or 8 hrs AFTER ibuprofen)
CNS: Tinnitus
Reye syndrome: CNS effect (dont use in kids under 14)
P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors (Thienopyridine derivatives) Examples
Clopidogrel (Plavix)
Ticagrelor (Brilinta) ( reversible)
Prasugrel (Effient) most effective at plt aggregation
Ticlopidine (no longer available)
Cangrelor (IV infusion)-max inhibition of platelet aggregation within 2 mins (reversible)
P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors: MOA
MOA: Irreversible inhibition of ADP pathway of platelets; blocks the ADP receptor on platelets;
no effect on prostaglandins
inhibit binding of ADP to P2Y12 receptor on platelets → inhibit activation of GPIIb/IIIa receptors required for platelets to bind to fibrinogen and to each others
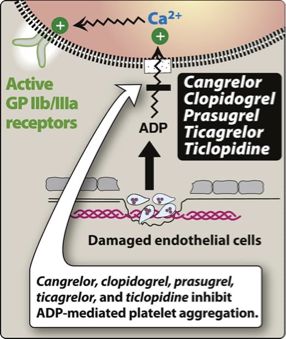
Which P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors binding is reversible
Ticagrelor and cangrelor
Which P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors binding is irreversible
Clopidogrel and Prasugrel
Which P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors require a loading dose?
The PO ones → for faster anti-platelet effect
Clopidogrel (Plavix): MOA/Use/Instructions/Hold
-with or without aspirin
-Max inhibition of platelet aggregation is 3-5 days
-duration of antiplatelet effect is 7-10 days
MOA: Prodrug: CYP450 system activates it via (CYP2C19)
avoid other CYP450 2C19 inhibitors (eso/omeprozole)
polymorphisms of cyp2c19 create a decreased clinical response (decreased efficacy→ gonna have a stroke/mi)
inhibitors cause clopidogrel to not be metabolized (doesn’t become active) → we just pee it out
Hold for procedure: 5 days
Genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19
-decreases clinical response in CYP2C19
-decreased efficacy of clopidogrel (never gets activated)
-increases chance of CV or cerebrovascular event
Ticagrelor (Brilinta): MOA/dosing/Hold
MOA: PO Reversible ADP inhibitor
BID, shorter duration but faster onset
may inhibit new platelets that are infused
Dosing: BID. Give with loading dose. Take w/ 81mg of aspirin (higher dose will impair MOA)
MAX inhibition of platelets aggregation is 1-3 hrs when given with loading dose
Hold for procedure: 5 days
Tricagrelor (Brilinta): Antidote
recombinant factor 7a suggested
Prasugrel (Effient): MOA/Dosing
MOA: irreversible inhibitor of ADP receptor
most effective at platelet inhibition
Dosing: take with aspirin (81-325mg)
-max inhibition of platelet aggregation is 2-4hrs
-hold for procedure: 7 days
Prasugrel (Effient): ADR/Interactions/Hold/Antidote
ADR: BLEEDING (worse of the 3 p2y12adp inhibitors) black box warning
Contraindicated in pts w/ prior TIA or stroke (not primary prophylaxis)
Drug Interactions: any other drug that increases leeding risk (no NSAIDs or warfarin. only tylenol allowed (not antiplatelet activity))
Hold: 7 days (like aspirin)
Antidote: platelet infusion
Adverse effects of PP2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors
Bleeding (black box): tricagrelor, prasugrel, cangrelor
Decreased efficacy when used with aspirin >100mg (Black box): Ticagrelor (T=too much aspirin)
prolonged bleeding time
thrombocytopenia
TTP (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura)
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors: Examples/Use
Eptifibatide (Integrillin)
Tirofiban (Aggrastat)
use for pt with acute coronary syndromes, along with heparin and aspirin
-most potent
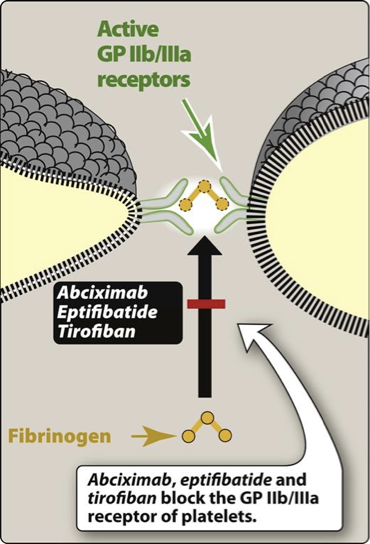
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors: MOA/AE
MOA: Target platelet IIb/IIIa receptor complex - final pathway for platelet aggregation
-given IV
Adverse effect: Bleeding
Anti-Platelet Potencies
most to least potent
GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors >
Thienopyridine derivatives (effient, Brilinta, Plavix) >
aspirin

Pregnancy categories of anti-platelet drugs
Category B:
-Prasugrel, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban, Clopidogrel
Category C:
-Aspirin (sometimes), ticagrelor
How long to hold for procedure (anti-platelets)
Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor = 5 days
Prasugrel = 5-7 days
Aspirin = 7 days
Warfarin (Coumadin): MOA (CYP enzyme)
MOA: Inhibits Vitamin K dependent, hepatic coagulation factors: 2, 7, 9, 10, & protein C and S
peak effects delayed for 72-96 hrs (may need to bridge with another anticoagulant)
→ results in production of clotting factors with diminished activity
can be used with heparin for bridging
metabolized by CYP450 2C9 = many drug interactions
Warfarin: PK/dosing
no loading dose
half life: 40-72 hours
Warfarin: Pregnancy Category/Antidote
Pregnancy Category X
sometimes used in breastfeeding women
can cross into placenta → hemorrhagic disorders
(If pregnant and needs anticoagulant - GIVE HEPARIN)
Warfarin: Monitoring
-Monitor INR weekly for first few weeks, then every 2 (adjust dose as needed)
-INR= aim for the middle of the range
-Higher INR → indicates higher level of anticoagulation
-hold: 5 days (might bridge with injectable)
watch for drug interactions
-maintain consistent amount of vitamin K in diet
Warfarin: adverse reactions/Warnings
Adverse reactions: bleeding and many more
Use with Vit K may decrease anticoagulant effect (also used as antidote)
-purple toe syndrome (caused by cholesterol emboli from plaques)
DO NOT USE W/ NSAIDS
-Use acetaminophen (Tylenol) for pain/fever
Dabigatran (Pradaxa): MOA/Use/CI
MOA - direct thrombin inhibitor (factor 2a)
Use: For reducing risk of stroke and systemic embolim in pts w/ non valvular Atrial fibrillation; used in place of warfarin
CI: contraindicated in pts with mechanical prosthetic heart valves
How long to hold Dabigatran (Pradaxa) for procedure?
24-72 hours
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) reversal agents
Idarucizumab (Praxbind) and activated charcoal
Dabigatran ADR/Precautions
ADR: contains tartaric acid → causes reflux (pts will take with food and proton pump inhibitors)
Precautions: if dose is missed, the effectiveness can wane within 15 minutes of the missed dose
Direct oral Factor Xa inhibitors
-rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
-Apixaban (Eliquis)
-Edoxaban (Savaysa)
all are PO agents
Direct oral factor Xa inhibitors: MOA/Indications
MOA: inhibits factor Xa
(→reduces production of thrombin from prothrombin)
Indicated: Used in place of warfarin or LMWH to prevent venous thrombosis after hip/knee replacement surgery
Approved to prevent stroke in pts w/ afib
In what situation would you reduce dosages of a direct oral factorXa inhibitor?
when taking with other P-pg inhibitors such as clarithromycin, verapamil, and amiodorone
Direct oral factor 10a inhibitors: ADR & reversal agent
ADR: bleeding
Reversal agent: Andexxa (coagulation factor X)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto): CYP isoenzyme: MOA
metabolized by CYP 3A 4/5 and CYP 2J2 isoenzymes to inactive metabolites
Apixaban (Eliquis): CYP
-metabolized by CYP 3A4, with CYP enzymes 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2J2 all sharing minor metabolic roles
Xarelto and Eliquis should be avoid when taking
-strong P-gp and CYP 3A4 inducers (phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, St. John wort)
-it can reduce the efficacy of the factor 10a inhibitors
Heparin: MOA and reversal agent
-injectable, rapid-acting, interferes with formation of thrombi
MOA: binds to antithrombin III→ rapid inactivation of coagulation factors (Thrombin (F2a) and 10a) → prevents fibrin formation
Reversal Agent: Protamine Sulfate
Heparin reversal agent
reversal agent: protamine
Heparin: Uses and pregnancy category
-treats acute venous thromboembolism (DVT, PE)
-used before operation and in pt's with acute MI
-pregnancy Category C (anticoagulant of choice)
How do you monitor Heparin?
activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
(UFH only, not LMWH bc they only inhibit F10a
-anticoagulant effect: IV=minutes, SC=1-2 hrs
What is the traditional heparin therapy?
unfractionated heparin SC or IV, obtained from pork intestinal mucosa
LMWH (Low molecular weight heparins) Examples
Dalteparin (Fragmin)
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
LMWH MOA and administration route
inhibition of Xa by antithrombin (not long enough to inhibit thrombin)
Route: SQ administration
benefits of using a LMWH compared to other antiplatelet options
-equal efficacy
-increased bioavailability from SQ site (anticoagulant effect=4 hrs)
-less frequent dosing (longer half life than UFH)
LMWH/heparin monitoring & ADR
Monitor factor Xa levels for renal impairment, pregnancy, obesity
-ADR: Bleeding, thrombocytopenia (less than UFH), hypersensitivity (allergic rxn): anaphylaxis, alopecia, cataracts, osteoporosis, urticarial, chills fever (with long term therapy)
-avoid in alcohol use disorder and some surgeries (brain, eye, spinal cord)
how to treat HIT (Heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
-systemic hypercoagulable state (1-4% of pts)
-treated with UFH x7 days
-surgical pts have highest risk
-do platelet counts frequently
Argatroban (acova)
-anticoagulant derived from L-arginine used in prophylaxis and to treat HIT, used during PCI in pts who have risk for HIT
-direct thrombin inhibitor
Argatroban (acova) monitoring and ADR
-monitor with aPTT, hemoglobin, hematocrit
-anticoagulant effects are immediate
-ADR: bleeding
Bivalirudin (Angiomax)
-anticoagulant used to treat HIT
-direct, selective thrombin inhibitor
Fondaparinux
-synthetically derived pentasaccharide anticoagulant that selectively inhibits factor Xa
-SC injection
-used to treat DVT, PE, prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism (in orthopedic and abdominal surgery)
-ADR: BLEEDING
Anticoagulant Pregnancy Categories
Category B: Heparin, LMWH, argatroban, bivalirudin, apixiban
Category C: Dabigatran, rivaroxaban
Category X: Warfarin
How long to hold for procedure - anticoagulants
Heparin - 4-6 hours
LMWH - 12-24 hours
Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixiban = 24-72 hrs
Warfarin - 5 days
what kind of clots are antiplatelets usually used for? What are the antiplatelet meds?
Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor, etc
-Used for ARTERIAL clots, due to platelet aggregation
prevent platelet aggregation
Anti-coagulants
-Warfarin, DOACs
-used for clots in veins or atria of heart due to fibrin meshes of RBCs
-useful in VENOUS thrombosis
Thrombolytics (fibrinolytic drug)
-break up and DISSOLVE the thrombus/clot (Clot busting)
-Enzymes that kick off process of breaking down proteins (fibrins) that form clot (convert plasminogen to plasmin)
-work better the faster they are started after clot formation
-increased local thrombi may occur: given aspirin or heparin to prevent this
-Alteplase (t-PA): derived from human melaona cells, recombinant DNA technology, Reteplase, tenecteplase
Thrombolytic agents ADR
-hemorrhage (they don't distinguish between unwanted thrombus and beneficial hemostatic plug)
-do not use in pregnancy, pts with healing wounds, or pt with hx of cerebrovascular accident, brain tumor, head trauma, intracranial bleeding, and metastatic cancer
Protamine sulfate MOA
-antagonizes the anticoagulant effects of heparin
-derived from fish sperm or testes
-positively charges protamine and negatively charged heparin=stable complex without anticoagulant effects
Protamine sulfate ADR
-allergy, dyspnea, bradycardia, hypotension
Vitamin K (Phytonadione)
-helps stop bleeding due to warfarin
-PO and IV preferred (Also SC)
-slow response (24hrs to lower INR)
-FFP (fresh frozen plasma) is faster
Idarucizumab (praxabind)
-used to reverse bleeding caused by dabigatran
-IV admin in emergencies
-ADR: thrombosis
Factor 10a (Xa)
-recombinant modified human protein
-IV
-used to reverse apixaban or rivaroxaban
-NOT approved for edoxaban reversal
-ADR: arterial and venou thromboembolism, MI, ischemic stroke, cardiac arrest, sudden death