Chapter 16 - Organic Synthesis + Analytical Techniques
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
why use reflux?
prevents loss of volatile compounds by evaporation
Quickfit apparatus
joints of equipment are greased with petroleum jelly before pieces are connected
how to obtain a pure substance
1) separating funnel - pour mixture into this with distilled water to separate organic and aqueous layer
2) then collect the organic layer depending on density of it compared to the aqueous layer
3) drying agent - dry with an anhydrous salt to the organic mixture to remove excess water
4) redistillation - fraction distil the mixture until the compound with lower boiling point boils
drying agents
-magnesium sulphate
-calcium chloride
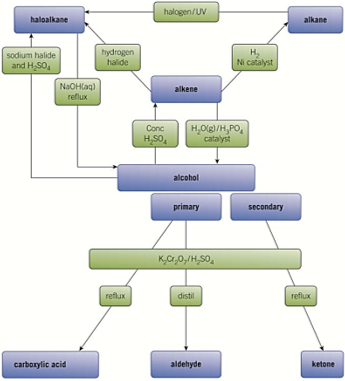
pathways -MEMORISE
.
mass spectrometry
-identifies the Mr of an organic compound
-2 molecules may have the same M+ peak but their fragment ion peak will be different as they fragment differently
molecular ion
M+ - the positive ion formed when a molecule loses an electron
mass-to-charge ratio (m/z)
-when the molecular ion reaches the detector, the m/z ratio is detected
-z = 1
m/z ratio of molecular ion = Mr of the compound
determining Mr from spectrum
M+ peak = the clear peak at the highest m/z value located furthest to the right
M +1 peak = very small peak next to M+ peak for carbon - due to isotopes of carbon, carbon-12 = 98.9%, carbon-13 = 1%
-other peaks are due to fragmentation
fragmentation
molecular ion breaks up into smaller pieces called fragments
-a fragment ion is formed which can be detected + appears
-a neutral or radical species is also formed but cannot be detected + does not appear
molecular ion+ → fragment ion+ + neutral/radical species
common fragment ions
CH3+ = 15
C2H5+ = 29
C3H7+ = 43
C4H9+ = 57
OH- = 17
structure of ions for m/z peaks
m/z peak at 15 → CH3+
m/z peak at 29 → CH3CH2+