Organizational Structure (1.1)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
organizational structure
the formal interrelationships and hierarchical arrangements of human resources within a business. Structure can vary depending on various factors of a business
Organizational charts
a diagrammatic representations of firms’ formal structures
Types of organization charts (5)
Flat (horizontal
Tall (vertical)
By product
By function
By region
Delegation
the passing on of control and decision-making authority to others. It involves the line manager entrusting and empowering staff to complete a task or project, but holding them accountable for their actions.
ADVs of delegation (2)
saves time by not letting the manager not tackle every single task --> focus on more strategic issues facing the organization
motivate and develop employees who feel that they are trusted their contributions are important
DIS of delegation (2)
cause confusion, feeling of inadequacy due to poor delegation
Span of control
the number of people who are directly accountable to a manager. Hence, the higher up a person is in a hierarchy, the wider their span of control tends to be. (IMPORTANT: CEO is directly involved with BOD, BUT indirectly has a large span on control)
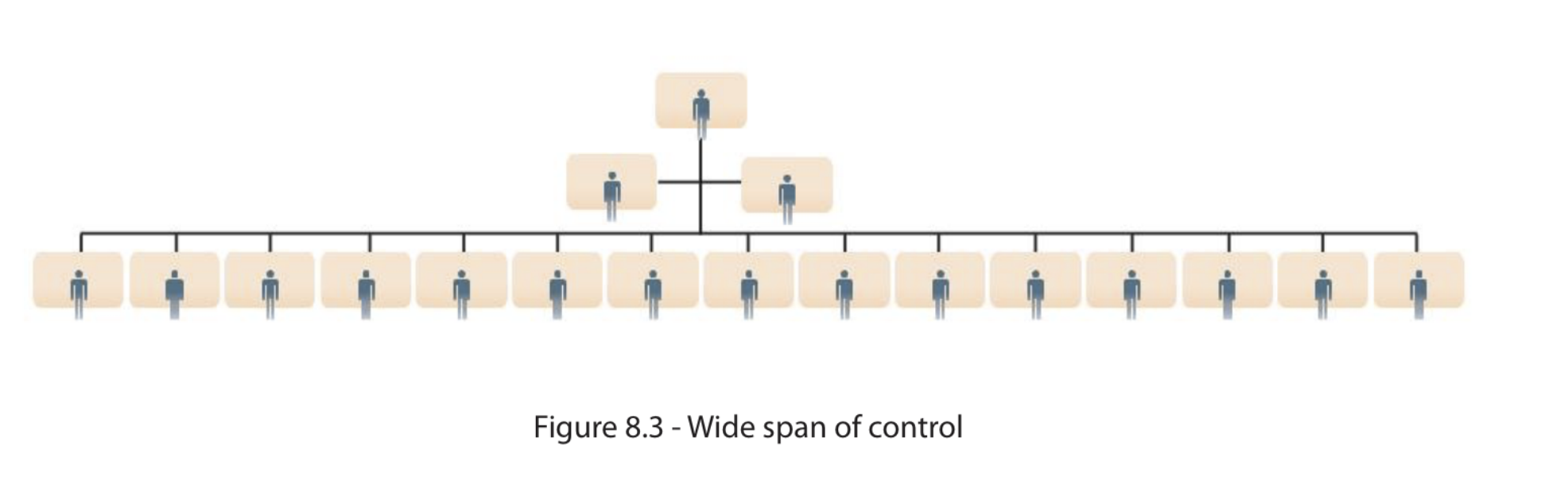
ADVs of span of control (consider. flat wide and narrow) (2)
wide span of control: fewer layers are needed --> helps cost control as there are fewer managerial positions
flatter structure --> communications between the different levels should be more effective
DIS of span of control (consider. flat wide and narrow) (2)
fewer subordinates who are accountable to a manager
bigger teams may be less productive due to lack of team spirit and cohesiveness
The degree of control granted to a manager depends on MOST
Manager: the more skilled and experienced the manager, the more likely that they would have a wider span of control
Organizational structure: narrower spans of control may be required in cultures that require managers to closely monitor and control their subordinates. BUT, democratic cultures tend to delegate and empower subordinates, allowing for wider span of control
Subordinates: highly skilled staff are more likely to work in smaller, dynamic teams with their line manager
Task: complex, urgent and important tasks tend to require a narrower span of control as communication will be more important.
level of hierarchy
organization structure based on ranking system. Each hierarchical level refers to a different rank with its associated degree of authority and responsibility.
Line manager: person directly above an employee on the next hierarchical level
ADVs of level of hierarchy (both long/short)
clear lines of authority --> can improve the coordination and productivity of workers
establish departments or teams to create a sense of belonging in the workplace, act as a form of motivation
DIS of level of hierarchy (both long/short)
departmentalisation: workers are isolated from their official teams.
Tend to be rather inflexible --> prove problematic when there are changes in the external environment that may require changes
chain of command
the formal line of authority through which communications and orders are passed down in an organization. It can be seen through a firm's organization chart.
Bureaucracy
the execution of tasks that are governed by official administrative and formal rules of an organization. Characterized by prescribed rules and policies, standardized procedures and formal hierarchical structures.
Bureaucracy is governed by (5)
Continuity: follows official rules rather than taking high risks that jeopardises survival and continuity.
Rules and regulations
Hierarchical structures
Accountability: conducted with written evidence of compliance with the firm's policies.
Formality makes all workers accountable for their performance
centralization
the process by which the activities of an organization, like decision-making, become concentrated within a particular group within that organisation. It is made by a very small number of people. Usually the senior leadership team of directors, simply hold onto decision-making authority and responsibility.
ADVs of centralization (4)
rapid decision making, better control, better sense of direcion and efficiency
DIS of centralization (4)
added pressure to staff, inflexibility, possible delays in decision making, demotoivating employees due to the lack of opportunities to make genuine contribution
decentralization
the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those related to planning and decision-making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group and given to smaller factions within it.
ADVs of decentralization (5)
input from the workforce, speedier decision-making, improved morale, improved accountability, teamwork
DIS of decentralization (4)
costly, some loss of control, communication issues, greater chances of mistakes
decentralized or centralized? (6)
the size of organization, sxale of importance of decision, level of risk. corporate culture, management attitudes and competencies, use of technology

delayering
the process of removing one or more levels in the hierarchy to flatten the organization structures. This reduces the number of layers and widens the span of control.
ADVs of delayering (3)
reduced costs, improves communication, ecourages delegation and empowerment
DIS of delayering (3)
creates anxiety, increased workloads, slower decision-making
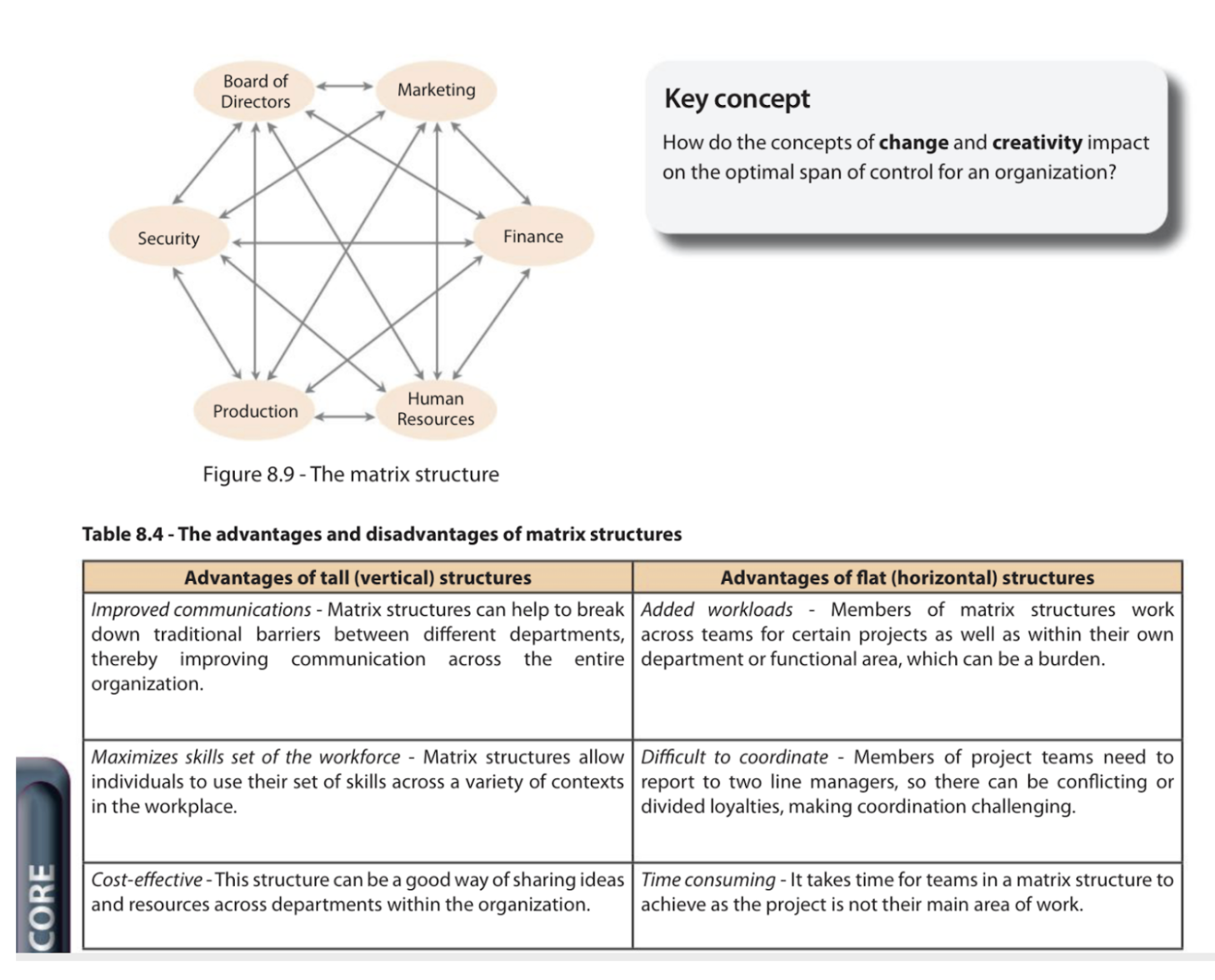
matrix structure
the flexible method of organizing employees from different departments to temporarily work together on a particular project. Functional departments still exists, although the project team has the opportunity to with other colleagues
Flat organizational structure
Flat organizations have fewer levels of in the hierarchy
Managers tend to have a wider span of control
ADVs of Flat organizational structure
More opportunities for career development due to importance of delegation
Improved communication due to fewer layers
Cheaper to operate with less managers
Reduces power distance between senior and junior staff → less alienation
Tall organizational structures:
Many levels of hierarchy
Managers tend to have a narrower span of control
More traditional approach for organizations
Position in the hierarchy indicates status and level of authority
ADVs Tall organizational structures:
Quicker and more effective communication in smaller teams
Easier to control and manage
Increased efficiency and productivity due to specialization of labor
Many levels so opportunities for promotion
ADVS & DIS of matrix structure