Chapter 6: Functions of Integument; Hair
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the functions of the integument?
protection from external environment
vitamin D synthesis
secretion
absorption
immune function
temperature regulation
sensory reception
What does protection from external environment mean?
Protects body from injury, harmful substances, microbes, extreme temperatures, and UV radiation
Prevention of water loss/gain
Epidermis is water resistant, not waterproof
Water lost by sweat and transpiration
What does vitamin D synthesis mean?
Formation of vitamin D3
precursor to calcitriol = increases absorption of calcium and phosphate from diet
regulates blood calcium levels
What does secretion mean?
Waste products secreted onto skin surface during sweating
What does absorption mean?
Skin absorbs some chemicals/drugs but blocks others
Selectively permeable
Suitable for transdermal administration of some drugs
What does immune function mean?
Dendritic cells in epidermis and dermis capable of initiating immune response
What does temperature regulation mean?
Dermal blood vessels capable of vasoconstriction to conserve heat or vasodilation to release heat
What does sensory reception mean?
Receptors detect stimuli (e.g., touch, pressure)
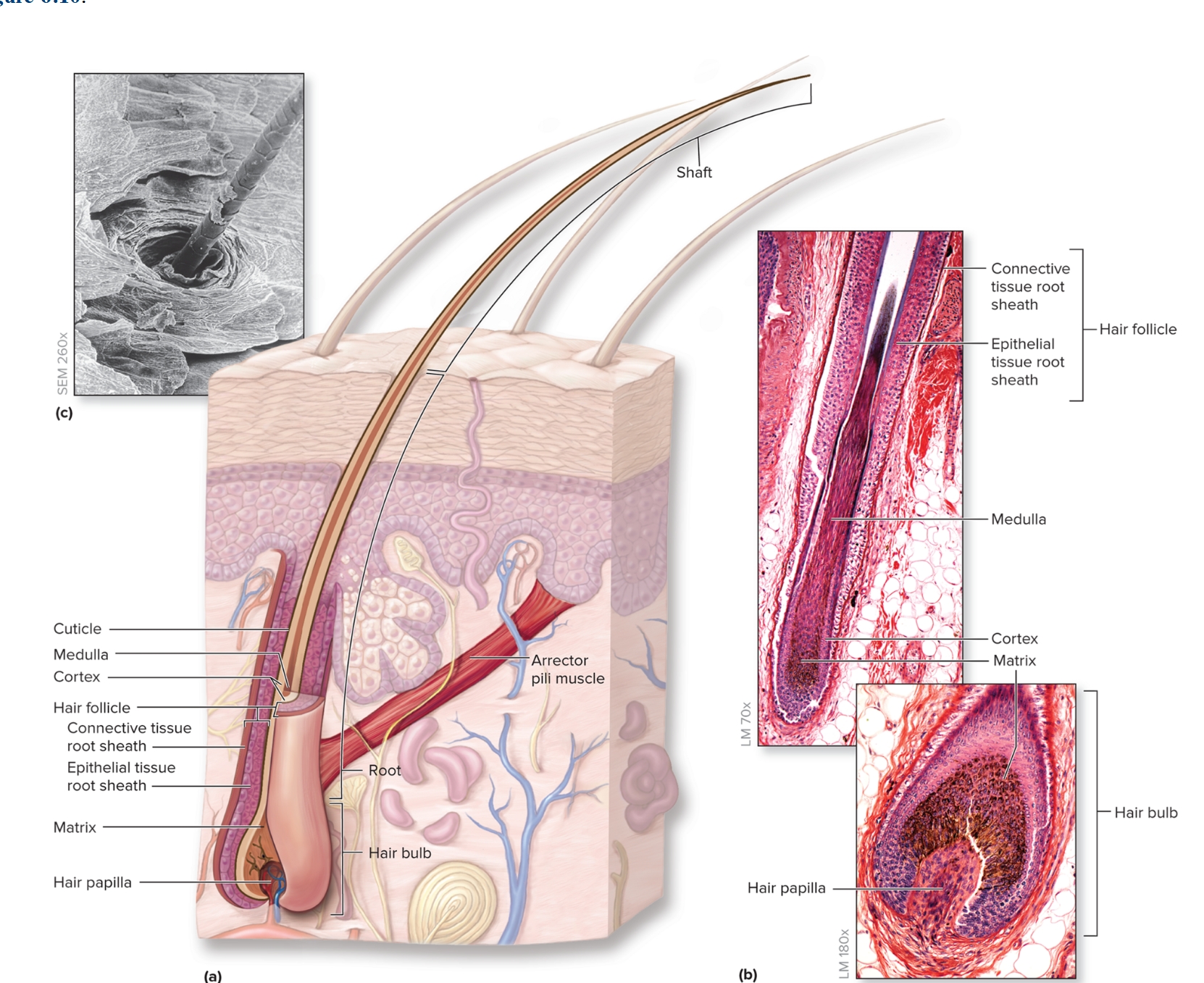
What is hair?
found almost everywhere on the body
keratinized cells form slender filament
Grows from hair follicles
three types:
lanugo, vellus, terminal
What is lanugo hair?
fine, unpigmented, downy hair, appears in last trimester
newborn hair
What is vellus hair?
fine hair, primary human hair, found on upper and lower limbs
What is terminal hair?
coarser, pigmented, longer, on scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes, men’s beards
during puberty, replaces vellus hair in axillary and pubic regions
What are the components of hair?
Hair follicle: oblique tube surrounding hair root, extends into dermis and sometimes subcutaneous layer
Arrector pili: thin ribbons of smooth muscle extend from hair follicle to dermal papillae, elevates hair with contraction, “goosebumps”
What are the functions of hair?
Protection on head, from sunburn and injury, in respiratory system and ears – hair traps particles, debris
Heat retention
Sensory reception: root hair plexuses detect light touch
Visual identification