Light Metals, Non Ferrous alloys (Aluminium)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Advantages of Al for plastic deformation and forming
FCC crystal structure
Good formability
Low hot-strength
Mill products
Flat rolled products
Rod bar wires
Tubular products
Extruded shapes
Two classes of Al wrought products
Mill products
Forging
Flat rolled products divisions
Foil
Sheet
Plate
Foil thickness
Less than 0.2mm
Sheet thickness
0.2-6mm
Plate thickness
Over 6mm
Flat product production
Ingot casting and Hot and Cold rolling
Strip casting and finish rolling
Ingot casting and hot and cold rolling
ingot casting and homogenization
hot rolling
cold rolling
Strip casting and finish rolling
Dont solidify metal completely
Solidifies when it is plastically deforming at the same time
Only for certain Al alloys
International Allot Designation System (IADS)
PUT IN TABLE
Designation system for aluminum alloys
Can you age harden pure Al?
No → no secondary phases
Only certain Al alloys are age hardenable
Non heat treatable Al alloys (Strain hardened)
Al
Al-Mn
AL-Mg-Mn
Al-Mg (5000 series)
Work hardening
High corrosion resistance
Reduces ductility
Weldable
Work hardened Al-Mg have 4 times higher yield strength than pure Al
Work hardening rate is not the same for every alloy.
Heat treatable Al alloys
AL-Mg-Si (6xxx)
Al-Cu-Mg (2xxx)
Al-Zn-Cu (7xxx)
Al-Cu-Mg (2000 series)
If cold worked some of the 2000 series alloys respond better to ageing.
High strength good ductility.
Often stored in a fridge to slow down age hardening to keep the metal in a workable condition.
Aluminium wrought alloys
Aluminum casting alloys are specific types of aluminum alloys that are designed to be used in the casting process.
Molten aluminum is poured into a mold to form a desired shape.
Ability to be melted and cast into complex geometries while maintaining desirable mechanical and physical properties.
Maintains strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance.
Can aluminium alloys be cast by any of the casting processes?
Yes
Casting affects properties mainly porosity through solidification rate → which determines grain size. (dendrite arm spacing.
Most important casting processes for Al
Sand
Permanent mold
Die casting
Sand casting
Disposable sand mold, slow cooling rate
Permanent mold
Metallic permanent mold, gravity cast or low pressure assisted, medium cooling rate
Die casting
Metallic permanent mold, high pressure injection, very high cooling rate.
Aluminium
FCC crystal structure
MP → 600 degrees celcius
Maleable → 12 slip systems
Low yield strength → 7-17MPa
Strain hardenable
G → 70Gpa
Excellent corrosion resistance
high electrical and thermal conductivity
Most effective strengthening mechanism for Al?
Age hardening
Two types of Aluminium alloys
Wrought alloys
Casting alloys
Advantages of Al for casting
Low melting temps
Relatively goof fluidity
Excellent melt-oxidation resistance
Negligible solubility for all gases bar hydrogen
Relatively good surface finish
Disadvantages of Al for casting
Shrinkage
Hydrogen porosity
Hot-tearing / hot-cracking
Reactivity with steel tools
Shrinkage in Al
Volumetric shrinkage: (3.5-8%) occurs during solidification due to density difference between liquid Al and solid Al
Linear shrinkage: (~1.3%) occurs during cooling from solidus to RT
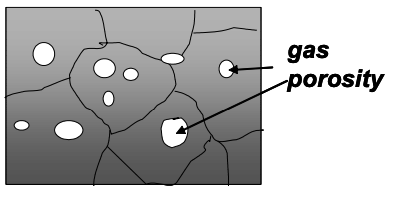
Hydrogen porosity in Al
Effects impact and ductility
Due to the difference in liquid and solid solubility of H in Al.
H2 precipitates out and produces rounded gas holes with smooth internal surfaces.
can be reduced by argon degassing
Hot-tearing or hot-casting (Disadvantage of Al for casting)
Macroscopic tears or cracks in the casting
Occur due to thermal and mech stresses during solidification
Die design and hot-strength of the alloy are important
What elements may casting alloys contain?
Si, Mg, Cu, Zn, Fe, Li, Mn, Ni, Sn, Ti
Why is Silicon important for casting alloy systems?
Increases fluidity
Reduces Coefficient of thermal expansion.
Good weldability
Good corrosion resistance
Aluminium 3xx series
Aluminium-Silicon with magnesium and/or copper (Most important alloys)
Most important alloy system
Al-Si
Al-Si hypoeutectic
A356
Main alloy used in automotive applications.
Contains some Mg
Si particles (phase) are pointed and coarse.
Adding sodium or strontium can can modify Si shape from coarse to fine → Increasing strength and ductility.
Al-Si Hypereutectic alloys
Excellent wear resistance
Contains some Cu
Phosphorus modifies silicon shape to spherical precipitates → inscreasing ductility.
F (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
As-cast condition.
T1 (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
Quenched from casting temperature and naturally aged at room temperature.
T4 (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
Solution heat treated
Quenched
And naturally aged at room temperature.
T5 (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
Quenched from casting temperature
Artificially aged.
T6 (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
Solution heat treated
Quenched
Artificially aged
T7 (Temper designation for aluminium casting alloys)
Solution heat treated
Quenched
Artificially overaged (stabilized)
Aluminium 8xxx series
Aluminium-Lithium Alloys
Properties of lithium in al alloys
Light
Reactive with moisture
Problems with Al-Li
Low thermal stability
High anisotropy (directionally dependant ) of properties.
Susceptible to local deformation
Scattered values of fracture toughness
With increasing lithium → Density decreases and youngs modulus increases