Anatomy and Physiology of the Human Heart and Circulatory System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the primary function of the heart in the circulatory system?
To pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing waste.
What are the main components of the circulatory system?
The heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), and blood.
What is the significance of the unity of form and function in the heart's anatomy?
The structure of the heart is designed to efficiently perform its function of pumping blood.
What is the cardiovascular system composed of?
The heart and blood vessels.
What is the function of arteries?
To take blood away from the heart.
What is the function of veins?
To take blood towards the heart.
What do capillaries do?
They connect arteries and veins, distributing nutrients to tissues and collecting wastes.
What are the two major circuits of the circulatory system?
The pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit.
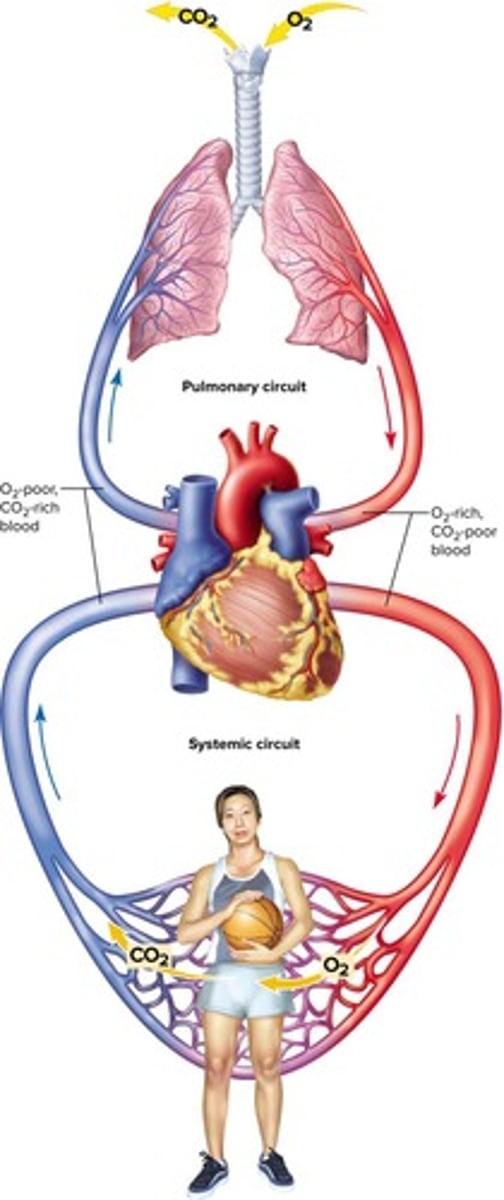
What does the pulmonary circuit do?
Carries blood to the lungs for gas exchange and back to the heart.
What does the systemic circuit do?
Supplies oxygenated blood to all tissues of the body and returns it to the heart.
Where is the heart located?
In the mediastinum, between the lungs.
What is the size of the heart at any age?
The size of a fist.
What are the two layers of the serous pericardium?
The parietal layer and the visceral layer (epicardium).
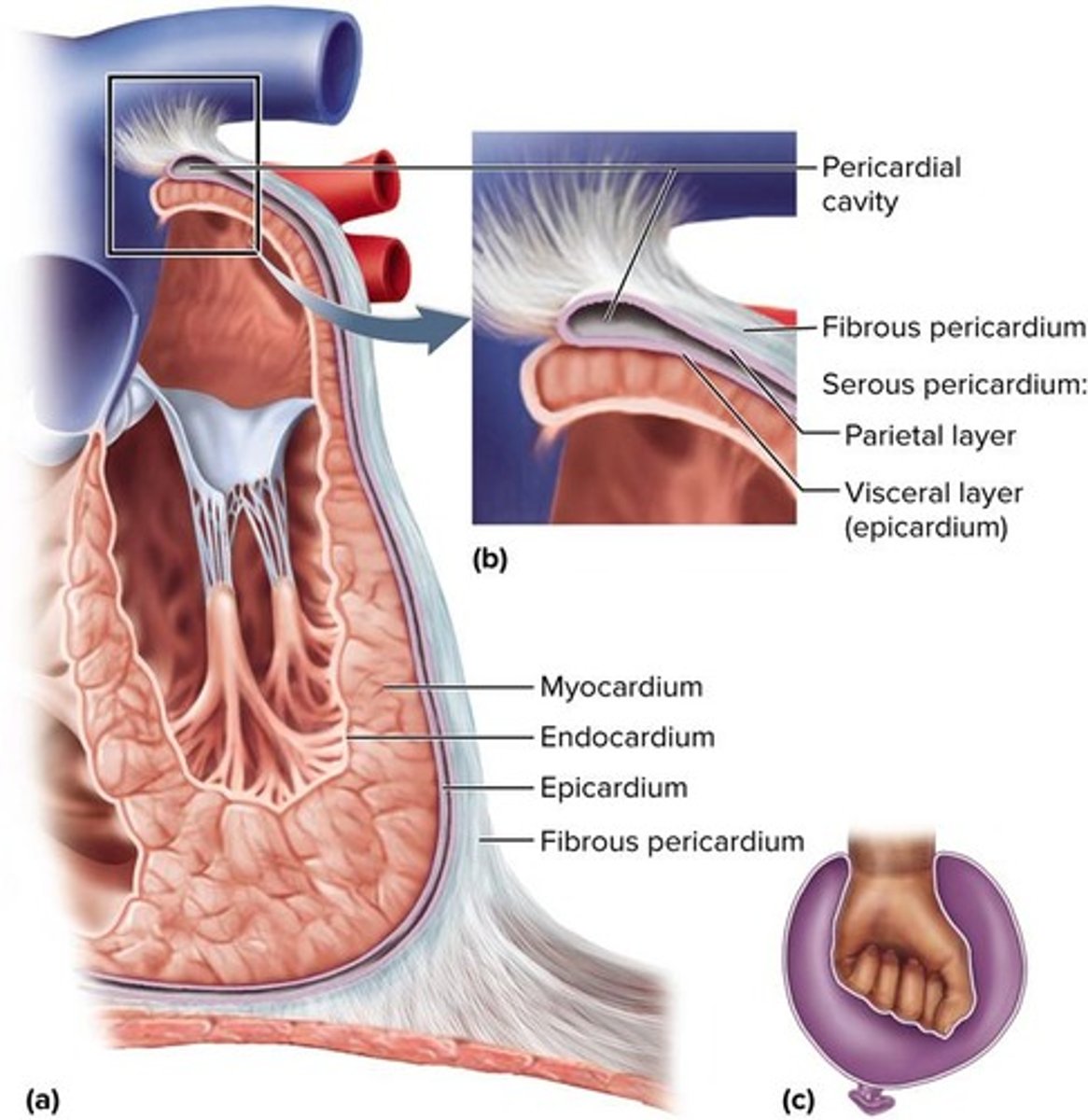
What is the function of the pericardium?
To allow the heart to beat without friction, provide room to expand, and resist excessive expansion.
What is the myocardium?
The layer of cardiac muscle that is proportional to its workload.
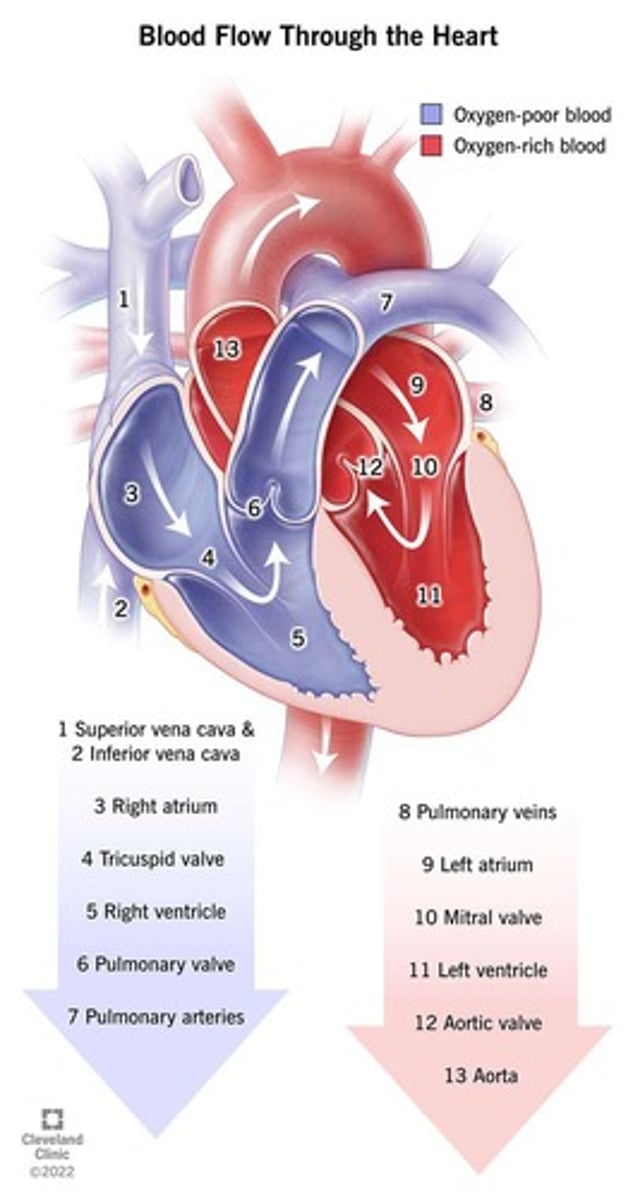
What are the four chambers of the heart?
Right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle.
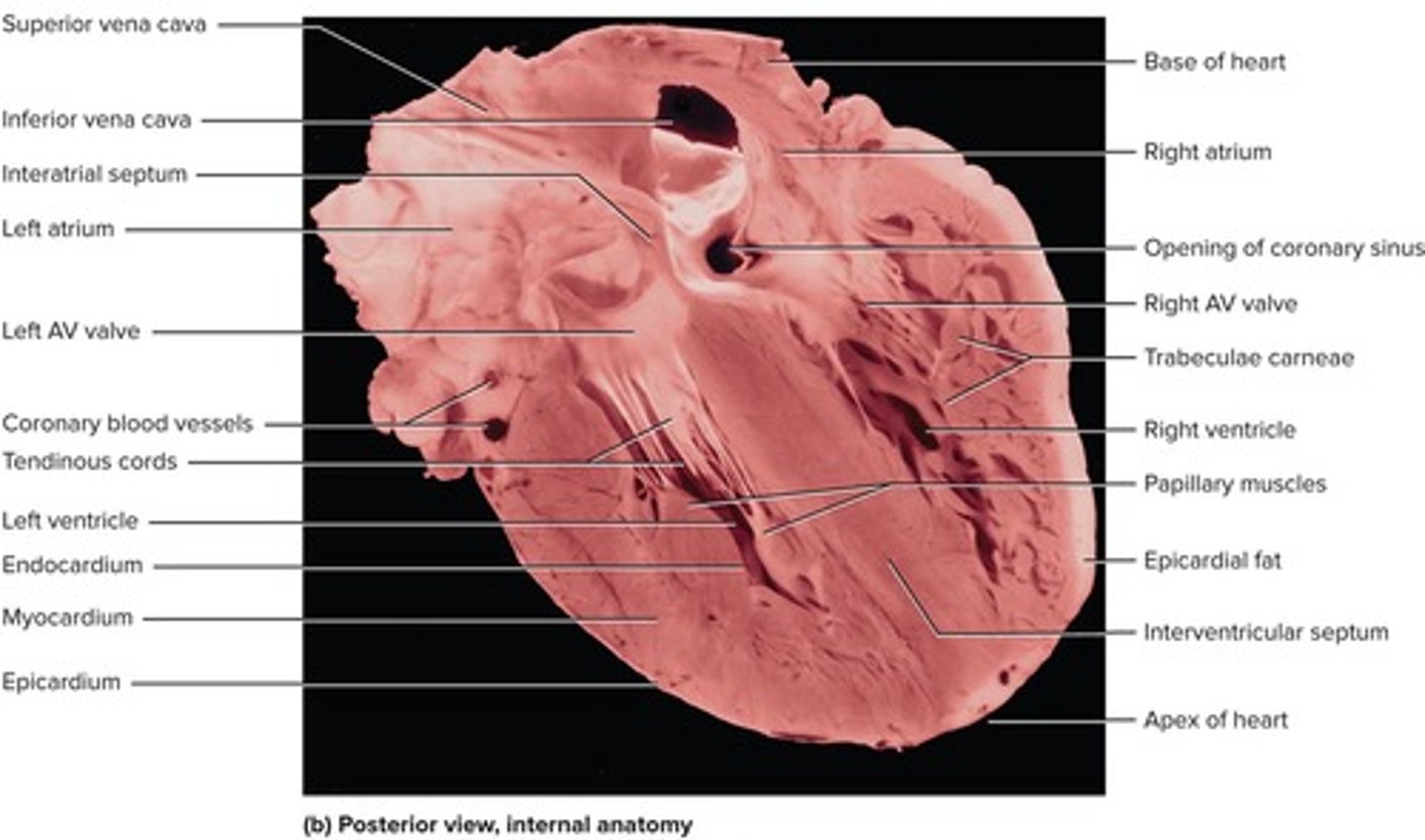
What separates the right and left atria?
The interatrial septum.
What is the function of valves in the heart?
To ensure one-way flow of blood through the heart.
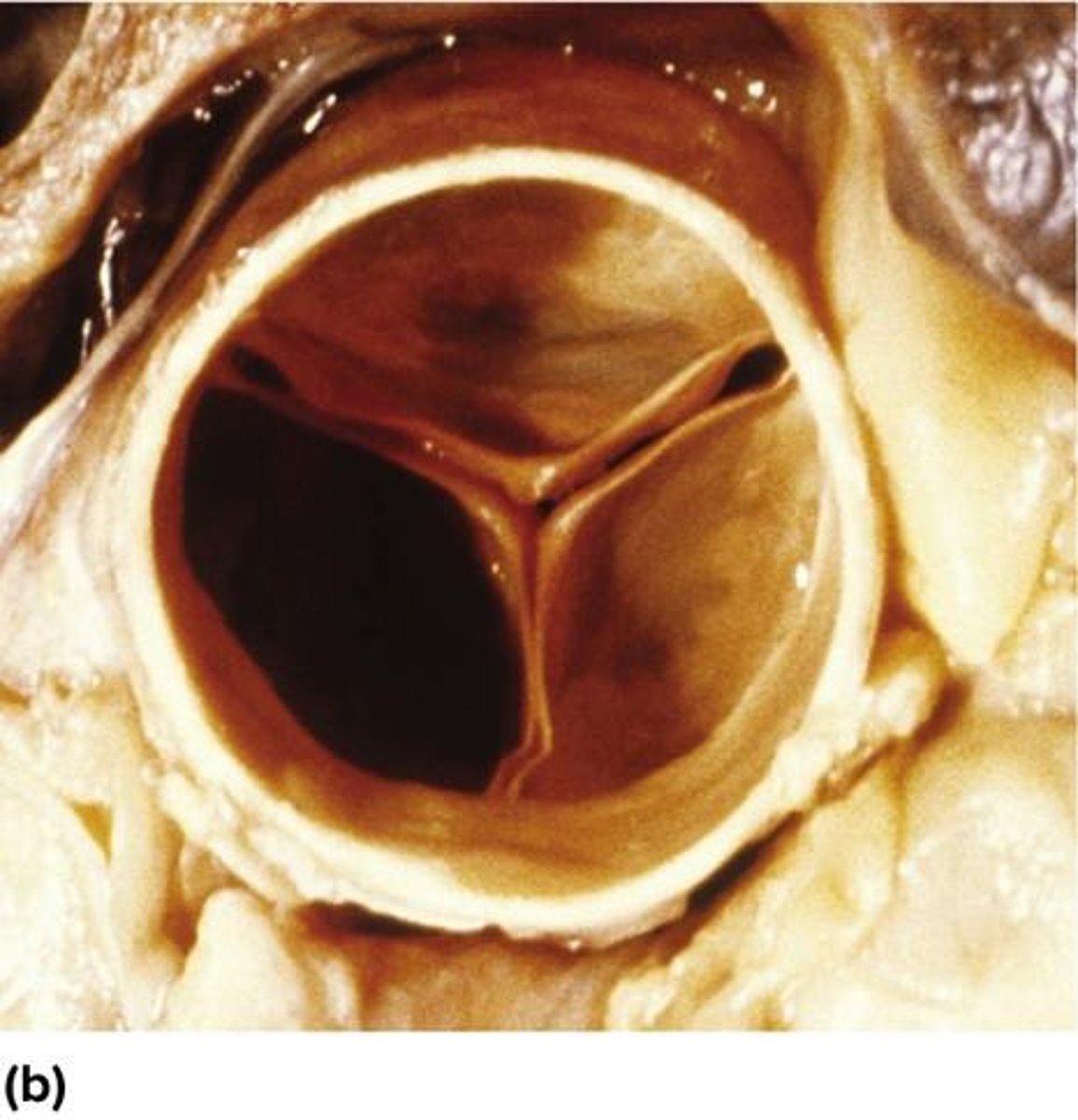
What are the two types of heart valves?
Atrioventricular (AV) valves and semilunar valves.
What is angina pectoris?
Chest pain from partial obstruction of coronary blood flow.
What is a myocardial infarction (MI)?
Sudden death of a patch of myocardium resulting from long-term obstruction of coronary circulation.
What are cardiomyocytes?
Striated, short, thick, branched cells that make up cardiac muscle.
What is the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
It acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, generating rhythmic electrical signals.
What is the cardiac cycle?
One complete contraction and relaxation of all four chambers of the heart.
What is the normal resting heart rate for adults?
Typically 70 to 80 beats per minute.
What is tachycardia?
A resting adult heart rate above 100 beats per minute.
What is bradycardia?
A resting adult heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute.
What is valvular insufficiency?
Any failure of a valve to prevent the backward flow of blood.
What is the function of the coronary circulation?
To supply blood to the heart muscle itself.
What is the significance of preload in stroke volume?
It is the amount of tension in ventricular myocardium immediately before contraction.
What is the effect of increased afterload on stroke volume?
It decreases stroke volume.
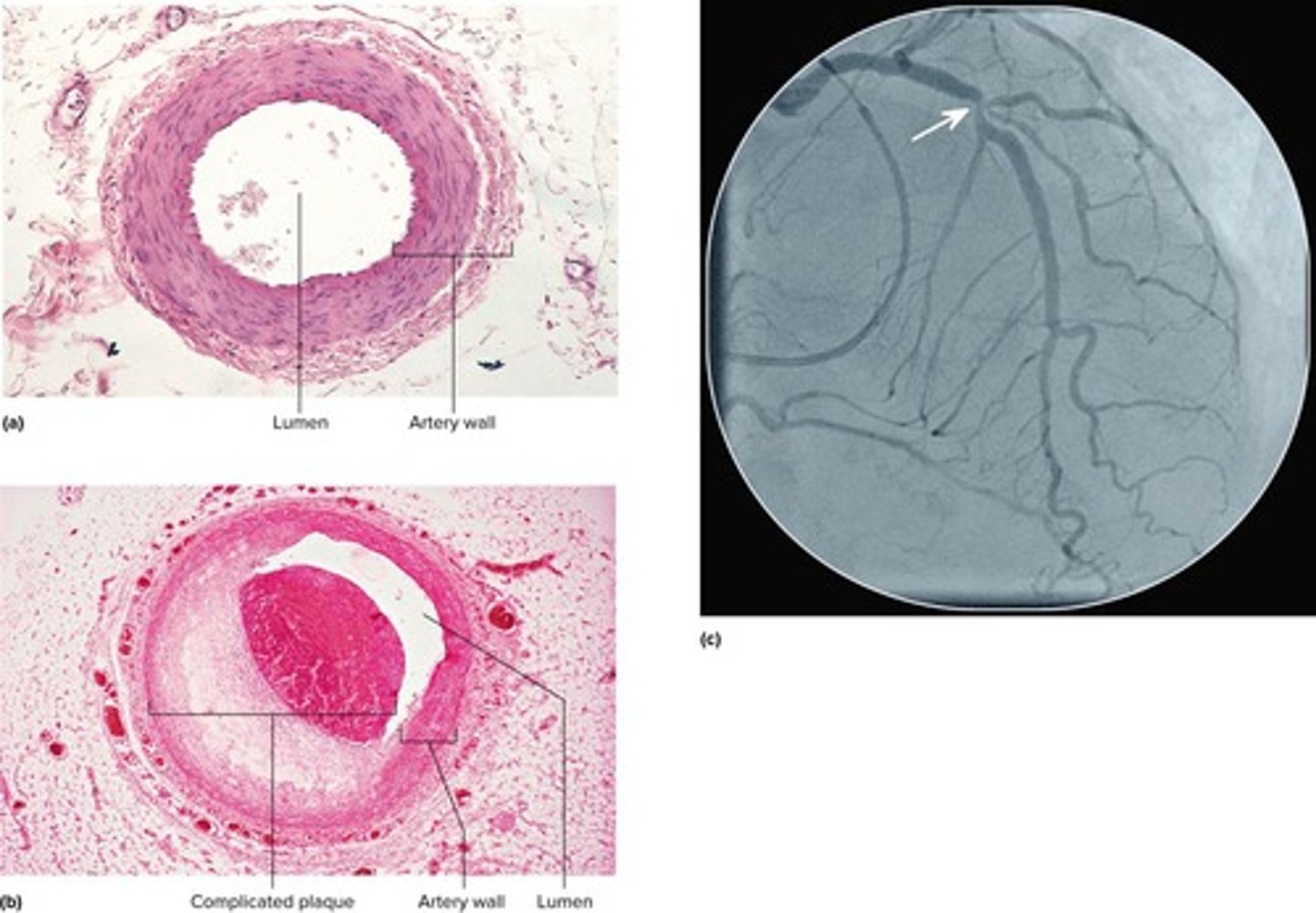
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
A constriction of the coronary arteries, usually due to atherosclerosis.
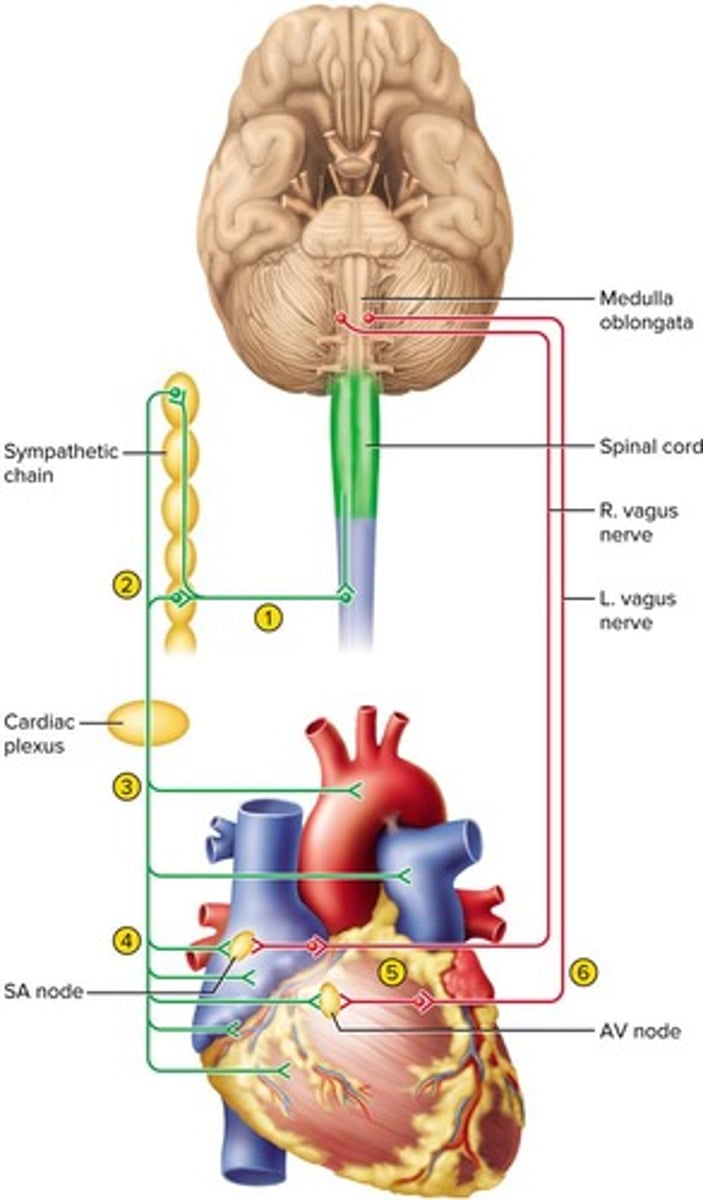
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in heart function?
It controls heart rhythm and contraction through sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation.
What is the cardiac output (CO)?
The amount of blood ejected by each ventricle in one minute.
What factors can increase heart rate?
Stress, anxiety, drugs, heart disease, or fever.
What is the significance of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
They join cardiomyocytes end to end and facilitate electrical and mechanical connections.
What is the role of gap junctions in cardiomyocytes?
They allow ions to flow between cells, enabling coordinated contraction.
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
It provides structural support and electrical insulation between atria and ventricles.
What happens during isovolumetric contraction?
Ventricles contract without ejecting blood, and all four valves are closed.
What is the purpose of defibrillation?
To reset the heart to sinus rhythm by depolarizing the entire myocardium.