Mammary Gland Development and Lactation Processes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Mammary Gland
Modified exocrine glands evolved to produce milk.
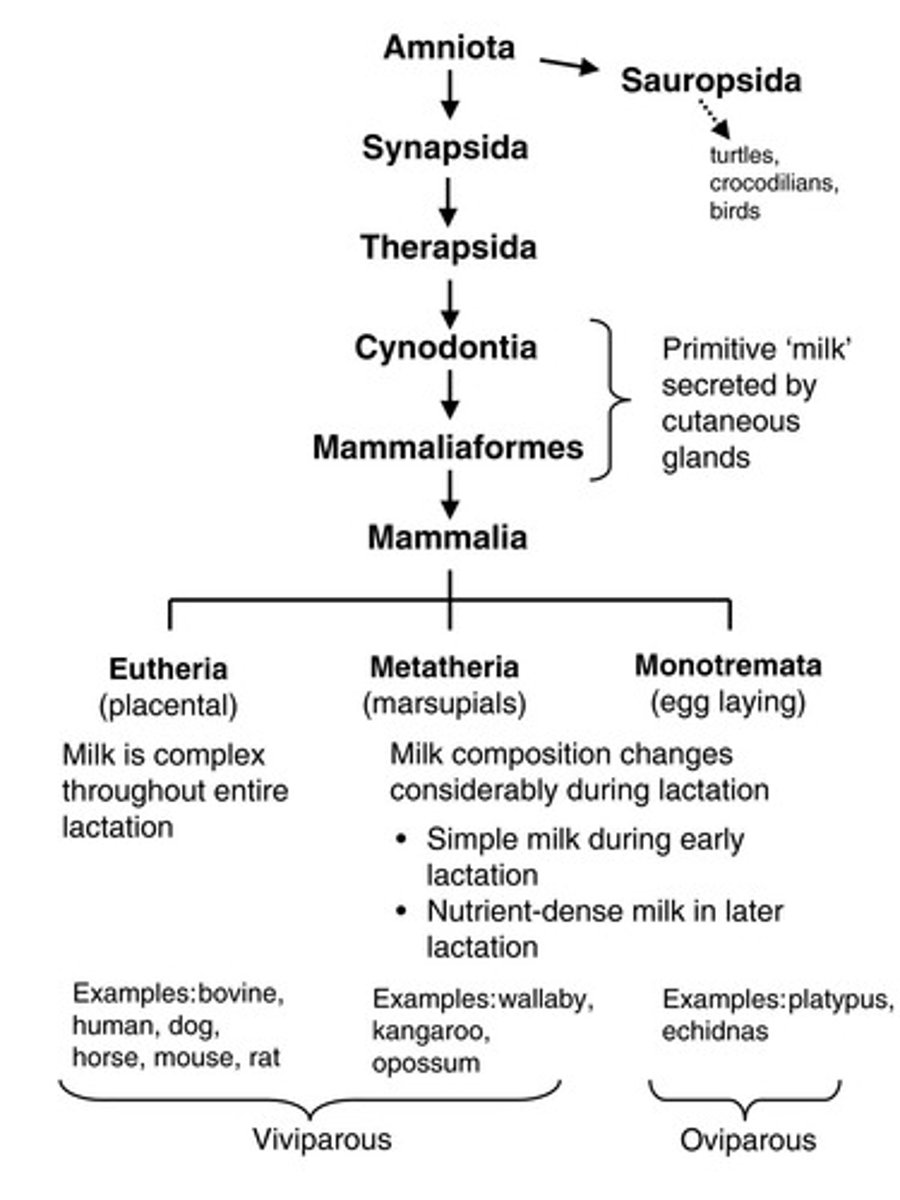
Monotremes
Early mammals that secrete milk onto skin.

Marsupials
Mammals with teats but less developed mammary systems.
Eutherians
Mammals with fully developed mammary glands.

Colostrum
First milk providing nutrients and immunity to neonates.
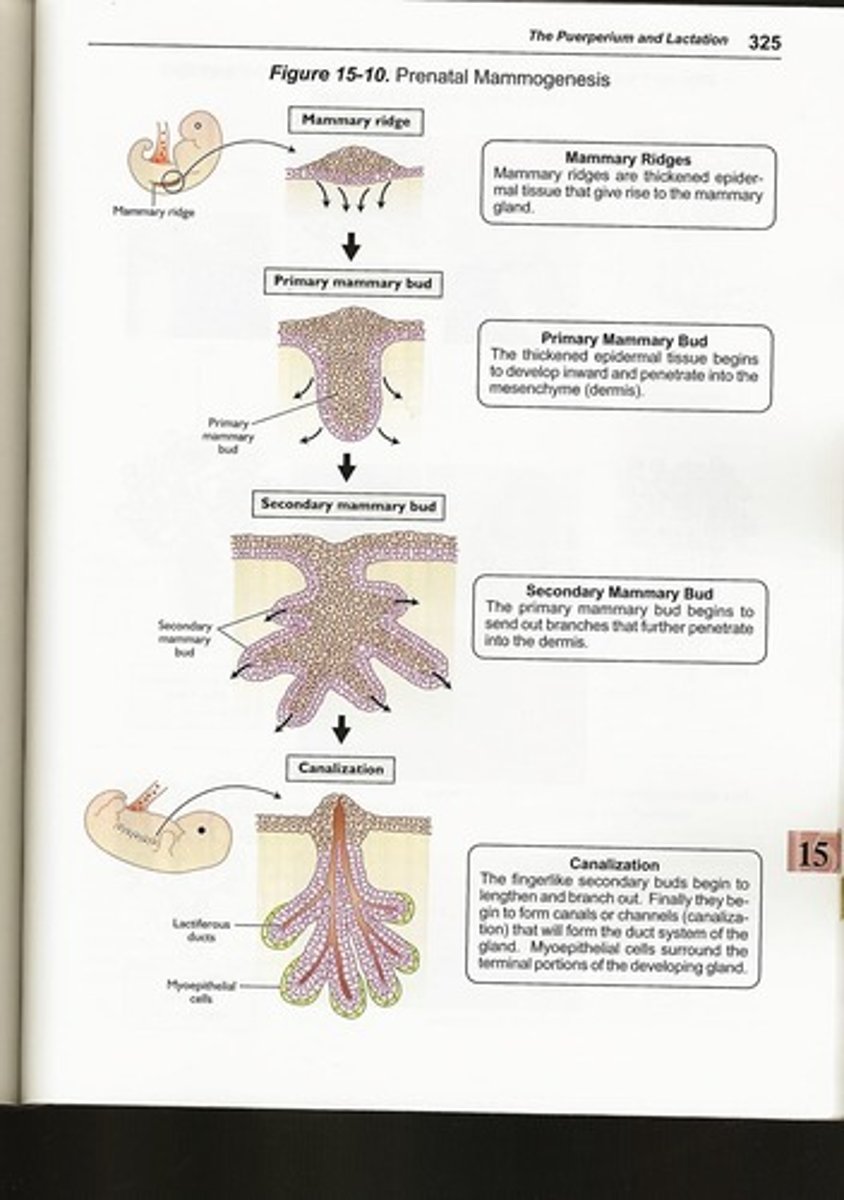
Mammogenesis
Growth of mammary gland through various life stages.
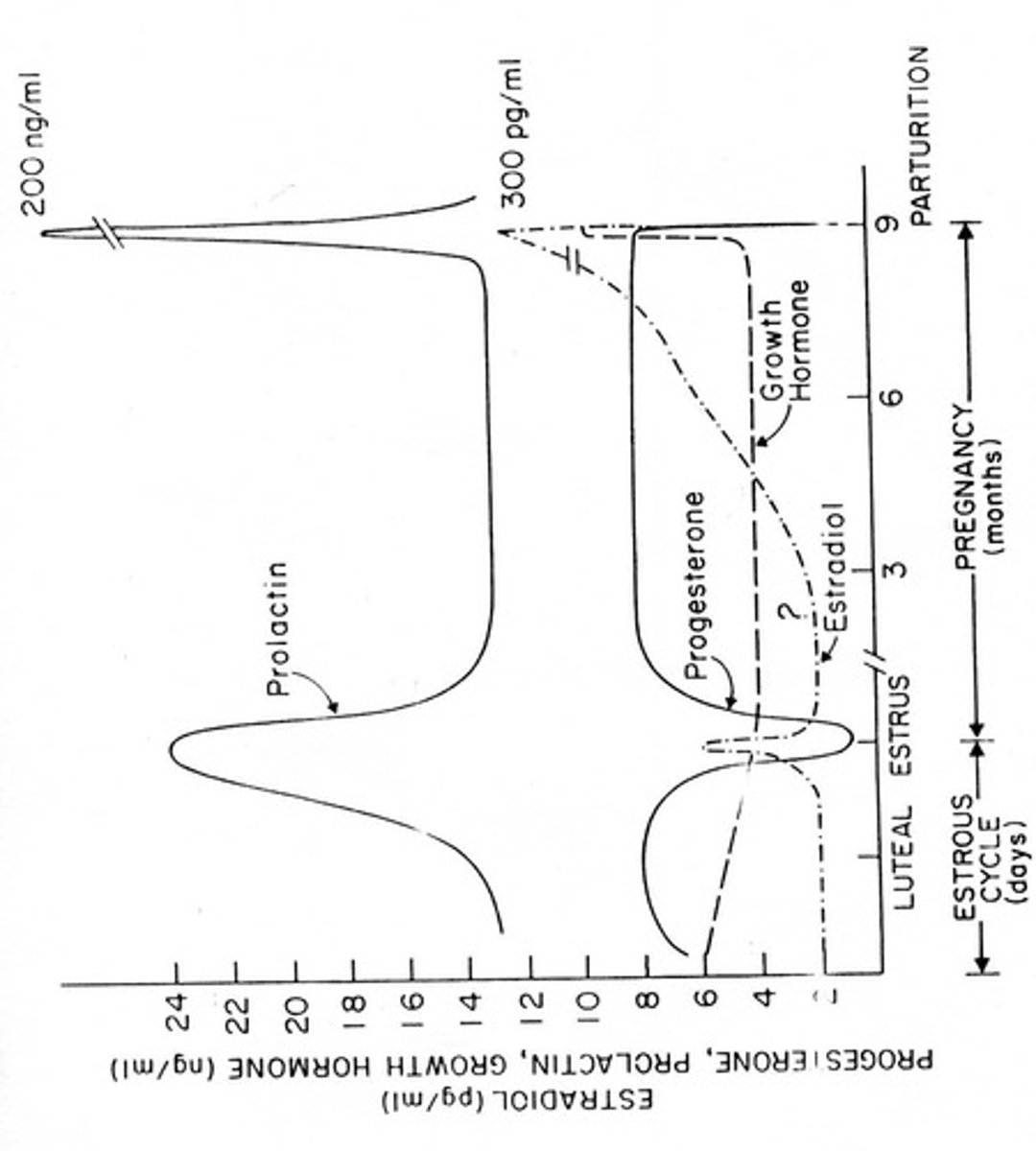
Lactogenesis
Transition from pregnancy to lactation at parturition.
Galactopoiesis
Maintenance of lactation through suckling and nursing.
Involution
Transition to non-lactating period after weaning.
Primary Bud
Initial growth stage of mammary gland influenced by insulin.
Cortisol
Hormone that synergizes with estrogen and prolactin.
Estrogen
Hormone promoting ductal growth and branching in puberty.
Progesterone
Hormone stimulating alveolar development before parturition.
Mammary Alveoli
Structures synthesizing and secreting milk components.
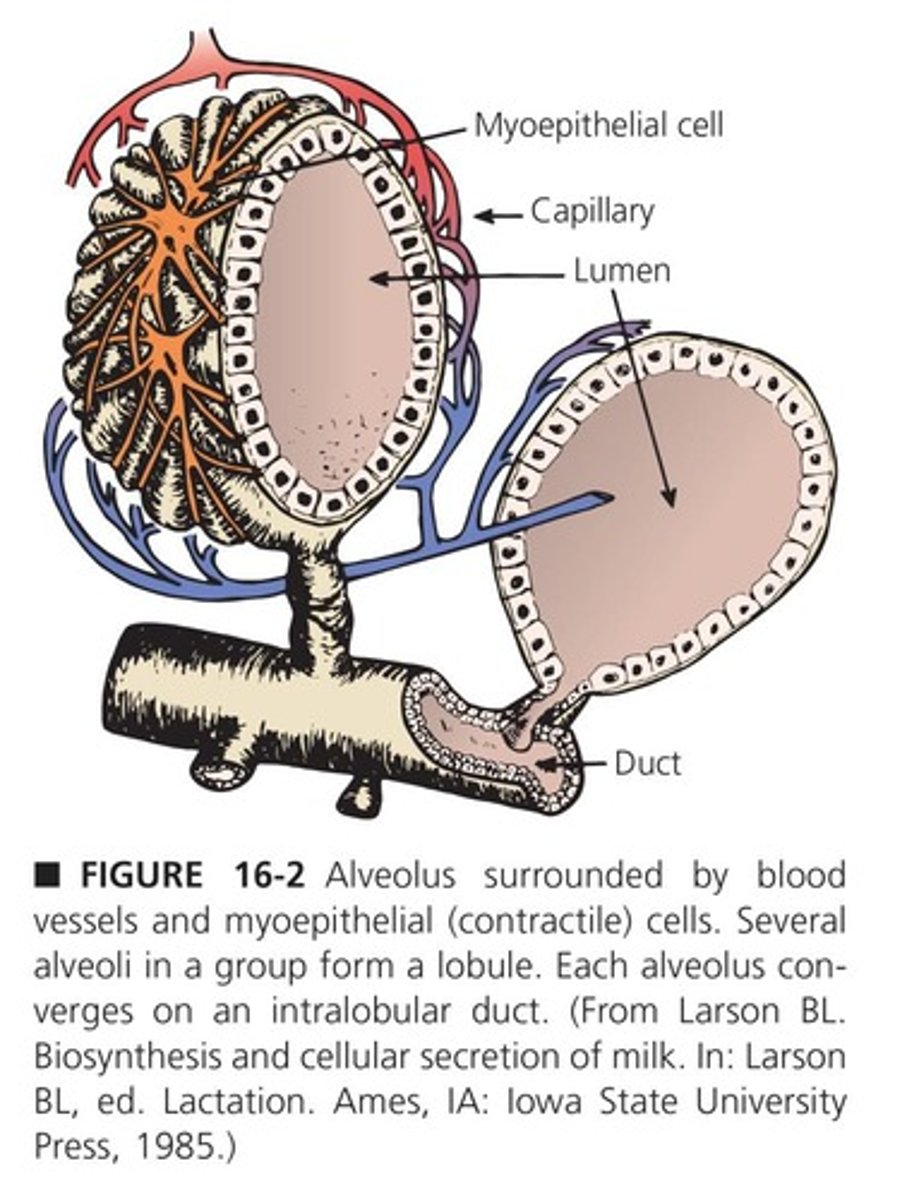
Secretory Epithelium
Cells that produce milk components in alveoli.
Myoepithelial Cells
Cells that contract to expel milk into ducts.
Prolactin
Hormone crucial for initiating and maintaining lactation.
Thyroid Hormone
Essential for normal milk production and metabolic rate.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Enhances metabolism but lacks direct lactogenic activity.
Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I)
Peptide necessary for growth, similar to insulin.
rbST
Recombinant bovine somatotropin used to enhance milk production.
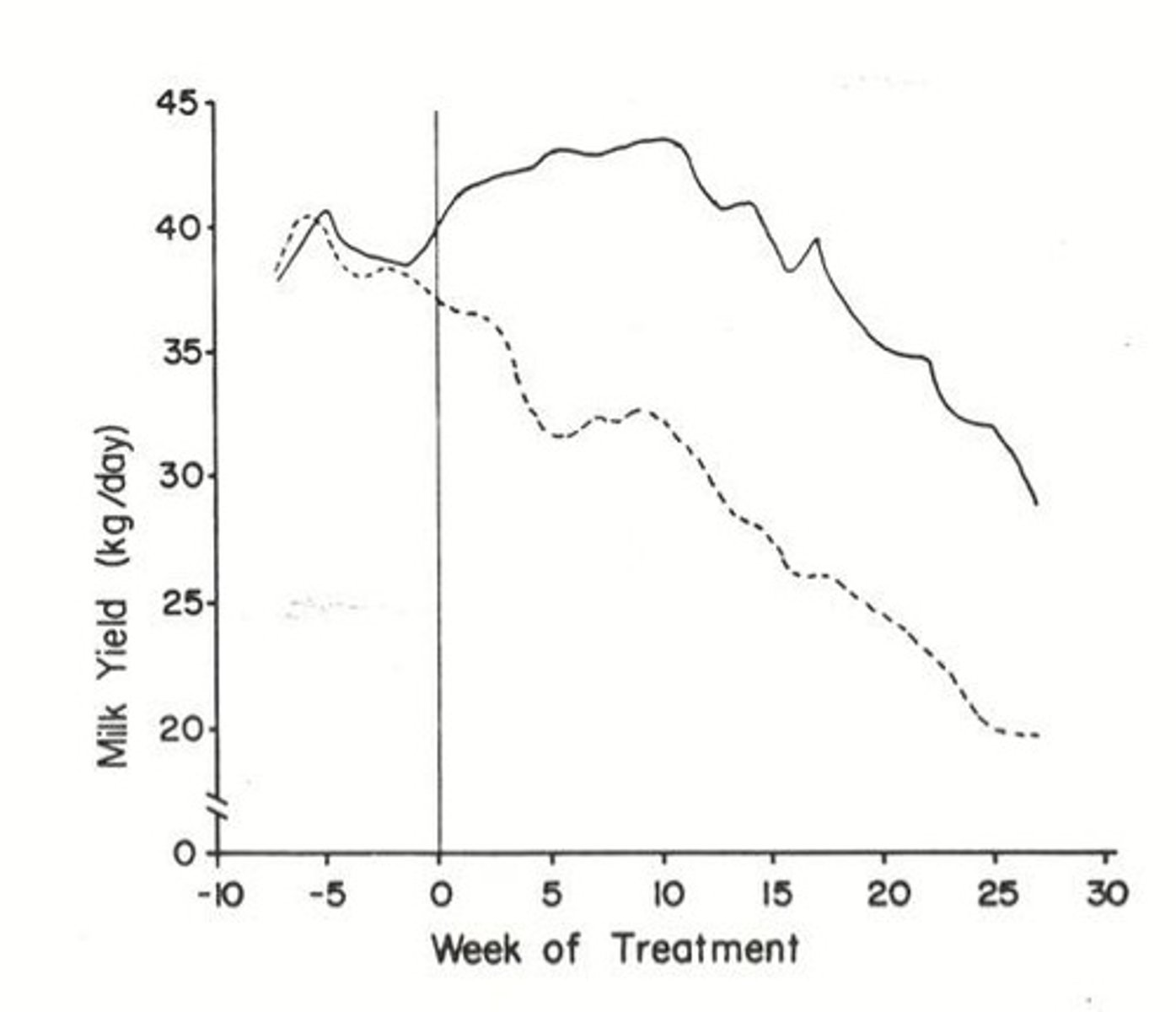
Nutritional Status
Modulates response to growth hormone and lactation.
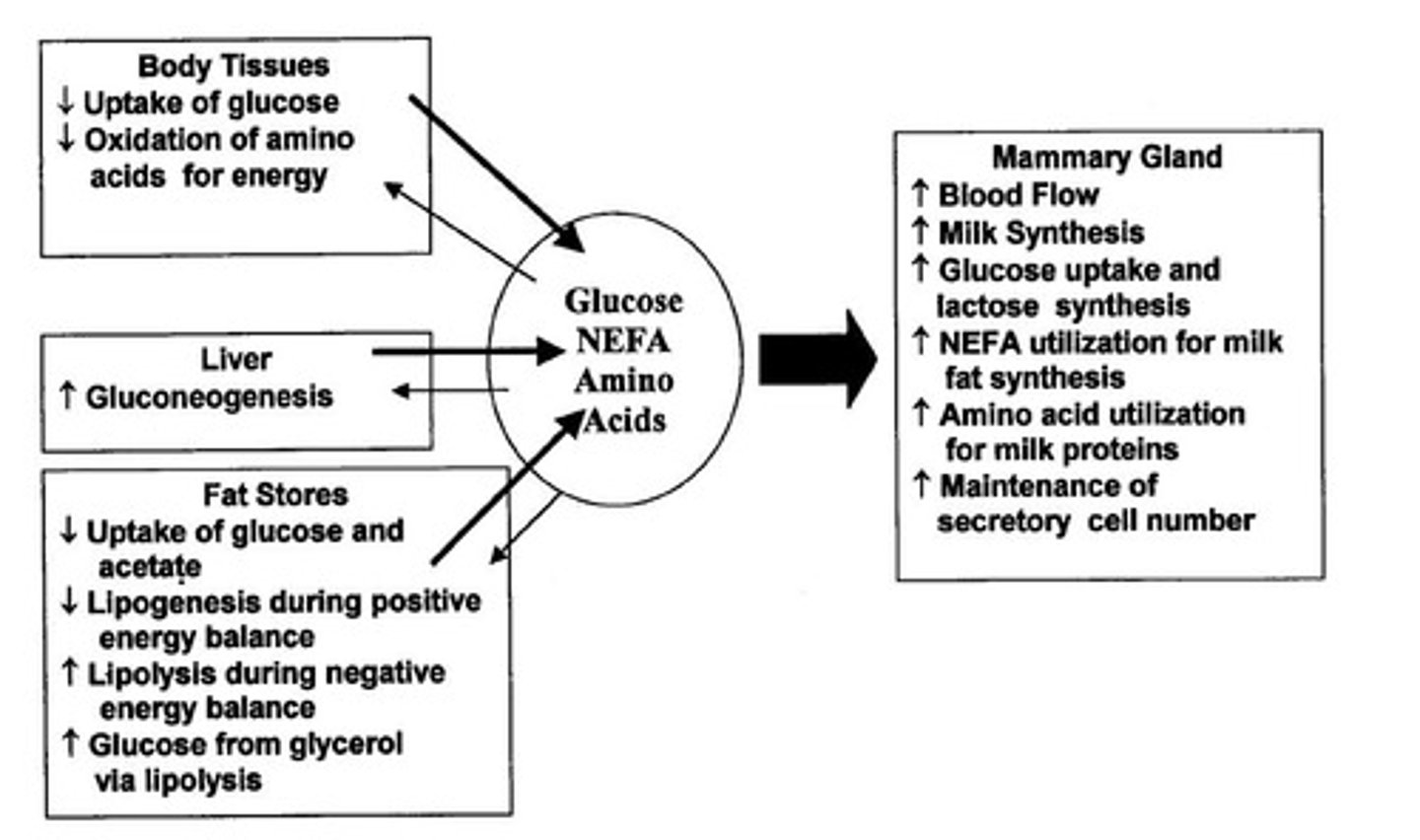
Hormonal Requirements
Include thyroid hormone, prolactin, cortisol, and GH.
Human Safety
Declared safe by health associations for rbST milk.
End Bud Formation
Final stage of alveolar development during puberty.