IGCSE Computer Science Hardware
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What are the 4 components of a computer
input, output, processing, storage
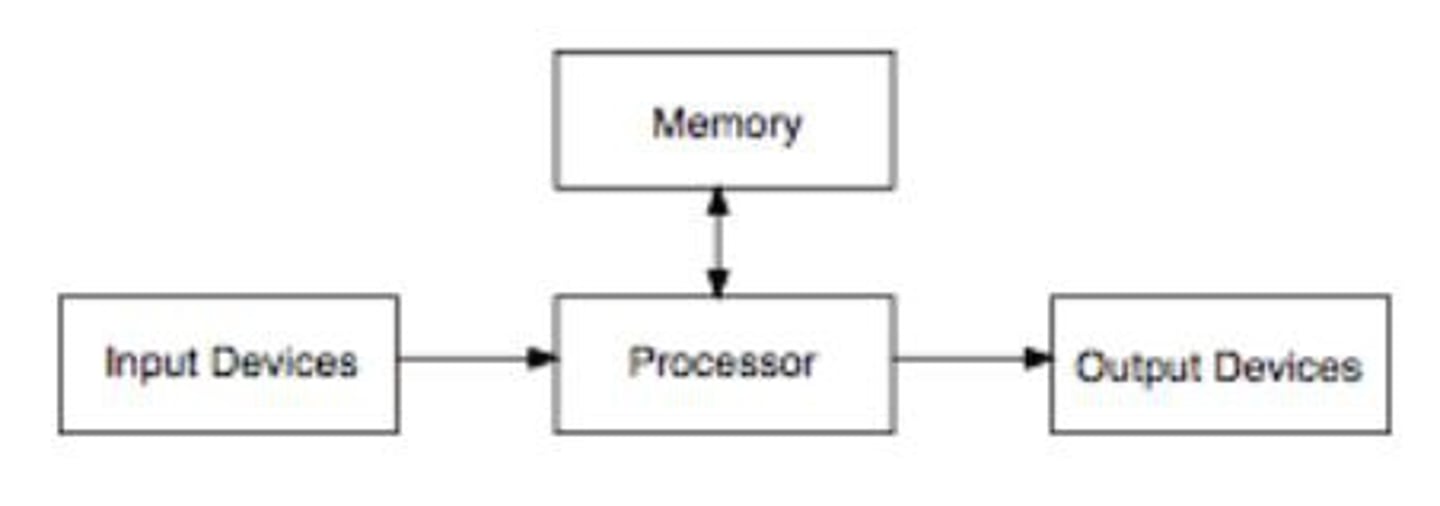
What is the purpose of the CPU
it processes the data and controls the flow of data between the computer's other units

Von Neumann Architecture
This is when data and instructions are stored in the same memory (RAM) in binary as a stored program.
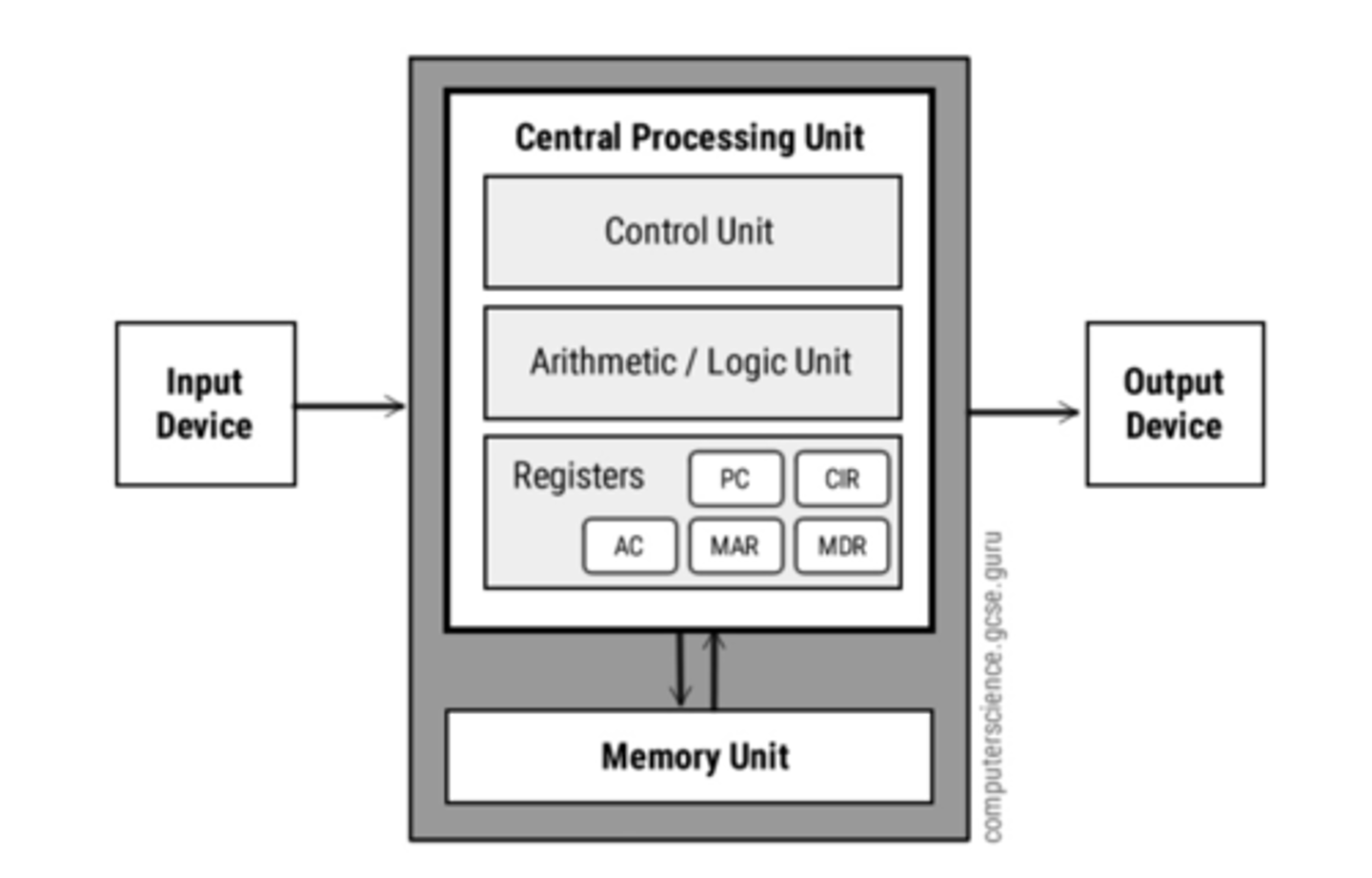
The Control Unit
Component of a processor that directs and coordinates most of the operations in the computer.
And decodes instruction
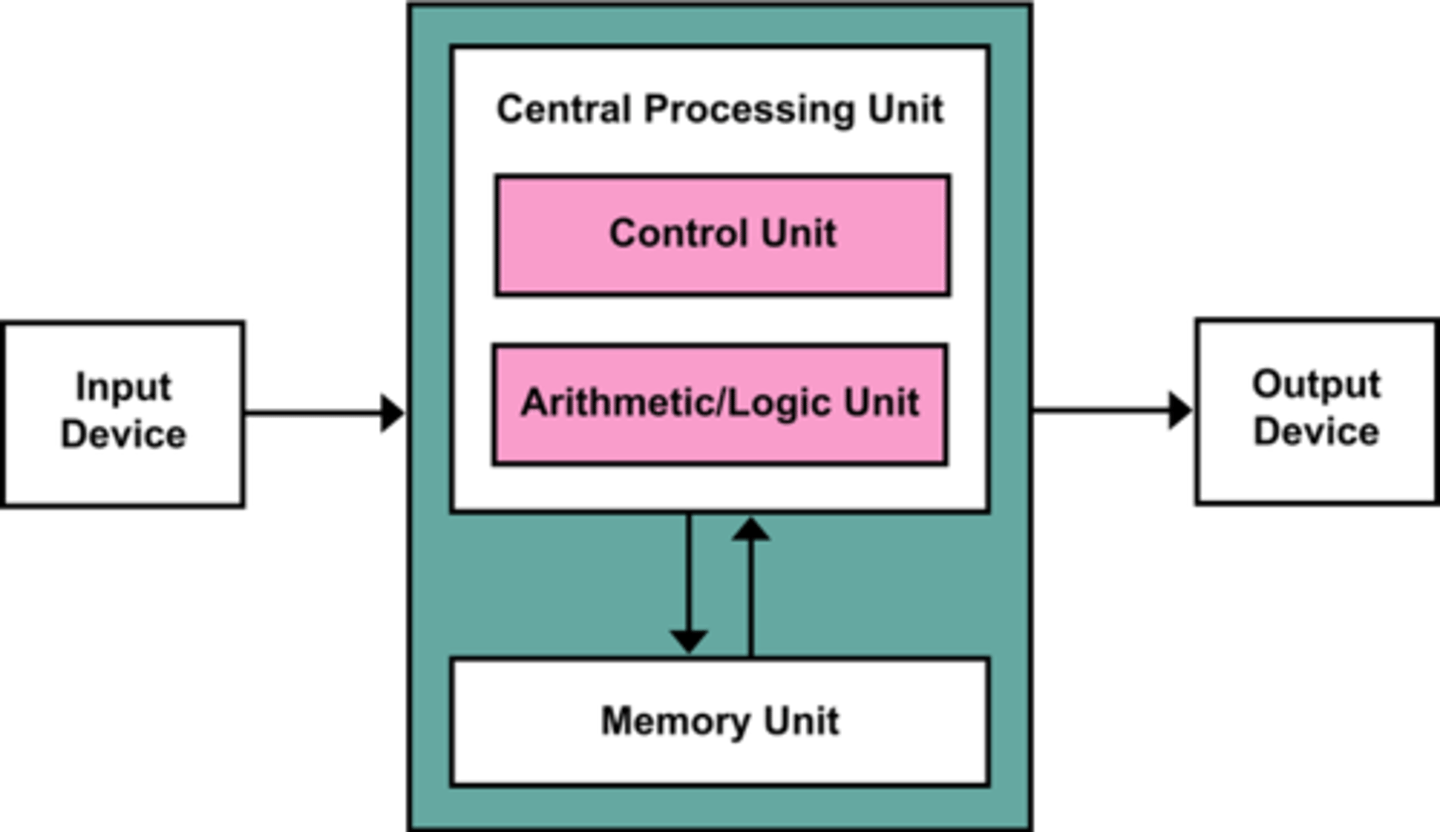
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The part of the central processing unit that performs arithmetic computations and logical operations.
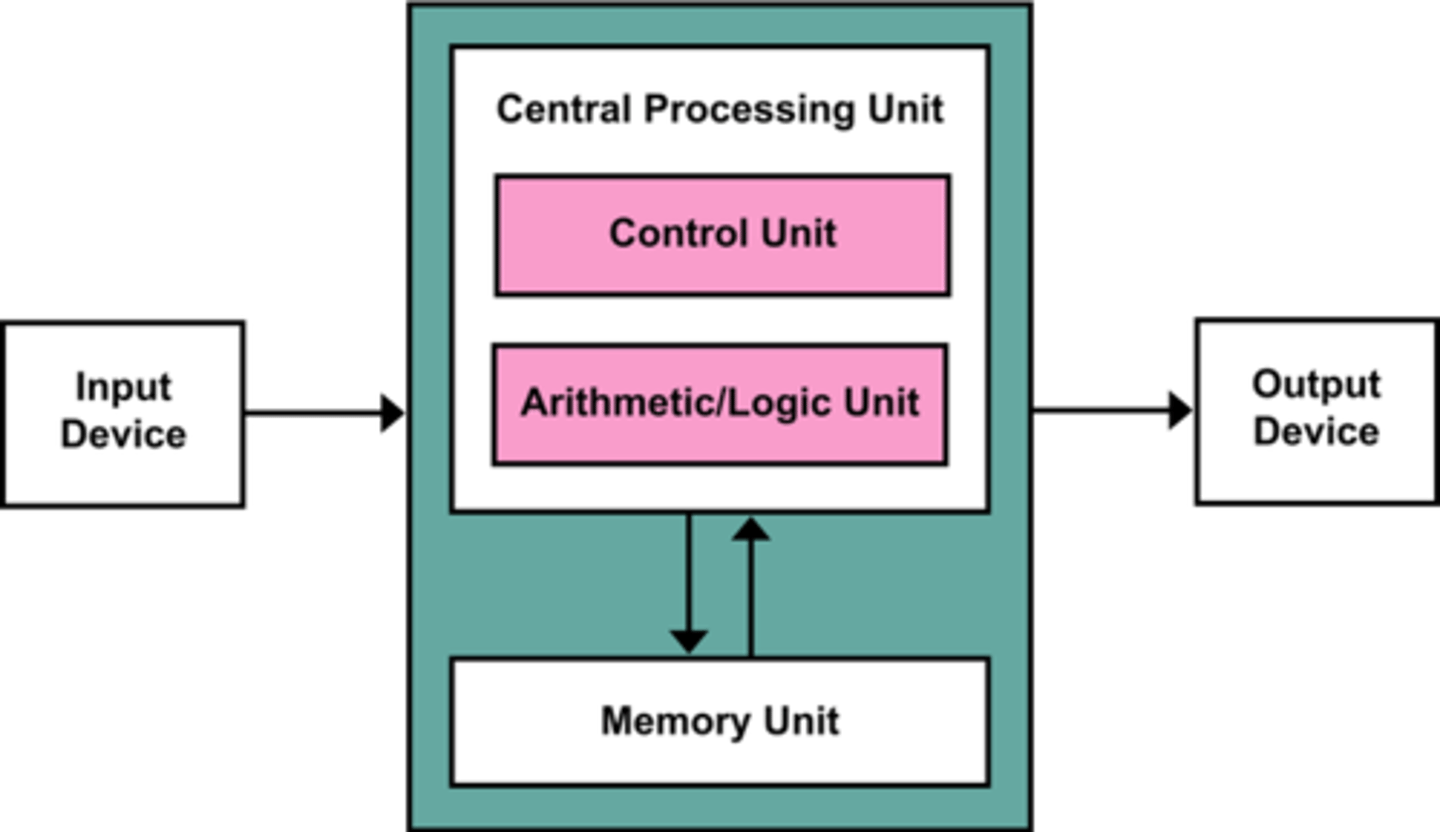
Registers
Small, high-speed storage locations that temporarily hold data and instructions.
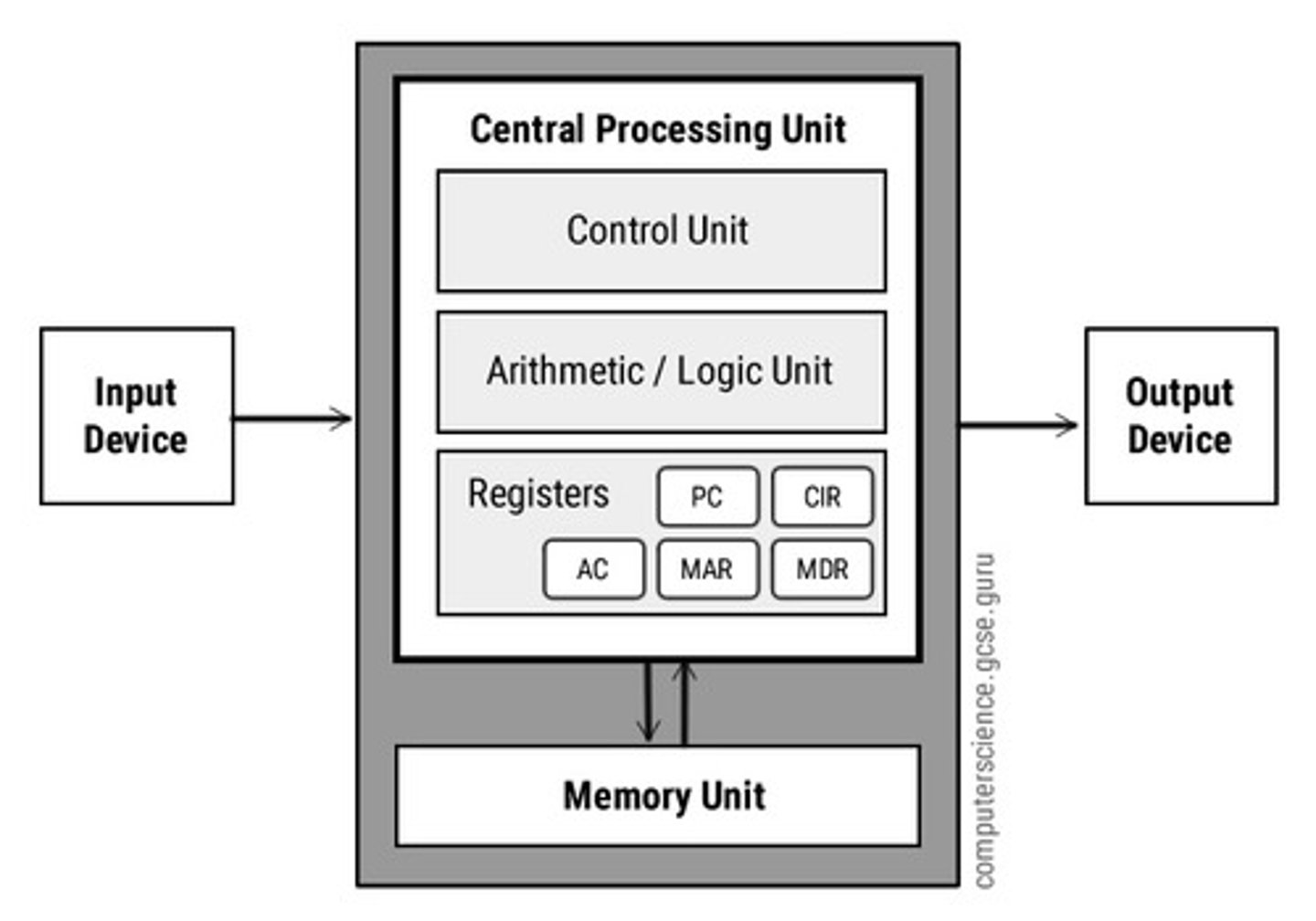
Program Counter (PC)
The register that contains the address of the next instruction to be executed
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Holds memory address for data or a instruction about to be used by the CPU
Memory Data Register (MDR)
holds the data that is being transferred either to or from the memory unit
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
holds the instruction currently being executed or decoded
Accumulator (ACC)
holds the result of an instruction before it is transferred to memory
CPU architecture
Unit 3 Computer architecture and
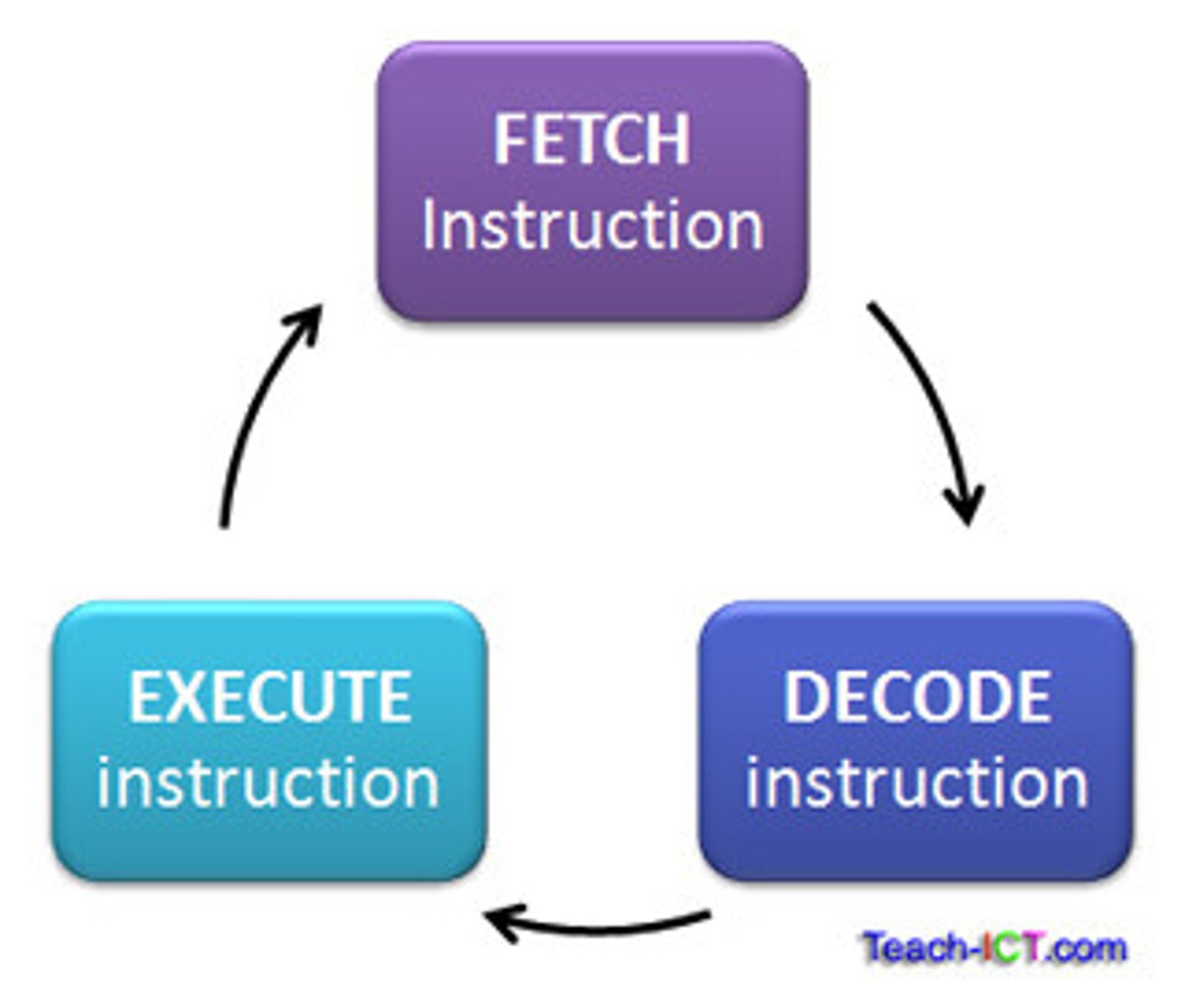
Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
The process that the CPU uses to retrieve and execute instructions
Buses
Collection of wires that carry signals between various components of the computer system
The three buses that make up the system bus are
The Address Bus, The Data Bus, The control Bus
The Address Bus
transfers addresses from the CPU to memory
Data Bus
transmits data from the CPU to memory or input/output controllers
Control Bus
transfers control signals from the control unit to other components in the computer system such as memory or input/output controllers
Memory Unit (MU)
Store's instructions and processes that the computer needs regularly while processing
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Temporary memory a computer uses to store information while it is processing.
What are the 3 factors that affect a CPU's performance
Clock Speed, CPU cores, Cache
Cores
The Number of Processing units
Cache
A component that is faster than the ram, but slower than the Registers
Clock Speed
Cycles per second measured in hertz
Instruction Sets
A set are commands and operations that the central processing unit can process.
Opcodes
Gives the CPU a precise job to happen
Operands
The actual data required for a specific job
What is an embedded system?
a computer implemented as part of a larger system.
What is an input device?
Device that inputs data into the computer
keyboard
An input device that enters data with letters, numbers, symbols, and special function keys.
optical mouse
uses optical sensors that emit and sense light to detect the mouse's movement
What is a microphone?
An audio input device that allows a user to enter sounds into the computer system.
What is a touch screen?
A special type of screen which reacts to human touch.
What are the types of touch screens
Resistive, Capacitative, infra red
What is an automatic input device
A device that functions on little to none human reaction
Examples of automatic input devices
Sensors, scanners, digital cameras
What is a sensor
An input device that takes readings from the environment such as temperate or light.
What is a barcode
A series of dark and light parallel lines of varying thickness
What are QR codes?
a type of 2D code that is used to provide easy access to info through a smart phone

What is an output device?
a device that outputs data from the computer
Examples of output devices
Monitors, touch screens, projectors, printers, speakers, actuator
What is the the difference between memory and storage
Memory is the microchips and transistors that the computer needs to operate,
Storage refers to the device used to store documents and files
Primary Storage
The main storage area in a computer where data is stored for quick access by the CPU.
magnetic hard drive
A hard drive consisting of
(Platters) Circular metal plates covered in a magnetic material
A electromagnetic read write head
A spindle
A track and sector
How is a HDD written into
The hard drive spins the metal disk(s) at a high speed using a motor
A read/write arm, controlled by an actuator, moves the head over the surface of the disc to the location of the data
The data is read/written using electromagnets
Solid State Hard Drive
Very fast storage drive with no moving parts. Faster than traditional spinning hard drive. Currently more expensive.
What is a flash drive
A collective term used to refer to any drive (typically usb) that uses flash technology
Optical Drives
A drive that is used to read disc drives
What is virtual memory?
a portion of the hard disk designated to function as additional RAM
what are Network interface Cards
A component used in computers to give them the ability to connect to the internet wired or wirelessly
What is a Mac Address
is a unique number stored in each NIC so it can be used to identify a device on a network.
What is an IP address?
a unique string of numbers separated by periods that identifies each computer using the Internet Protocol to communicate over a network.
What is a character set
All the characters and symbols that can be represented by a computer system where Each character and symbol is assigned a unique value;
What is sample resolution
Number of bits per sample
What is the sample rate
the number of samples taken per second
Define resolution
the number of pixels in the image
What is colour depth?
the number of bits used to represent each colour
serial simplex
Data is transmitted one bit at a time in a single direction on one wire
Serial-Half-duplex
Data can be transmitted in both directions on a single wire but only one bit at a time can be transmitted in one direction at a time
Serial-Full-duplex
Data can be transmitted in both directions at the same time on a single wire one bit at a time
Parallel-Simplex
Multiple wires transmit one bit at a time in one direction
Parallel-Half-duplex
Multiple wires send multiple bits of data in both directions but only one direction at a time
Parallel-Full-duplex
Multiple wires send multiple bits of data in both directions at the same time
Advantages of serial data transmission
The data will arrive in the order it is sent
It is less likely to have errors
Serial transmission is cheap over short and long distances as the cost of wire is fairly inexpensive
Disadvantages of serial
Data transmission is slow, especially over long distances as only small quantities of data can be transmitted at a time
Serial transmission is expensive over very long distances as the cost of wire dramatically increases
Advantages of parallel
Parallel transmission is fast as large quantities of data can be transmitted at any one time
Disadvantages of parallel
transmission is expensive over short distances as multiple wires need to be purchased. Transmission is very expensive over long distances as the cost of wires dramatically increases with the distance
How are packets transfered
Data is broken/split/divided into packets
Each packet (could) take a different route
A router controls the route/path a packet takes
... selecting the shortest/fastest available route/path
Packets may arrive out of order
Once the last packet has arrived, packets are reordered
If a packet is missing/corrupted, it is requested again
How does aysmetric encryption work
In asymmetric encryption two keys are used:
Public key: a key known to everyone
Private key: a key known only to the receiver
Both keys are needed to encrypt and decrypt information
Where
Person A uses a public key to encrypt their message
Person A sends their message over the network or internet
Person B decrypts the message using their secret private key
Symmetric encryption
Use a key + algorithm to encrypt data
uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data
The aglorythm is used to convert plain text to ipher text
What are the characteristics of a robot
Mechanical structure
Electrical compinets
Are programable
Expert Systems
Have a knowlage base, a rule base, interference engine and an interface
Machine learning
When a program has the ability to automatically adapt toits own procceses and or data
How does antivirus work
Scans for viruses on computer
Using a record of known viruses
Removes any viruses found.
How do Led screens work
consist of two conductive layers. The top layer is flexible. When the screen is touched the two layer connect, completing a circuit
How do capacitative screens work
Made up of a protective layer, a transparent conductive layer and a glass substrate. Touching the screen changes the electrostatic field of the conductive layer
Benefits of resistive and uses
+ Cheap to produce.
+ Resistant to surface contaminants
+ Can be activated with nearly every object (stylus, finger, gloved hand)
Ised in kiosks
Advantages of infrared
+ Excellent image quality,
+ high precision
+ durable
+ allows for multiple touches at the same time
- Requires a bare finger or stylus for activation
Used in smartphones
Dlp projectors
DLP systems use millions of micro-mirrors arranged in a grid on a microprocessor within the projector.
Light is shone through colour filters and the mirrors. The position of the mirrors can be altered to change the intensity of the light
LCD projectors
LCD projectors use three mirror filters to separate an image into red, green and blue wavelengths. The three images are then combined to produce the full colour image which is passed through the lens on to the wall/screen
How do inkject printers work
Have a print head which moves across the page
Spray liquid ink droplets from ink cartridges through very fine nozzles onto the paper (these are in the print head)
The droplets can be piezoelectric or thermal bubble technology
Inkjet printers produce high quality hard copies of digital images or documents
Laser printers
Are very fast when making multiple copies of a document
Are useful for high volume print jobs for example producing leaflets
LCD screens
LCD screens are made up of millions of tiny liquid crystals.
The display is made of pixels arranged in a matrix
Led screen
Light emitting diodes (technology);
Similarity between phishing and pharming
Both are methods of social engineering, where you pose as a real person to steal people's information
Why is HDD a good storage device
It is cheaper per unit has longevity
How do USB drives flash data
Data is flashed onto silicone chips
Uses nand nor technology and transistor to controlo electrons
How do cookies work
Web server sends cookie to browser. Users infor is stored on an encrypted file
The cookie is stored in the hdd
Why is SSD usefal
Small and compact
High capacity
High speed
What is a url
Text based version of a web addres
What are methods of preventing spying
Drop down boxkes
On screen keyboard
Blockchain
A block chain acts as a ledger
How does RLE work?
a data compression technique that replaces repeated values with a count and the value itself
System software
Provides the services the computer requires e.g operating system and utility software
Application Software
Software that provides the services the user requres
Functions of os
Managing memory
Managingperipherals
Managing files
Managing profiles
Multitasking
Functions of a web browser
Stores bookmarks
Allows multiple tabs
Provides navigation tools.
Stores cookies