PLTW Medical Interventions Unit 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is "Medical Intervention"?
Something is done to alter the course of a disease, or something is done to improve someone's overall health
Parts of Medical Interventions
-Diagnosis
-Treatment
-Prevention
ELISA step 1
Sample Prep- DNA is separated from cells
ELISA step 2
PCR Amplification- copies of the DNA are made for testing
ELISA step 3
PCP Purification- Isolate DNA
ELISA step 4
Sequencing PCR- Variable length copies of DNA are made
*Variable length DNA sequences allow the experimenter to have tons of copies that are only different by 1 base pair)*
ELISA step 5
DNA Sequencing- separates variable length copies and reads the sequence of other letters
ELISA step 6
Sequence Analysis- BLAST compares your unknown sequence to a database of known organisms
**This database is the National Center for Biotechnology Information, or NCBI**
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay
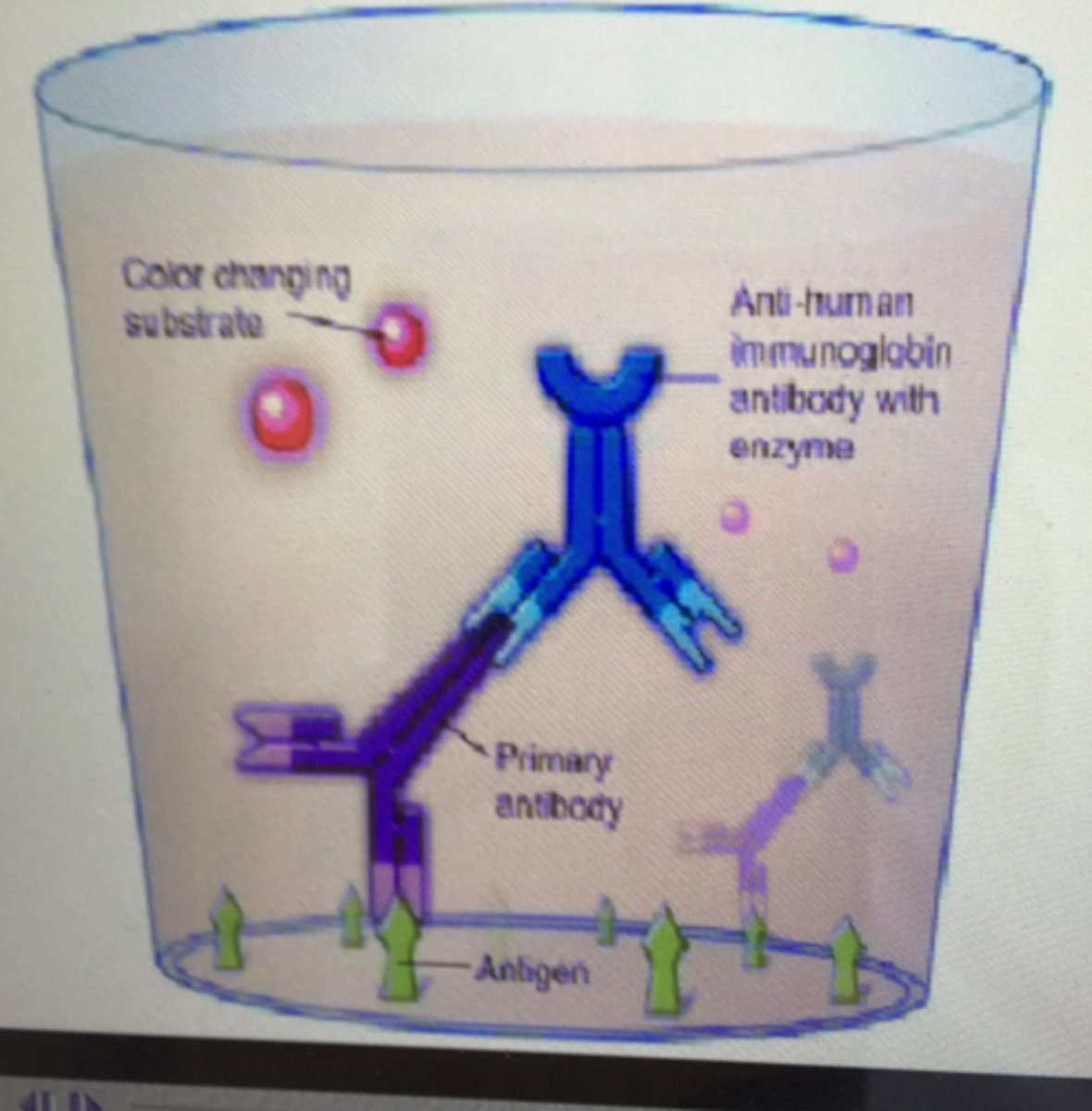
ELISA experiment process
1. Add bio sample
2.Add primary antibody
3.Add enzyme-linked secondary antibody
4.Add substrate- breaks down & color changes
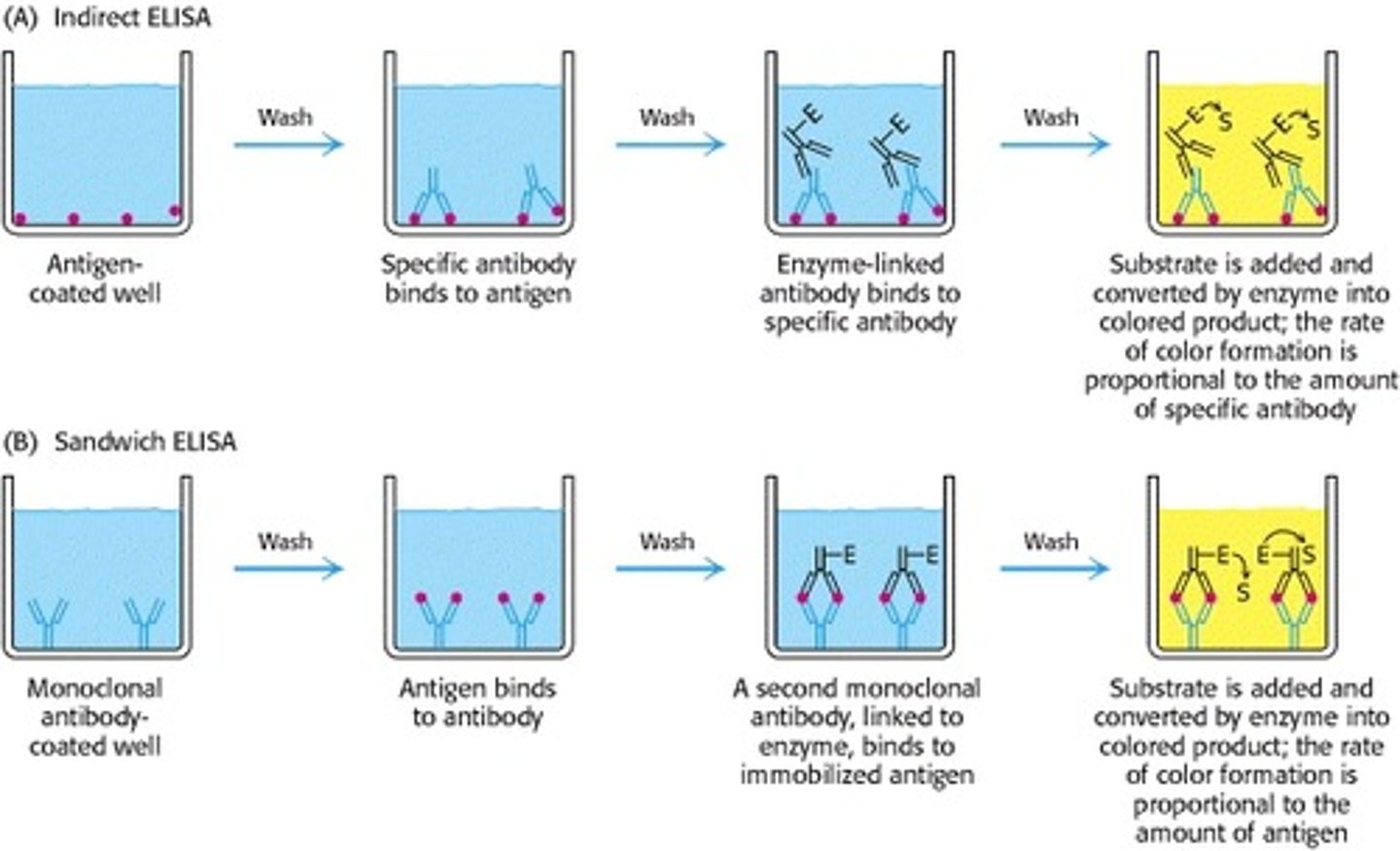
What does an INDIRECT ELISA test look for?
looks for the presence of a certain ANTIGEN
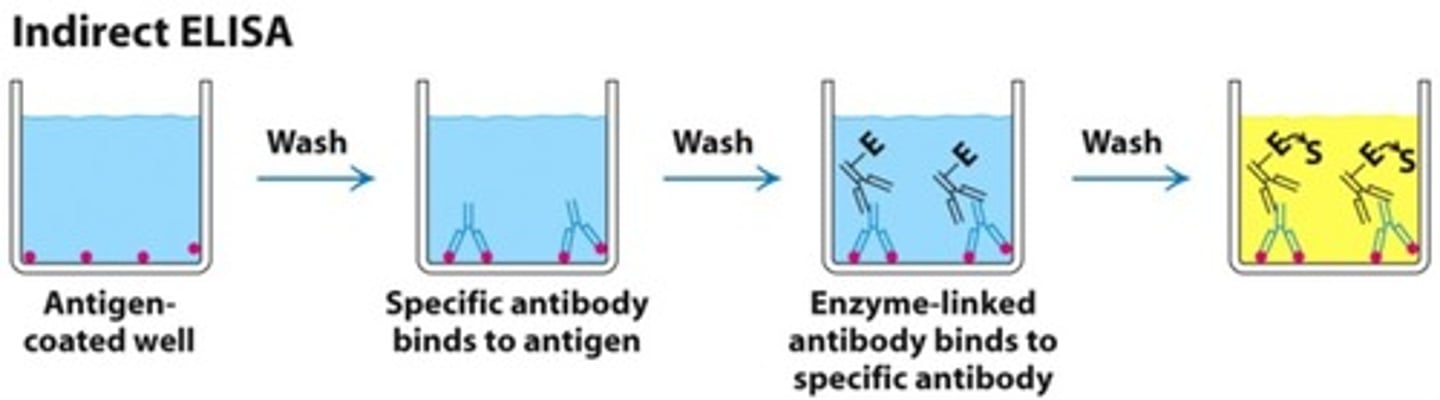
What does a DIRECT ELISA test look for?
looks for the presence of certain ANTIBODIES
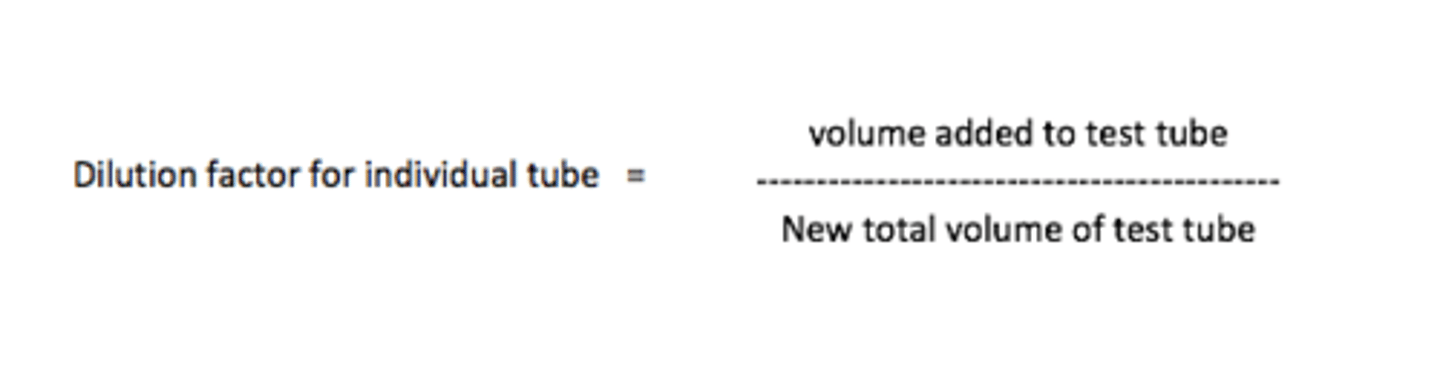
How to calculate Tube Dilution
what you're adding/what you have total
(what you're adding to the tube divided by what you now have total)
How to calculate Final Dilution
*first final dilution will always be the same as the first tube dilution*
-Using first final dilution, multiply it by the next tube dilution in the sequence (the second test tube, not the first one). Multiply that result by the NEXT tube dilution in the sequence, and so on.
what does the substrate do in an ELIZA test?
binds to the enzyme and breaks down, creating a color change (if antigens are present)
when are ELISA tests performed?
When medical professionals already have an idea as to which illness a patient may have
what are the units for concentration?
nanogram/microliter (ng/μl)
At the end of an ELISA test, if a patient's test tube is darkly-colored, this means...
they've had the disease for a long time (long enough for it to build up within their system)
At the end of an ELISA test, if a patient's test tube is lightly-colored, this means...
they've had the disease for a short amount of time
Why is it a good idea to repeat ELISA tests several times?
Repetitive testing allows for more definite results/patient diagnosis
What is an instance in which ELISA tests aren't accurate?
When a patient has been vaccinated and already has the antibodies for the antigen (disease) they're being tested for. Could skew results.
Antibiotics_____treat viruses
Antibiotics CANNOT treat viruses. Viruses and bacteria are two different things.
ELISA process (image)
(ONLY LOOK AT TOP ROW OF THIS IMAGE)