Physics Exam 3 & 4 (Final)
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
In an Bohr model, what is inside of the nucleus?
protons and neutrons
1 unit of charge =
1.6 x 10^-19 Coulombs
if we apply enough energy equivalent to the binding energy of the electron, we can cause what
the electron to be emitted
electron volt
unit of energy; very low compared to the use of joules
atomic mass unit (dalton) is
one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Atomic mass unit is equal to what number?
1.6605x 10^-27 kg
What does the number 12 represent in this picture? (Top number next to the element carbon)
12 represents the mass number of the element (number of protons and neutrons)
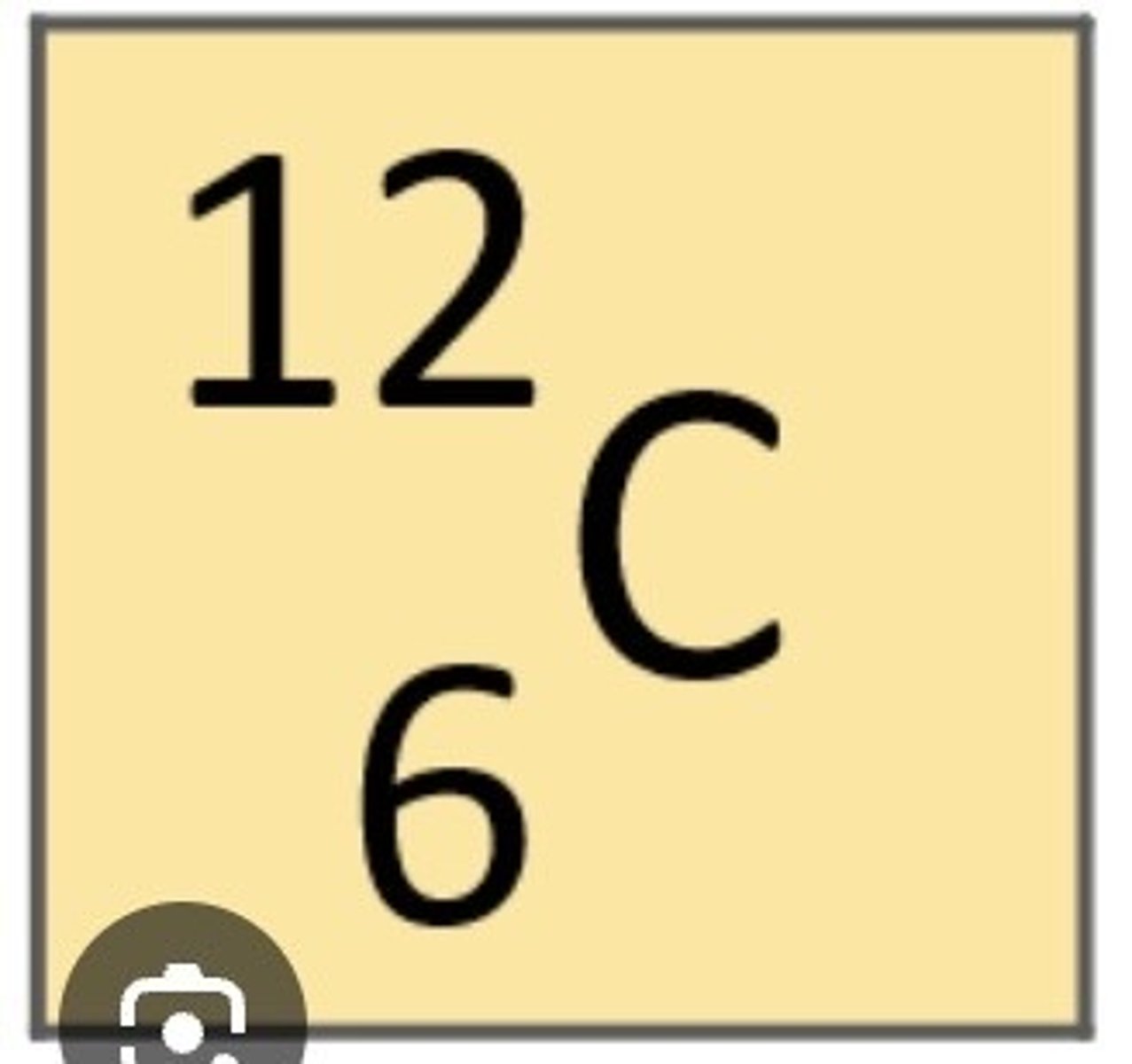
What does the number 6 represent in this picture? (Bottom number next to the element carbon)
6 represents atomic number (number of protons)
nuclear binding energy define
the energy required to decompose an atomic nucleus into its component protons and neutrons
mass defect
mass defect is the mass equivalent of the binding energy
nuclear binding energy equation (albert einstein's equation)
E=mc^2
E= energy in joules
M= mass kg
C= velocity of light in a vacuum 2.998x 10^8
1 amu is equal to
931 MeV
Isotopes have the same number of ______but different number of _________
proton number; atomic and neutron number
Isotopes are dealing with the same ______
element
isostones have the same number of ______ but different number of _________& ______
same number of neutrons but different atomic and mass number
isobars have the same number of ______ but different number of _________& ______
same mass number but different atomic number and number of neutrons
Which nuclear configuration has the same atomic, mass, and neutron number?
isomers
what makes something radioactive?
The neutron to proton ratio is too high or too low, and therefore the nucleus is unstable and will become radioactive
Beta particles are
the same thing as an electron except is resides outside of the nucleus
disintegration define
an unstable atom that reconfigures itself to become stable again
dps is an abbreviation for
disintegration/sec
1 dps is the same thing as a
Becquerel (Bq)
Curie (Ci) equals what number
3.7x10^10 dps
Half Life (T½) define
transformation of a disintegration for the time it takes for the transformation to occur (that it takes 50% of the atoms to decay)
Decay constant (λ) is
λ= 0.693/t 1/2
half life equation
A= λxN
A= activity in Bq/dps
λ = 0.693/t 1/2
N= # of atoms
Decay Formula
A= Aoxe^ -λT
Ao= original activity
λ = decay constant
T= elapsed time
e = a number
physical half-life define
half-life of a substance as it sits on a shelf in vial
biological half-life
when we take into account that we "leak" (urine,sweat) which makes us not a perfect vial, thus eliminating the radio nuceide in other ways
Teff = (formula)
T½ phys x T½ bio/ T½ phys + T½ bio
Secular Equilibrium
half life of the parent is much more greater then the daughter
relative daughter activity
decreases and appears to decay with the longer half-life
transient equilibrium
If the half-life of the parent is not much longer than that of the daughter.
beta emmiters
occurs when the proton and neutron ratio is too high; occurs for atomic number is less then 82
radioactivity is determined by the
arrangement/ratio of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
Alpha particles are
consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay
alpha emission define
occurs when the proton and neutrons ratio is too low, only occurs for atomic numbers greater than 82
What is the equation for binding energy
Q= Mp - Md - M alpha - 2Me -
Q = Total energy released
M = mass
P = parent
d = daughter
e = electrons
Explain what happens during a decay scheme
energy transitions from parent to daughter as a function of the atomic number; meaning the atomic number will go down and to the left on periodic table
Beta particles occur how?
when the neutron and proton ratio is too high, making the nucleus unstable
Neutrino define
negative charge that are so small that they go right through matter
What type of energy is shared by neutrino and a beta particle?
maximum energy
mean energy is what fraction of the Emax?
1/3 of the Emax
Positrons
have the same mass as an electron but are positively charged; neutron to proton ratio is too low with lower atomic masses
annihilation radiation define
when the beta + collides with a free electrons, it will convert into energy, photons in the form of two 5ll Kev are emitted that are 180 degrees apart
electron capture
When the neutrons to proton ratio is too low to add an electron so they pull an electron into the nucleus to form another neutron
Electron capture puts the nucleus into an excited stage to produce what?
gamma ray
electromagnetic waves
when we get too high of a frequency waves, they penetrate like gamma and characteristic waves
photon
a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy
2 types of electromagnetic radiation
1. Gamma rays
2. x-rays
Gamma rays define
emitted from an excited nucleus following radioactive decay
X-ray definition
form of electromagnetic radiation similar to visible light but shorter in wavelength
short wavelength
What is a metastable state?
A metastable state is a long-lived excited state that is longer than the ordinary excited state but has a shorter lifetime than regular ground state.
What are the 2 types of x-rays?
1. characteristic x-rays
2. Bremsstrahlung x-rays
Characteristic x-rays define
Electrons that drop down from shells towards the nucleus and give off characteristic x-rays
Bremsstrahlung x-rays
Beta particles approaches the nucleus and is accelerated redically, emits braking x-rays as it moves outward occur when charged particles are interacting with matter as projectiles
how do you minimize the charged particles in a x-ray
using a material that has a low atomic number
How do maximize the production of x-rays?
using materials with high atomic masses
Auger electron
When an outer shell electron is kicked out of an atom; emitted instead of a characteristic x-ray occasionally
conversion electron
rather than having a gamma ray emitted the energy is transferred to an orbital electron and that electron is what gets released
When does ionization occur?
when an incident photon interacts with orbital electron and imparts a sufficient amount of energy to expel it from the atom
ionizing potential define
amount of energy required to ionize the least tighly bound electron of an atom
Linear Energy Transfer (LET) define
average energy deposited per unit half-length traveling by incident radiation; how much is lost per unit
Why is LET not an accurate measruement?
Because it only takes the average . The only thing that it is good for is seeing high vs low radiations
High LET =
alpha; 7,200 times bigger than beta particles; loses lots of energy in a short range, meaning it does not go very far
Low LET =
everything else such as Beta, gamma, x-rays
Pair production
a photon that is greater than or equal to 1.02 MeV
Half value layers only stay consistent for ______
monoenergetic
State why a positron will not exist naturally on its own for a long period of time
because it will annihilate a free electron and produce two 511 Kev 180 degrees
Compton scattering define
moderate energy photon, photon interacts with an electrons that has a binding energy much lower than the incident photon (outer shell electron) and ionize it
Lower energy photons
photoelectric absorption (because compton scattering energy has become less and less energy)
What are the 2 critical restrictions of radiation exposure?
1. only in air
2. only from electromagnetic radiation such as gamma and x-rays
Common unit and SI unit for radiation exposure
common unit: Roentgen (R)
SI unit: Columb/kg
Absorbed dose definition
any type of radiation in any medium; no restrictions
absorbed dose common and SI units
Common units: Rad = 100 engs/g
SI units: gray (gy) = 1 J/K
- 1 gy = 100 rad
Equivalent dose define
considers both the quantity and quality of radiation in people; only measured in living people
Equivalent dose formula
absorbed dose x quality factor (QF) = equivalent dose
QF for alpha dose =
20
QF for gamma, x-rays, and beta =
1
Common unit and SI unit for QF
Common unit: Rem
SI unit: Sievert (sv)
- 1 sv = 100 rem
2 methods to calculate radiation exposure
1. Gamma constant: getting R/hr to cancel
R * cm^2/mCi * hr
2. Exposure rate: if we do not know gamma's constant
x( at 1 ft) = (6)*(curies)*(MeV)
Inverse square law
This is used to calculate the exposure rate at a different distant
Formula: I1D1^2 = I2 D2^2
Half value layer
thickness of a shield that will attenuate 50% of the beam; probability that 50% is getting shielded
Half value layers only stay consistent for ____
monoenergenic
Patients are more likely to do what with lower energy x-rays?
Absorb the x-rays, making the images not clear
Low energy x-rays are more likely to be _____ causing what to happen?
Shielded; causing the energy exiting to be disproportionate
Allowing higher energy x-rays to come out, does what for the diagnostic image and the patient?
helps minimize the radiation dose to patient and to get the clearest diagnostic image
Formula(s) for half value layer
I = Ioe^-mx
M = 0.693/HVL
X= thickness of shield
OR
I = Io/2n
n = # of HVL
What is the info that we need to know to figure out how much shielding we need for an x-ray room (Diagnostic x-ray sweeps)
1. Max Kvp = highest energy coming off
2. Max mA = maximum current in milliamps
3. Workload: how much time in a given week will that tube be energized : mA* min/week
4. use factor (u): have to configure the % of each wall of the room that will get hit by a beam: 6 walls to be considered
5. Occupancy Factor (T): knowing whats on the other of the room; we need a floor plan to see where everything is at
Restricting areas for radiation
greater than or equal to 2 mR/hr; controlled access or shield it.
No posting required means
We won't have to put up a sign if it is under 5 mR/hr.
What is the range of radiation that is required to put up a "caution radiation area" sign?
If it is greater than or equal to 5 mR/hr but less than 100 mR/hr

If the radiation is above 100 mR/hr, what sign would you put up?
"caution High Radiation area"

When would you need to put a "Caution, radioactive materials" sign up?
if you have any sort of radioactive materials in a room; restricted so people who are not trained in radioactivity cannot access them.
Dose Limit: General Public
100 mrem/year
Deep dose equivalent (DDE)
whole body dose, 1 cm deep into skin
5,000 mrem/year
why do you wear a dosimeter at the collar?
Because if you wear a lead apron, your neck and face are not covered. So you must track how much radiation is getting onto your skin neck up.
Lens dose equivalent (eye dose) limit
15,000 mrem/year in United States
Shallow dose equivalent (SDE)
50,000 mrem/year; skin dose equivalent
Extremity dose equivalent
Knees and elbows down: 50,000 mrem/year