Biogeochemical cycles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
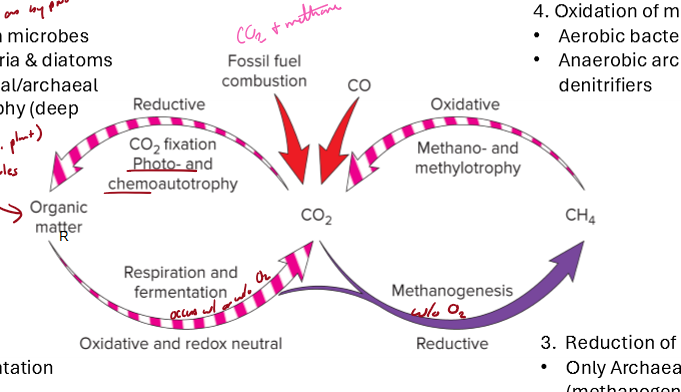
What are the main steps of the carbon cycle?
Carbon fixation - CO2 to organic matter by photo and chemoautotrophy
Respiration/Fermentation - Organic matter to CO2 by heterotrophs
Methanogenesis - Reduction of CO2 to CH4 by anaerobic archaea methanogens (anaerobic)
Methanotrophy - Oxidation of methane by aerobic bacter and anaerobic archaea and denitrifiers
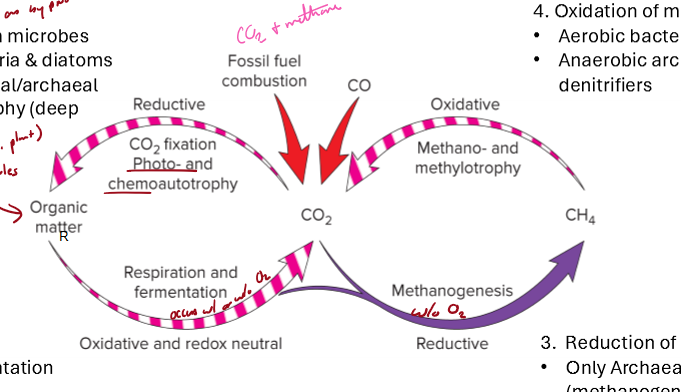
What organisms perform carbon fixation?
oxygenic - microbes, marine cyanobacteria, diatoms
anoxygenic - bacterla/archael chemolithoautotrophy
What is methanogenesis and what organisms perform this?
production of methane from organic matter, CO2, or H2. done by methanogenic archaea
What steps of the carbon cycle are anaerobic?
Carbon fixation from CO2 to organic matter sometimes
Reduction of Co2 to CH4
What role does the molecules play in the nitrogen cycle?
NH4+/NH3
NO3-
NO2-
N2
NH4+/NH3 - e- donor, reduced
NO3- e- acceptor, fully oxidized
NO2- e- acceptor/donor, intermediate
N2
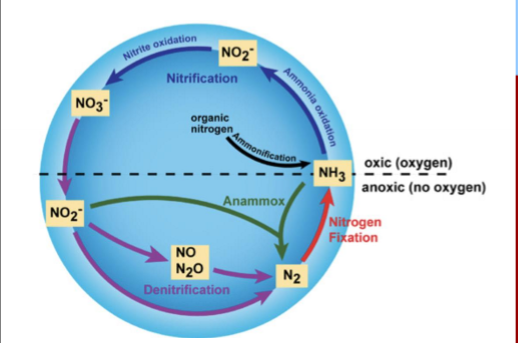
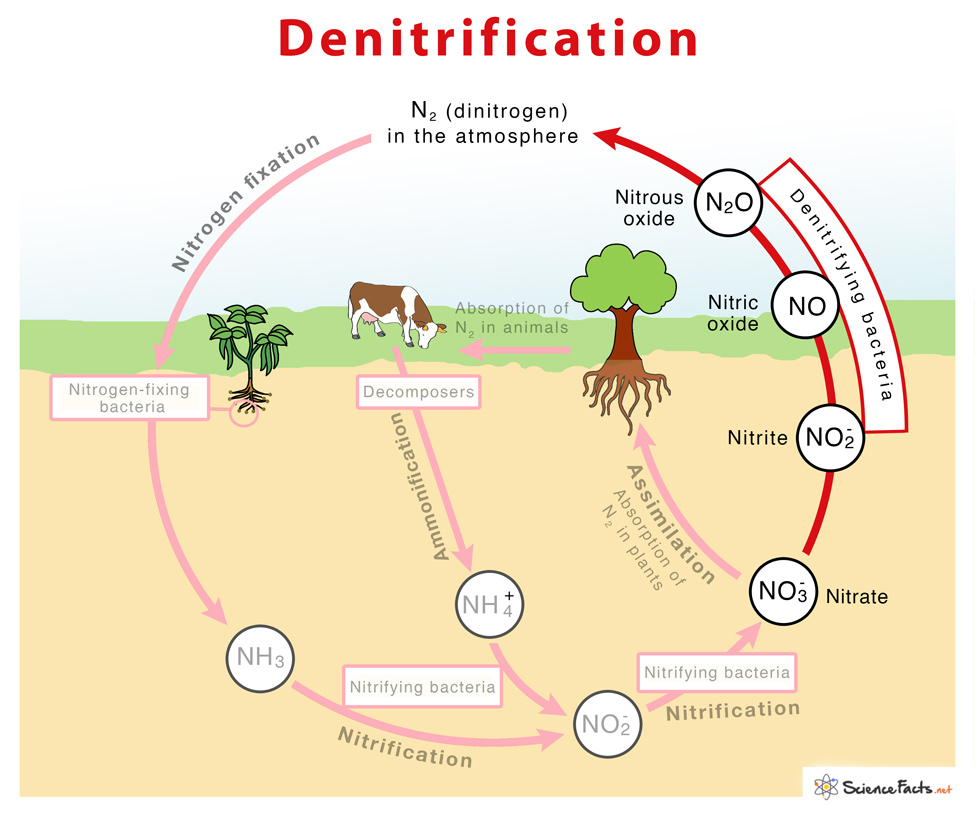
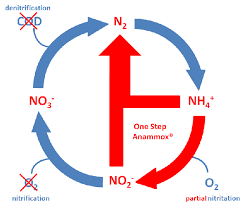
Briefly describe the steps of the nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation - N2 into usable NH3
Assimilation - conversion of NH3 into organic nitrogen within organisms, DNA, proteins, etc.
Ammonification/Mineralization - decomposing organic matter (DNA, proteins, etc) into ammonia (NH4)
Nitrification- NH4/NH3 to NO2- to NO3-
Denitrification - Conversion of NO3-/NO2- to N2 gas
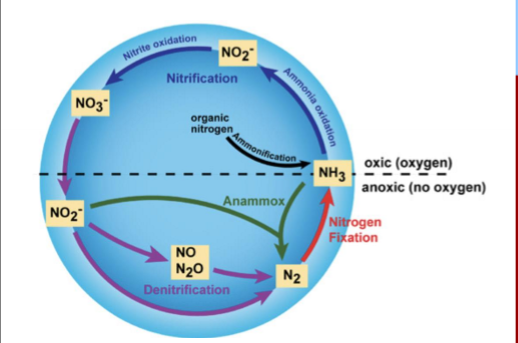
What happens in nitrogen fixation?
What organisms perform this?
What enzyme is used?
N2 to usable NH3
done by diazotrophs (bacteria and archaea that fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms)
done by symbiotes (ex. rhizobium) or free living bacteria
Nitrogenase enzyme
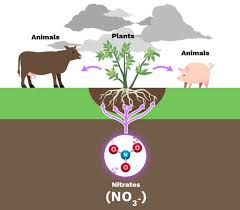
Describe assimilation
The process of converting ammonia (NH3) into organic nitrogen compounds, like amino acids and nucleotides, within living organisms. done by decomposers
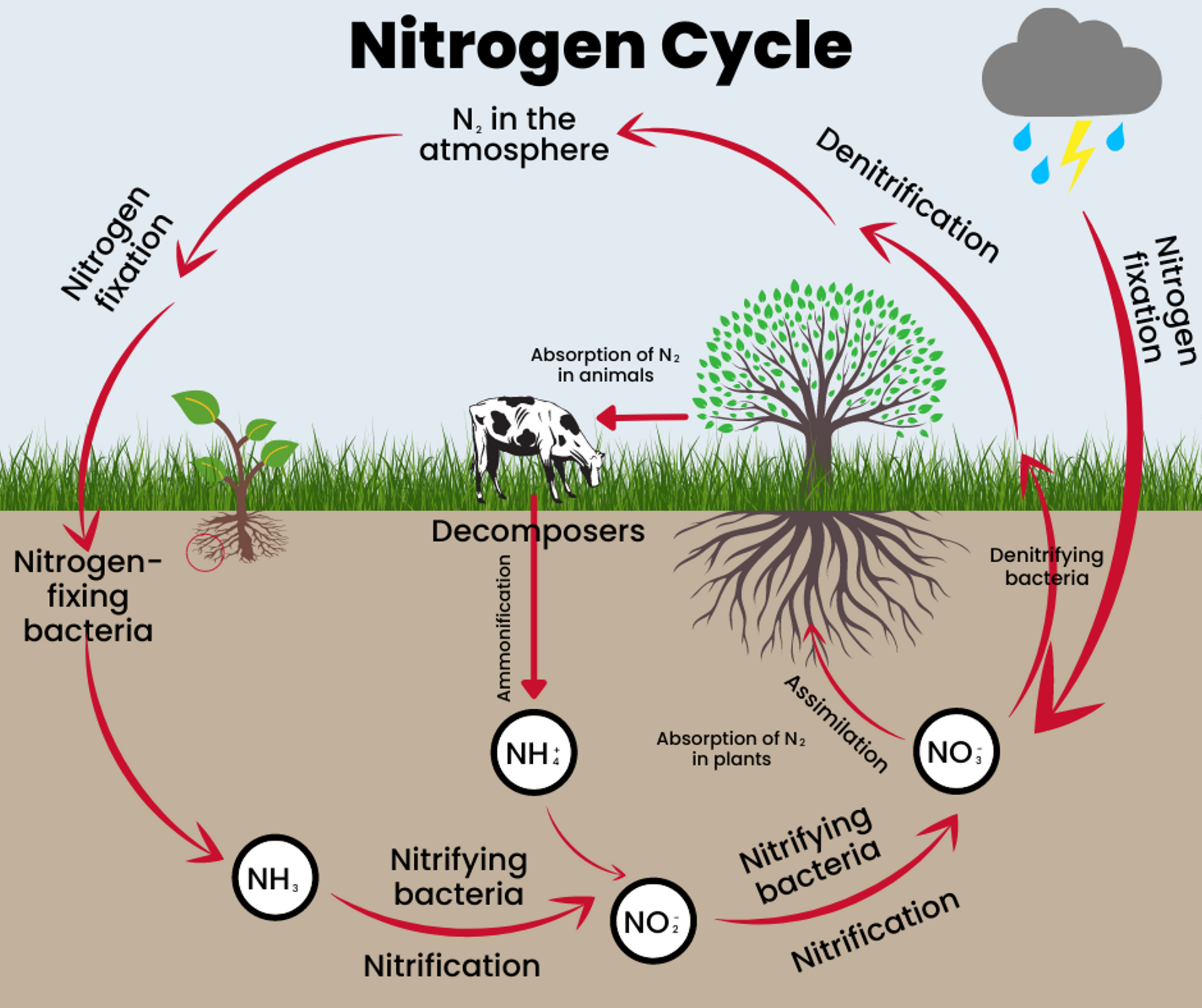
Describe the steps of nitrification
oxidation of ammonia to NO3-
NH3- to NO2- (Nitrite) by bacteria/archaea
NO2- to NO3- (Nitrate) by bacteria
aerobic process, requires O2
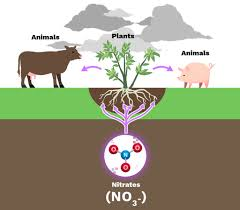
Is nitrification aerobic or anaerobic?
aerobic
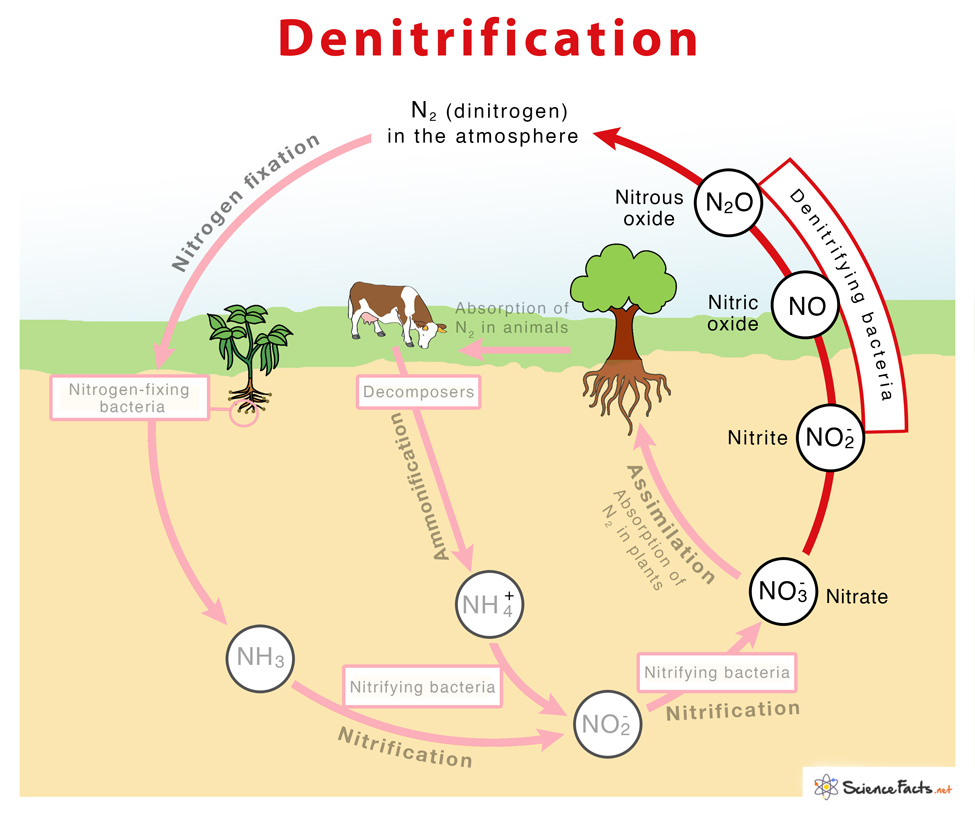
Describe denitrification
conversion of NO3- and NO2- to N2 gas
occurs in anaerobic environments like soil and sediment
done by diverse groups of chemoorganotrophs bacteria (Bacillus, psuedomonas)
detrimental to soil fertility
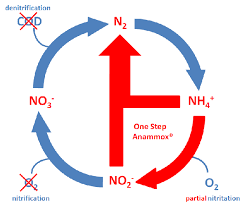
Describe anammox
anaerobic oxidation of ammonium (NH4+) to nitrogen gas (N2) using nitrite (NO2-) as the electron acceptor.
NH4 + NO2- —> N2 gas
carried out by specialized bacteria
role in wastewater treatment
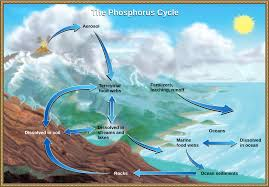
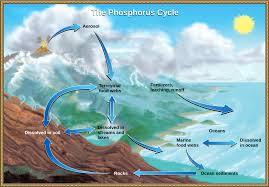
Briefly describe the phosphorous cycle
phosphorous needed for ATP and DNA
phosphorous leaches from weathering and agriculture runoff
forms organic and inorganic phosphate reserves ex. in ground
organic phosphate easily recycled by microbes
inorganic phosphate forms insoluble complexes
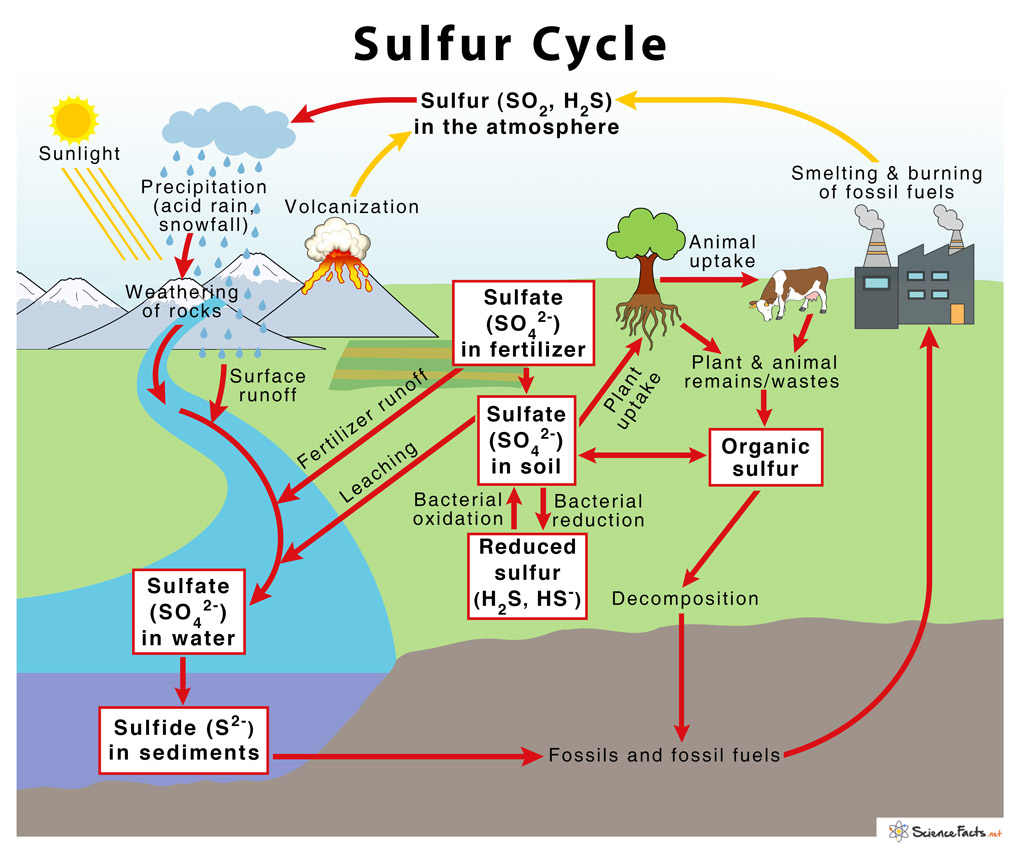
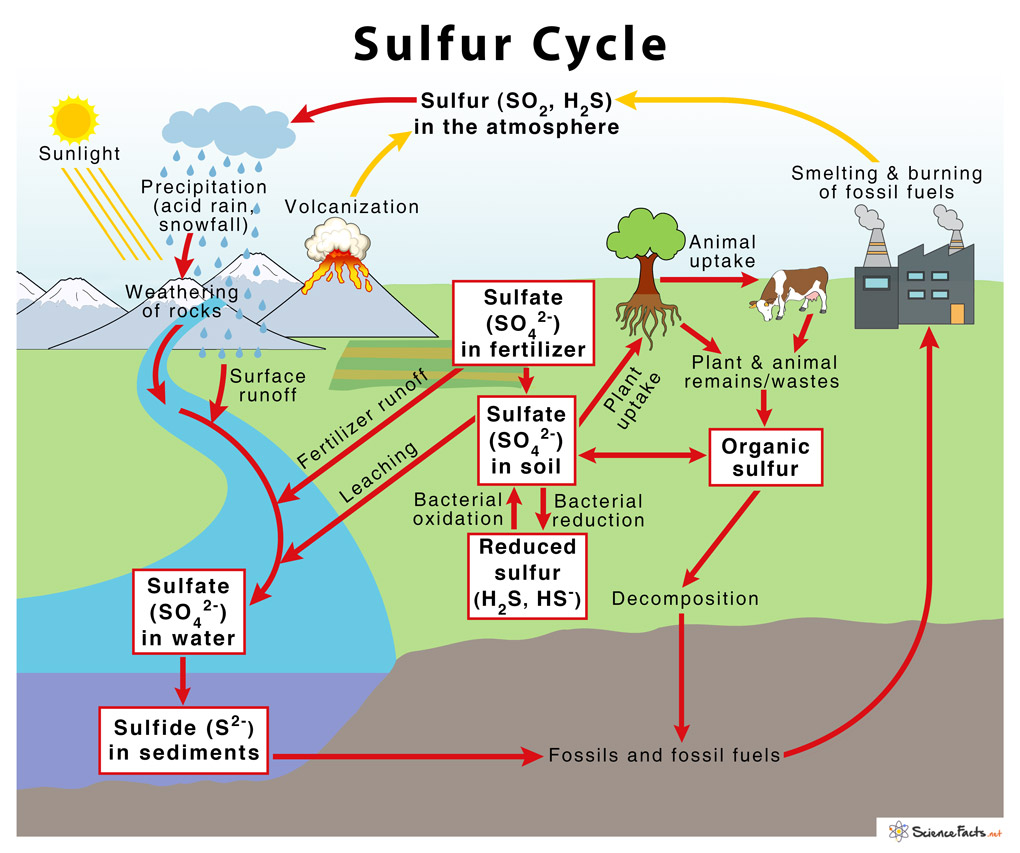
Briefly describe the sulfur cycle
sulfate (SO42-) reduced for amino acids/biosynthesis
Sulfate reduced to H2S (sulfide)
sulfide serves as an electron source for anaerobic photosynthetic microbes, becomes elemental sulfur and sulfate (SO4 2-)
What is methanotrophy and what cycle is it important in?
CH4 oxidized to CO2
occurs in carbon cycle
performed by aerobic bacteria and anaerobic archaea
Describe the production and removal of methane
methane produced from CO2 by methanogenic archaea
methane removed by methanotrophs and turned into CO2
Why is removing CH4 (methane) from the environment by methanotrophs important?
reduces greenhouse gases
What are the formulas for nitrate and nitrite?
NO3-
NO2-
Give a specific example of nitrogen fixation
conversion of N2 to usable NH3 ex. by rhizobium species
Give a specific example of ammonification
organic nitrogen (DNA, proteins, etc.) into ammonia ex. by decomposers
Give a specific example of nitrification
conversion of NH3 to NO2- to NO3-
ex. NH# to NO2- by nitrospira species
Give a specific example of denitrification
conversion of NO3- to N2 gas
ex. by denitrifying bacteria such as Pseudomonas
What role do nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria have in wastewater treatment?
They convert ammonia to nitrate and then to nitrogen gas, reducing nitrogen levels in wastewater.