Rad Bio: Unit 3 Exam
1/74
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
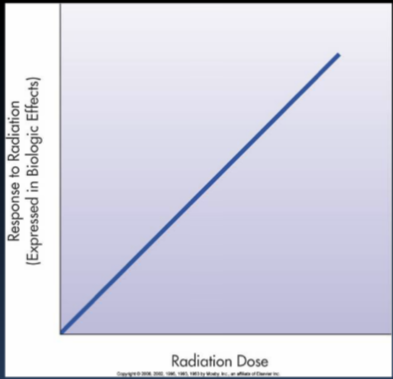
Linear non-threshold
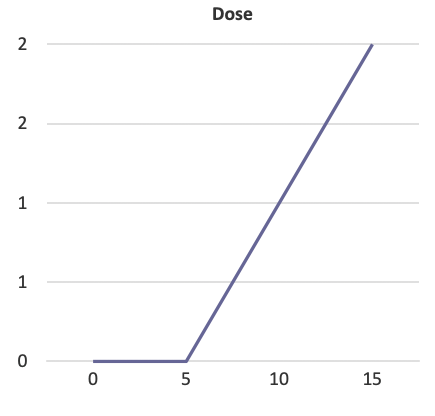
Linear threshold
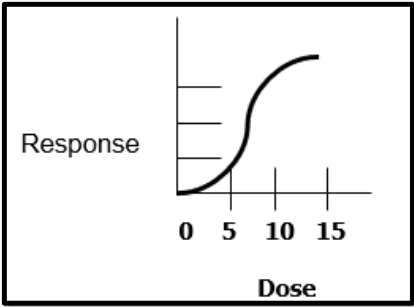
Non-linear non-threshold
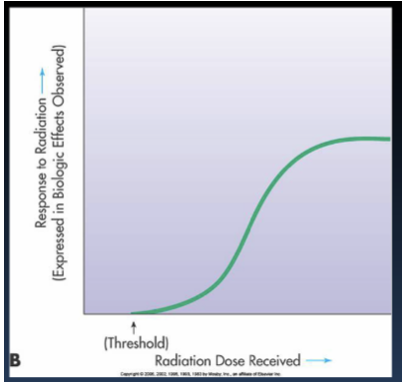
Non-linear, threshold
Linear response
Straight line - steady increase; response is directly proportional to the dose (ex. dose is doubled, response to radiation is doubled)
Threshold response
Intercepts dose axis at some value greather than 0; at lower doses (to the left of the line intersecting the dose axis) no response expected
Non-threshold response
Intersects dose axis at 0; any dose, regardless of size, carries some risk
Damage to one or just a few cells can produce a response
Non-linear response
Not a straight line; response is not directly proportional to the dose
Linear, non-threshold dose response relationship
Radiation induced cancer
Non-linear, threshold dose response relationship
Early effects of radiation and cataracts
Radiation Hormesis
Low doses of radiation are beneficial stimulating the activation of repair mechanisms that protect against disease
Radiation dose - response
A mathematical relationship between various radiation dose levels and the magnitude of the observed response
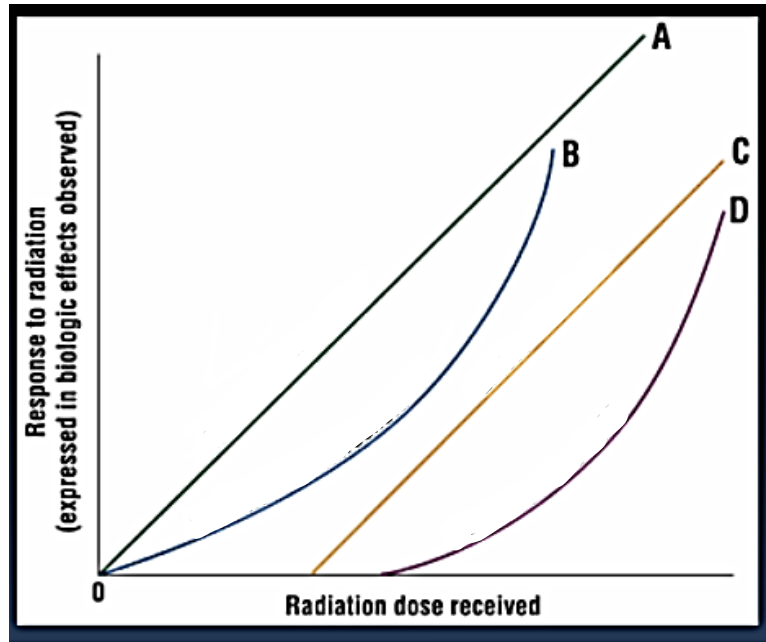
A
Linear non-threshold
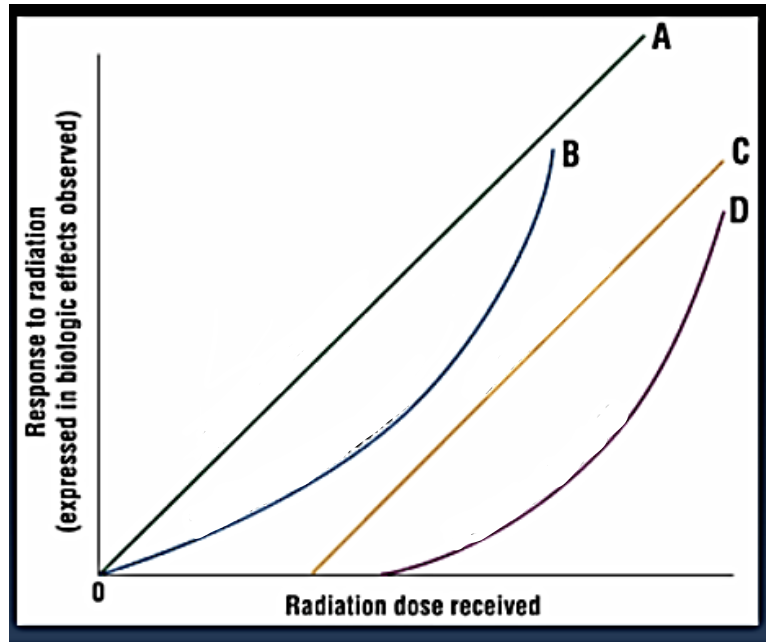
B
Non-linear non-threshold
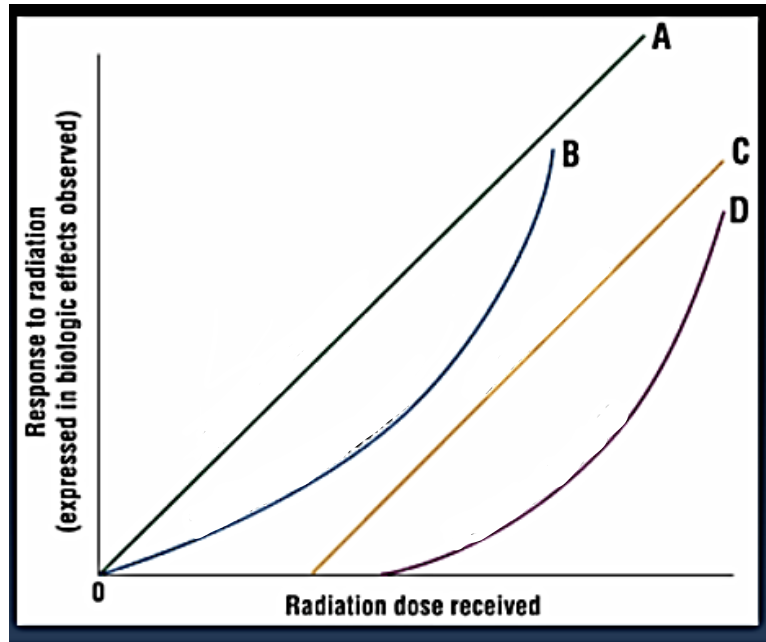
C
Linear threshold
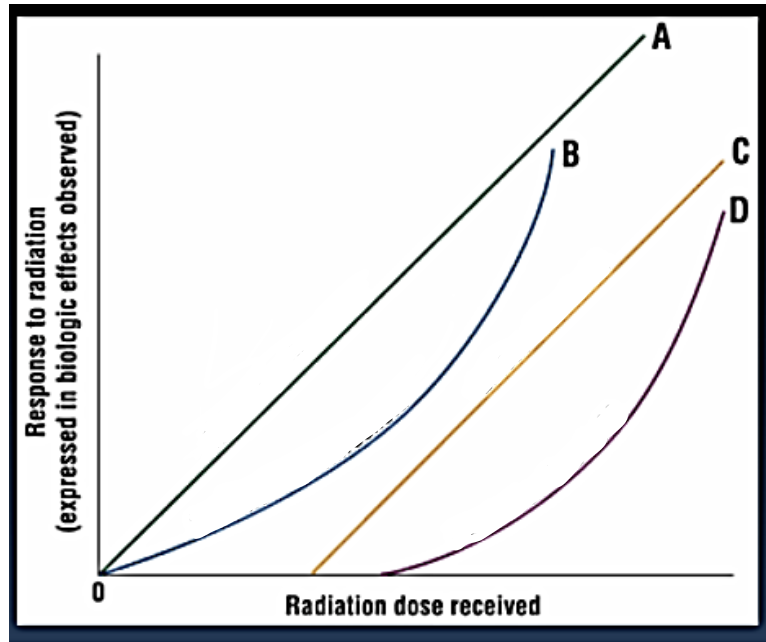
D
Non-linear threshold
Which dose response relationship tells us why its important to follow ALARA?
Linear non-treshold
In vivo
Inside the cell or body; increased radiosensitivity
In vitro
Outside the cell or body
What three main effects are possible of irradiation of macromolecules?
Main chain scission, cross linking and point lesions
Main Chain Scission
The breakage of the backbone of a long chain molecule, reduces viscosity of a solution in the cell (single or double strand break)
Cross Linking
Side of structure becomes “sticky” and will attach to neighboring macromolecules or other parts of the same molecule; increases viscosity of a macromolecular solution
What is another name for point lesions?
Base pair lesion
Point lesions
Disruption of a single chemical bond in a macromolecule causing a break (it is possible an incorrect molecule can be replaced)
What type of radiation most commonly causes point lesions?
Low let radiation
What type of radiation is more likely with direct effect?
High let radiation
DNA structure
Double stranded helix (twisted ladder) with side rails of ladder composed of sugar molecules bound together by a phosphate
What does adenine pair to?
Thymine
What does guanine pair to?
Cytosine
Mutations
Unrepaired damage of incorrect genetic material that can be transferred to a daughter cell that can occur in somatic and genetic cells
Single strand break
One bond is severed; one side of ladder, easier to repair, common with low let radiation
Double strand break
Both sides break, harder to repair, common with high let radiation
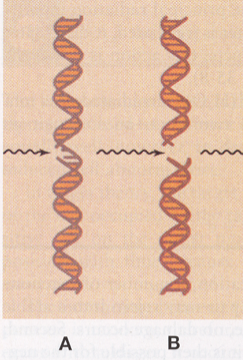
A?
Single strand break
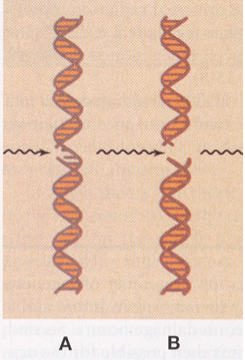
B?
Double strand break
With what radiation does single strand breaks occur more with?
Low let radiation
With what radiation does double strand breaks occur more with?
High let radiation
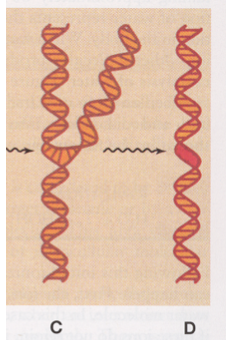
C?
Cross linking
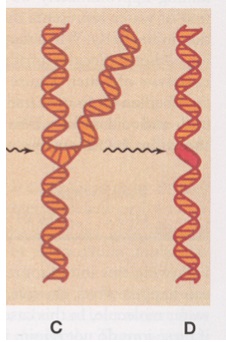
D?
Point lesion
Karotype
Chromosome map
What happens to chromosomal fragments?
Rejoin to configuration
Fail to rejoin and create an aberration
Join with another broken fragment creating a new chromosome
If there is irradiation in early interphase (pre s phase), if it is not repaired before the s phase what happens to the break?
It is replicated
If there is irradiation in late interphase (post s phase), what happens to the break?
It is only affected to one daughter cell
What phase of cell division is best to visualize radiation induced chromosome breaks microscopically?
Metaphase
Radiation induced malignant disease is caused by…?
Rapid proliferation of abnormal cells
Direct Effect
Irradiation to target molecule (DNA)
Indirect Effect
Irradiation to water (can later effect DNA)
The principal effect on radiation to humans is…?
Indirect effect
When water (H2O) is irradiation it loses an electron (e-), what is the molecule and charge after irradiation?
HOH+
After irradiation, the ejected electron (e-) tries to bond with another water molecule to form water again, what molecule and charge is now created?
HOH-
HOH+ breaks down into what?
H+
OH*
HOH- breaks down into what?
OH-
H*
What is H* and OH*?
Free radicals
Free radicals can create what two things?
Point lesions and toxins
What toxin is created from OH*?
H2O2
H2O2
Hydrogen peroxide
What toxin is created from H*?
HO2
HO2
Hydroperoxyl
Free Radicals
Uncharged, unstable molecules with excess energy that can be transferred to other molecules/DNA and distrupt bonds & produce point lesions
H* + O2 =
HO2
OH* + OH =
H2O2
What happens when radiation interacts with a target?
A hit occurs
Low LET and absence of oxygen = ______ hits
Low
Low LET and presence of oxygen = ______ hits
High
High LET and absence of oxygen = ______ hits
High
High LET and presence of oxygen = ______ hits
No additional
Double strand DNA breaks are more likely to occur after a dose of…?
High let radiation
Free radicals are an example of…?
Indirect effect
Single-target, single-hit
Simple cells, less radiation needed to cause cell death; non-threshold
Multi-target, single-hit
Human cells, more radiation needed to cause cell death; threshold
Low D37 = __________ radiosensitivity
High
High D37 = __________ radiosensitivity
Low
D37
Dose to kill 63% of cells
37% survival
DO
Mean lethal dose
Which has a greater mean lethal dose: low or high let radiation?
Low
Dq
Threshold dose