PHYS 215: Midterms
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
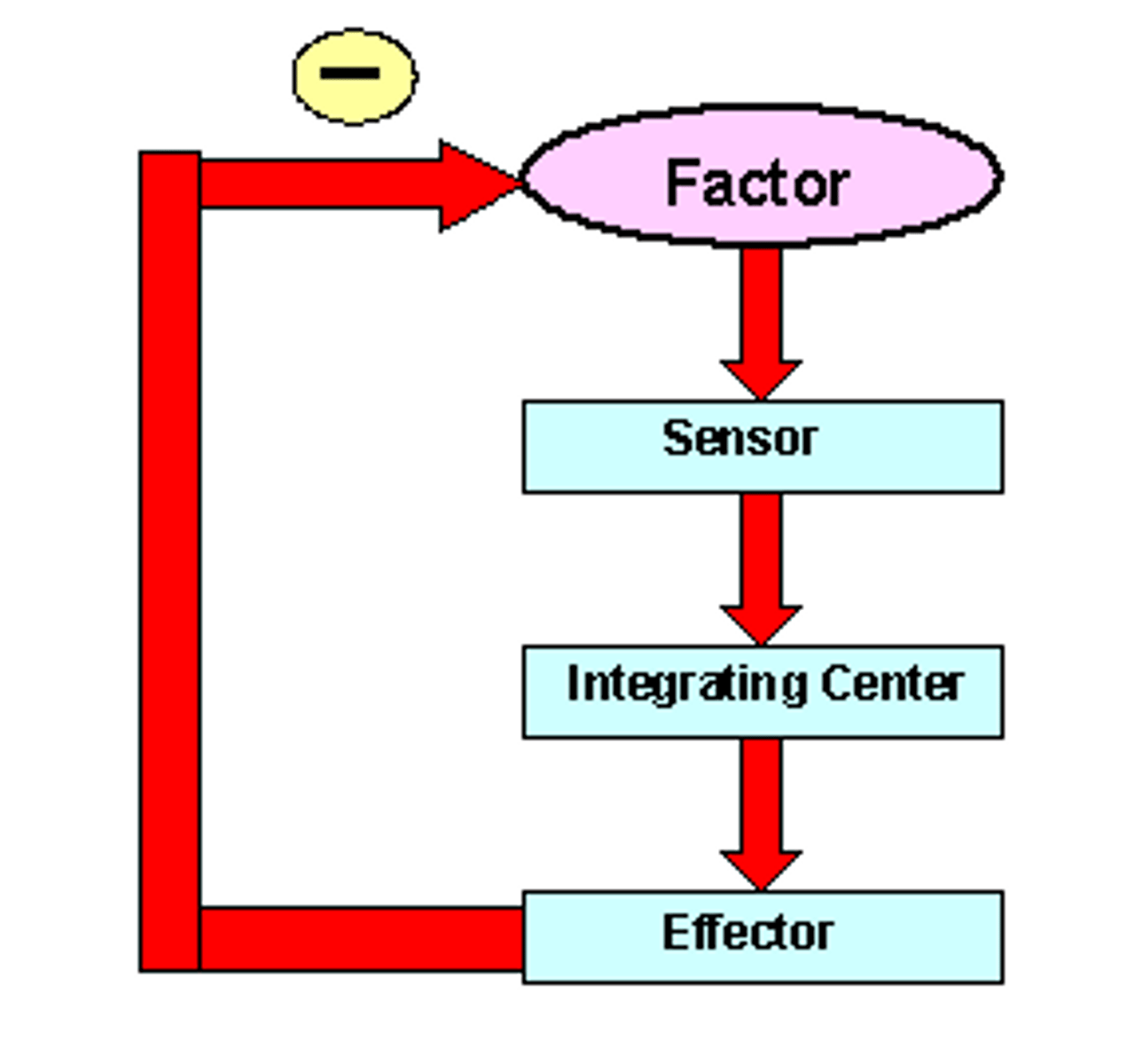
four parts of homeostatic control system
stimulus
receptor
control center
effector
negative feedback loop
-A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving
-ex: body temp, blood sugar
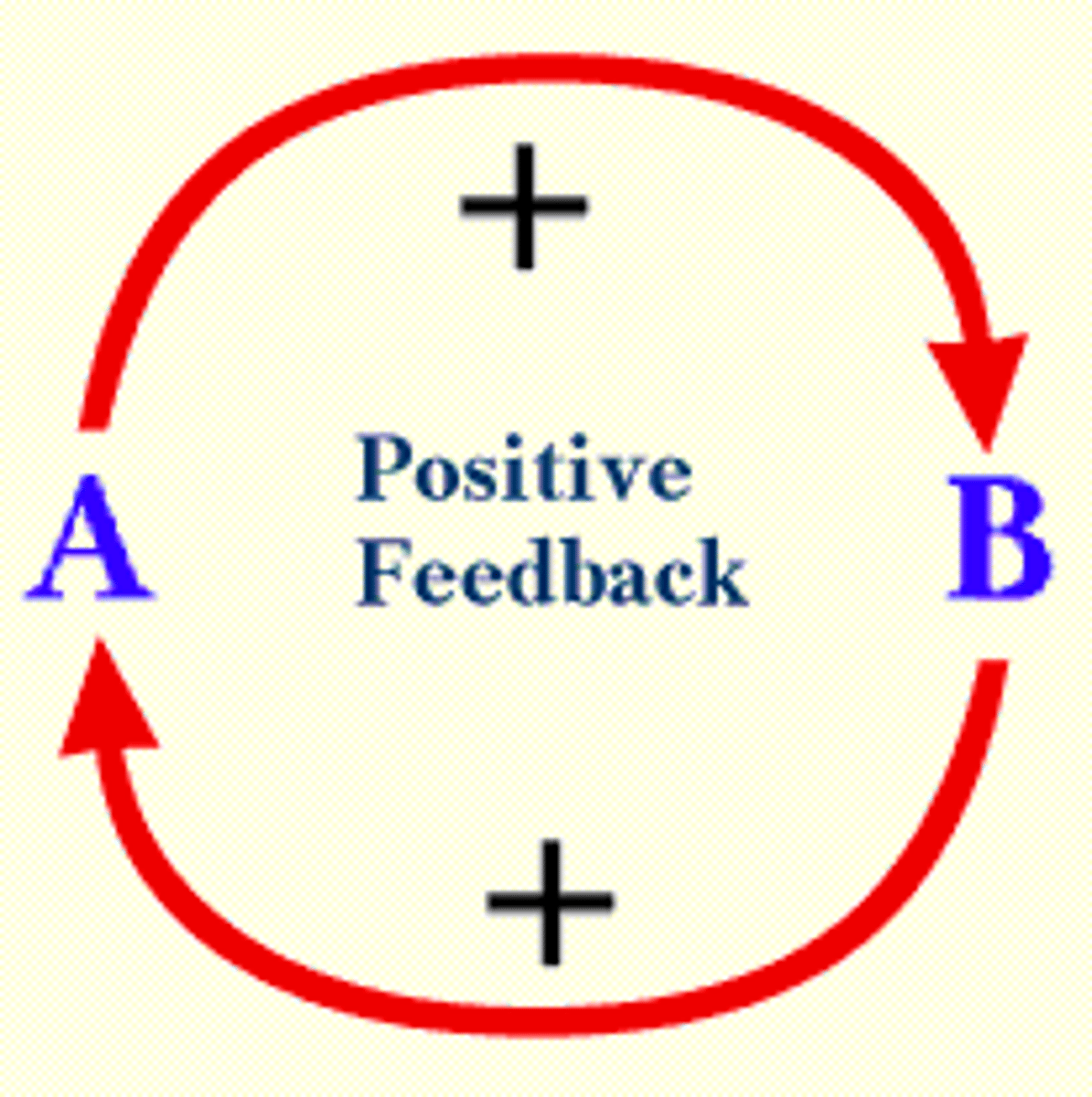
positive feedback loop
Causes a system to change further in the same direction/amplifies.
-ex: blood clotting, labor
why is negative feedback more common?
it keeps the body at a dynamic equilibrium
set point
a physiological level or setting that the body attempts to maintain through a self-regulating system
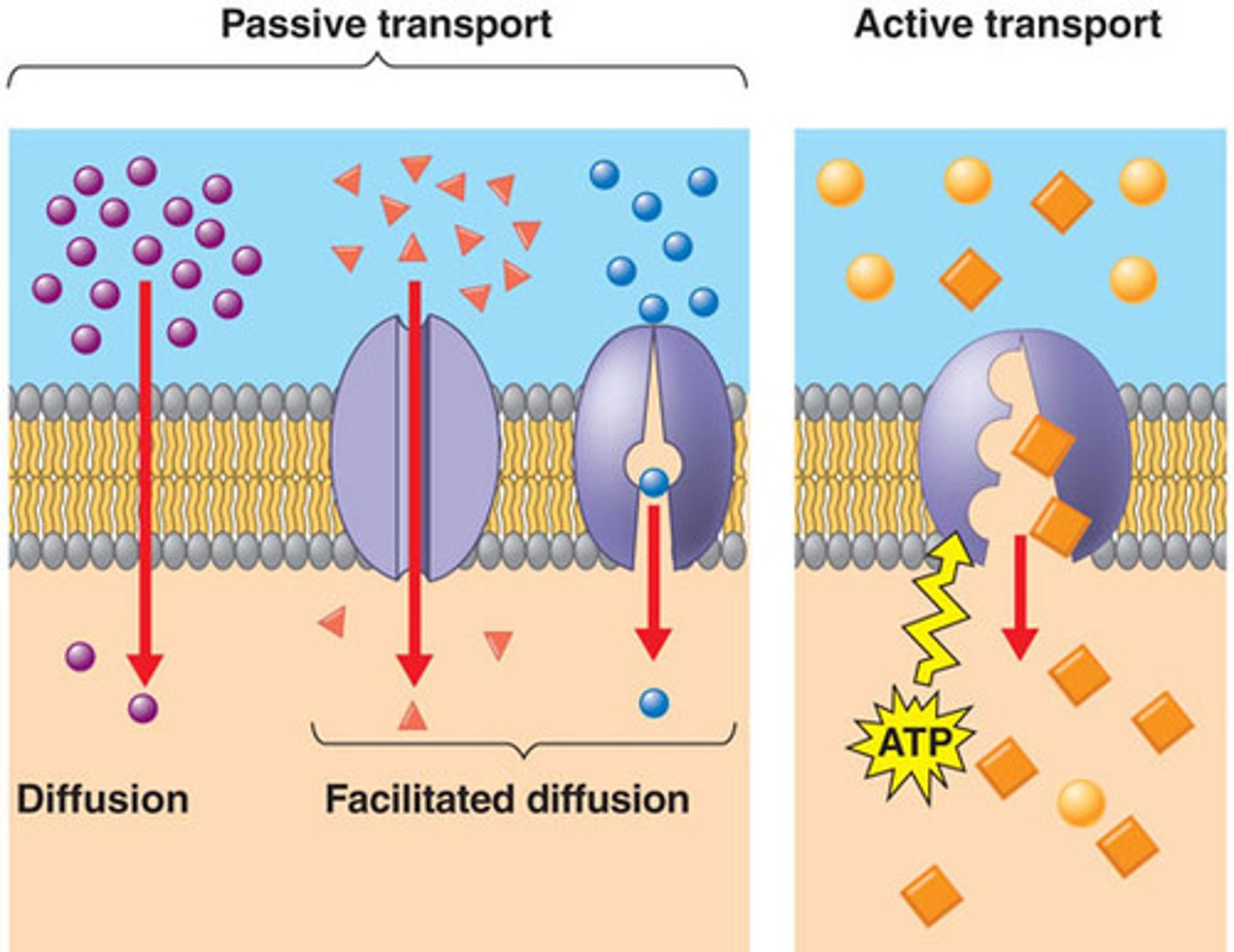
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
diffusion
moves with conc gradient
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels (carriers)
no ATP
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
what drives osmosis
osmotic pressure
osmotic pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane

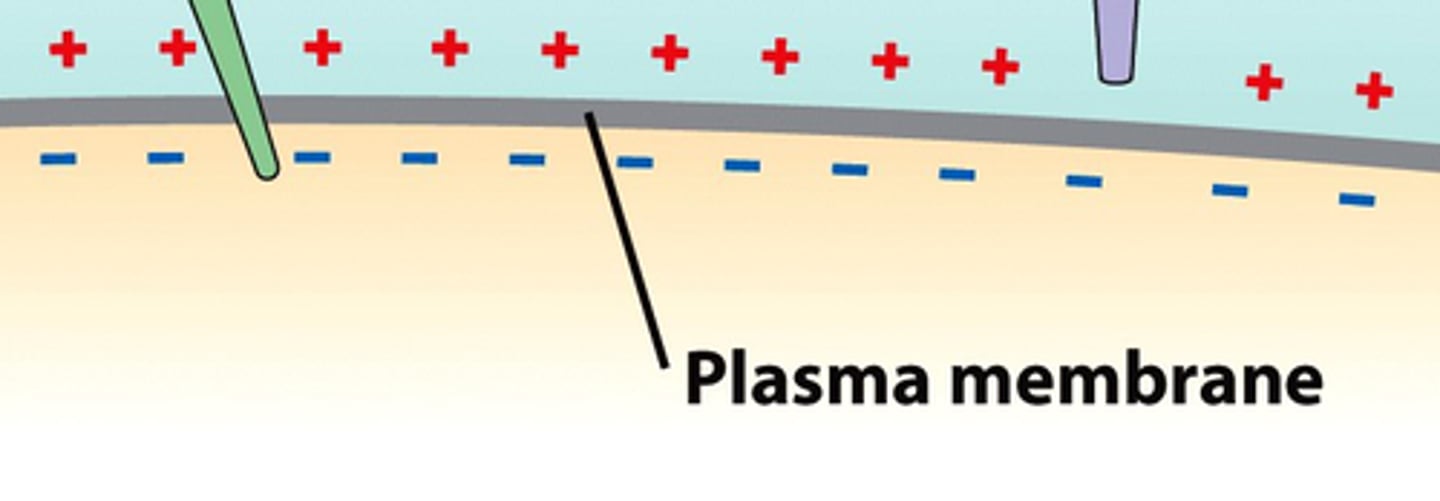
membrane potential
the voltage difference across a membrane
Na+/K+ pump
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in
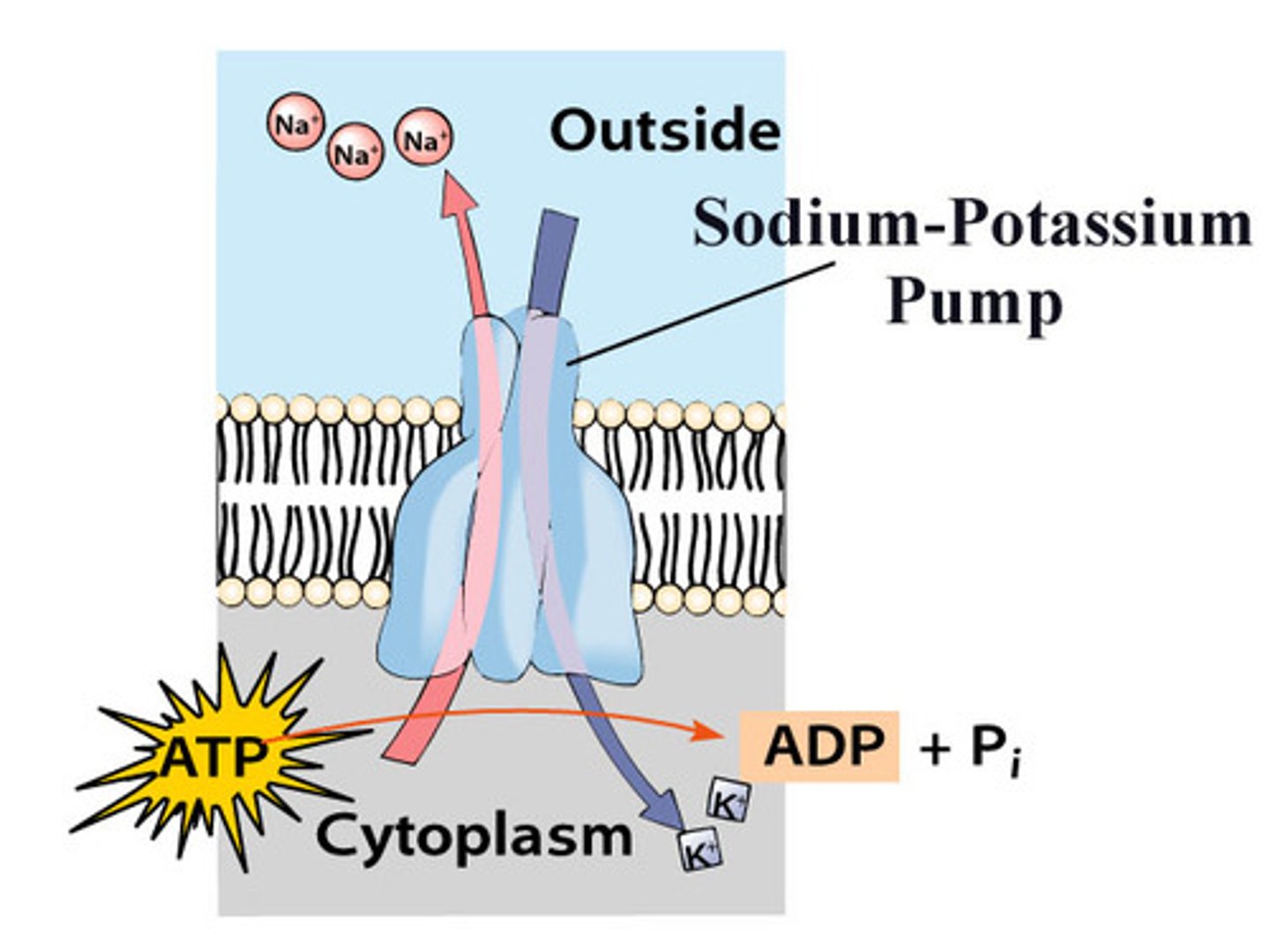
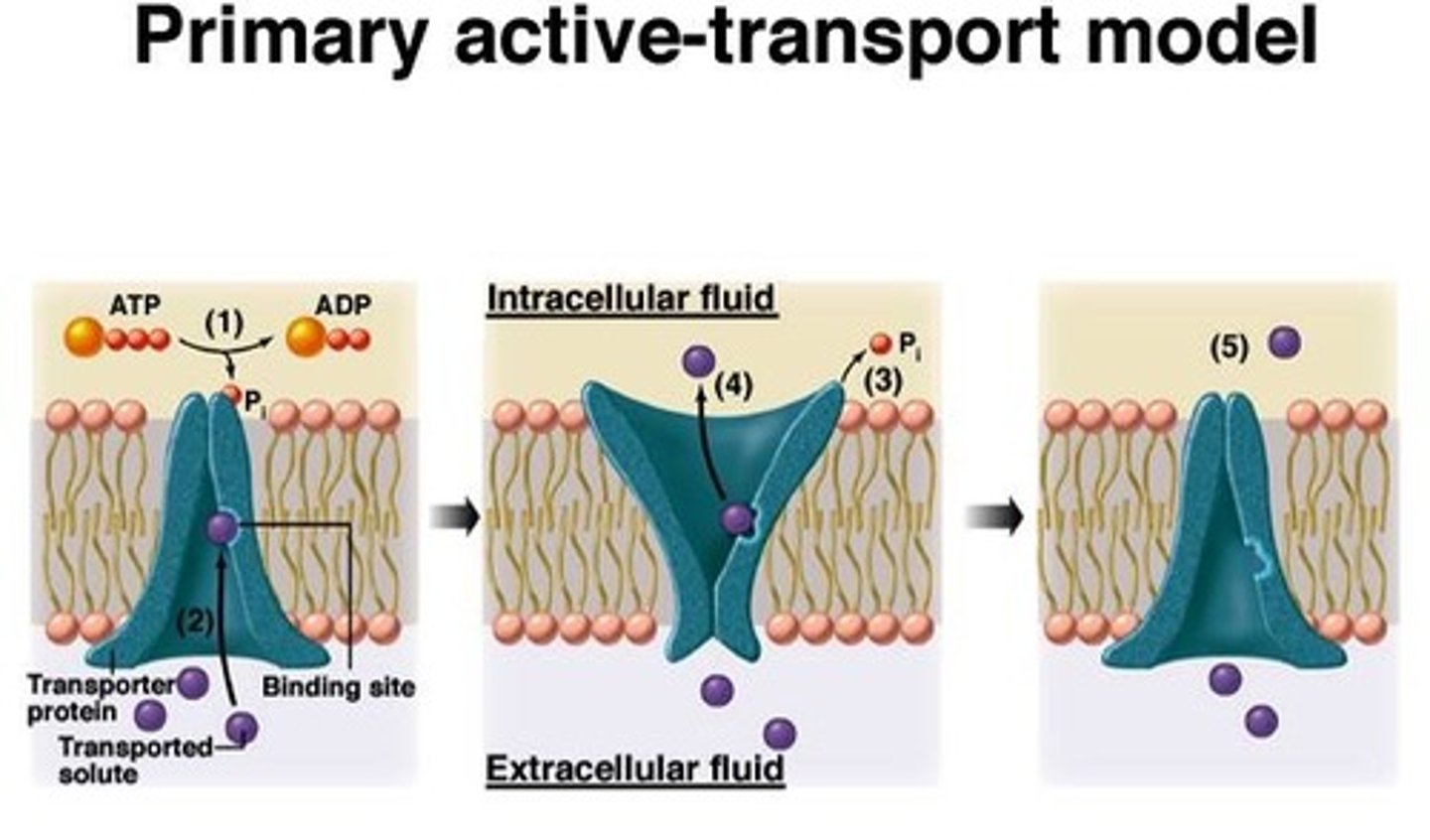
primary active transport
-Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP
-Ex: Na/K pump
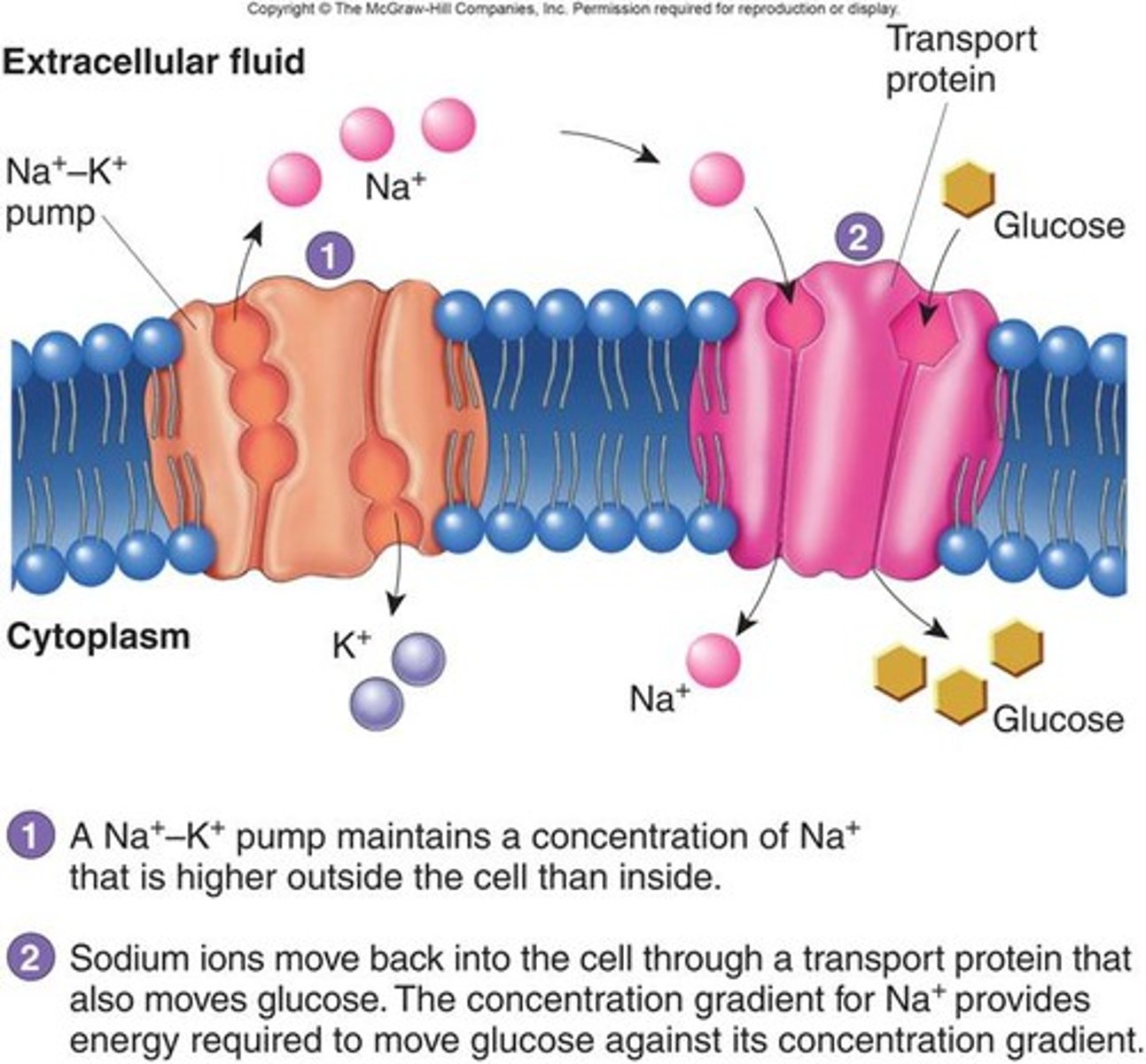
secondary active transport
-use preexisting gradient to drive transport of solute
-Ex: Na/Glucose Transporter
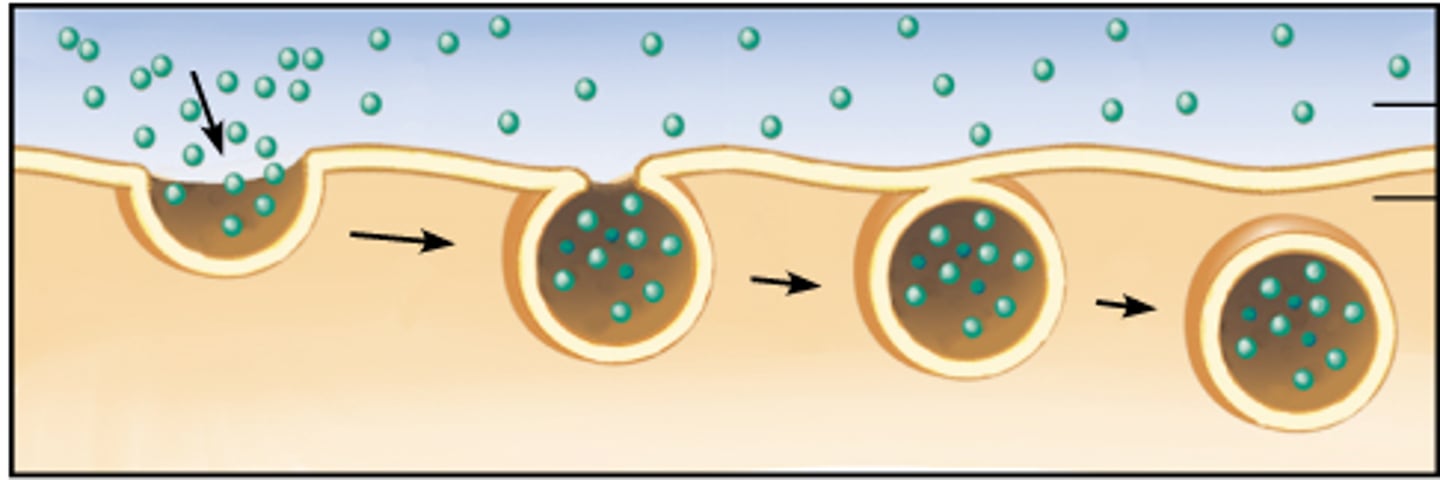
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
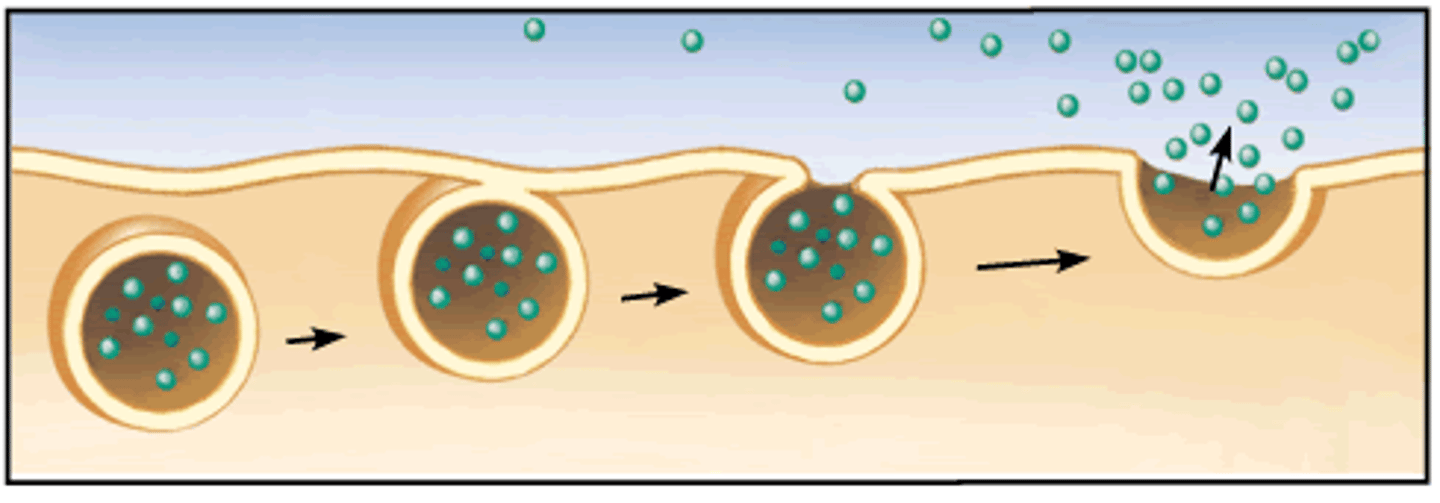
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
How does the plasma membrane maintain selectivity?
phospholipid bilayer
acts as a barrier to larger/charged molecules
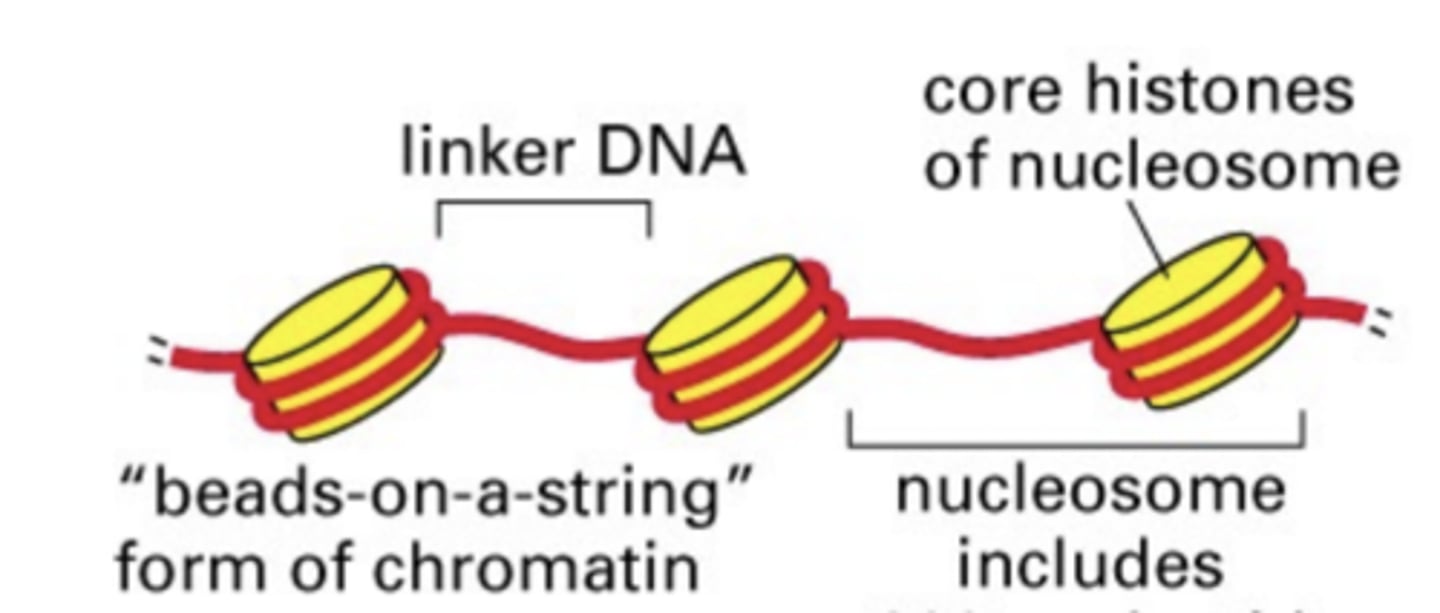
Chromatin
-granular material visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
-less condensed
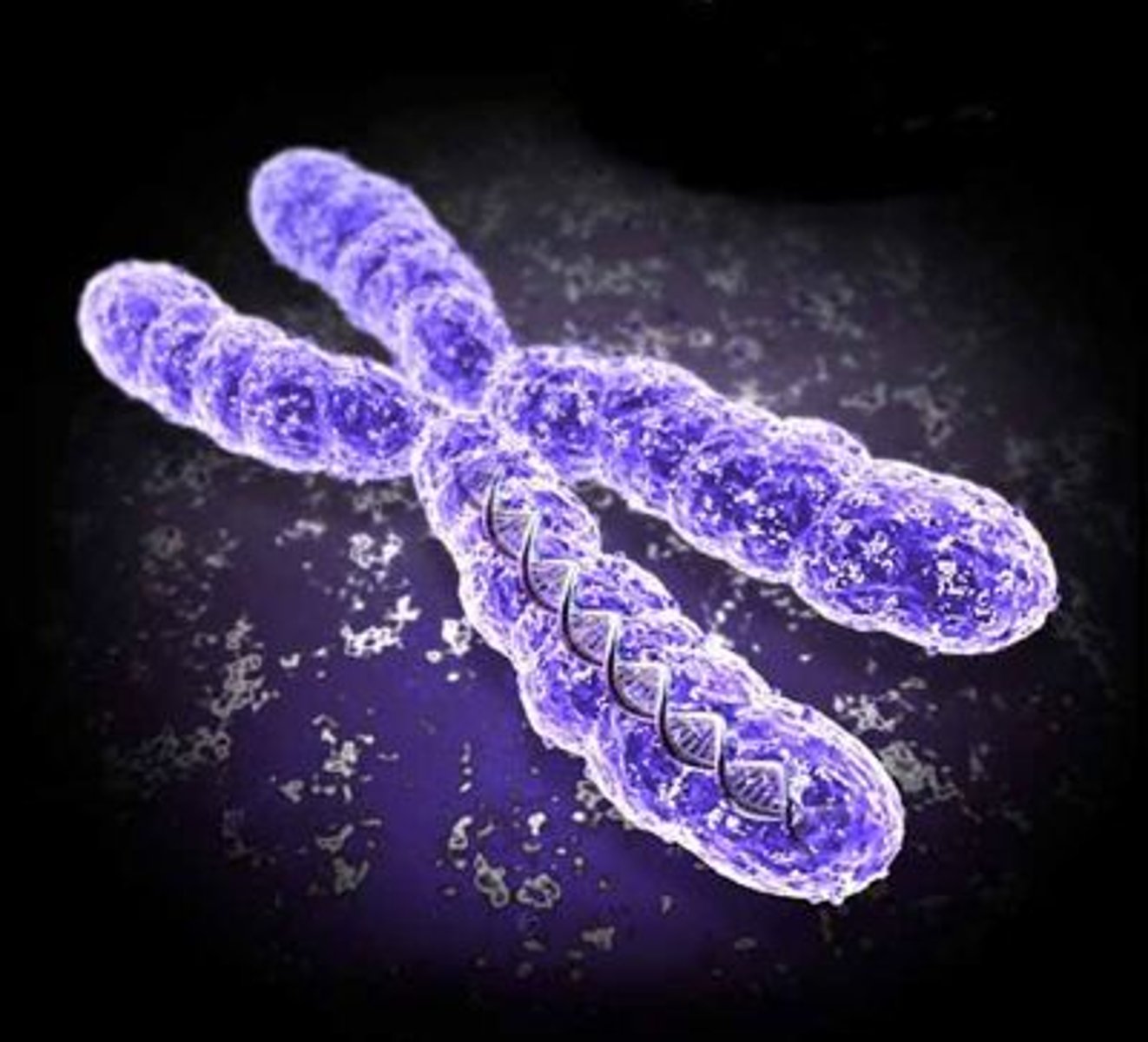
chromosomes
-threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
-more condensed
paracrine signaling
secreted molecules diffuse locally and trigger a response in neighboring cells
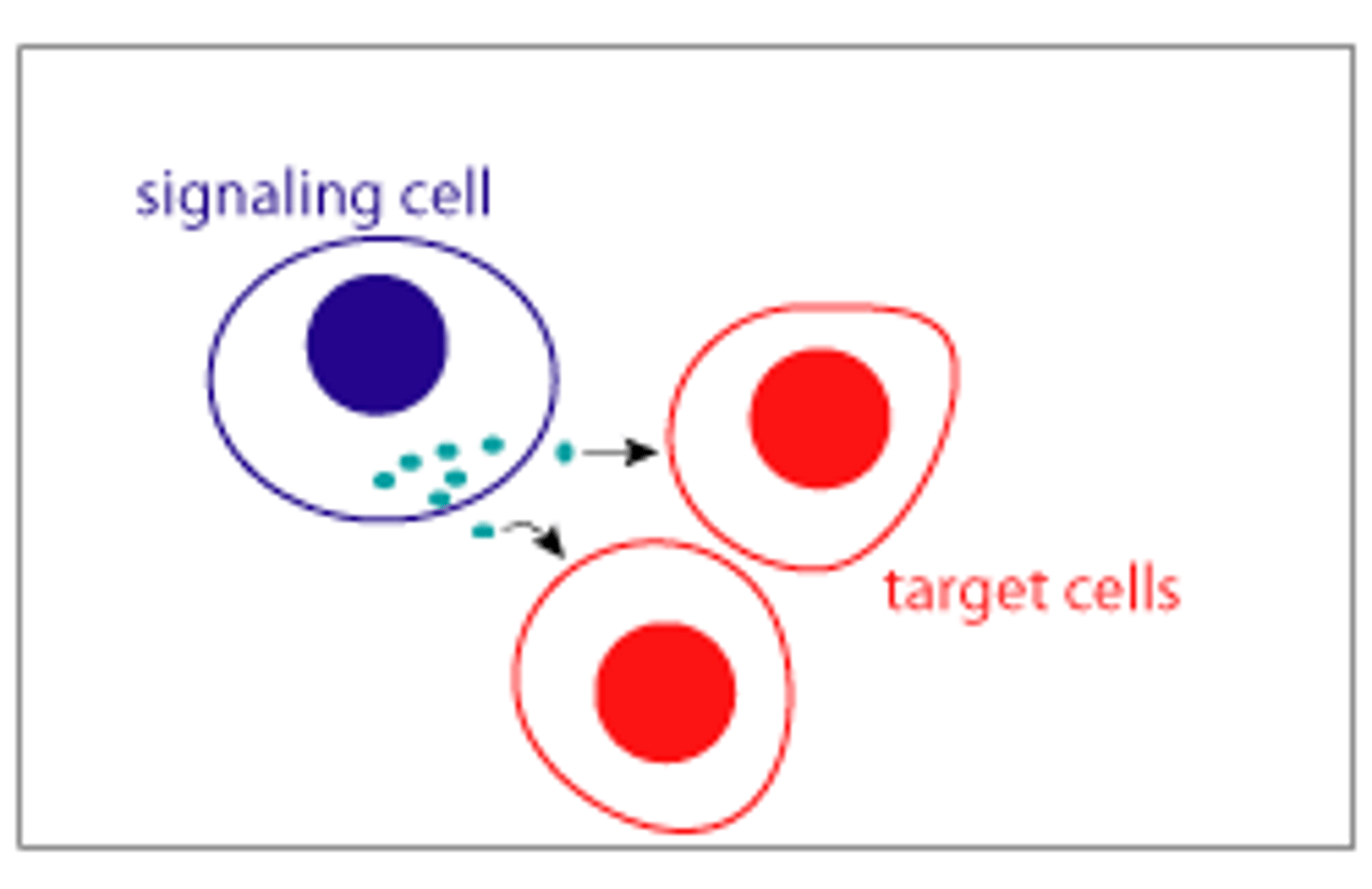
paracrine signaling example
growth factors, which stimulate nearby target cells to grow and divide
Neurotransmitter signaling
-synapse
-rapid-response and action
steroid signaling
-lipid soluble/nonpolar
-travel through bloodstream
-long-lasting effects
Signal Transduction
The linkage of a mechanical, chemical, or electromagnetic stimulus to a specific cellular response.
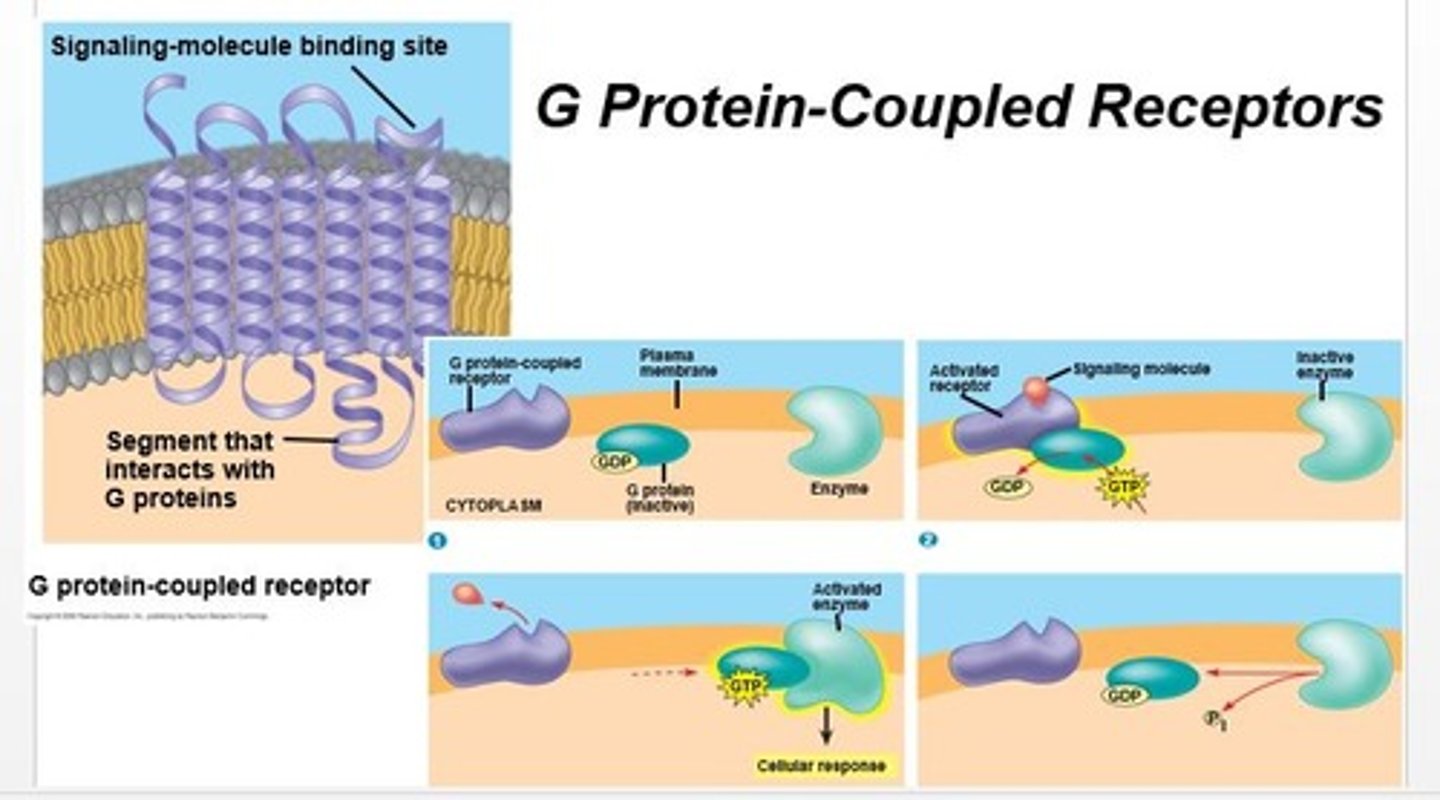
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
-large family of integral membrane proteins involved in signal transduction
-characterized by their 7 membrane-spanning alpha-helices
-utilize heterotrimeric G protein to transmit signals to effector cells
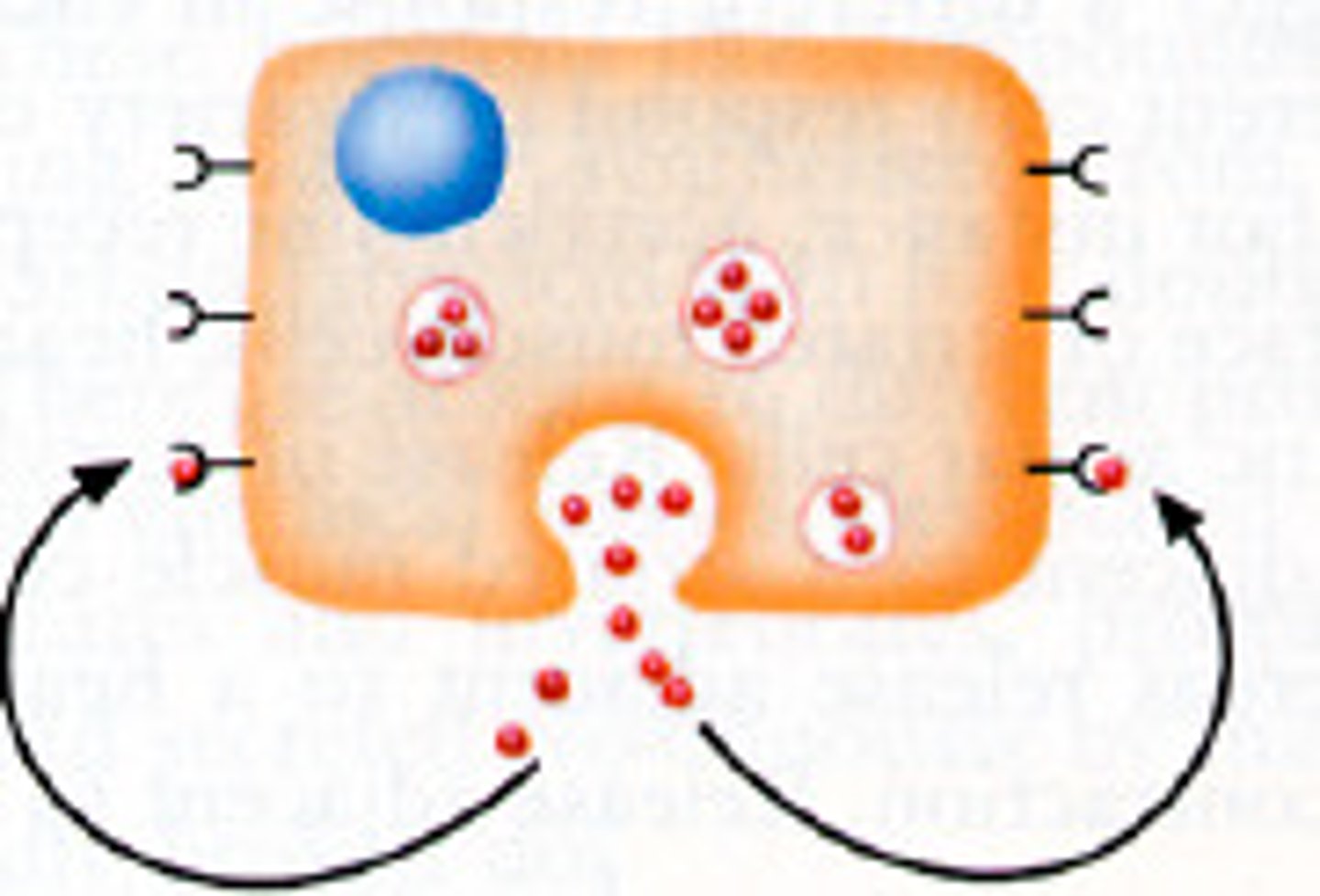
autocrine signaling
the target cell is also the secreting cell
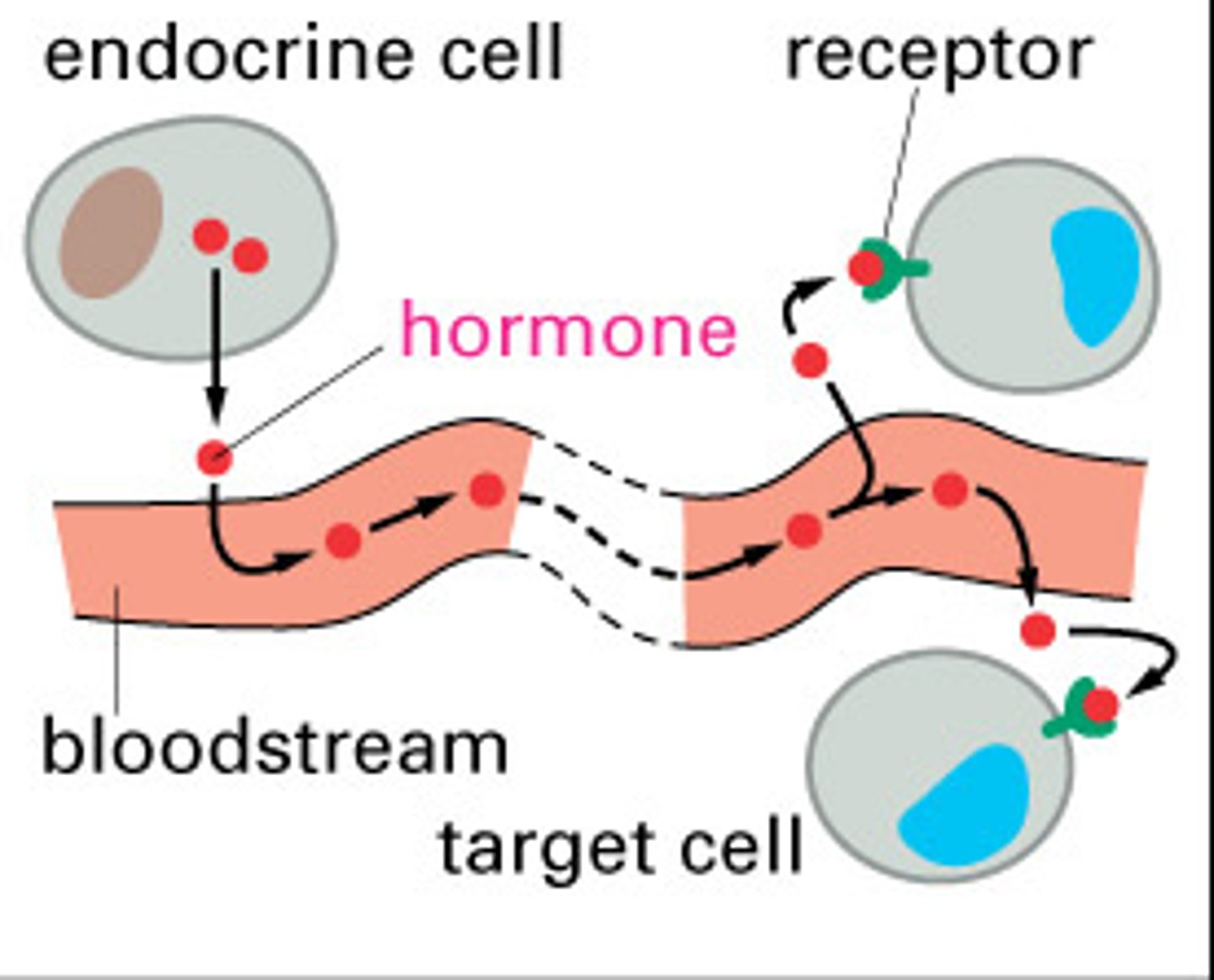
endocrine signaling
-secreted molecules diffuse into the bloodstream and trigger responses in target cells anywhere in the body
-slow, long-lasting
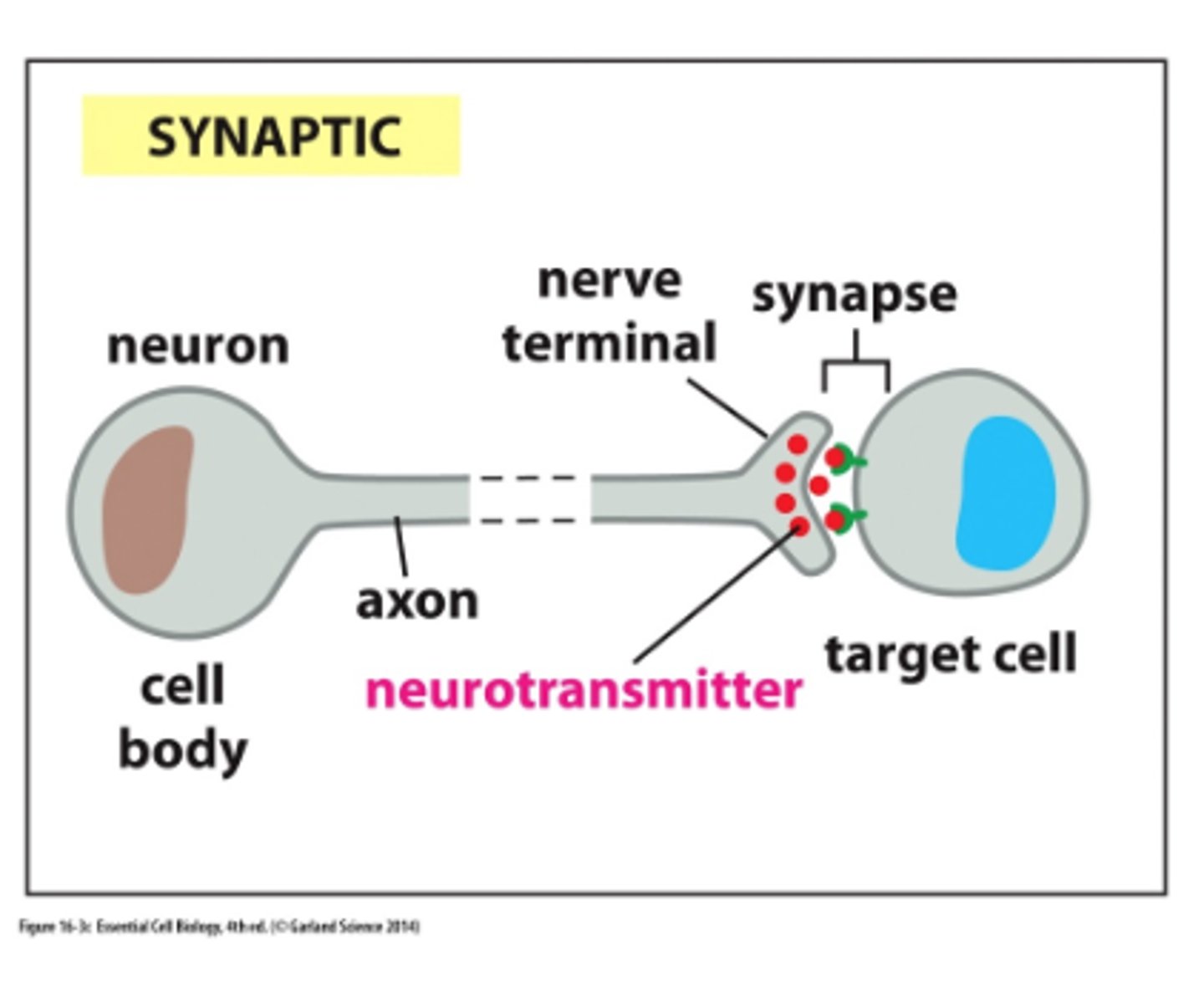
synaptic signaling
-a nerve cell releases neurotransmitter molecules into a synapse, stimulating the target cell
-rapid response
resting membrane potential of neuron
-70mV
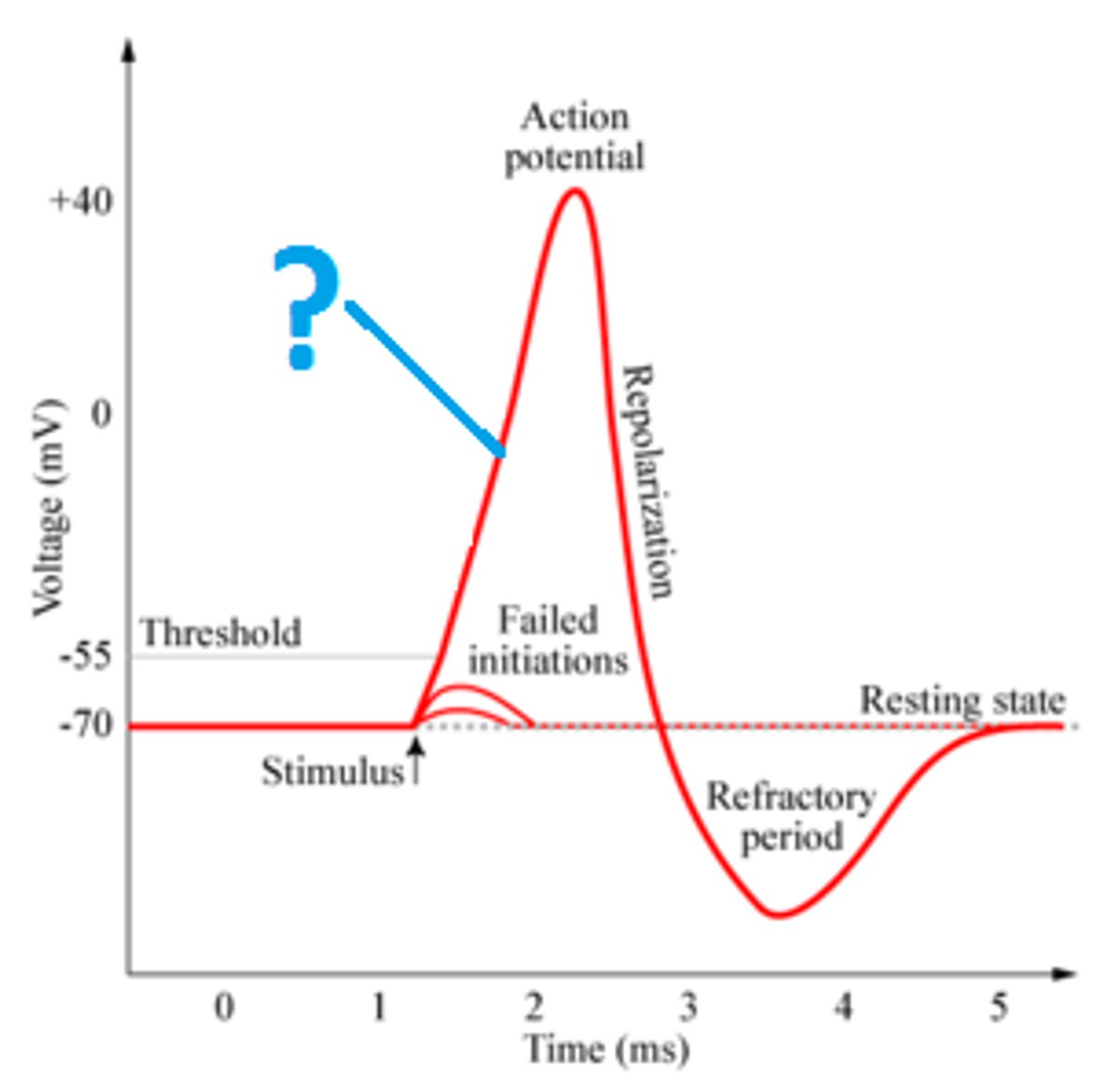
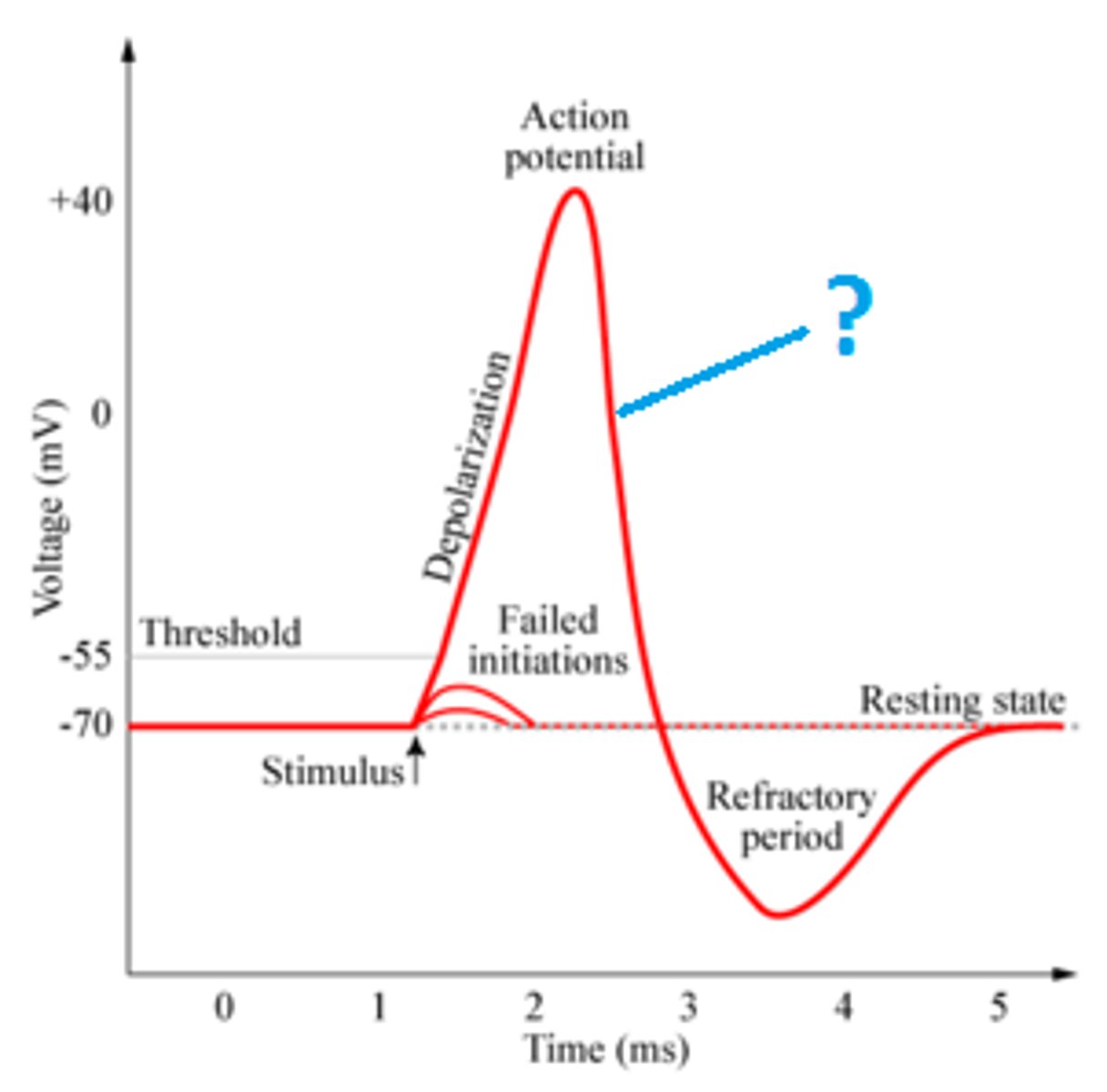
sequence of action potential
depolarization
repolarization
hyperpolarization,
refractory period
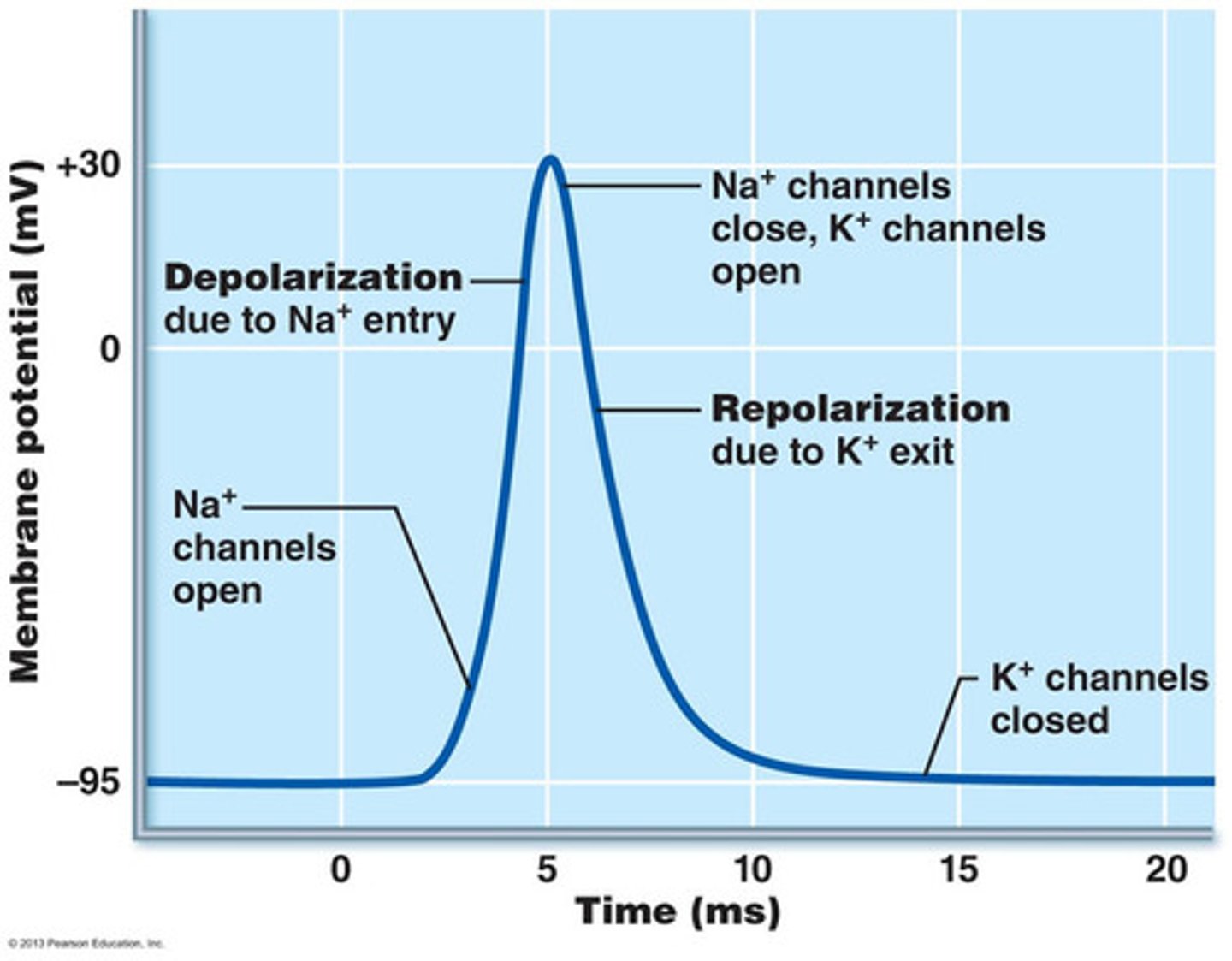
all-or-none principle
the law that the neuron either fires at 100% or not at all
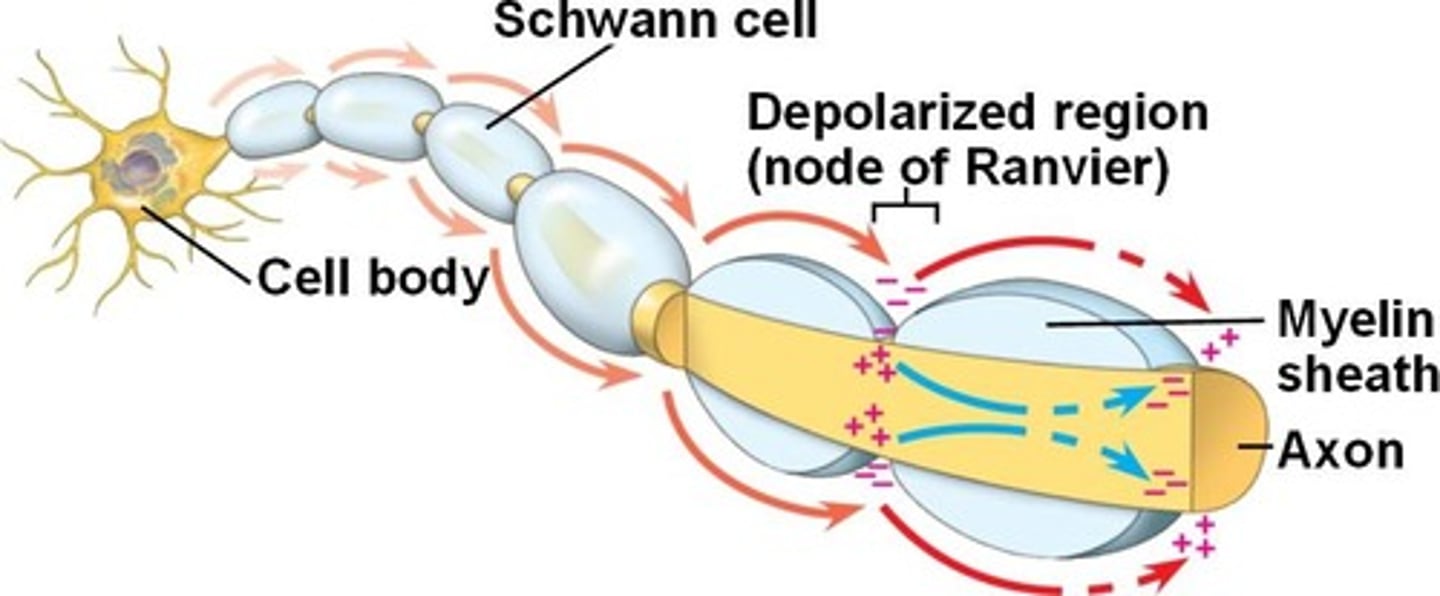
myelinization affect action potential propagation
-speeds up action potential
-acts as an electrical insulator
-saltatory conduction
saltatory conduction
the jumping of action potentials from node to node
how does synapse transmit to next neuron?
presynaptic neuron
vesicle
neurotransmitters
synaptic cleft
postsynaptic neuron
depolarization
-potential moves to less negative values
-influx of Na+
repolarization
-potential returns towards resting membrane potential after depolarization
-efflux of K+
3 major regions of the brain
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
forebrain
-develops into cerebrum and diencephlon (cerebral cortex)
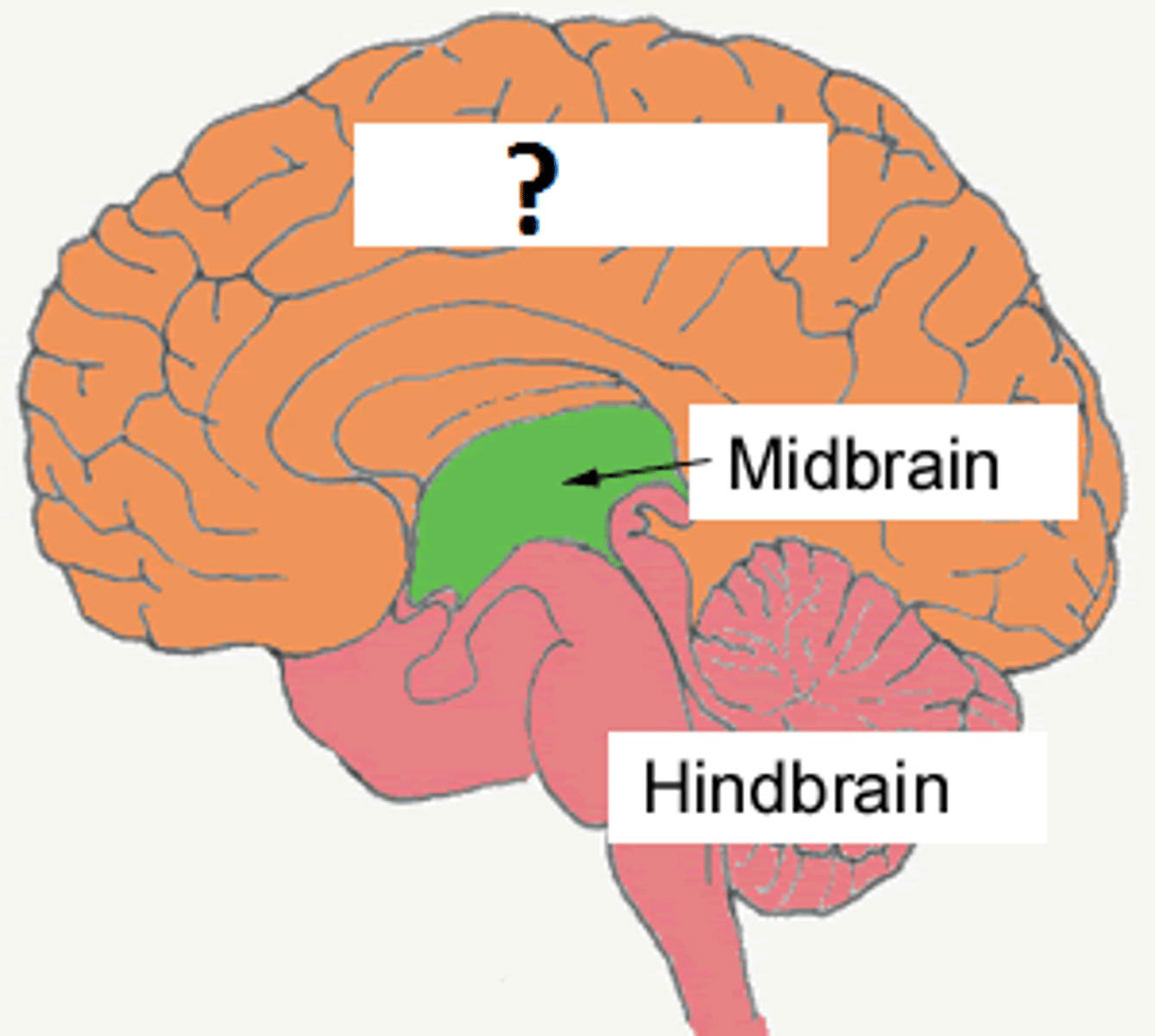
forebrain function
Perception, conscious awareness, cognition, and voluntary action
midbrain
Region between the hindbrain and the forebrain
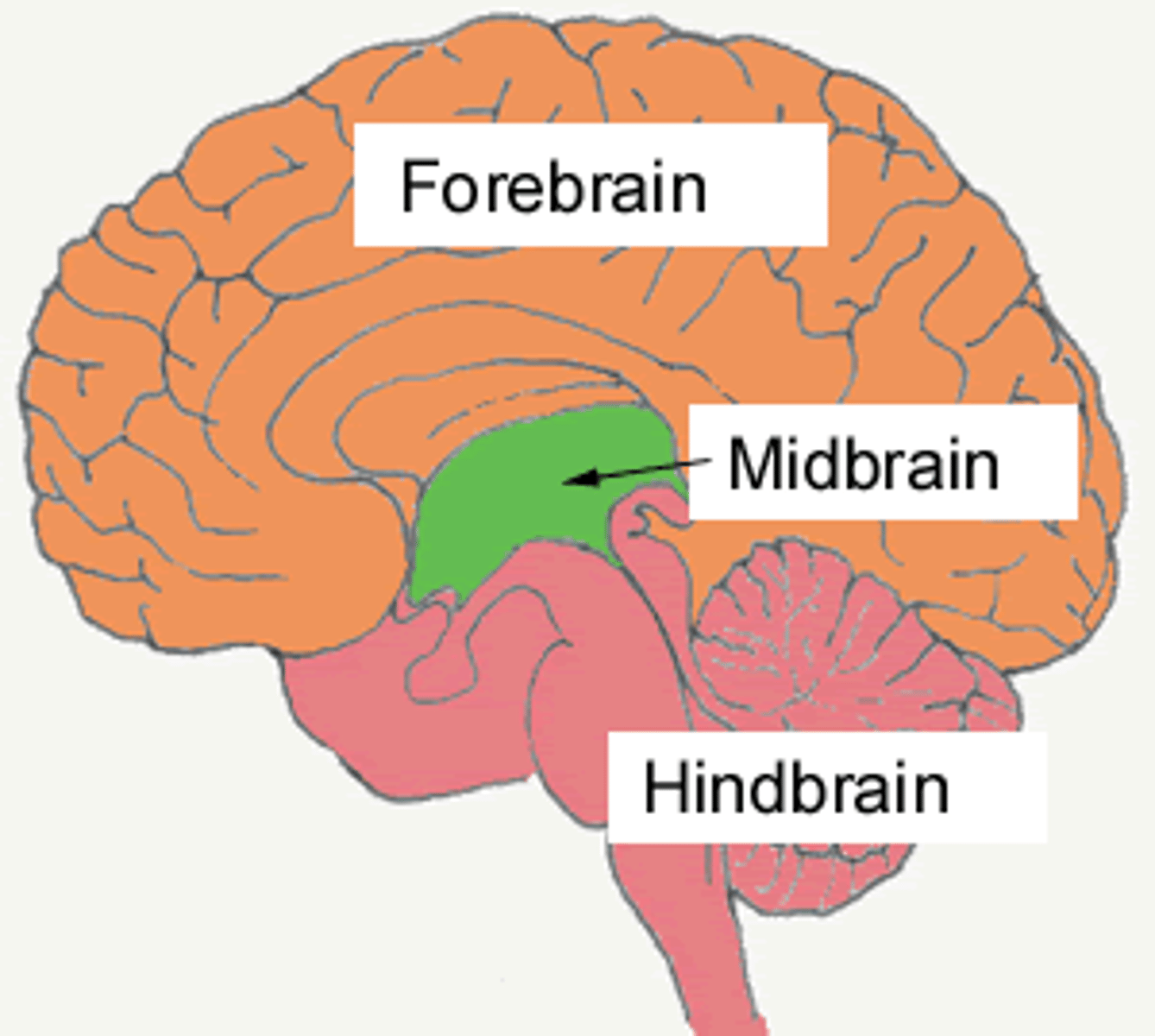
midbrain function
(mesencephalon) relay center for visual and auditory information, controls eye and bodily movements
hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
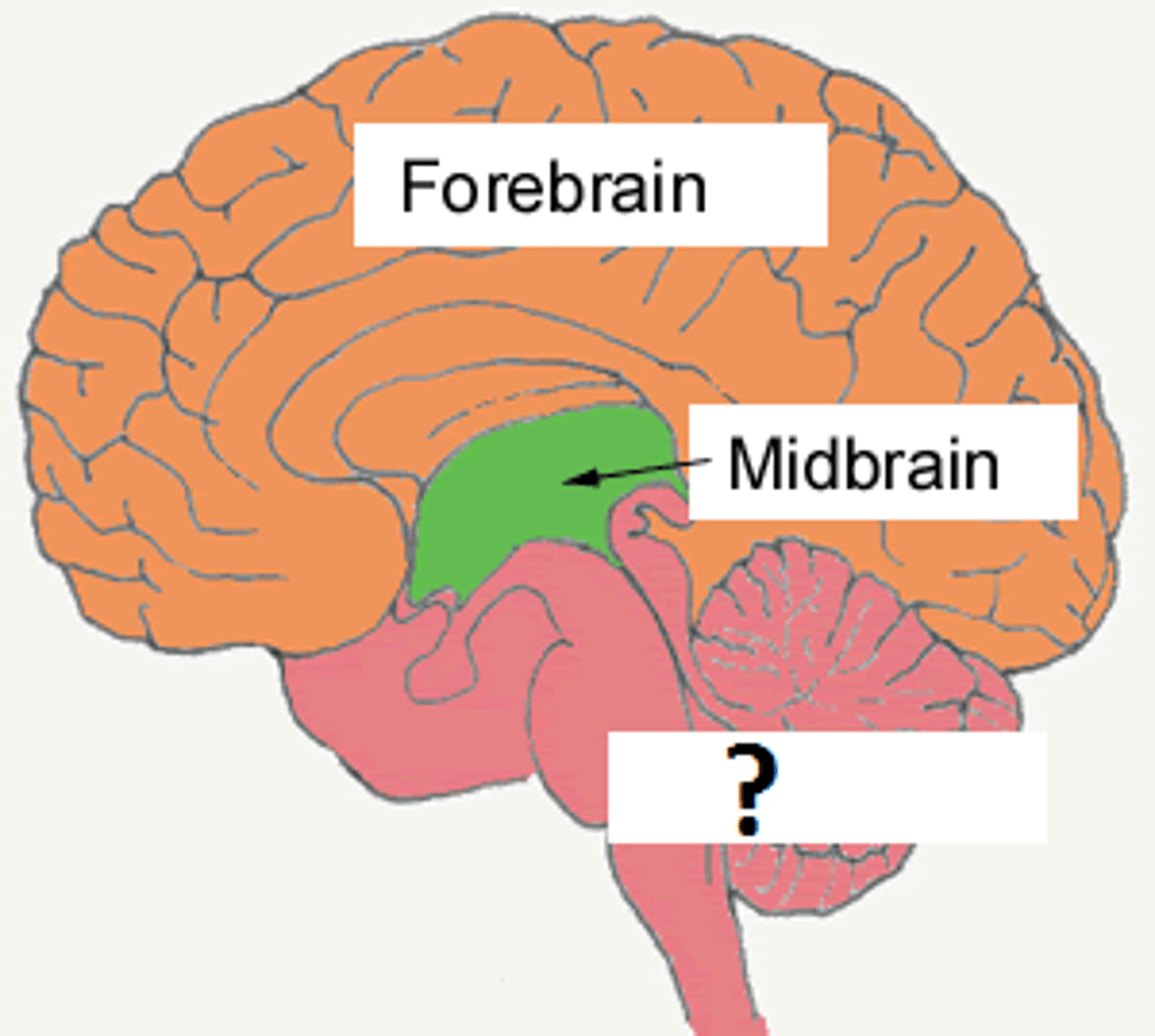
Hindbrain function
refined motor movements, vital functioning (breathing, digestion), arousal and alertness
Cerebellum function
coordination of voluntary movements and balance
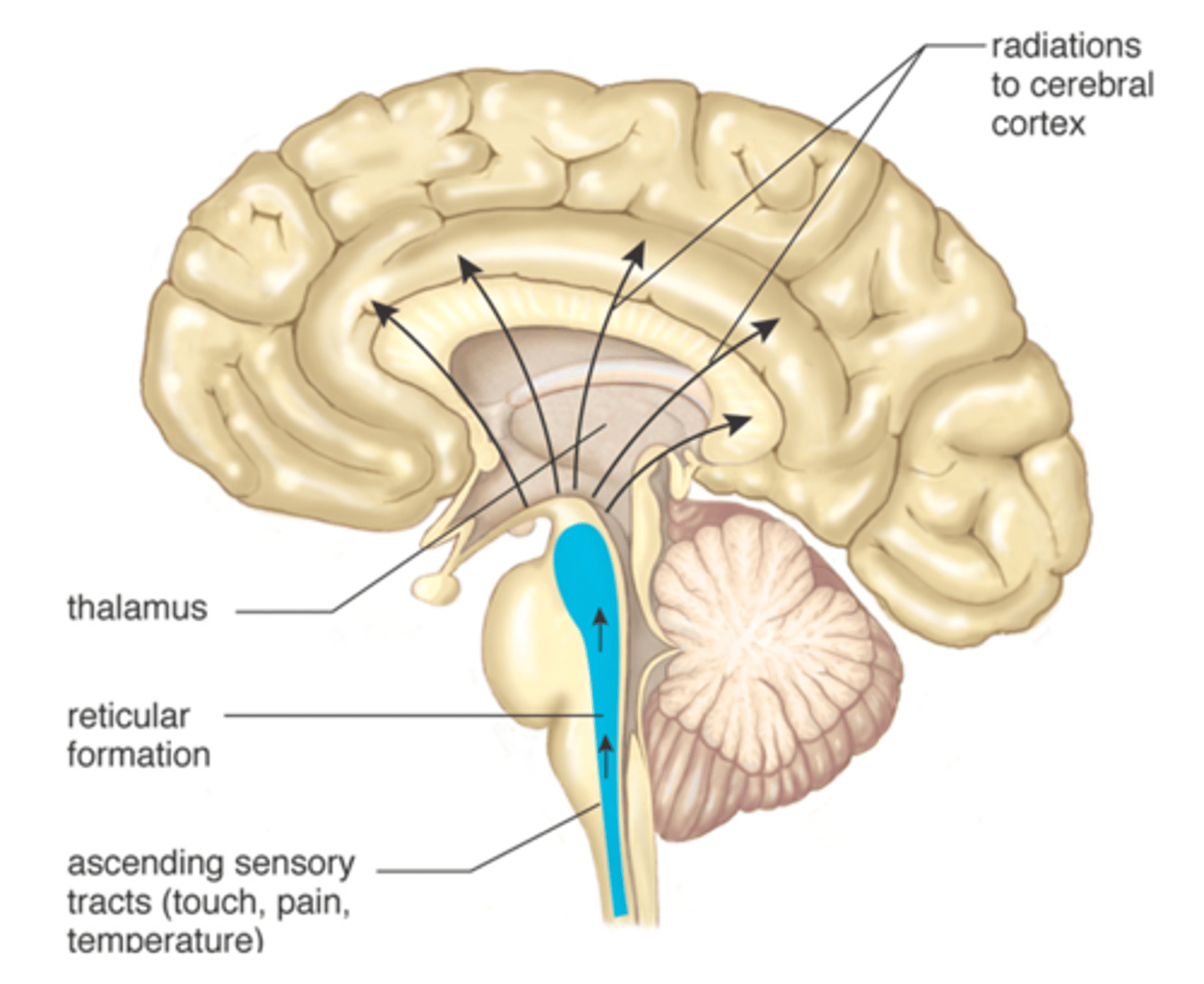
reticular activating system
-Located in the upper brain stem
-responsible for maintenance of consciousness, specifically: arousal, wakefulness, and attention
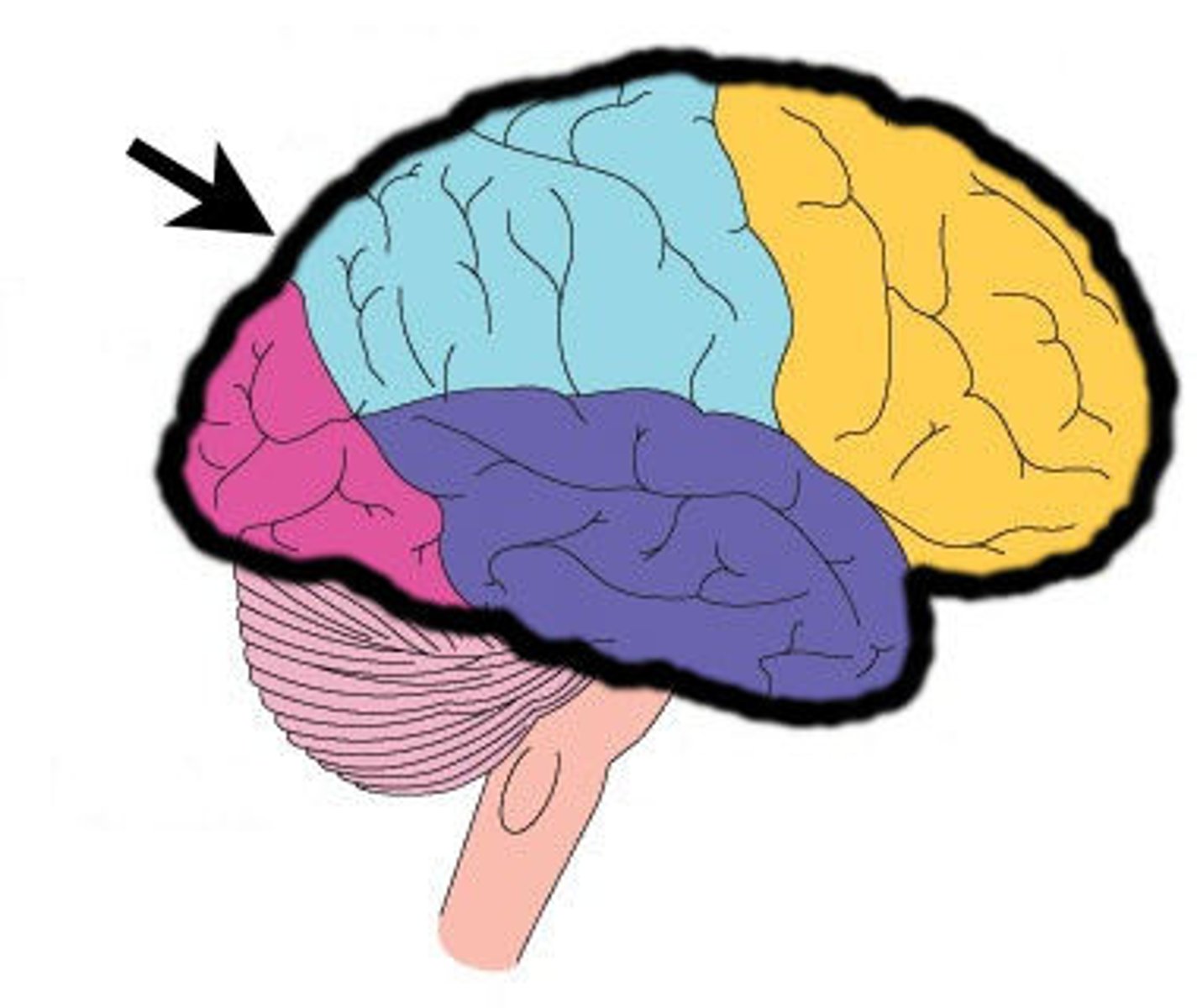
cerebral cortex
-information-processing center
-planning, learning, memory, complex emotion
regulation of sleep
-adenosine/homeostatic regulator decreases orexin neurons
-then decrease in monoaminergic neurons
-increased sleep centers
regulation of wakefulness
-suprachiasmatic nucleus, negative energy balance, & limbic system activity triggers:
-increase of orexin neurons
-increase of monoaminergic neurons
-travels to thalamus and cortex
-decreased sleep center activity
brain regions involved in consciousness
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
monoaminergic RAS nuclei
orexin-secreting neurons
acetylcholine-secreting neurons
sleep center (GABAergic neurons)
five special senses
olfaction, gustation, vision, equilibrium, hearing
Nociceptors
pain receptors
Photoreceptors
respond to light
Mechanoreceptors
respond to touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch
(hearing, equilibrium)
Chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals (olfactory and taste receptors)
sensory transduction
-the conversion of stimulus energy into a change in the membrane potential of a sensory receptor
-sensory receptor turns stimulus energy into electrical signal
general sense
widely distributed throughout the body
(Ex: touch, temperature, hunger)
special sense
any sensory system associated with a specific organ structure
(ex: smell, taste, sight, hearing, and balance)
CNS structures
brain and spinal cord
PNS function
-communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
-send info to brain, send commands to body
somatic division (PNS)
voluntary control of skeletal muscle
autonomic division (PNS)
involuntary control of glands and smooth muscle
two branches of autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic nervous system
-the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
-"fight or flight"
parasympathetic nervous system
-the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
-"rest and digest"
How does the CNS coordinate with the PNS to maintain homeostasis?
feedback loops