Markovnikov's Rule
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
How many products can be formed when an unsymmetrical alkene is reacted with a hydrogen halide?
2 products.
What is an unsymmetrical alkene?
When the groups or atoms attached to each carbon in the double bond are different.
Give an example of an unsymmetrical alkene.
But-1-ene.
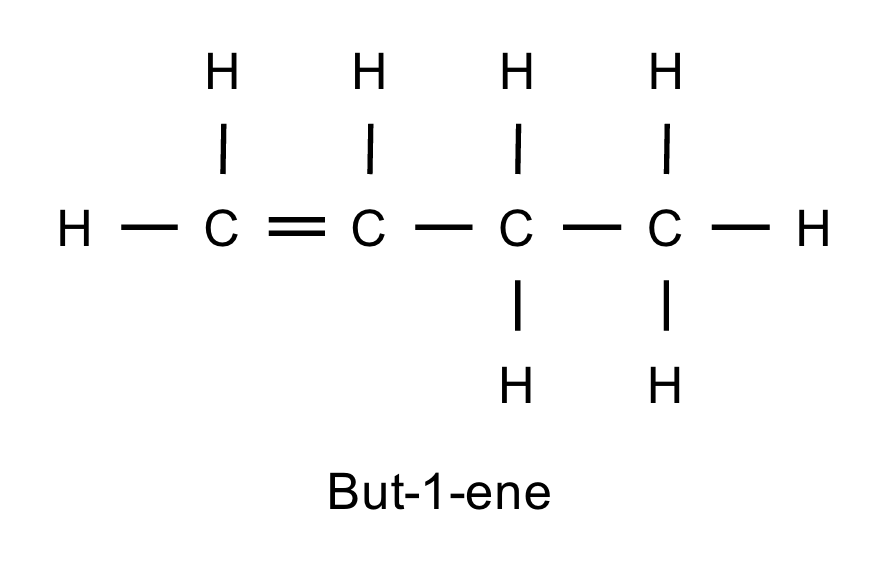
Give an example of the products formed in an addition reaction between a hydrogen halide and an unsymmetrical alkene.
When hydrogen bromide (HBr) and but-1-ene undergo an addition reaction, 1-bromobutane and 2-bromobutane can be formed.
Are the 2 products formed in equal amounts in an addition reaction between a hydrogen halide and an unsymmetrical alkene?
No.
The product that forms in higher quantities is known as the major product.
The product that forms in lower quantities is known as the minor product.
In the addition reaction between hydrogen bromide and but-1-ene, determine which is the major and minor product.
2-bromobutane is the major product.
1- bromobutane is the minor product.
What factor determines whether the product formed is a major one or a minor one?
The dominating product depends on the stability of the carbocation that is formed.
What is a carbocation?
A carbocation is an ion with a positively-charged carbon atom.
Carbocations only has 3 covalent bonds.
Carbocations are…
Highly reactive and unstable.
What does the stability of a carbocation depend on?
The stability of the carbocation depends on how many alkyl groups are bonded to the carbon atom with the positive charge.
What is an alkyl group?
An alkyl group is composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms e.g. a methyl or ethyl group.
What 3 categories do carbocations fall into:
Primary carbocation
Secondary carbocation
Tertiary carbocation
What is a primary carbocation?
In a primary carbocation, there is one alkyl group bonded to the carbon with the positive charge.
What is a secondary carbocation?
In a secondary carbocation, there are two alkyl groups bonded to the carbon with the positive charge.
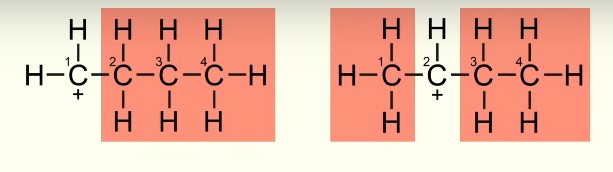
Explain why a secondary carbocation is more stable than a primary carbocation.
Secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations because there are 2 alkyl groups present to distribute its positive charge.
If 2 carbocation intermediates are possible in a reaction, which one will form more readily?
The most stable one.
In the addition reaction between hydrogen bromide and but-1-ene, the secondary carbocation is the more stable intermediate ∴ it is more likely to be formed.
This means more 2-bromobutane is formed than 1-bromo-butane, making 2-bromobutane the major product.
How do you determine how the major product forms?
Using Markovnikov’s rule.
What does Markovnikov’s rule state?
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen atom of the hydrogen halide is more likely to bond to the carbon atom which is attached to the greater number of hydrogen atoms.