Central and Peripheral Nervous System Overview
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Central Nervous System
Major division of the nervous system; includes brain and spinal cord.

Peripheral Nervous System
Contains all neurons outside the central nervous system.

Neurons
Specialized nerve cells for processing environmental information.
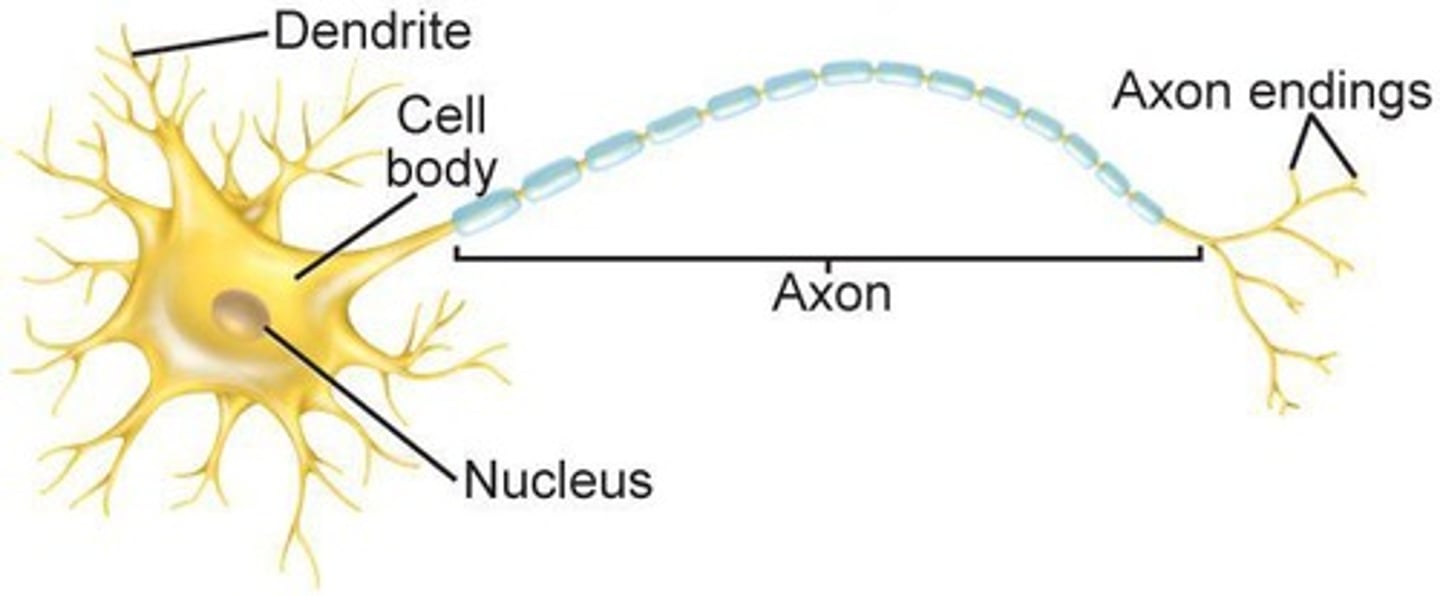
Dendrites
Receive impulses from other neurons and conduct them.
Axon
Transmits impulses to other neurons or muscles.
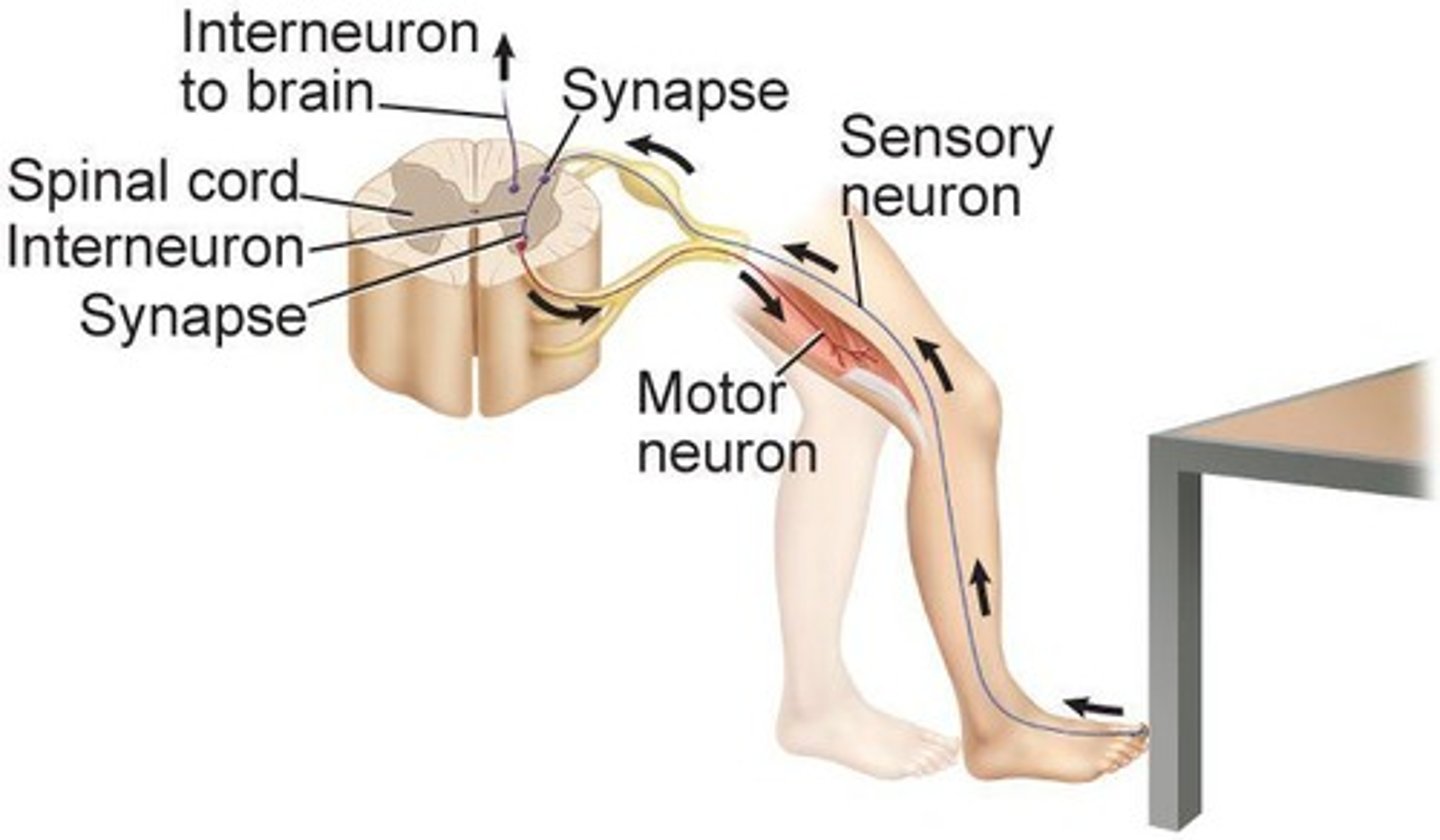
Sensory Neurons
Send impulses from receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons
Carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons.
Motor Neurons
Transmit impulses from CNS to glands or muscles.
Reflex Arc
Pathway of a nerve impulse involving sensory, interneuron, and motor neurons.
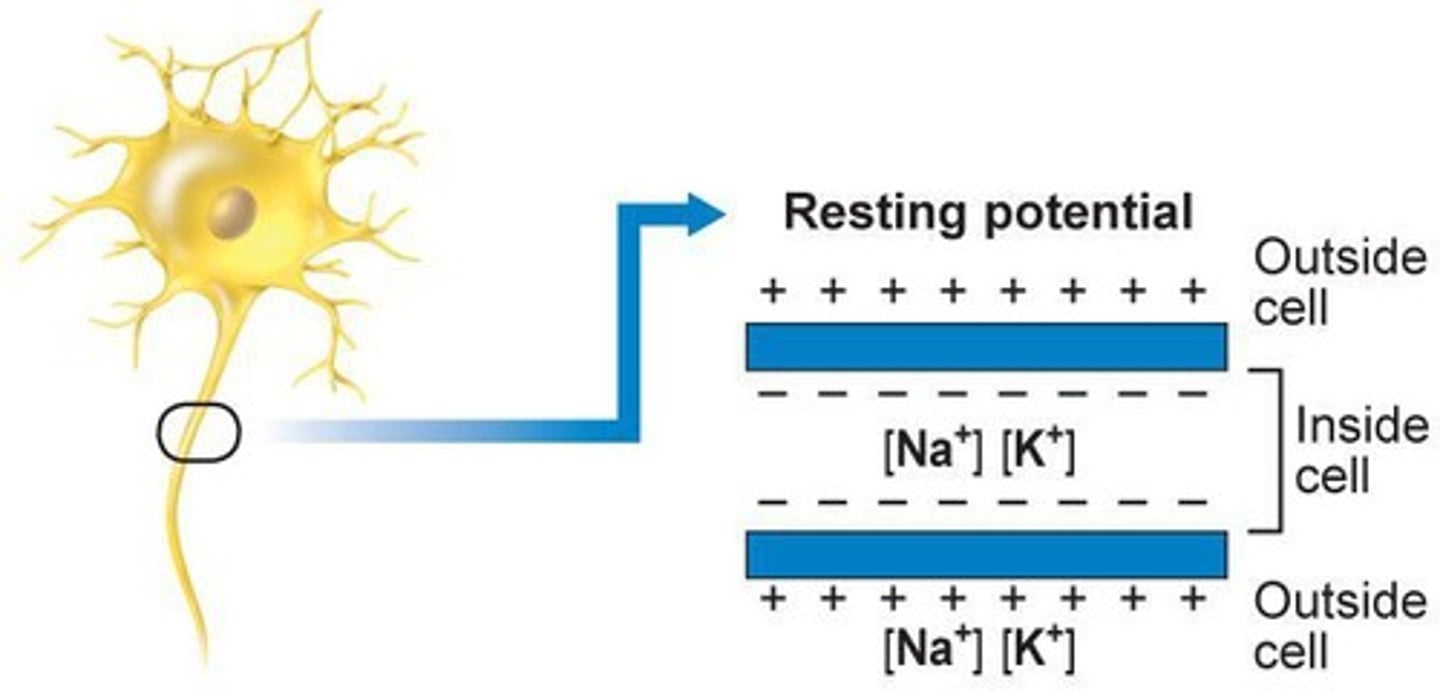
Action Potential
Nerve impulse caused by sodium and potassium movement.
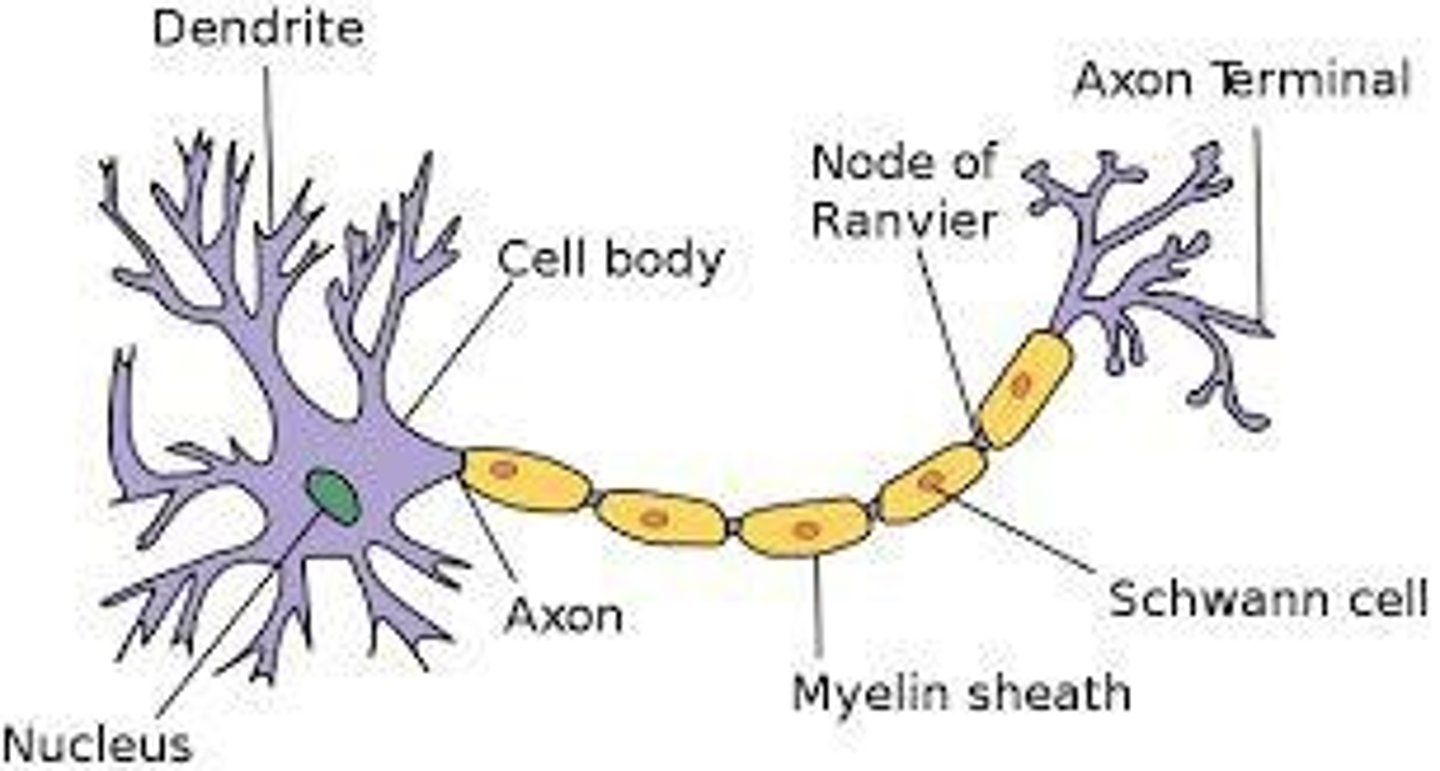
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath that speed up impulses.
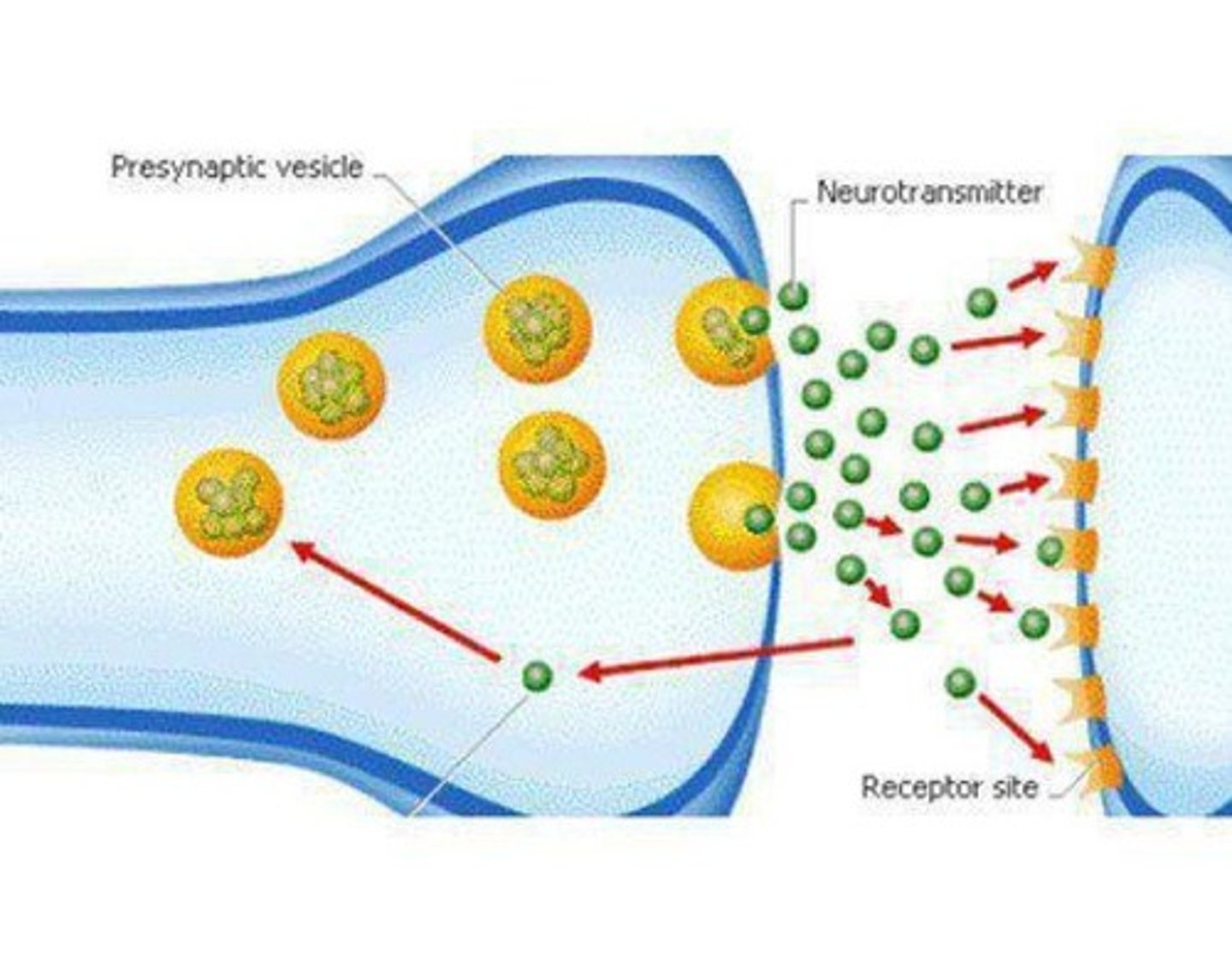
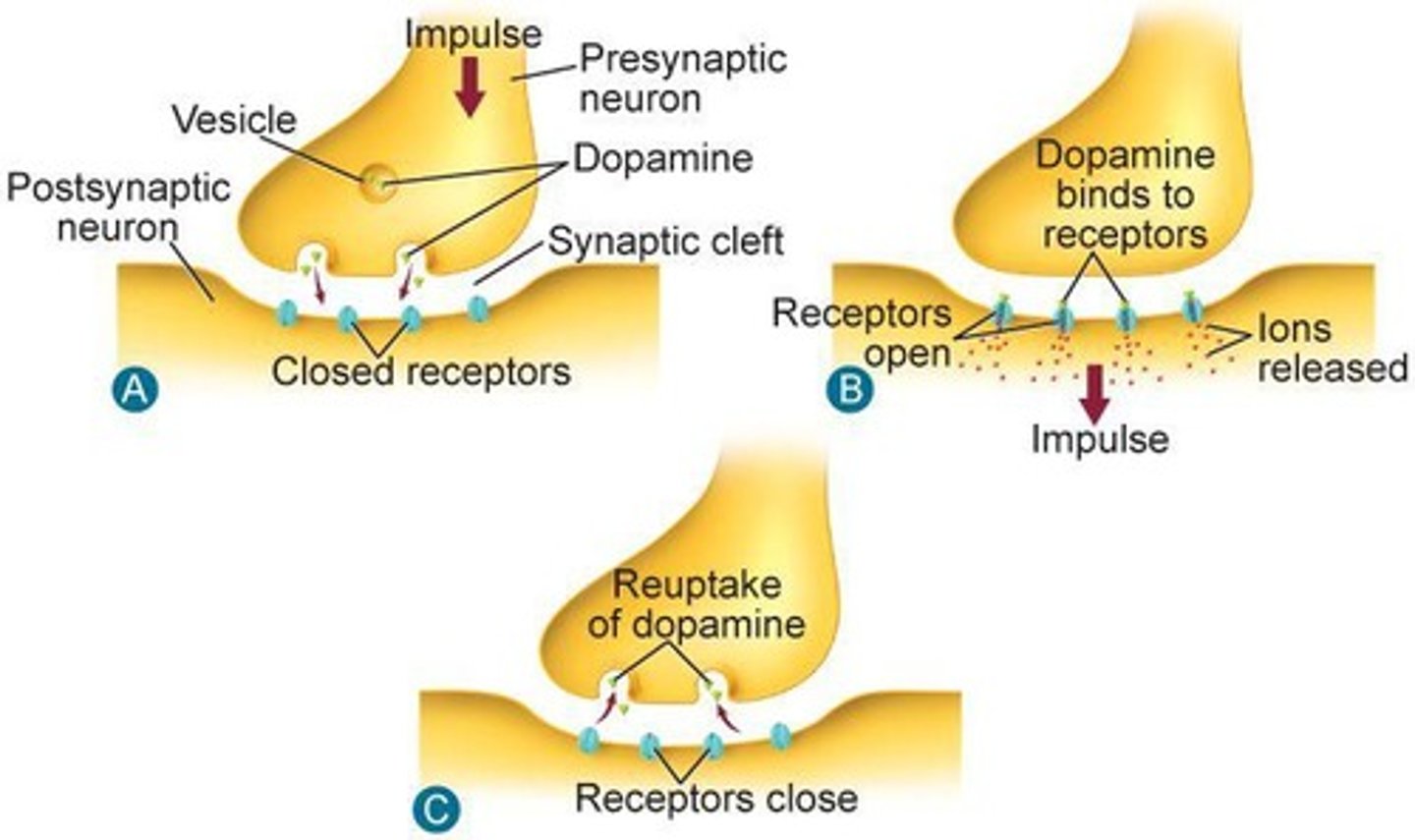
Synapse
Gap between axon of one neuron and dendrite of another.
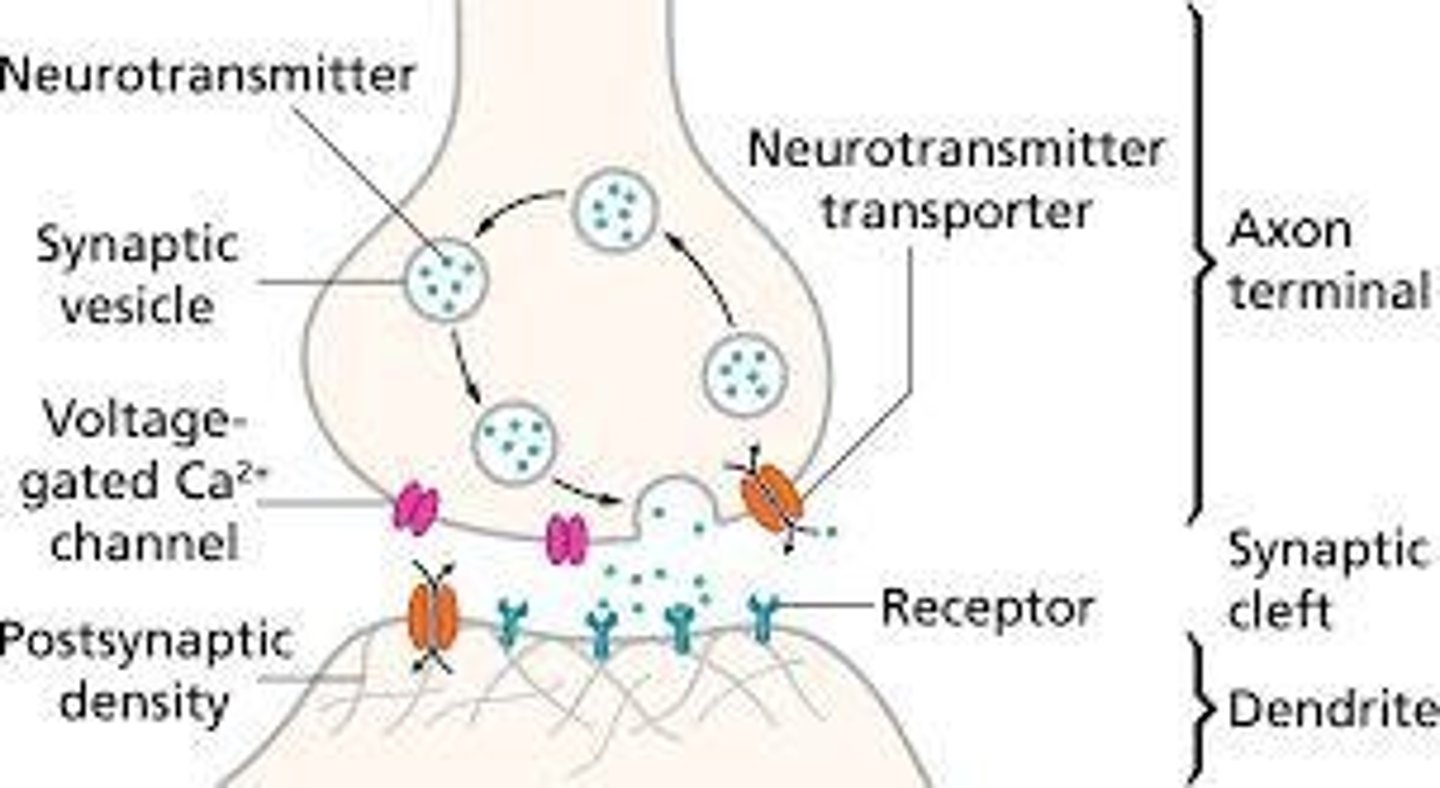
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across synapses.
Cerebrum
Largest brain part; responsible for thought and sensory perception.
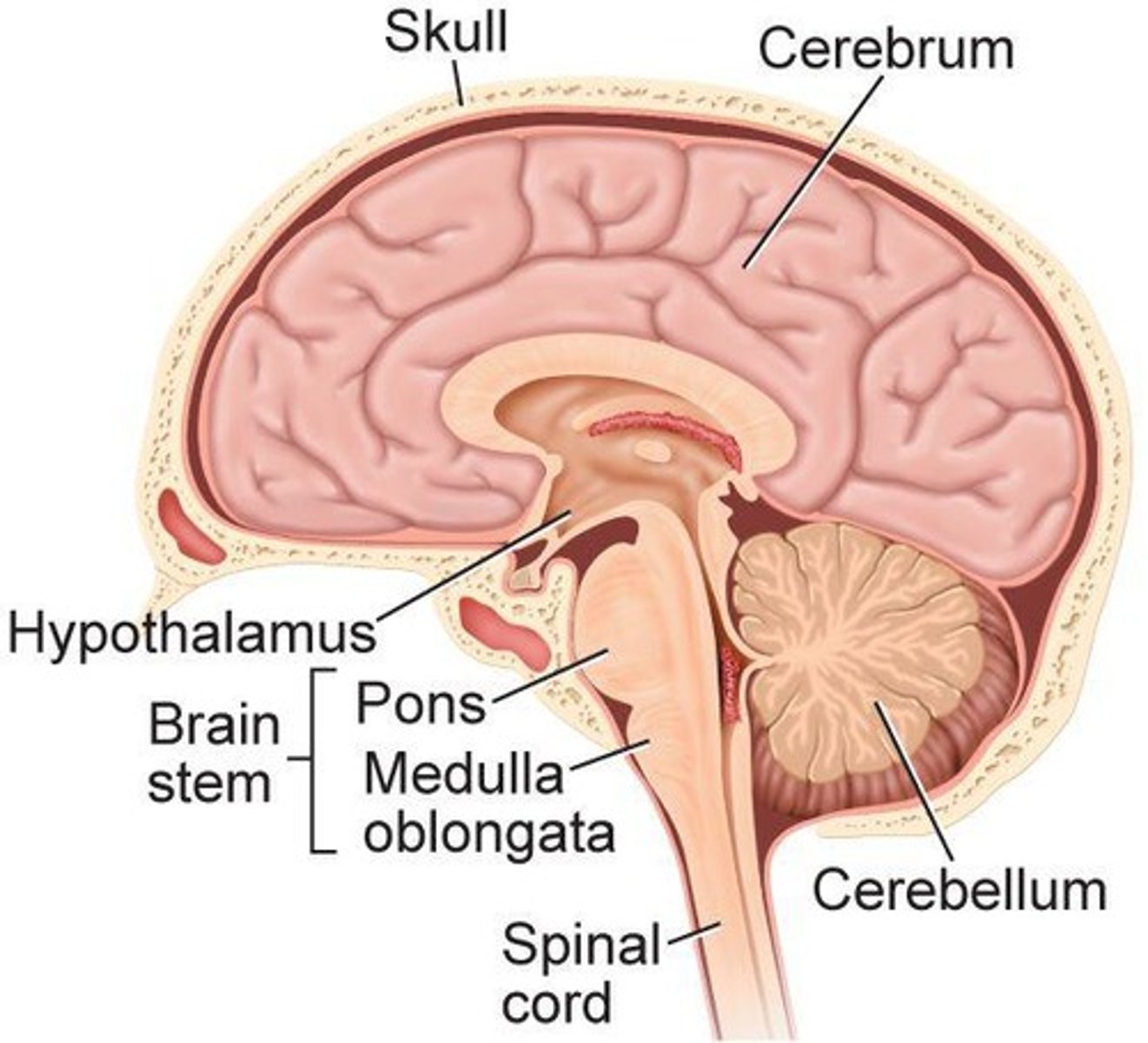
Cerebellum
Controls balance, posture, and coordination.
Brain Stem
Connects brain to spinal cord; regulates vital functions.
Medulla Oblongata
Controls breathing rate, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Pons
Aids in regulating breathing.
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis, including temperature and appetite.
Spinal Cord
Nerve column extending from brain; processes reflexes.
Somatic Nervous System
Relays information between external sensory receptors and CNS.
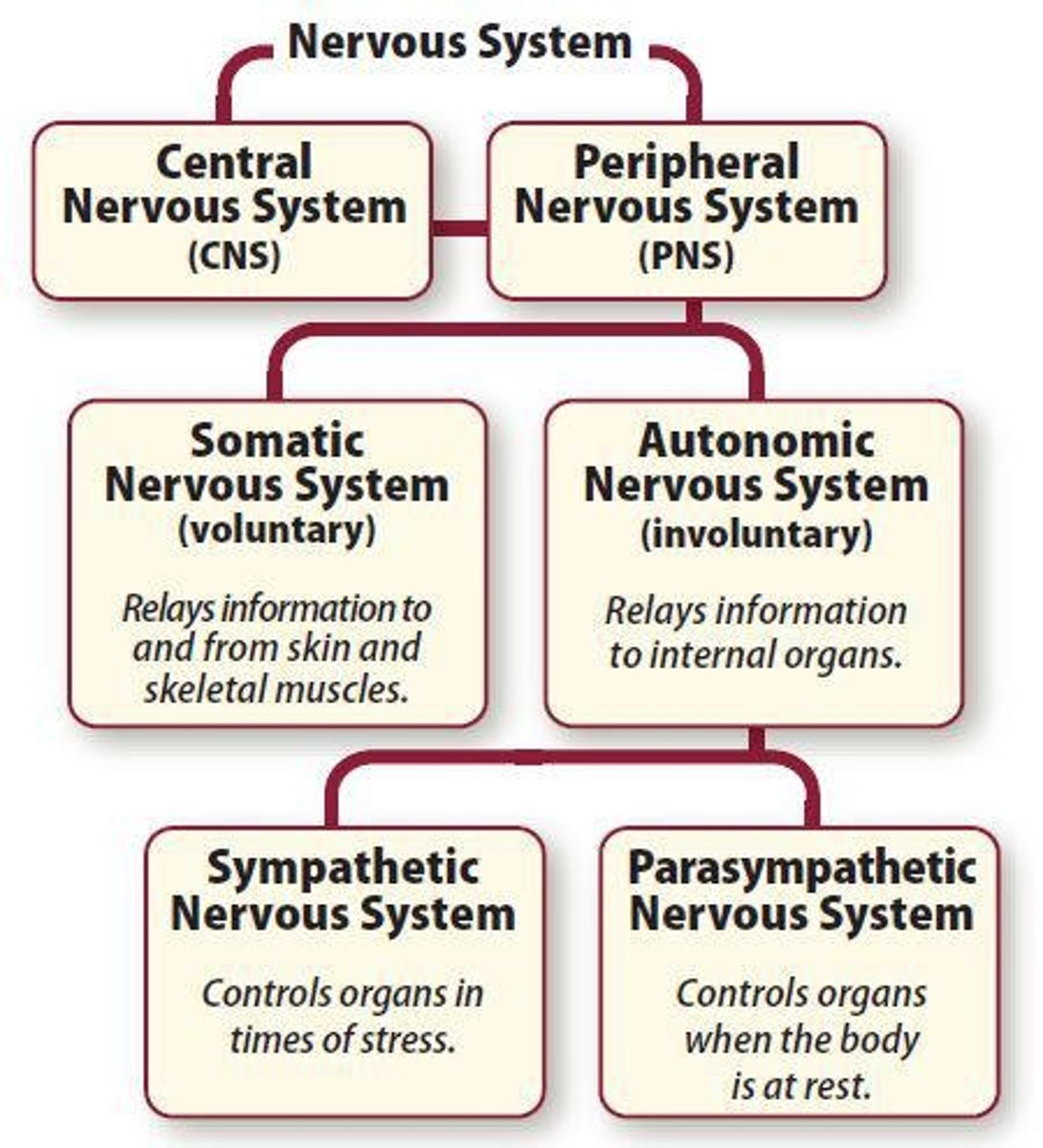
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary body functions; includes sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Prepares body for 'fight or flight' responses.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Promotes 'rest and digest' functions.
Autonomic Nervous System
Carries impulses to internal organs involuntarily.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Active during emergencies, increases heart and breathing rates.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Active during relaxation, conserves energy.
Taste Buds
Detect sweet, sour, salty, and bitter flavors.
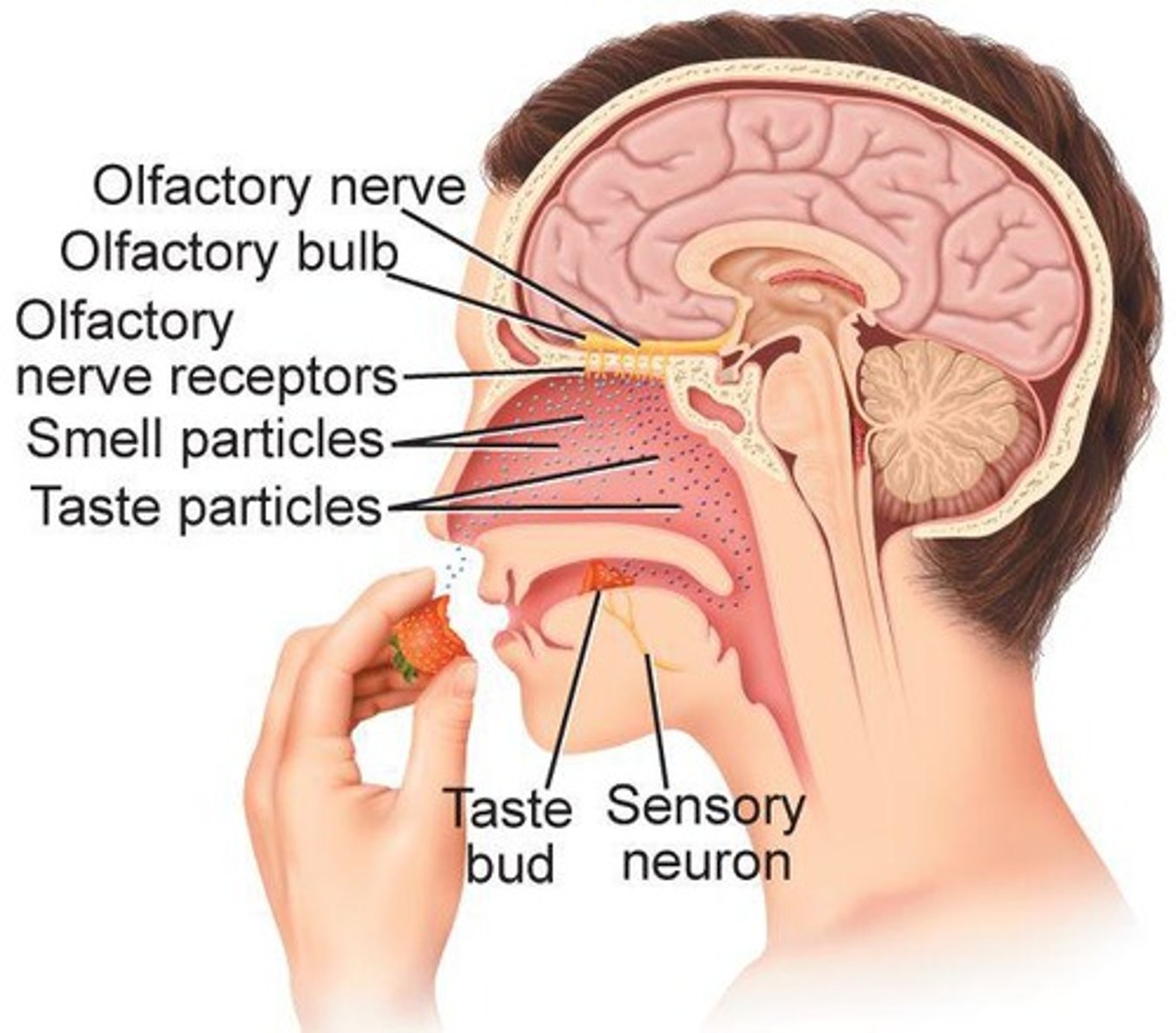
Sensory Receptors
Respond to temperature, pressure, and pain.
Cornea
Transparent front part of the eye.
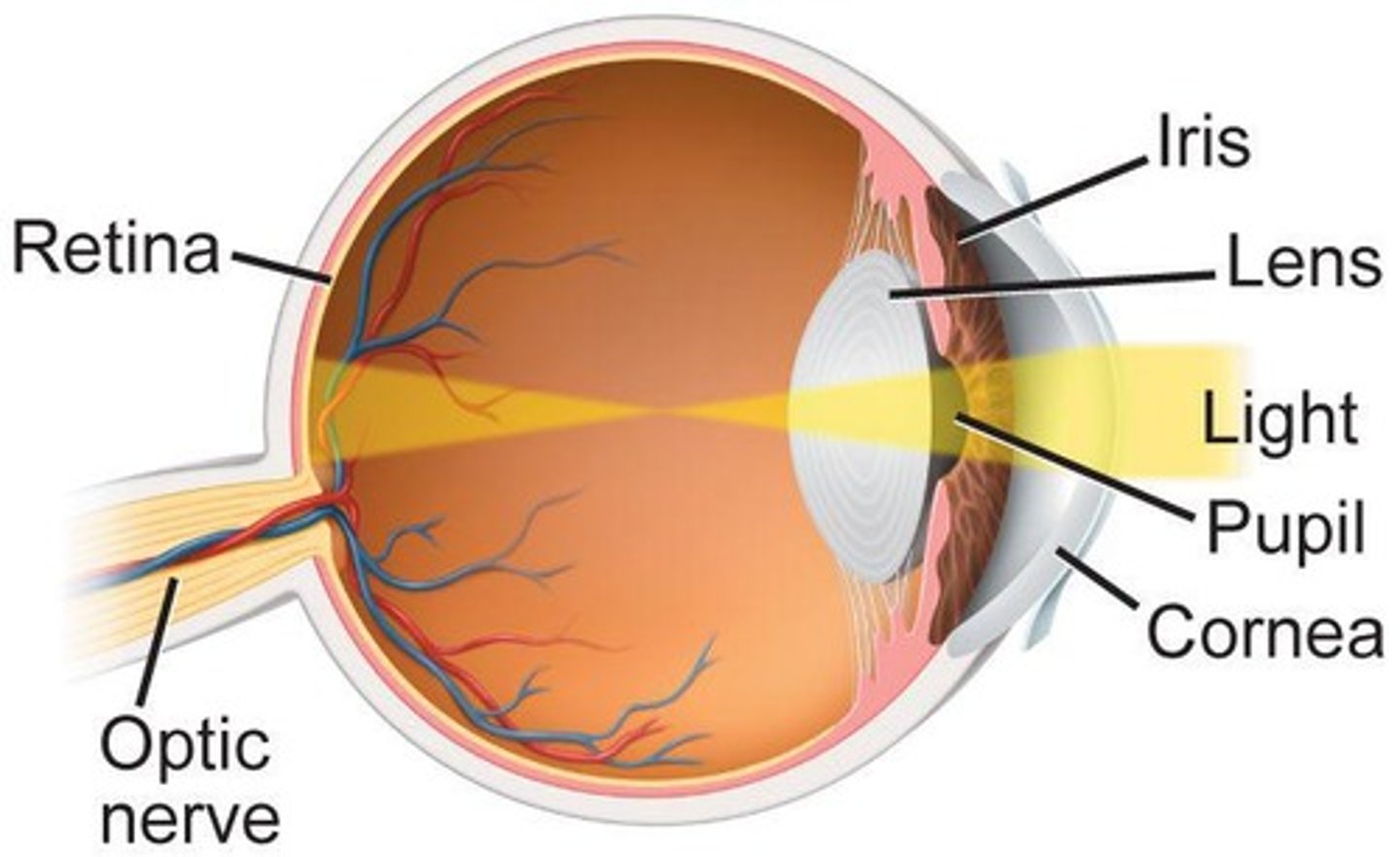
Pupil
Opening that regulates light entering the eye.
Lens
Inverts and projects images onto the retina.
Retina
Contains rods and cones for light and color detection.
Auditory Canal
Passage for sound waves to reach the tympanum.
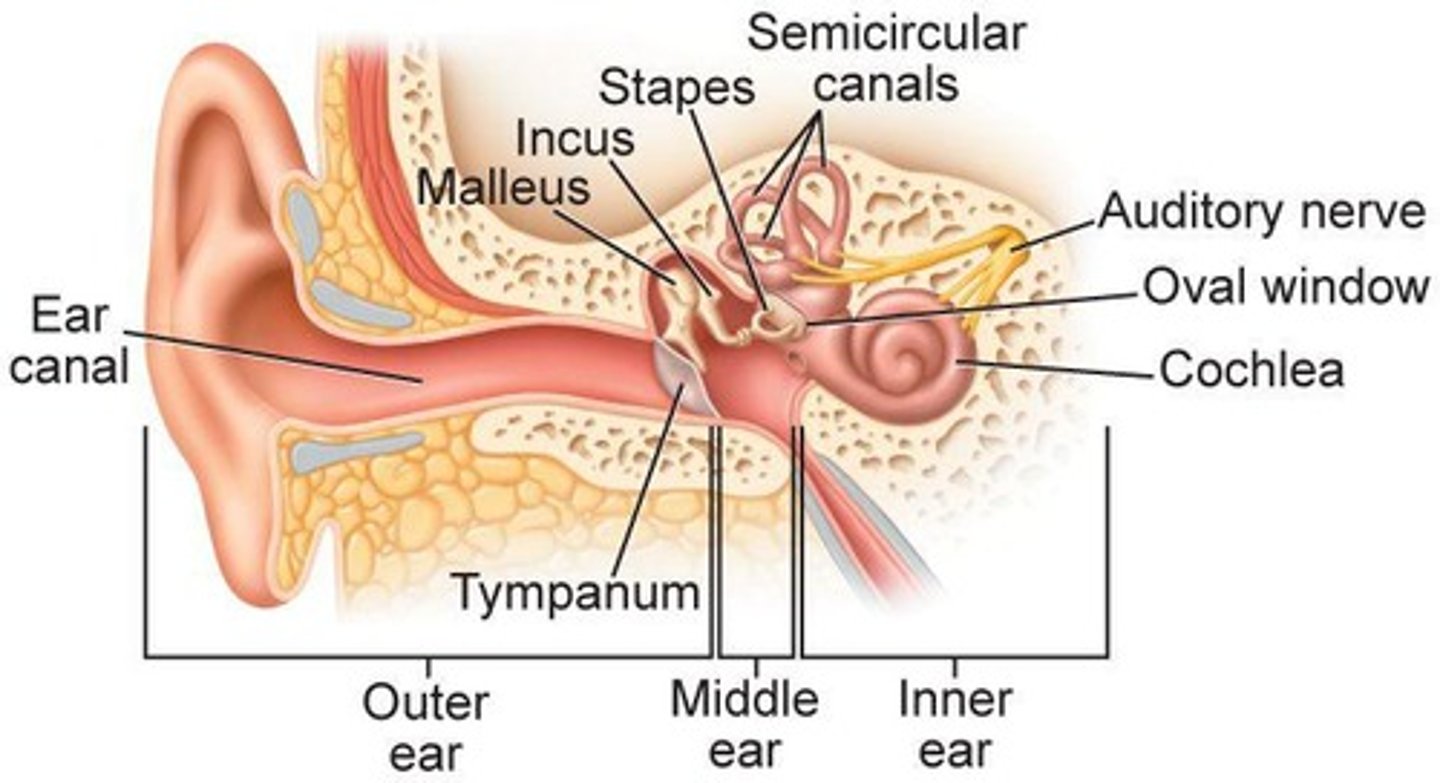
Tympanum
Membrane that vibrates in response to sound.
Cochlea
Fluid-filled structure generating nerve impulses from vibrations.
Semicircular Canals
Inner ear structures for balance and body position.
Drugs
Substances altering body function, natural or artificial.
Stimulants
Increase alertness and physical activity; examples include nicotine.
Depressants
Slow down the central nervous system; examples include alcohol.
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter often affected by drugs.
Tolerance
Need for increased drug amounts for same effect.
Addiction
Psychological or physiological dependence on a drug.
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger transmitting signals across synapses.
Reflex Arc
Pathway for reflex actions involving sensory and motor neurons.
Sensory Structures
Organs detecting motion, temperature, taste, smell, sight.
Counseling
Often necessary for overcoming drug addiction.
Digestive System
System converting food into usable forms and waste removal.
Digestive Tract
Muscular tube from mouth to anus for digestion.
Accessory Organs
Organs aiding digestion by secreting substances.
Peristalsis
Rhythmic contractions pushing food through digestive tract.
Mechanical Digestion
Physical breakdown of food, e.g., teeth.
Chemical Digestion
Breakdown of food by digestive enzymes.
Absorption
Nutrients taken into blood from small intestine.
Elimination
Removal of waste from the body.
Mucosa
Inner lining secreting mucus and digestive juices.
Submucosa
Connective tissue with blood and lymphatic vessels.
Muscularis Externa
Smooth muscle layers aiding movement in tract.
Serosa
Outer layer of digestive tract providing protection.
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva to aid in digestion.
Liver
Processes nutrients and produces bile for digestion.
Gallbladder
Stores bile produced by the liver.
Pancreas
Secretes digestive enzymes and buffers into intestines.
Small Intestine
Primary site for nutrient absorption.
Large Intestine
Absorbs water and forms waste.
Anus
Final part of digestive tract for waste expulsion.
Teeth
Mechanical tools for breaking down food.
Tongue
Muscle aiding in food manipulation and swallowing.
Serosa
Visceral peritoneum layer insulating organs.
Mesentery
Tissue supporting blood vessels in digestive tract.
Mucosa
Innermost layer of digestive tract.
Submucosa
Layer providing support and containing blood vessels.
Muscularis Externa
Layer responsible for digestive tract movement.
Oral Cavity
Area for mechanical processing and mixing food.
Pharynx
Muscular tube connecting mouth to esophagus.
Esophagus
Tube transporting food to stomach.
Stomach
Organ for chemical and mechanical food processing.
Small Intestine
Site for enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption.
Large Intestine
Responsible for dehydration and compaction of waste.
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva for food digestion and lubrication.
Mastication
Chewing process increasing food surface area.
Amylase
Enzyme initiating carbohydrate digestion in mouth.
Lipase
Enzyme starting lipid digestion in oral cavity.
Labia
Lips forming anterior boundary of oral cavity.
Uvula
Dangling structure at soft palate's posterior margin.
Gingivae
Gums surrounding the base of teeth.
Lingual Frenulum
Tissue connecting tongue to floor of mouth.
Pharyngeal Tonsil
Lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx.
Palatine Tonsil
Lymphoid tissue located at the entrance to pharynx.
Esophagus
Tube connecting throat to stomach.
Bolus
Moist mass of food entering digestive tract.
Peristalsis
Sequential muscle contractions moving food along tract.
Muscularis externa
Layer responsible for peristalsis in digestive tract.
Stomach
Muscular, expandable organ for food digestion.
Chyme
Soupy mixture of food and gastric secretions.
Rugae
Folds in stomach mucosa that flatten when expanded.
Pyloric sphincter
Regulates chyme release into duodenum.
Gastric glands
Secrete gastric juice in stomach for digestion.
Gastric juice
Acidic fluid containing enzymes for digestion.
Intestinal villi
Finger-like projections increasing intestinal surface area.