Overview of Body
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
aden/o
gland
adip/o
fat
anter/o
before front
caud/o
lower part of body
cephal/o
head
cyt/o -cyte
cell
end- endo-
in within inside
exo-
out of, outside, away from
hist/o- histio-
tissue
-ologist
specialist
-ology
science, study of
path/o pathy
disease, suffering, feeling, emotion
plas/i plas/o -plasia
developement, growth, formation
poster/o
behind, toward the back
-stasis -static
control, maintenance of a constant level
anatomic reference systems
used to describe locations of structral units of the body
4 main parts of the anatomic reference systems
body planes
body directions
body cavities
structural units
anatomy
study of the structures of the body
physiology
study of the functions of the structures of the body
anatomic position
body’s standard position
erect body facing forward
arms at side with palms facing forward
body planes
imaginary vertical and horizontal lines
divide the body into sections for depscriptive purposes
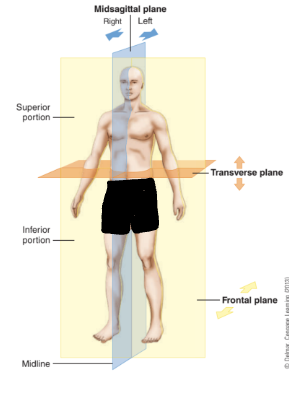
vertical plane
up and down
perpendicular to horizon
sagittal plane
vertical plane
dividing into unequal left and right parts
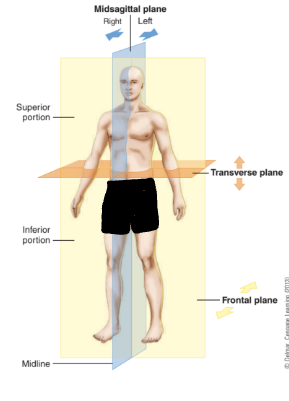
Midsagittal plane
“midline”
sagittal plane
dividing body into equal left and right halves
Frontal plane (coronal plane)
divides body into anterior and posterior
horizontal plane
flat crosswise plane, such as horizon
transverse plane
horizontal plane
divides the body into superior and inferior
ventral
front/belly side of the organ or body
dorsal
back of organ or body
anterior
situated in the front, the front, forward part of an organ
posterior
situated in the back, the back, the back part of an organ
superior
uppermost, above, towards the head
inferior
lowermost, below, towards the feet
cephalic
towards the head
caudal
towards the lower part of the body
proximal
situated nearest the midline or beginning of a body structure
distal
situated farthest from midline or beginning of body structure
medial
direction toward, nearer midline
lateral
direction toward, nearer side of the body, away from midline
bilateral
relating to or having two sides
Cavities in the body
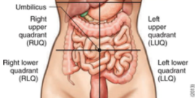
quadrants of the abdomen
right upper quad RUQ
left upper quad LUQ
right lower quad RLQ
left lower quad LLQ
peritoneum
multilayered membrane
protect and holds organs in place
in the abdominal cavity
parietal peritoneum
outer layer of peritoneum
lines the interior of abdominal wall
mensentery
fused double layer of parietal peritoneum
attaches parts of intestine to interior abdominal wall
visceral peritoneum
inner layer of peritoneum
surrounds organs in abdominal cavity
retroperitoneal
behinf the peritoneum
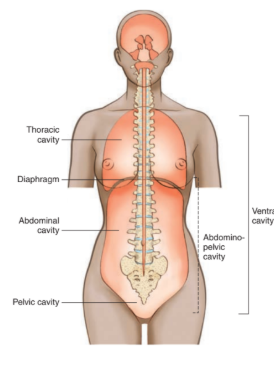
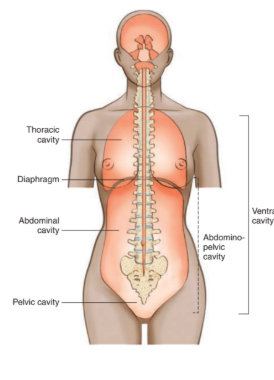
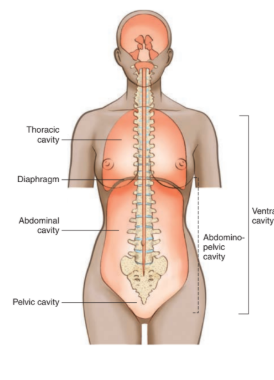
Body cavities
spaces within the body that contain and protect internal organs
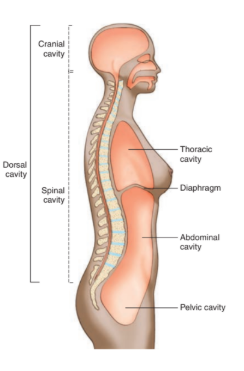
dorsal cavity
located along the back of the body and head
contains organs of the nervous system that coordinate body functions
divided into cranial and spinal
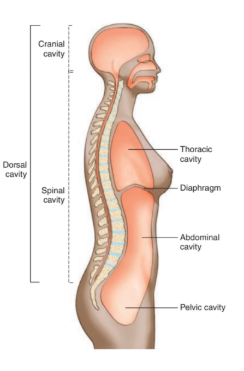
cranial cavity
located within the skull
surrounds and protects the brain
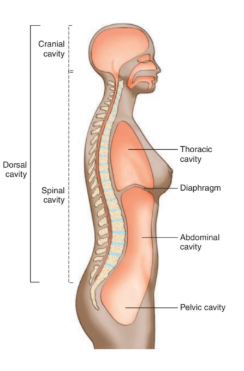
spinal cavity
located within spinal column
surrounds and protects the spinal cord
ventral cavity
located along the front of the body
contains organs that sustain homeostasis
homeostasis
process through which the body maintains constant internal environment
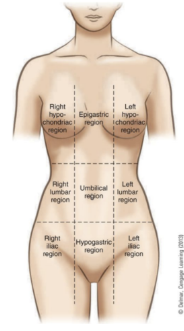
purpose of the regions of the thorax and abdomen
divides the abdomen and lower portion of thorax into nine parts
right and left hypochondriac regions
covered by lower ribs
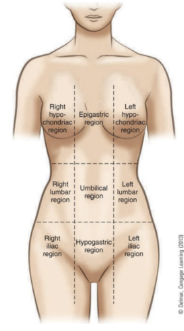
epigastric region
above the stomach
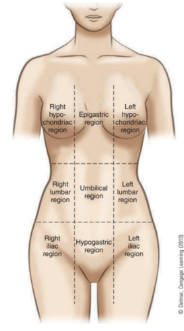
right and left lumbar regions
near the inward curve of the spine
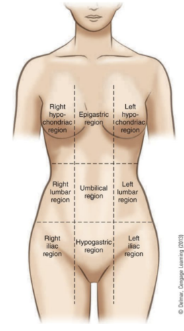
umbilical region
surrounds the umbilicus
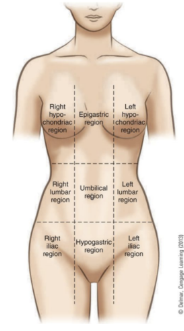
right and left iliac regions
located over the hip bones
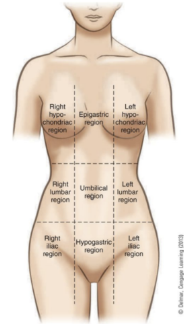
hypogastric region
below the stomach
cell
basic structural and functional units of the body
specialized and grouped to form tissues and organs
cytology
study of anatomy, physiology, pathology and chemistry of cells
cell membrane
tissues that surrounds and protects cells
cytoplasm
material within the cell membrane that is not part of the nucleus
nucleus
surrounded by the nuclear membrane, controls cell activities and helps cell divide
stem cells
unspecialized cells able to renew themselves for long periods of time
adult/stomatic stem cells
undifferentiated (unspeciailzed) cells found among differentiated
cells, repairs tissue
embryonic stem cells
can form any adult cell
can proliferate idefinitely in the lab
comes from cord blood in the umbilical cord and placenta
can be obtained from embryo produced by in vitro fertilization
gene
fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity
controls hereditary disorders and physical traits
geneitcs
study of transfer of genes and role of genes in health and disease
dominat gene
offspring will inherit the characteristic
recessive gene
if inherited from both parents
offspring will have the condition
if inherited from one parent
offspring will only carry the trait
human genome
complete set of genetic information of humans
Human genome project
completed in 2003
important step in genetics health and science
chromosomes
genetic structures in nuclei
contains DNA which makes genes
somatic cell
all cells excect gametes
46 chromosomes in 22 identically pairs and a sex chromosome pair
sex cell (gamet)
ovum or sperm
contains 23 single chromosomes
sex chromosome
x or y
xx female
xy male
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid
basic structure is the same for all organisms
found in all nuclei except erythrocytes (lack nuclei)
Unique for each individual
Used for identification ( forensics, paternity)
DNA provides information for
heredity
physical apperance
disease risks
other traits
double helix
two spiraling strands of DNA
genetic mutation
change of sequence of DNA
somatic cell mutation
cannot be transmitted
gametic cell mutation
can be transmitted genetically
genetic engineering
manipulation of genes for scientific/medical purposes
genetic(hereditary) disorder
pathological condition caused by absent/ defective gene
cystic fibrosis
affect respiratory and digestive systems
down syndrome
characteristic facial apperance
learning disabilities
physical abnormalities
hemophili
missing blood-clotting factor
spontaneous hemorrhages or severe bleeding after injury
huntington’s disease
nerve degeneration
resulting in uncontrolled movements and loss of mental abilites
muscular dystrophy
progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles
phenylketonuria (PKU)
enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase missing
can cause sever mental retardation
tay- sachs disease
fatal
fatty substance buildup in tissues and nerve cells
progressive blindness
paralysis
early death
tissues
group or layer of similarly specialized cells that perform specific functions
histology
study of the structure, composition and function of tissues
epithelial tissues
forms protective coverings for internal and external surfaces of the body
forms glands
epithelium
forms epidermis of skin and surface layer of mucous membranes
edothelium
lines blood and lymph vessels, body cavities, glands and organs
connective tissues
supports and connects organs and other body tissues
dense connective tissues
bones and cartilage
forms joints and framework of the